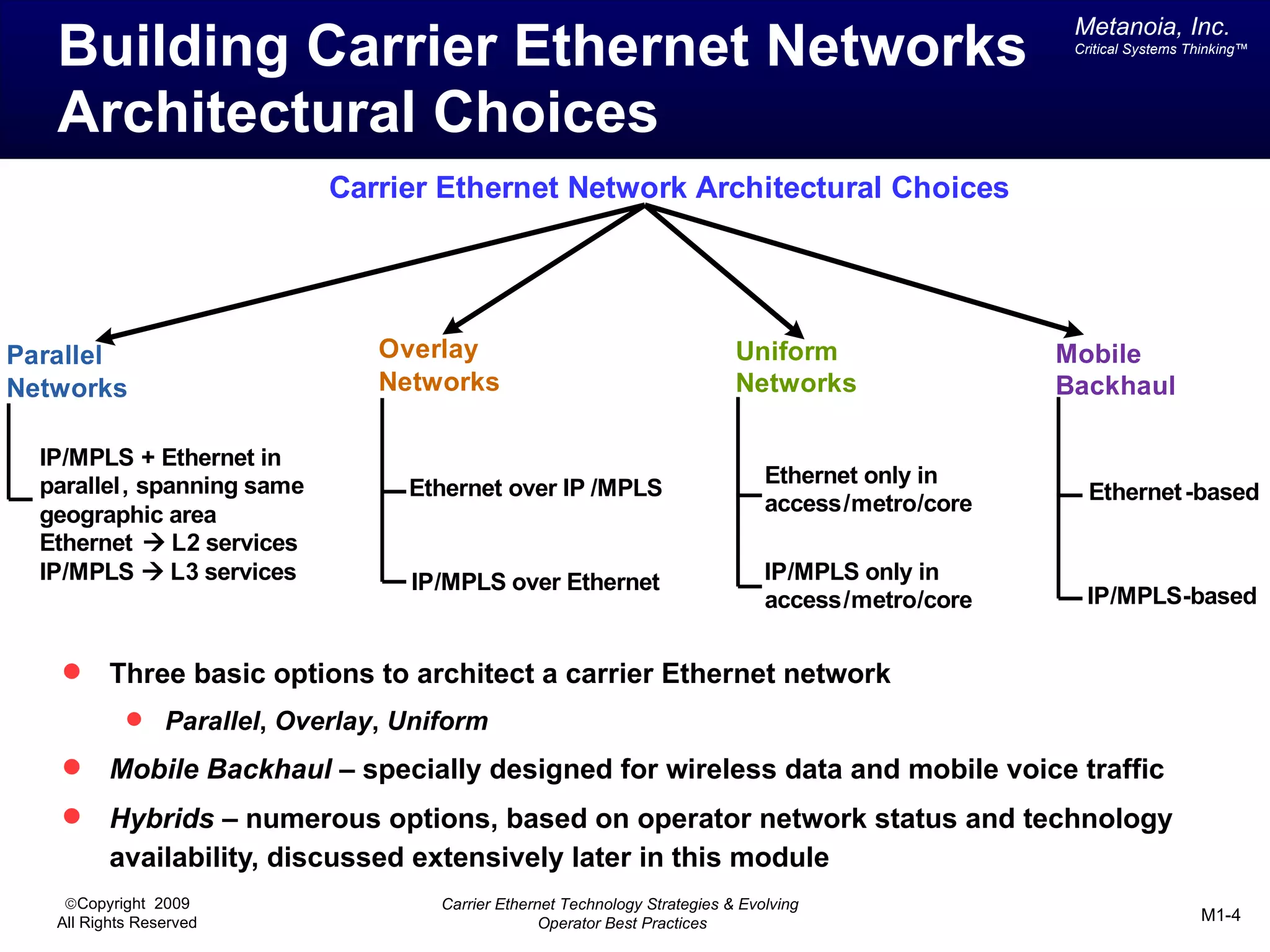
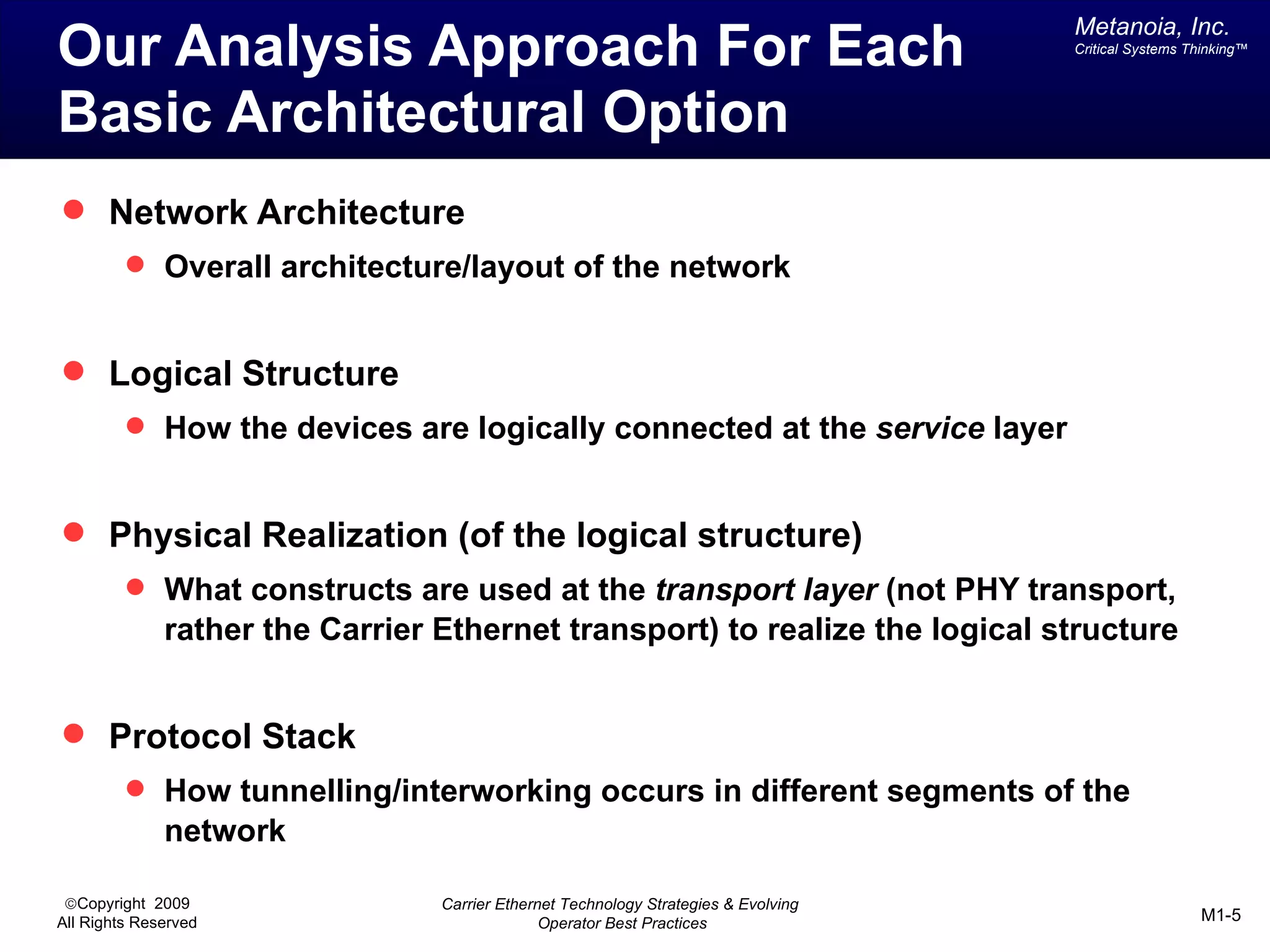
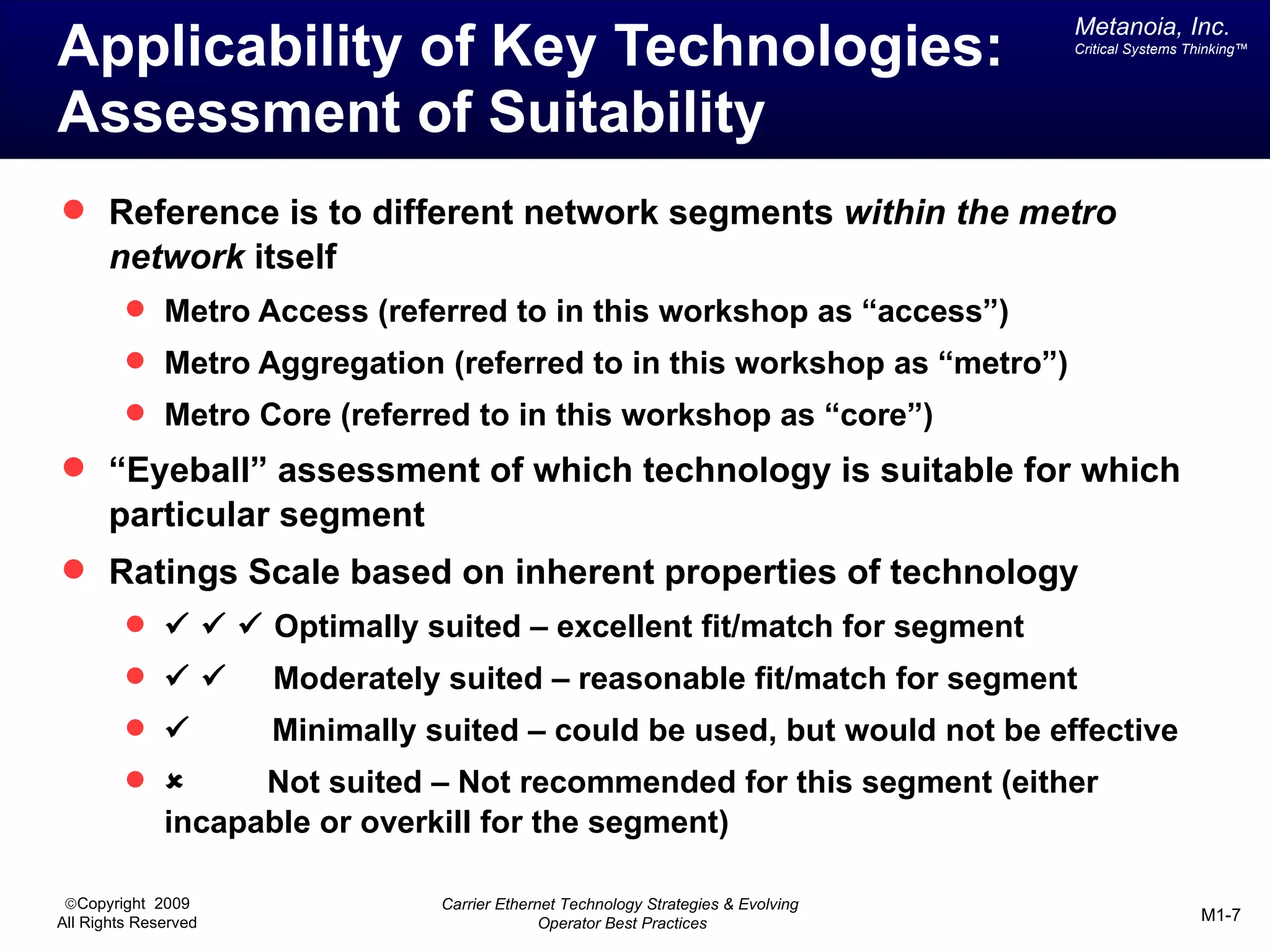
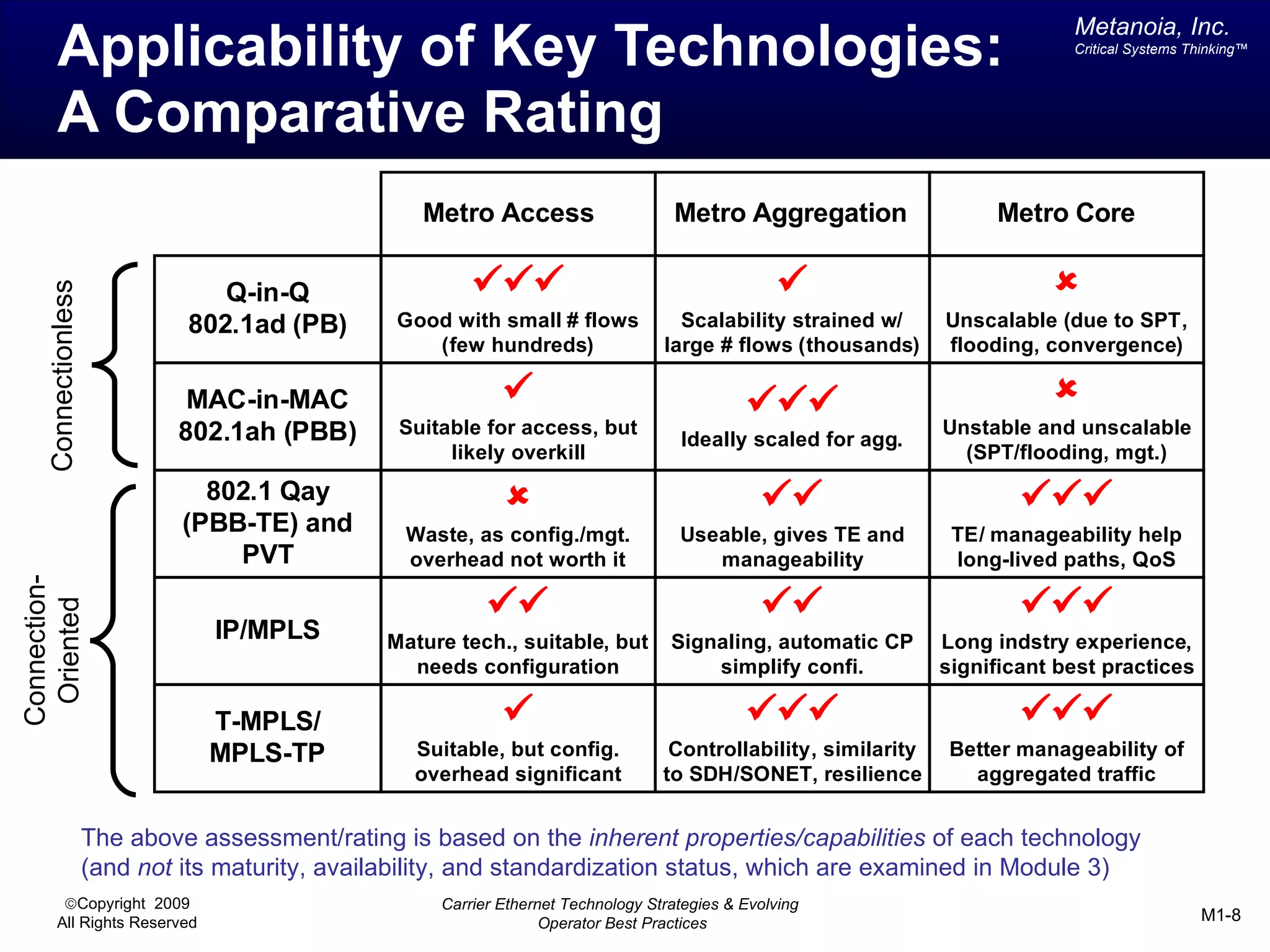
