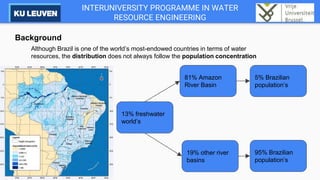
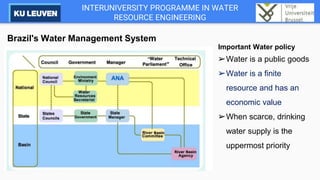
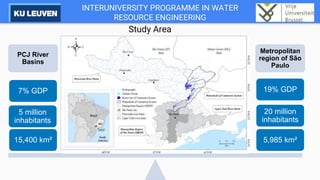
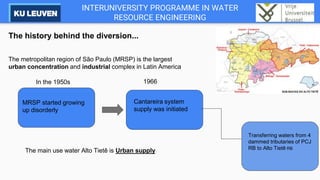
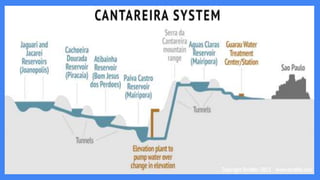
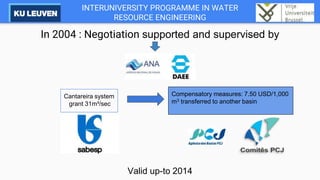
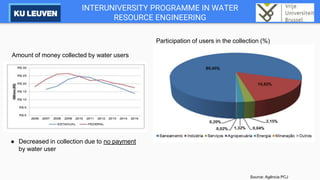
The Cantareira water supply system transfers water from four tributaries of the Piracicaba, Capivari, and Jundiaí (PCJ) River Basins to the Alto Tietê River Basin to supply the metropolitan region of São Paulo. This transfer has caused conflicts between the river basins over water availability and impacts development in the PCJ basins. A river basin committee was established to negotiate water allocations and resolve disputes, establishing compensatory payments for water transferred out of the PCJ basins. However, droughts have stressed the system and highlighted the need for improved coordination between basins and water demand management.