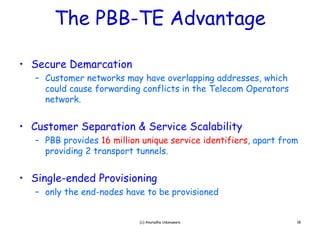
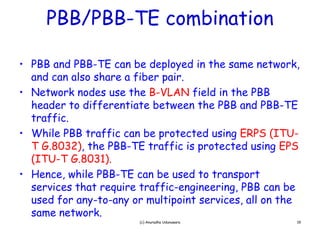
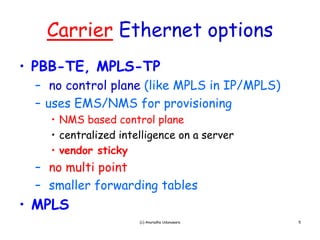
PBB-TE builds on Ethernet and PBB to enable carrier-grade transport of Ethernet services with traffic engineering capabilities like protected virtual circuits. It provides secure customer demarcation, large customer service scalability through unique identifiers, and single-ended provisioning. PBB-TE can be deployed alongside regular PBB in a network and provide protected transport of services while PBB is used for other services, all on the same infrastructure.





![QinQ
= 802 1QiQ
802.1QiQ
= 802.1ad
= P id Bridging (PB)
Provider B id i
[C-VLAN inner, S-VLAN outer]
In this scenario provider needs to learn
scenario,
all customer MACs.
(c) Anuradha Udunuwara 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pbbte-12662201447422-phpapp02/85/PBB-TE-7-320.jpg)

![Why Not VPLS End-to-End?
End to End?
• VPLS has scalability issues
– E.g. to connect 5 PE devices requires 20
LSPs [(n*(n-1)/2)*2] 40 PEs: 1 536
[(n (n 1)/2) 2], 1,536.
– Large bandwidth loss due to broadcast
retransmissions.
• VPLS requires new features
– Protection OAM discovery
Protection, OAM,
(c) Anuradha Udunuwara 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pbbte-12662201447422-phpapp02/85/PBB-TE-9-320.jpg)