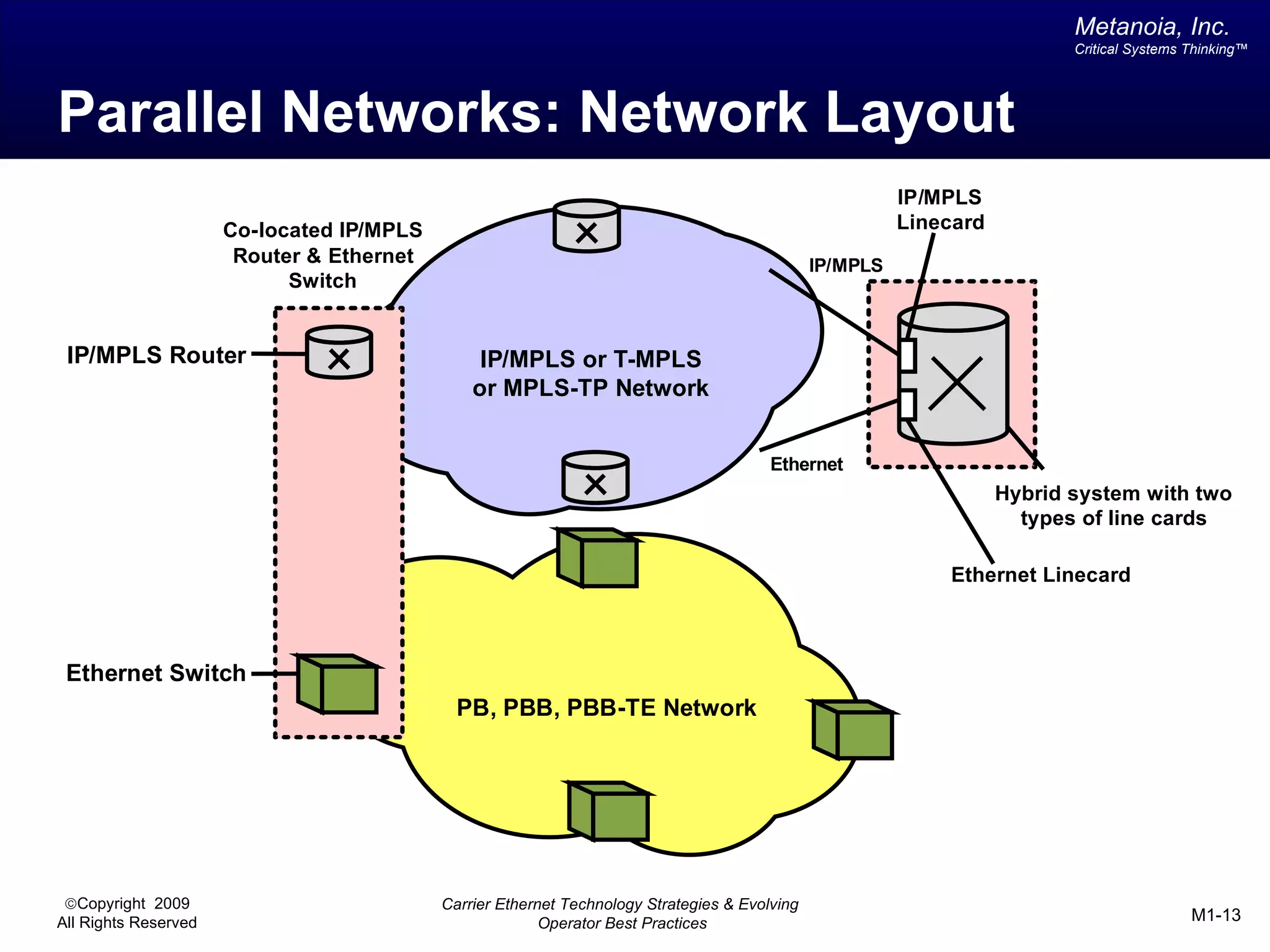
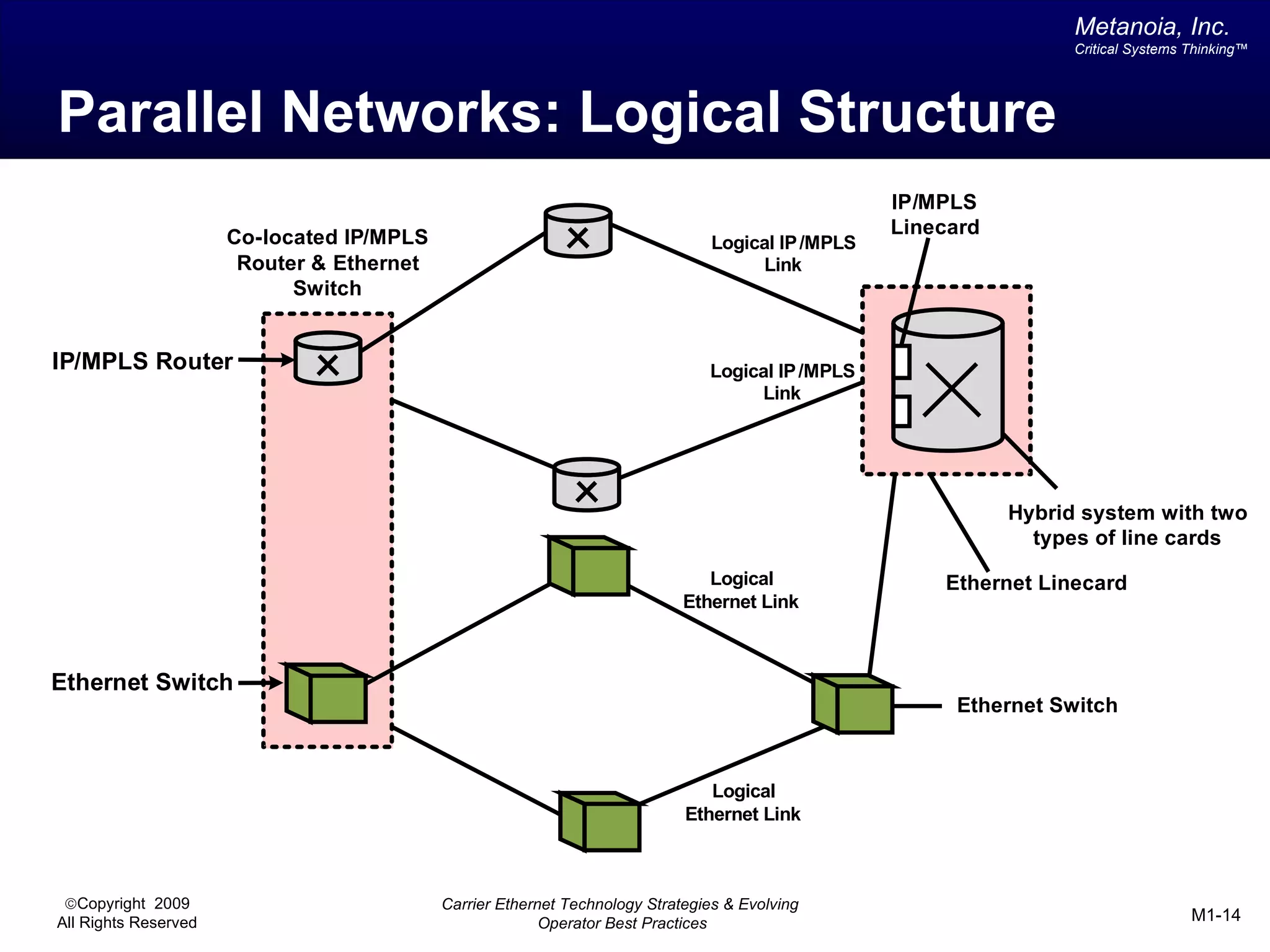
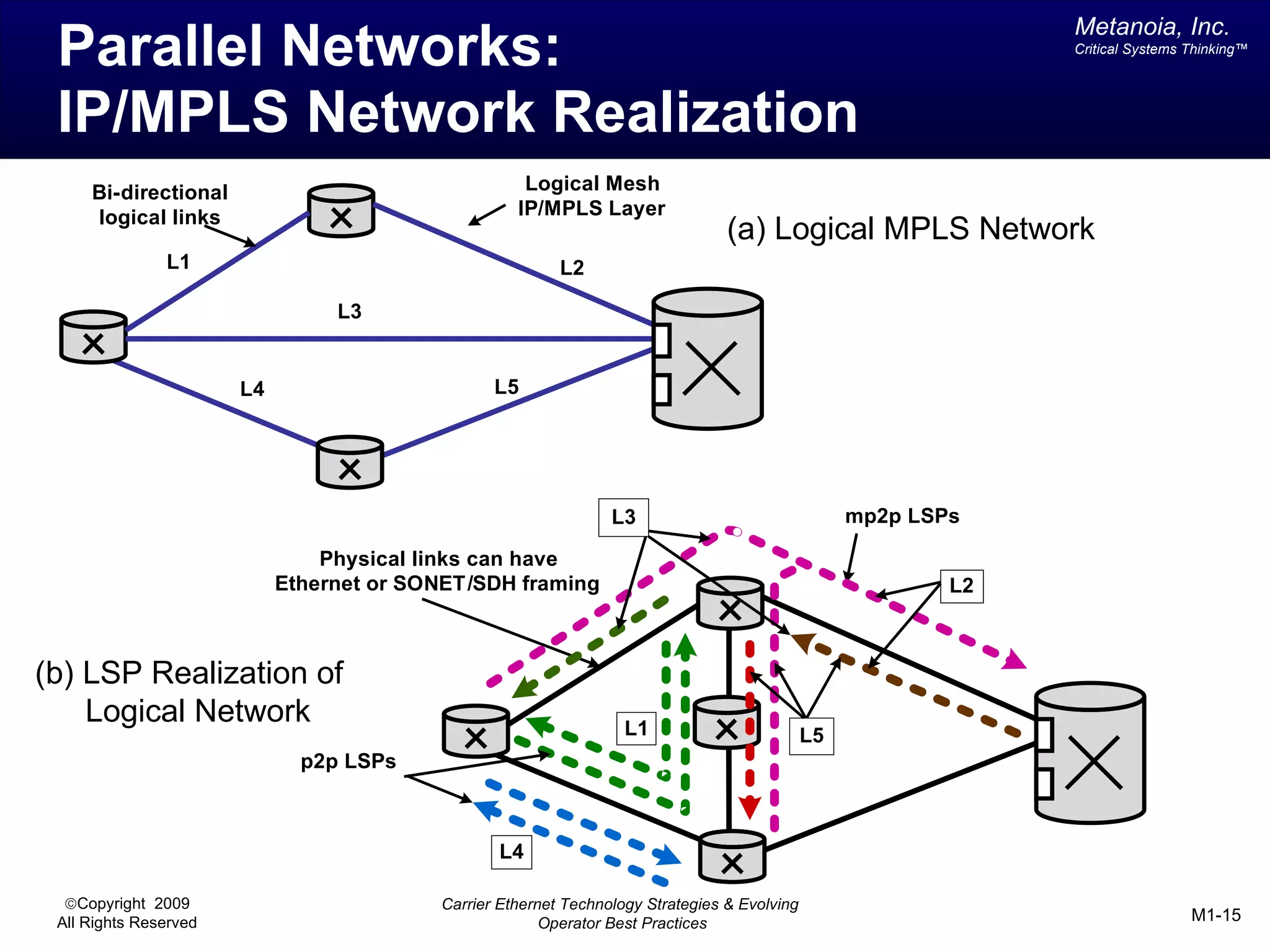
