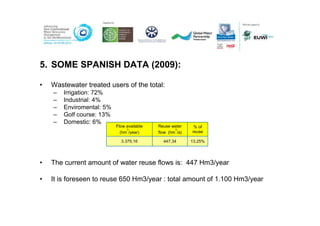
The document discusses a regional conference focused on advancing non-conventional water resources management (ncwrm) in the Mediterranean, highlighting the importance of stakeholder engagement and capacity building. It outlines the economic, social, and environmental benefits of water reuse for irrigation, as well as examples of successful collaboration between irrigation and other users in Spain. The conclusions emphasize that water reuse guarantees a higher water supply, especially in coastal areas, and the need for agreements between agricultural and domestic users regarding water rights.