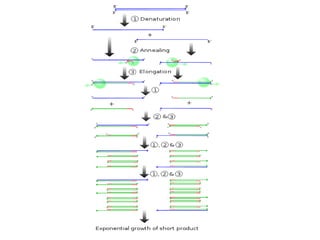
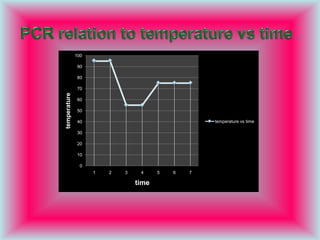
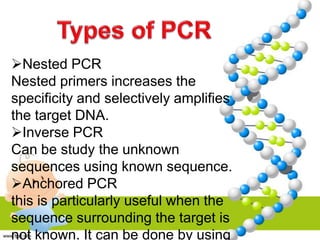
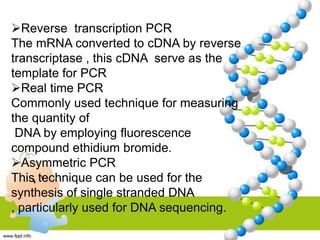
PCR is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample to denature the double-stranded DNA, anneal primers, and extend new strands using a DNA polymerase. This process is repeated many times, exponentially amplifying the target DNA sequence. PCR is widely used in scientific research and forensic analysis.