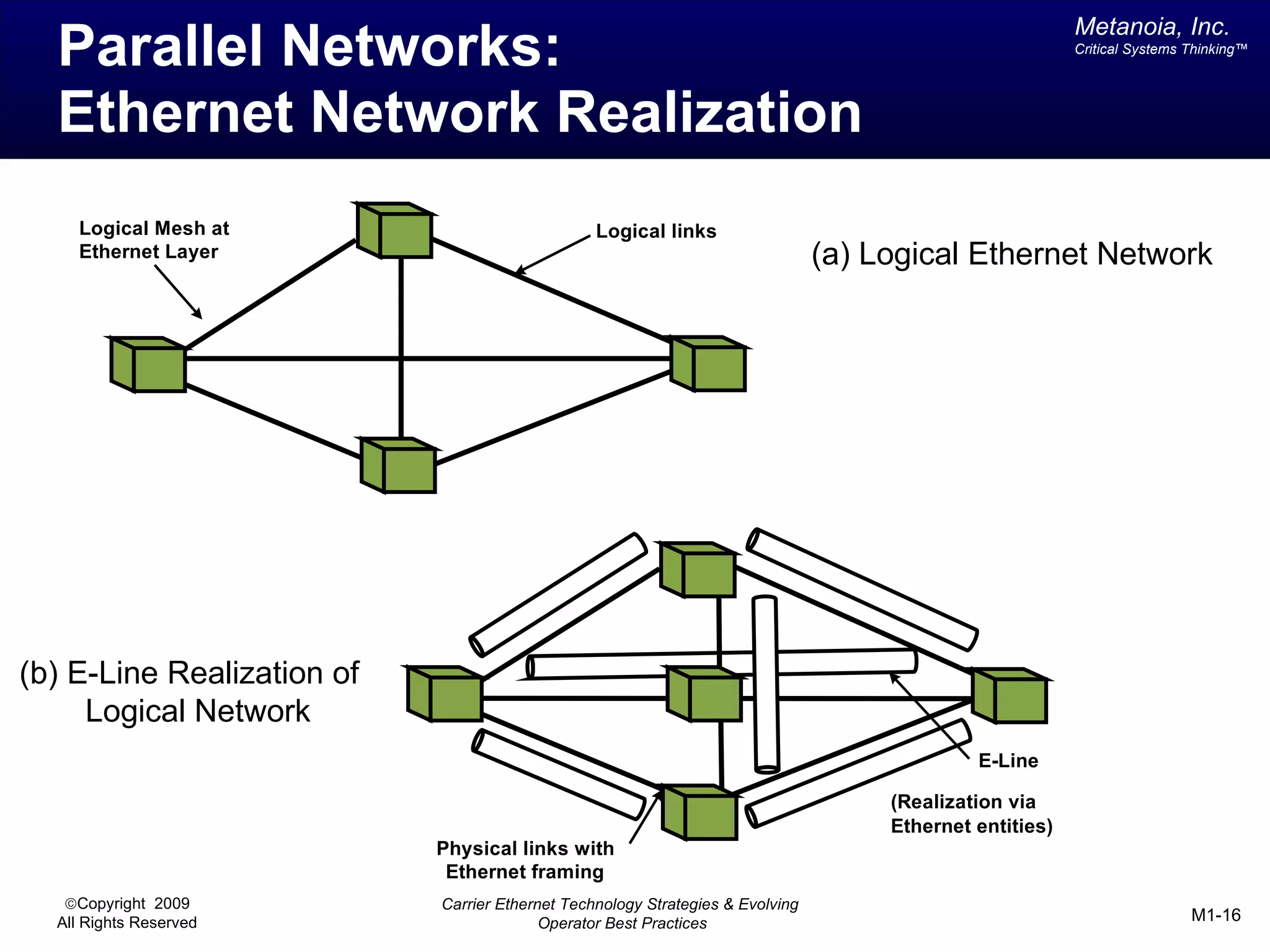
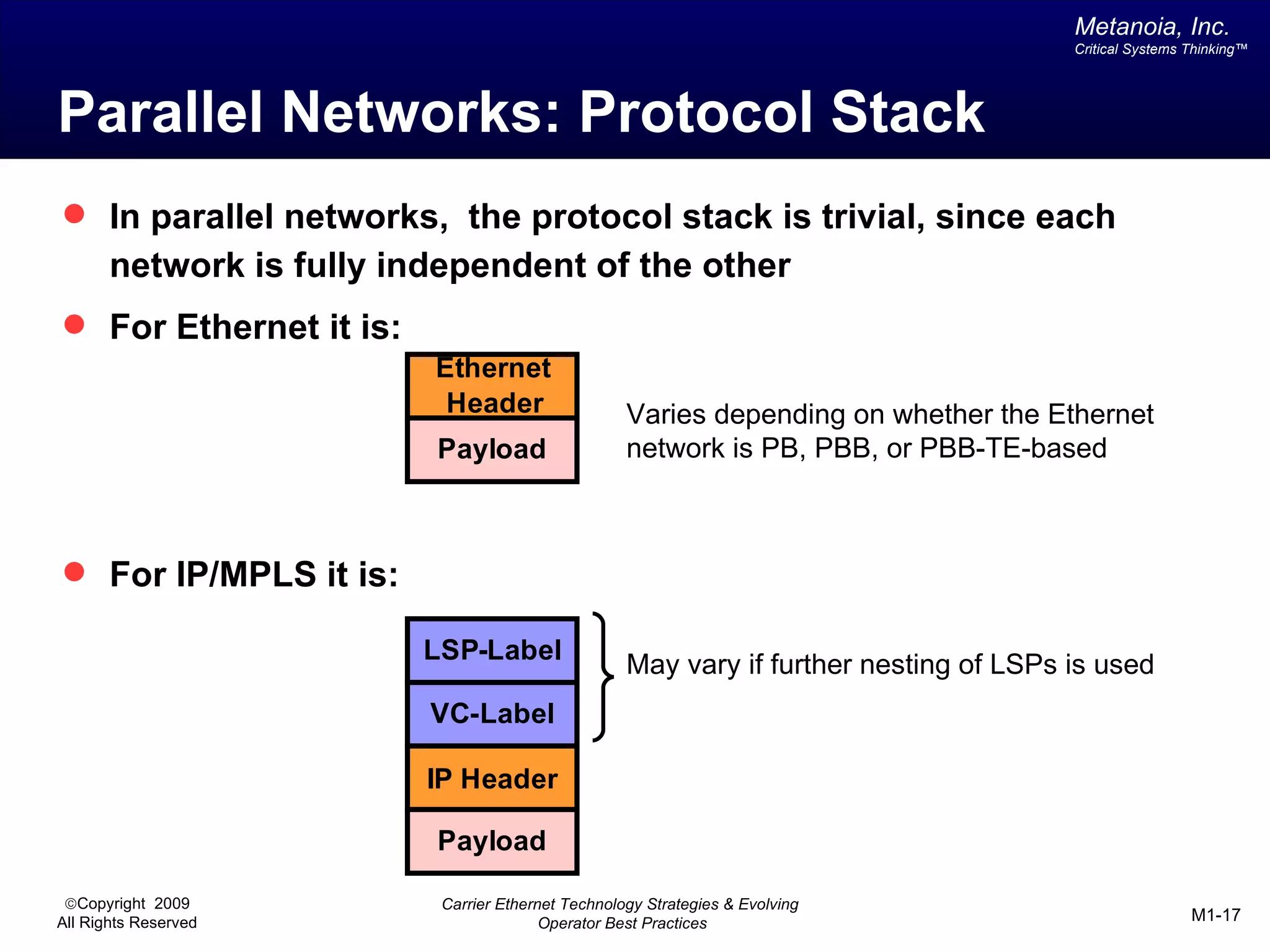
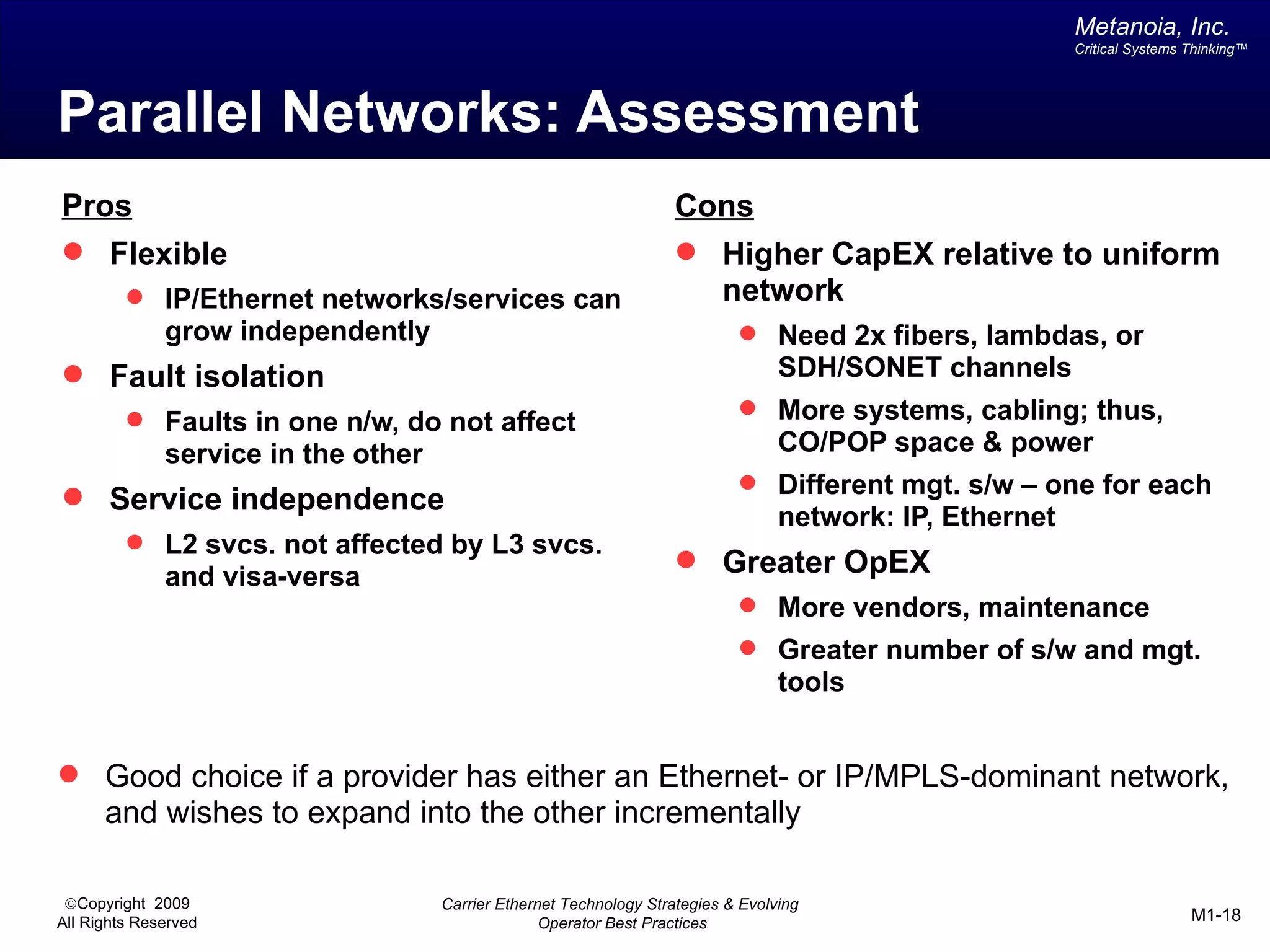
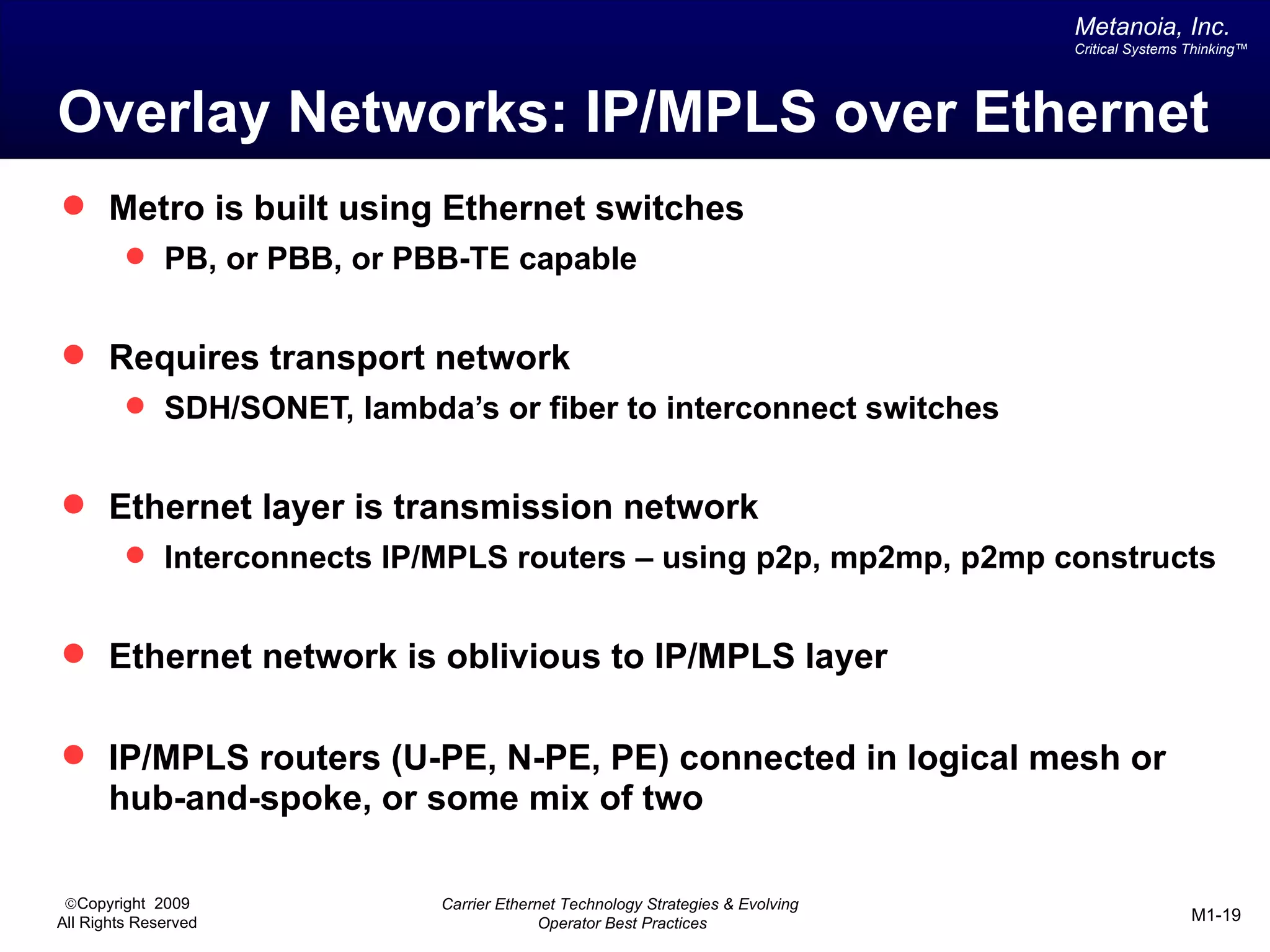
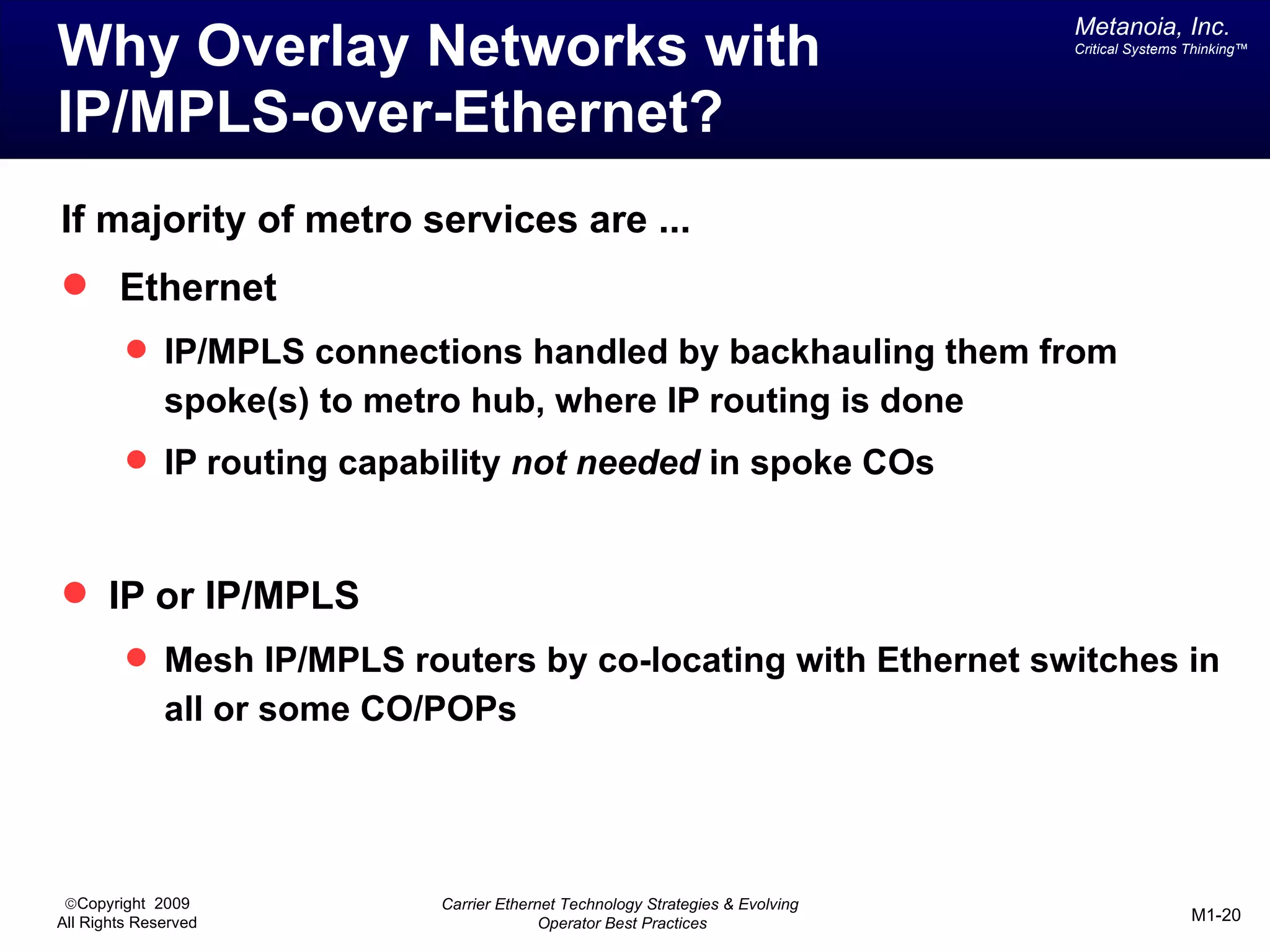
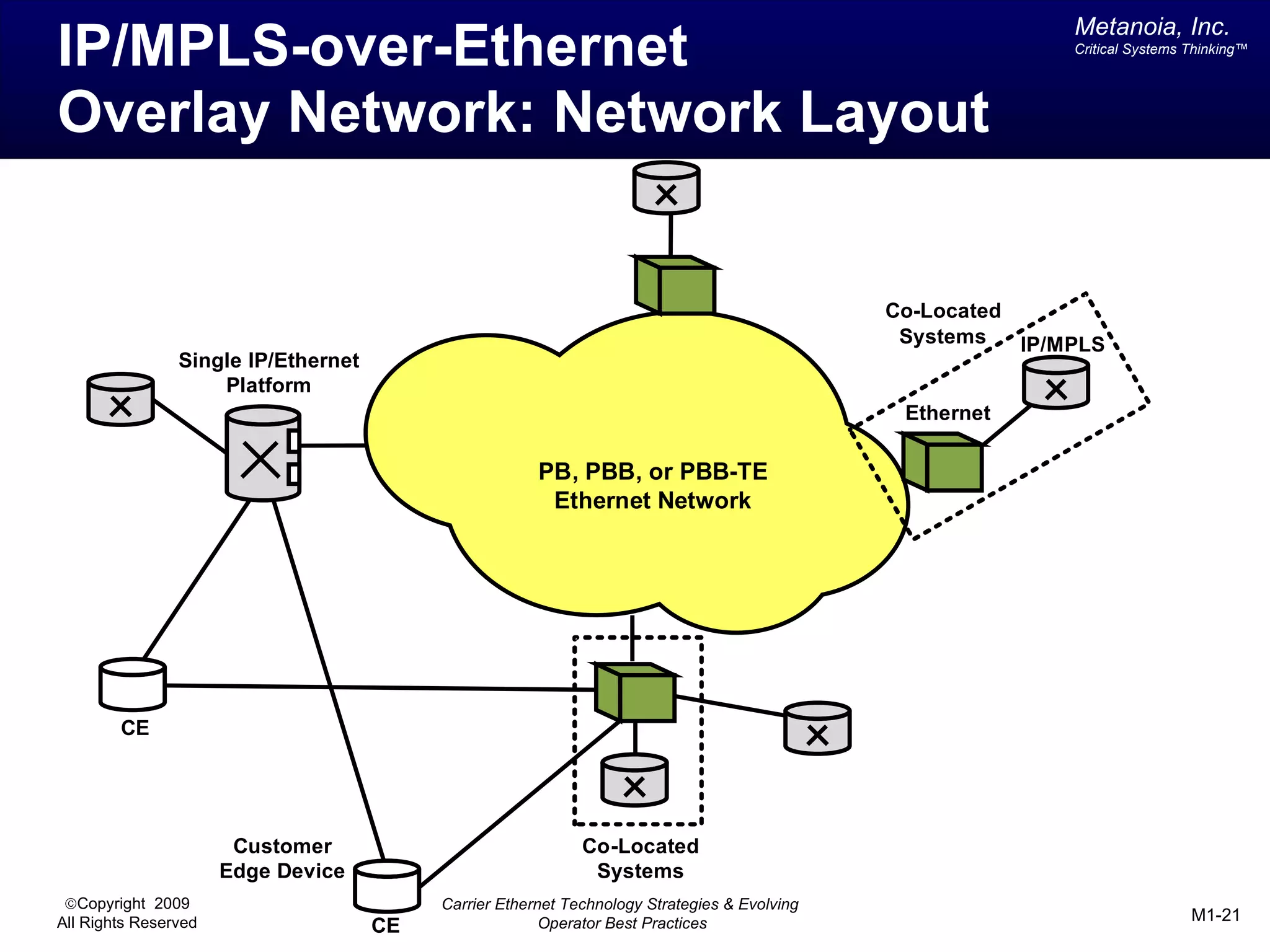
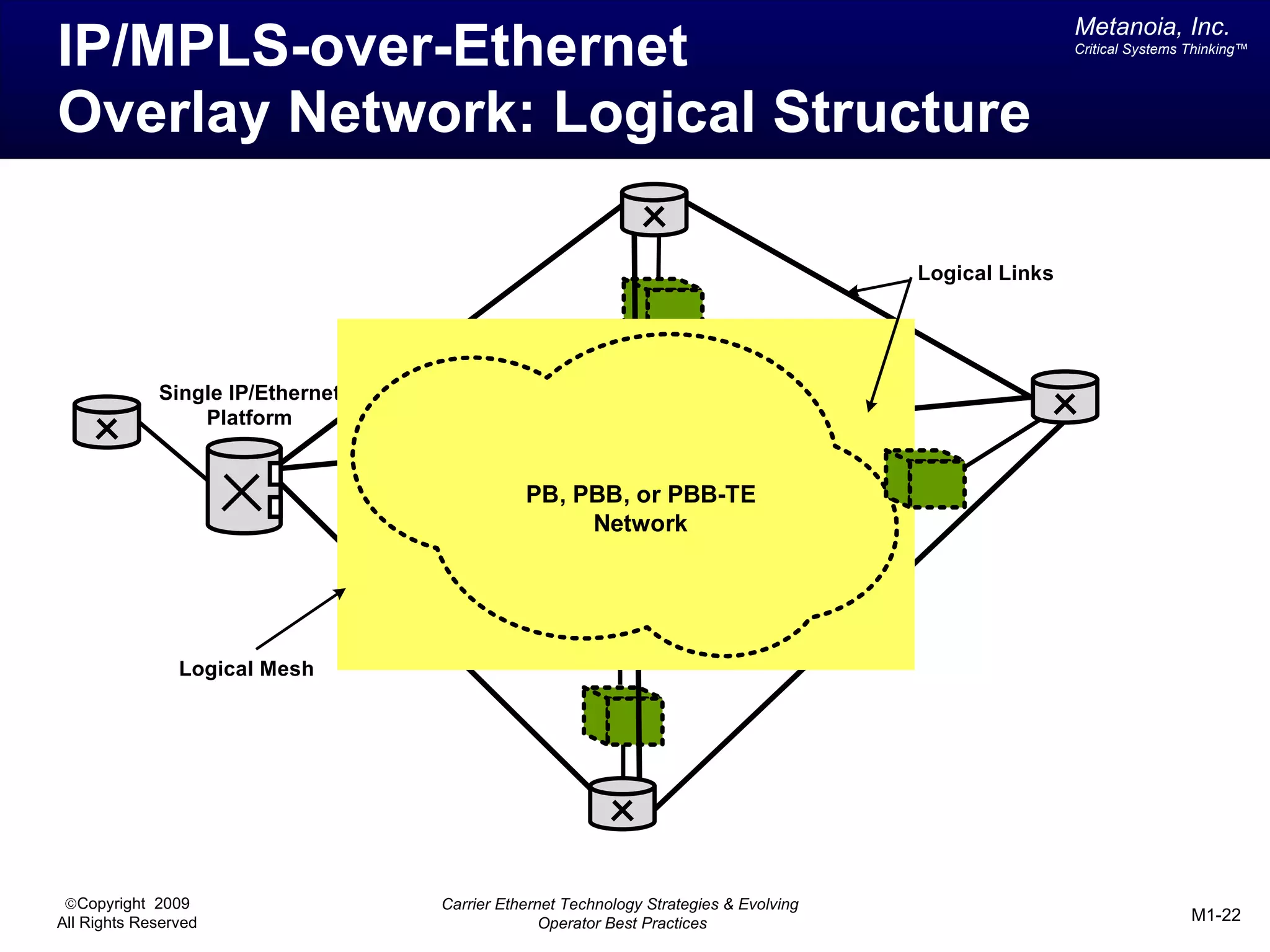
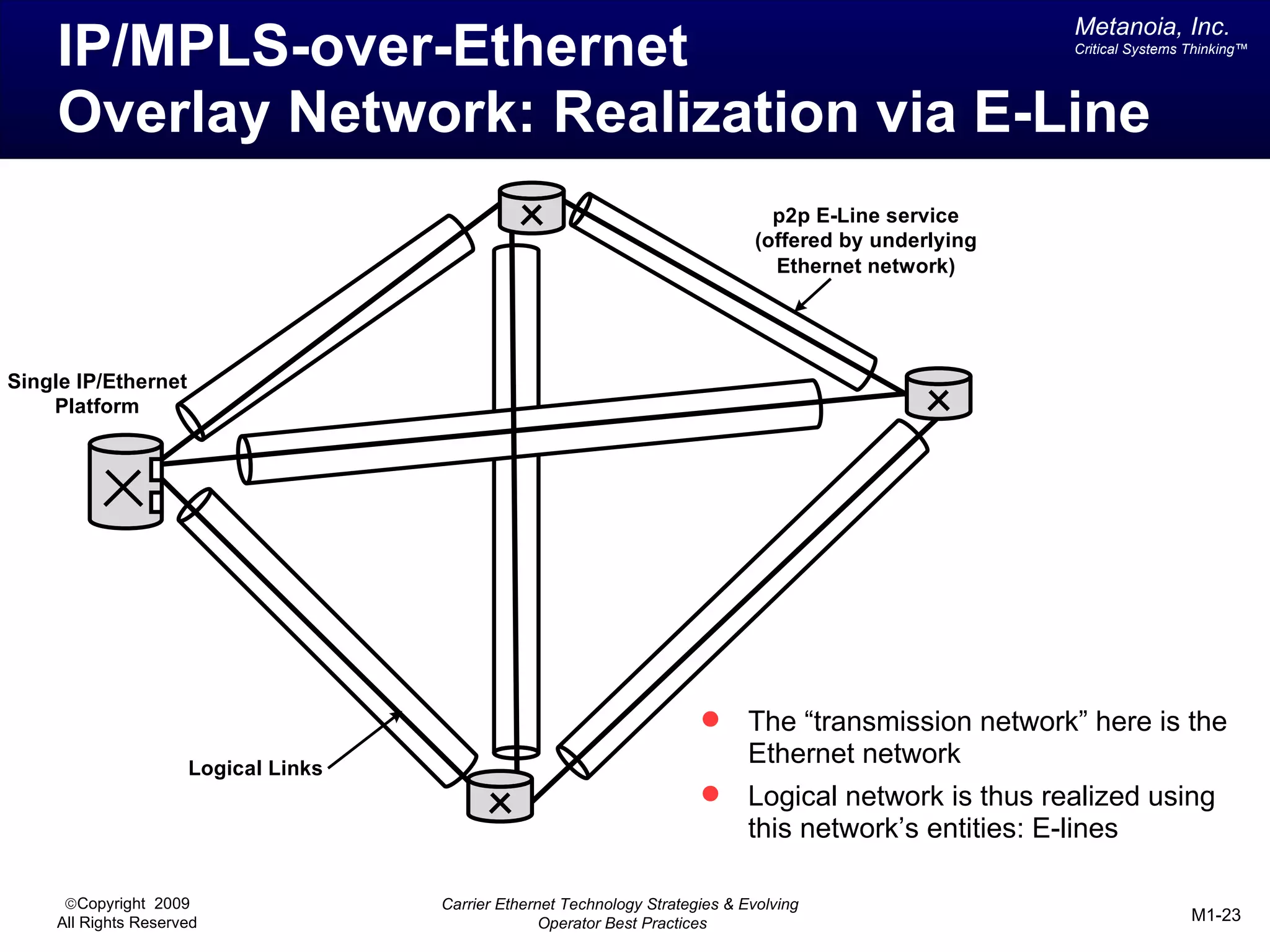
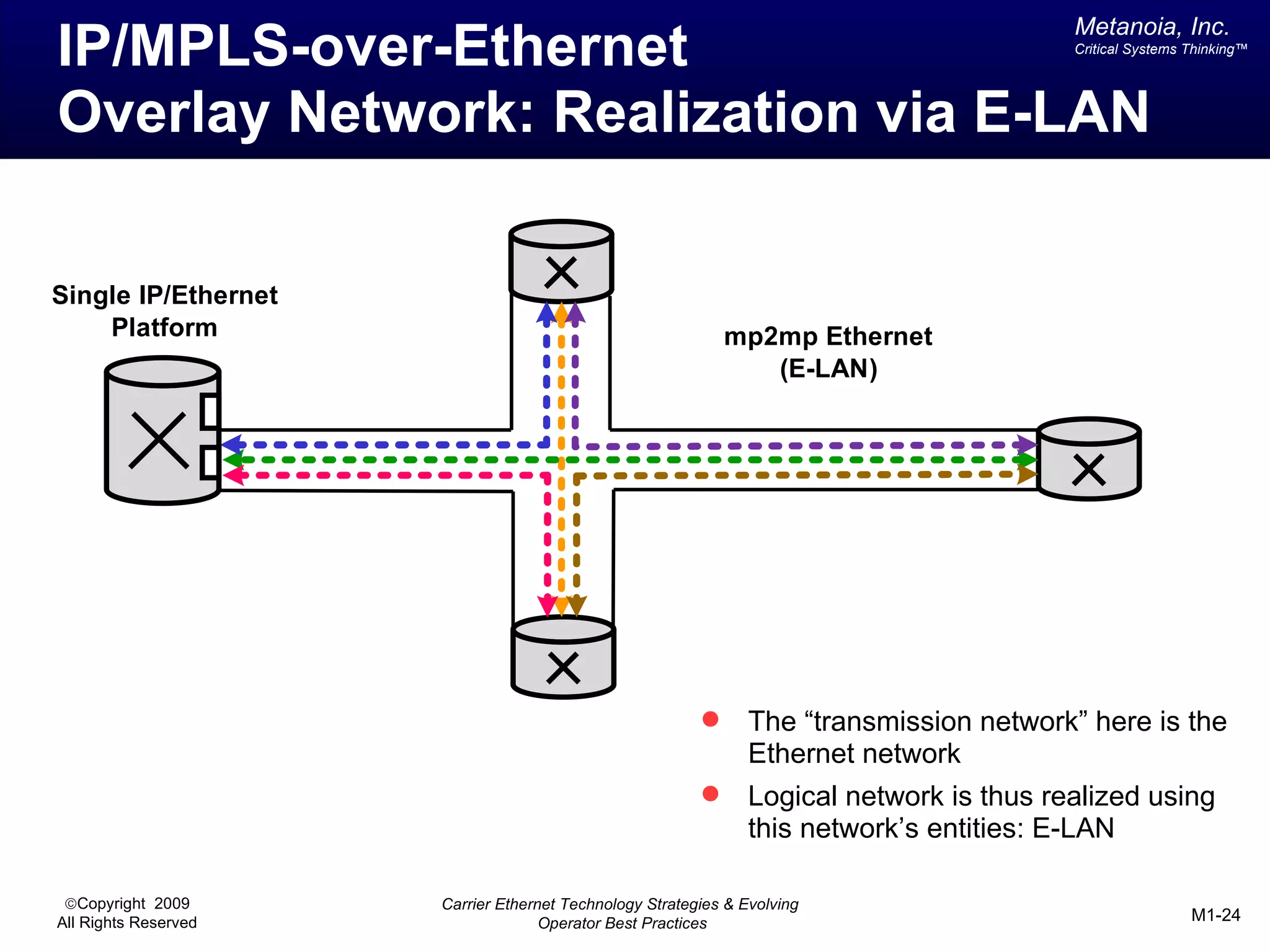
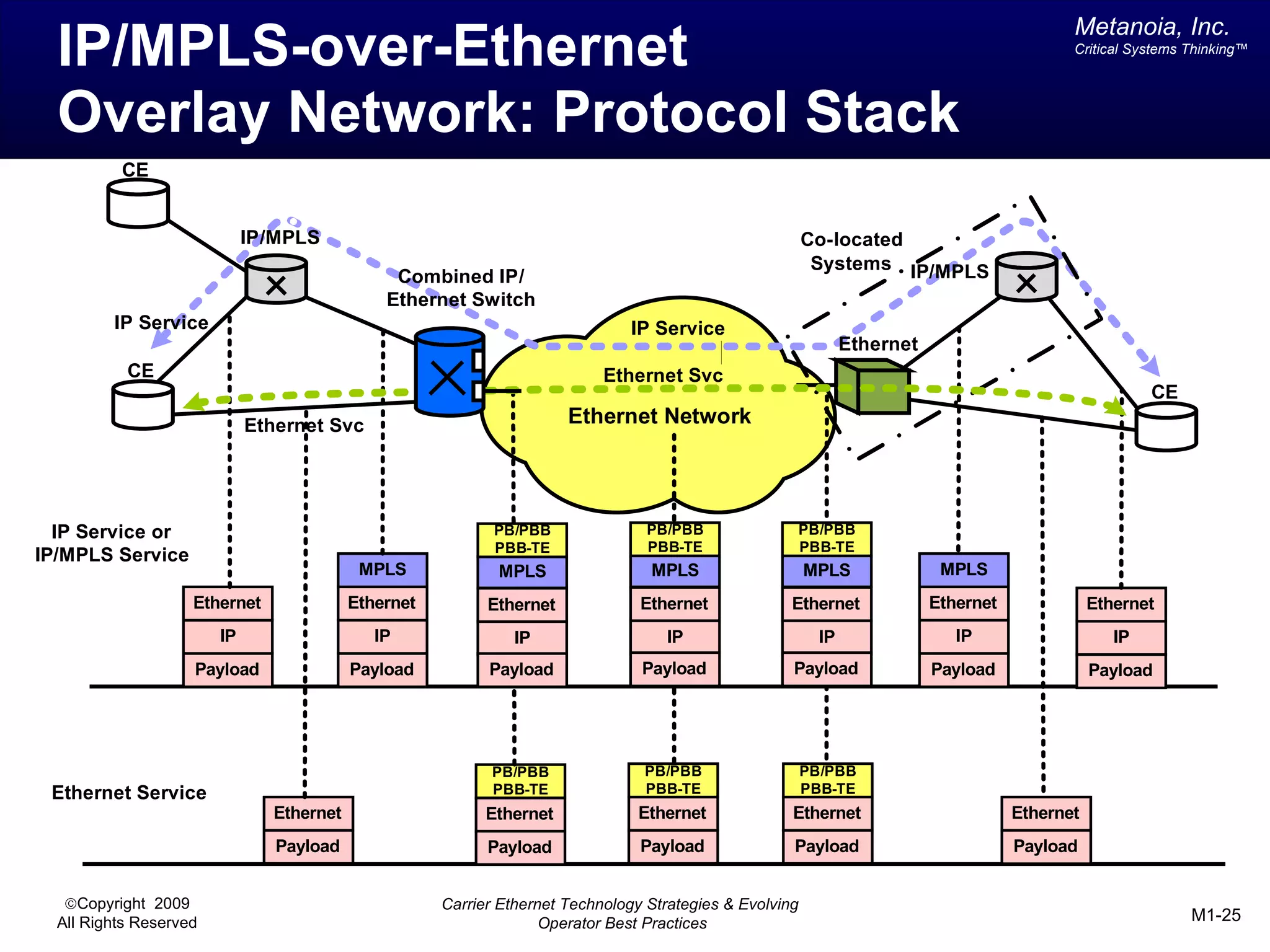
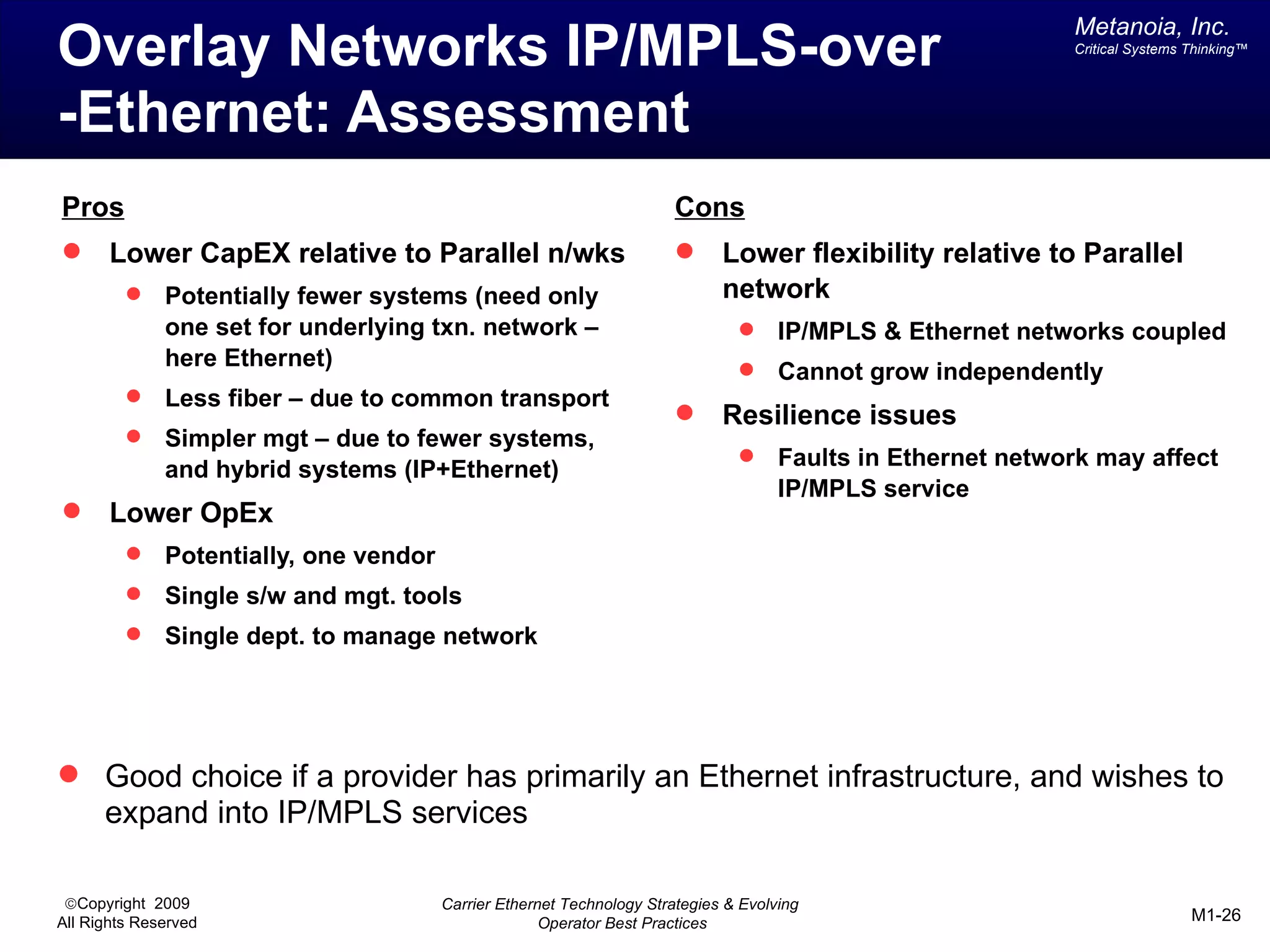
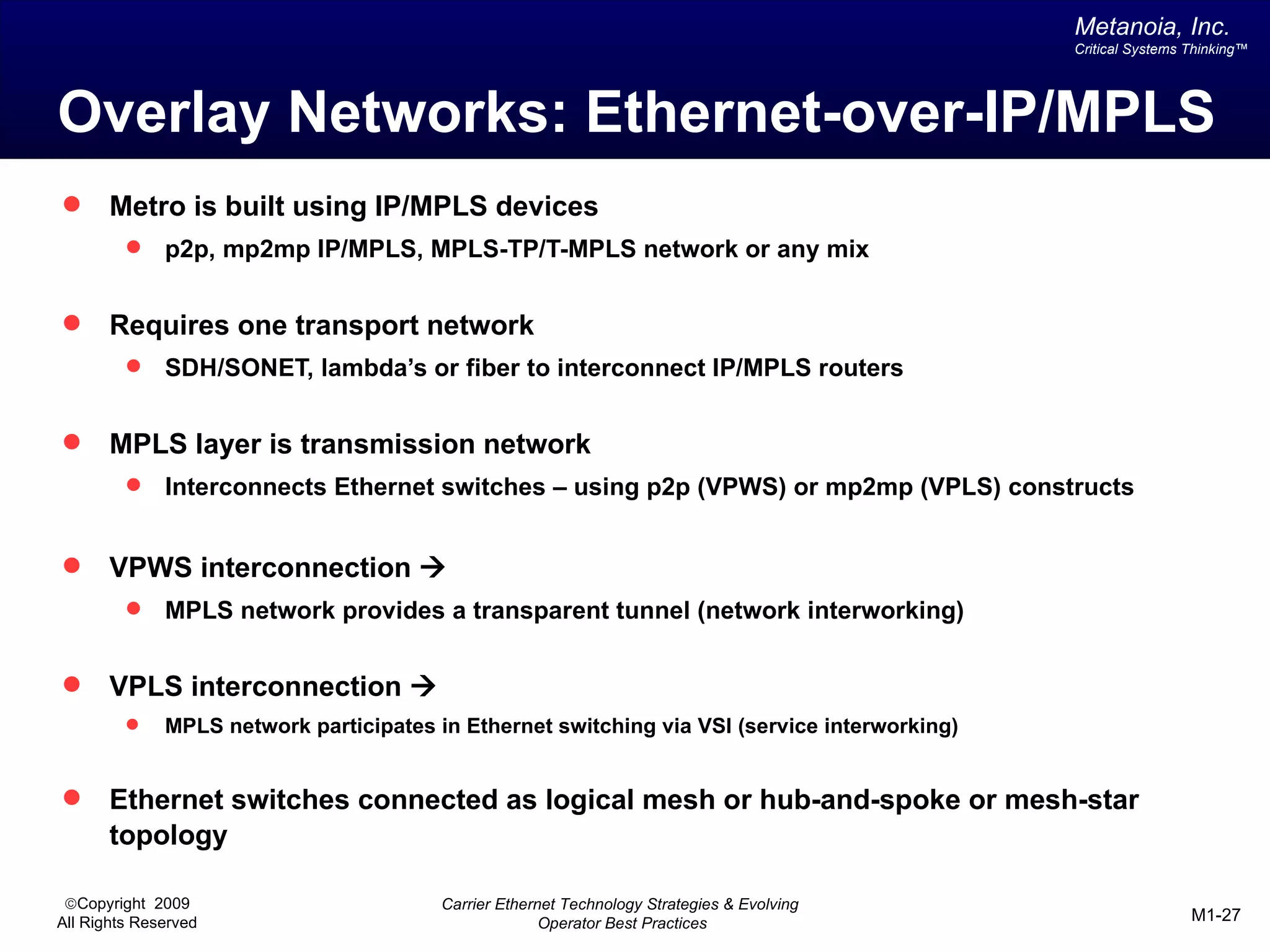
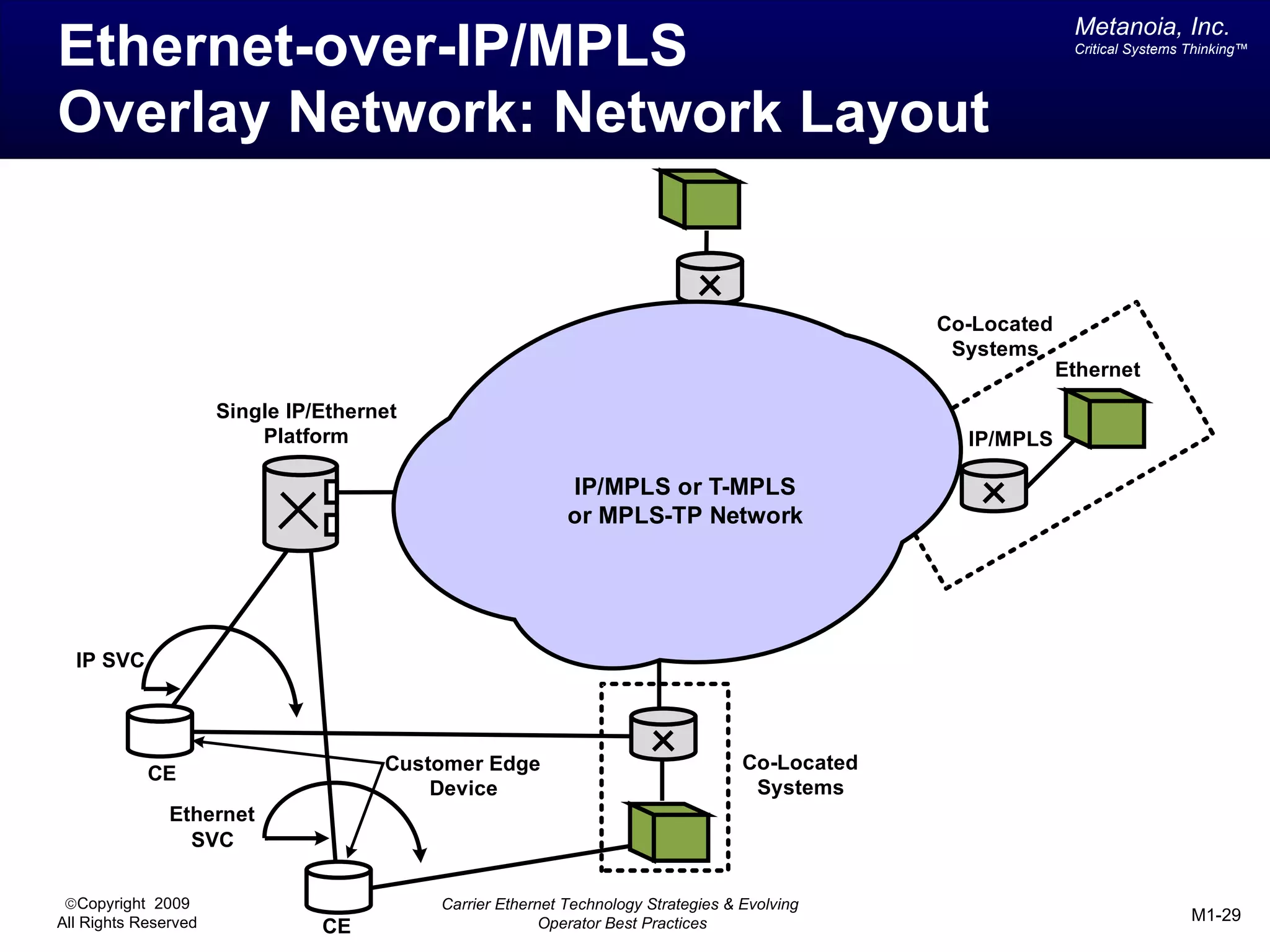
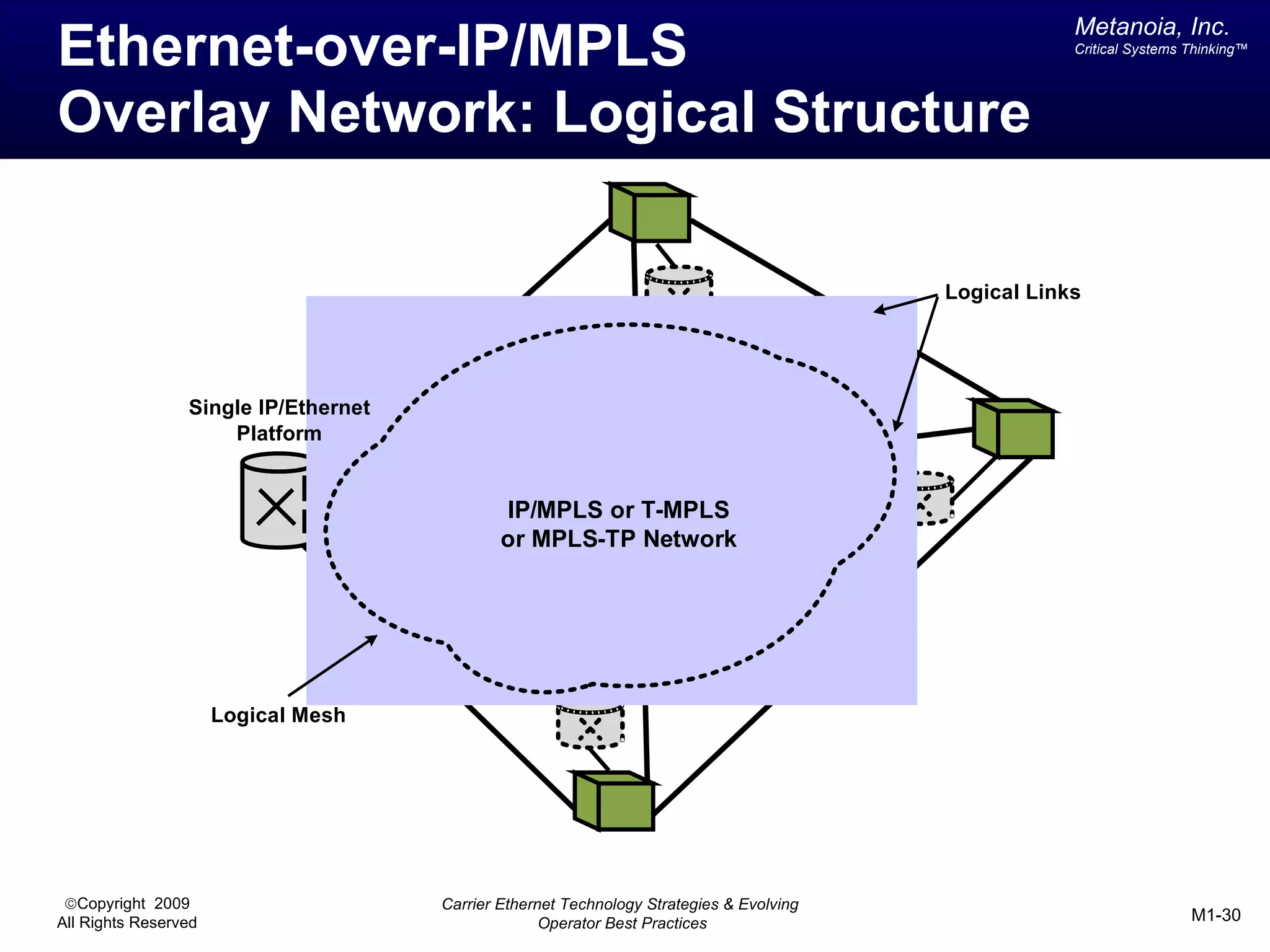
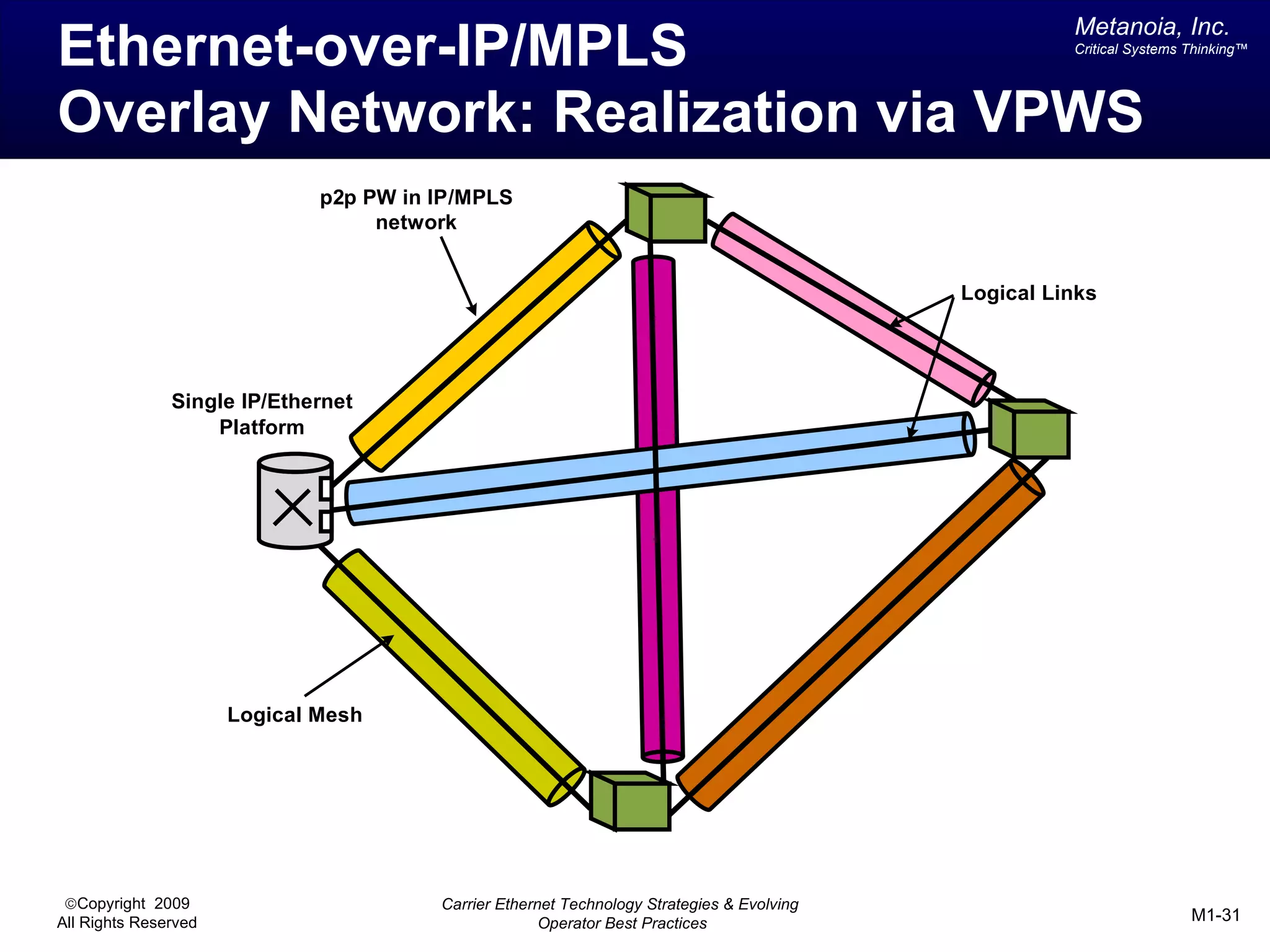
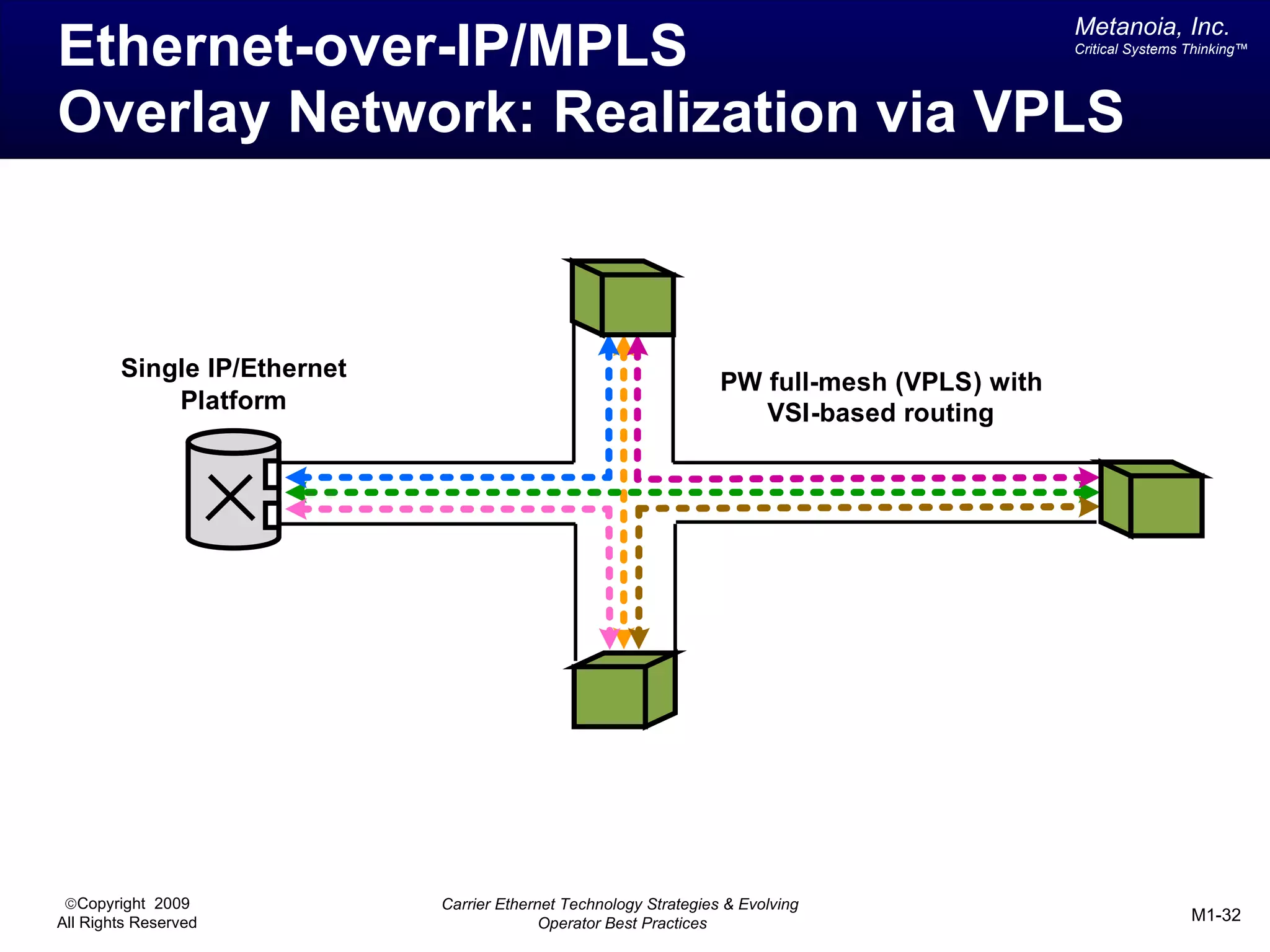
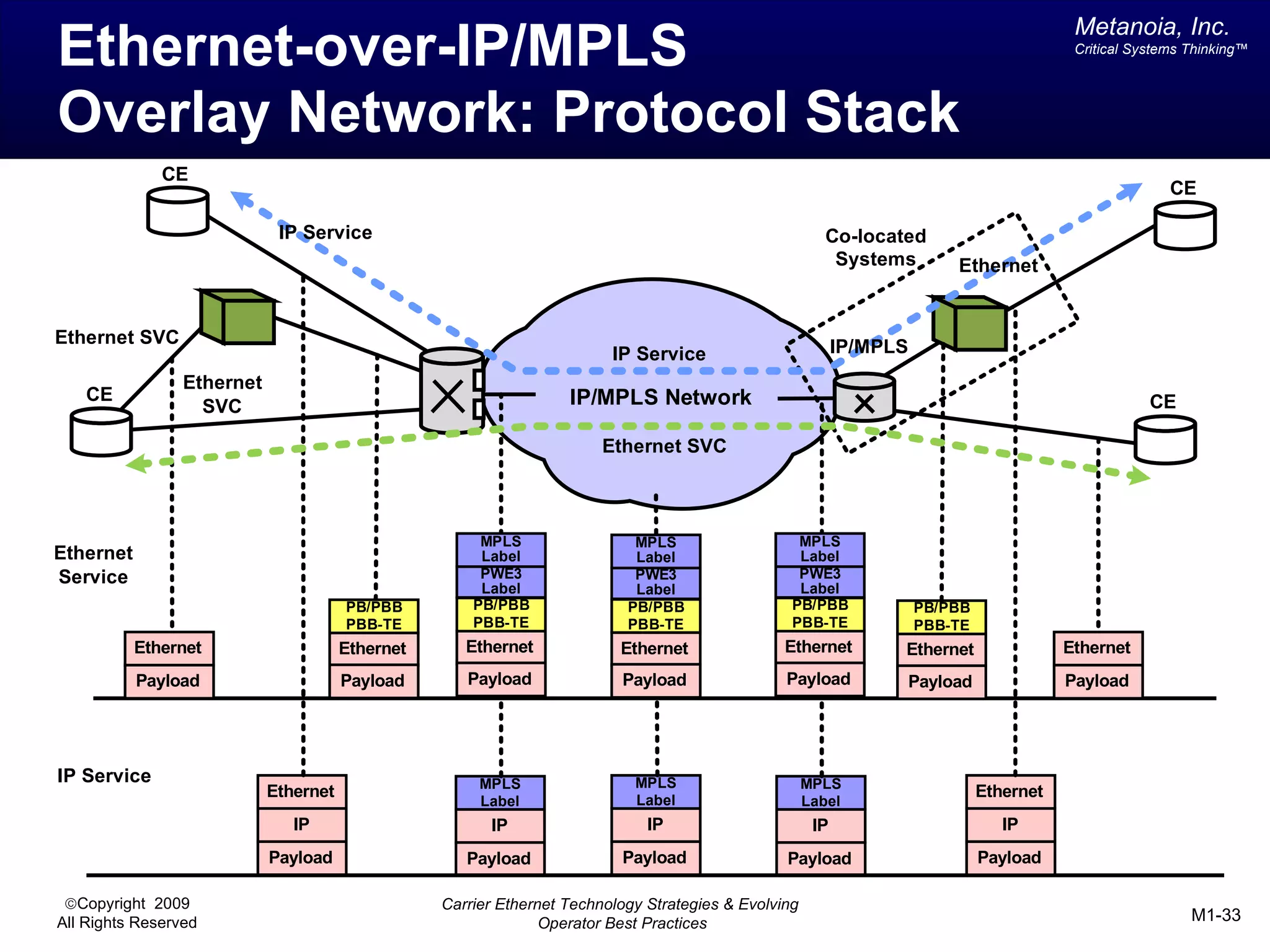
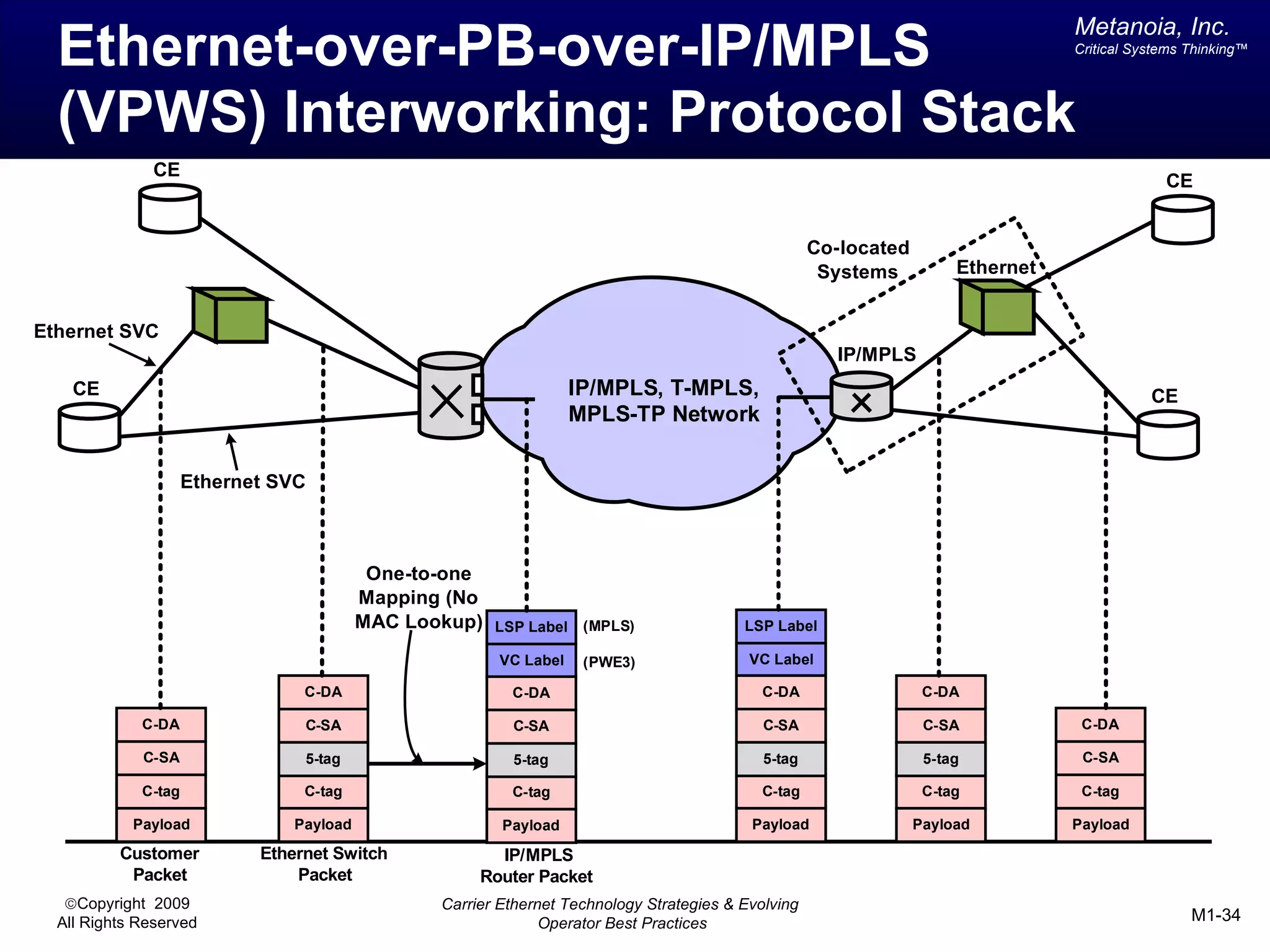
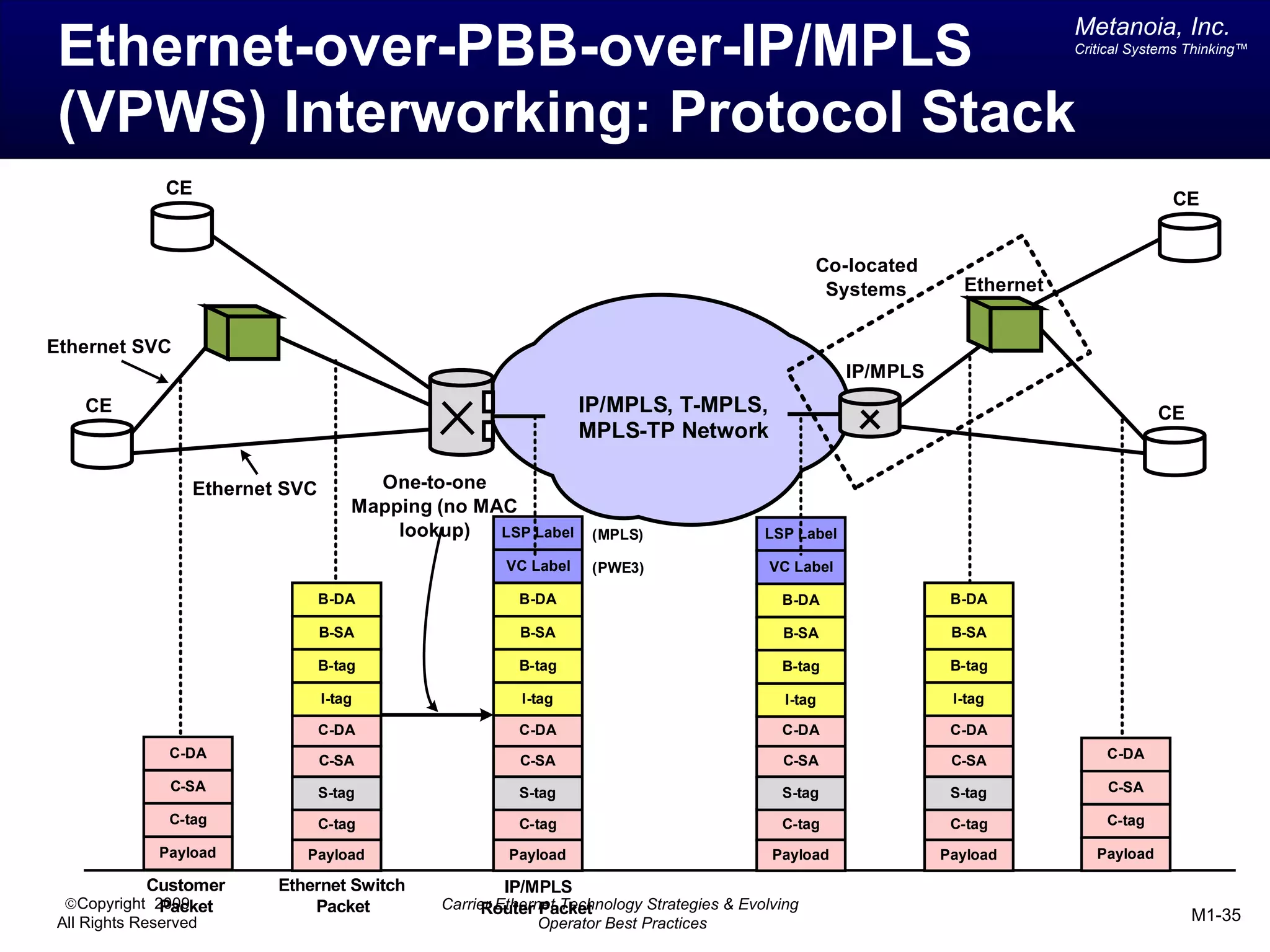
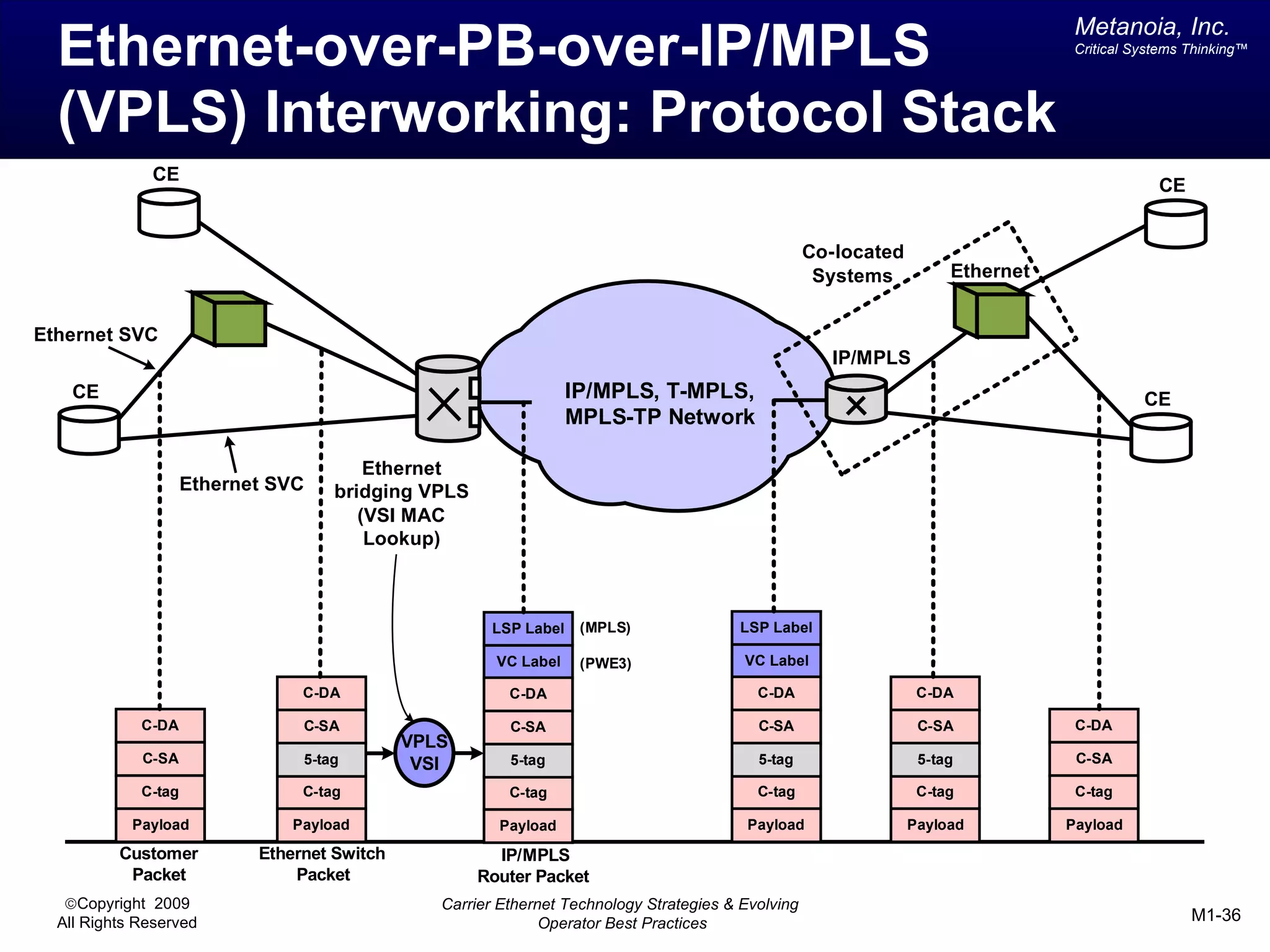
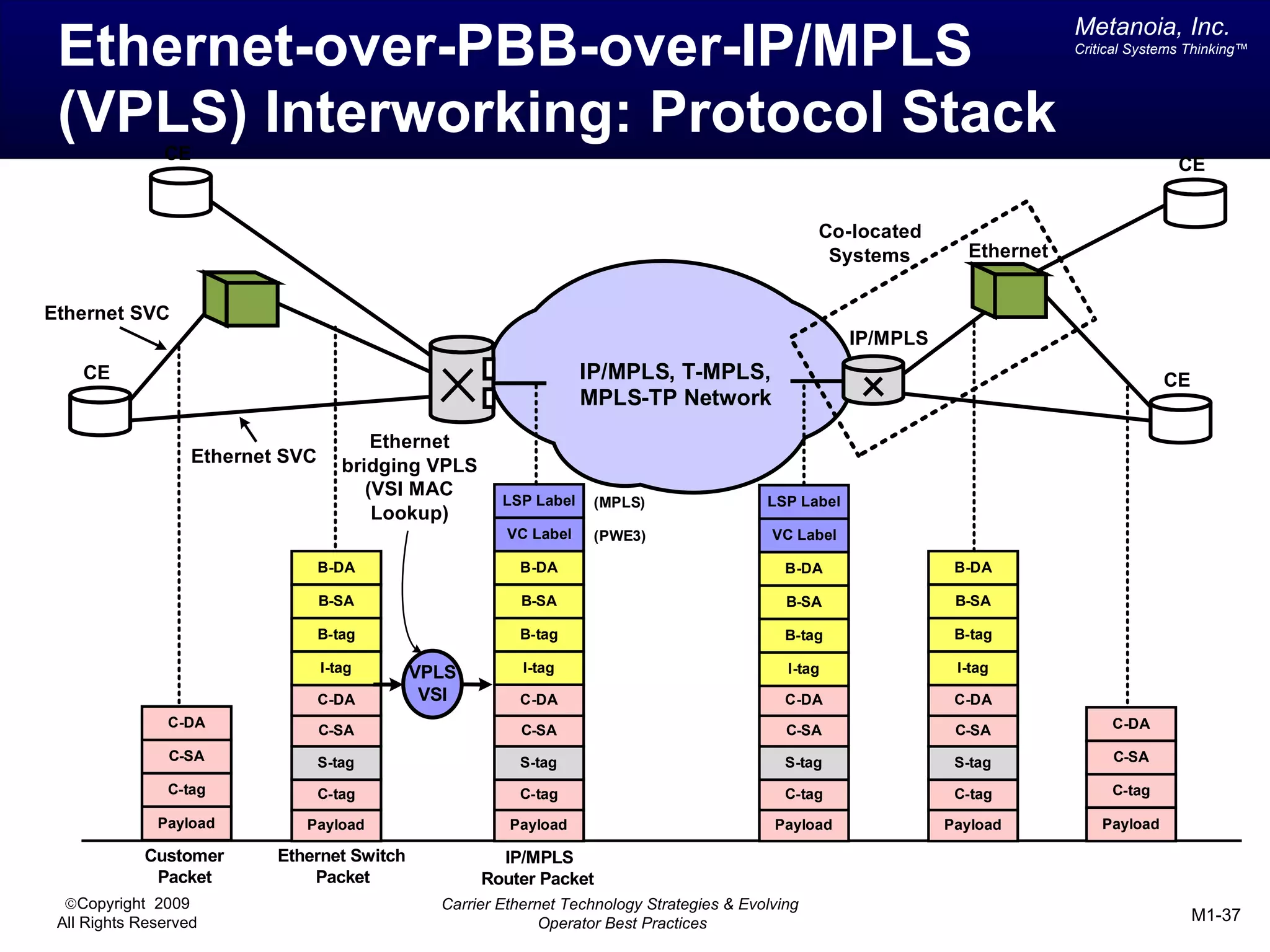
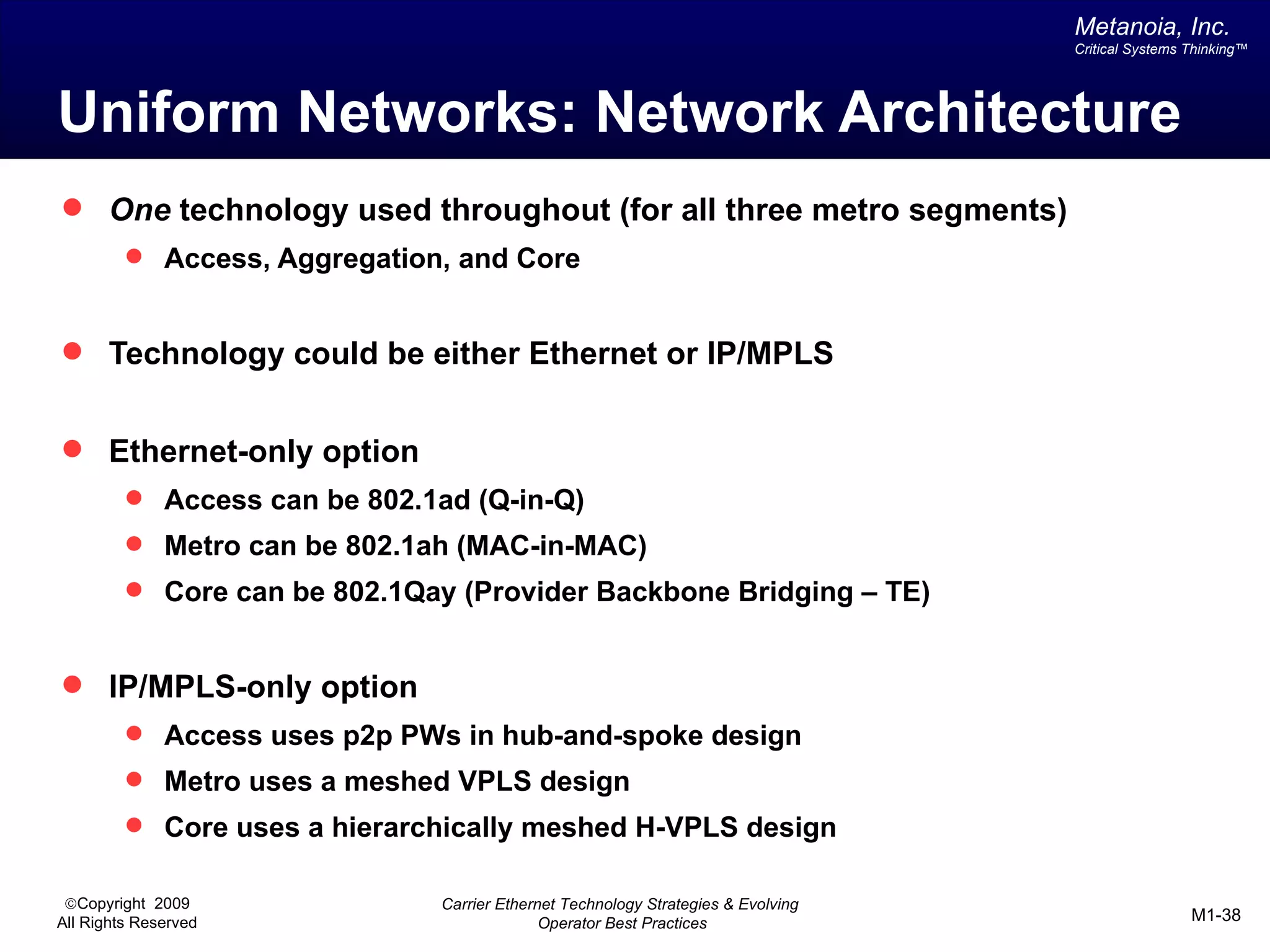
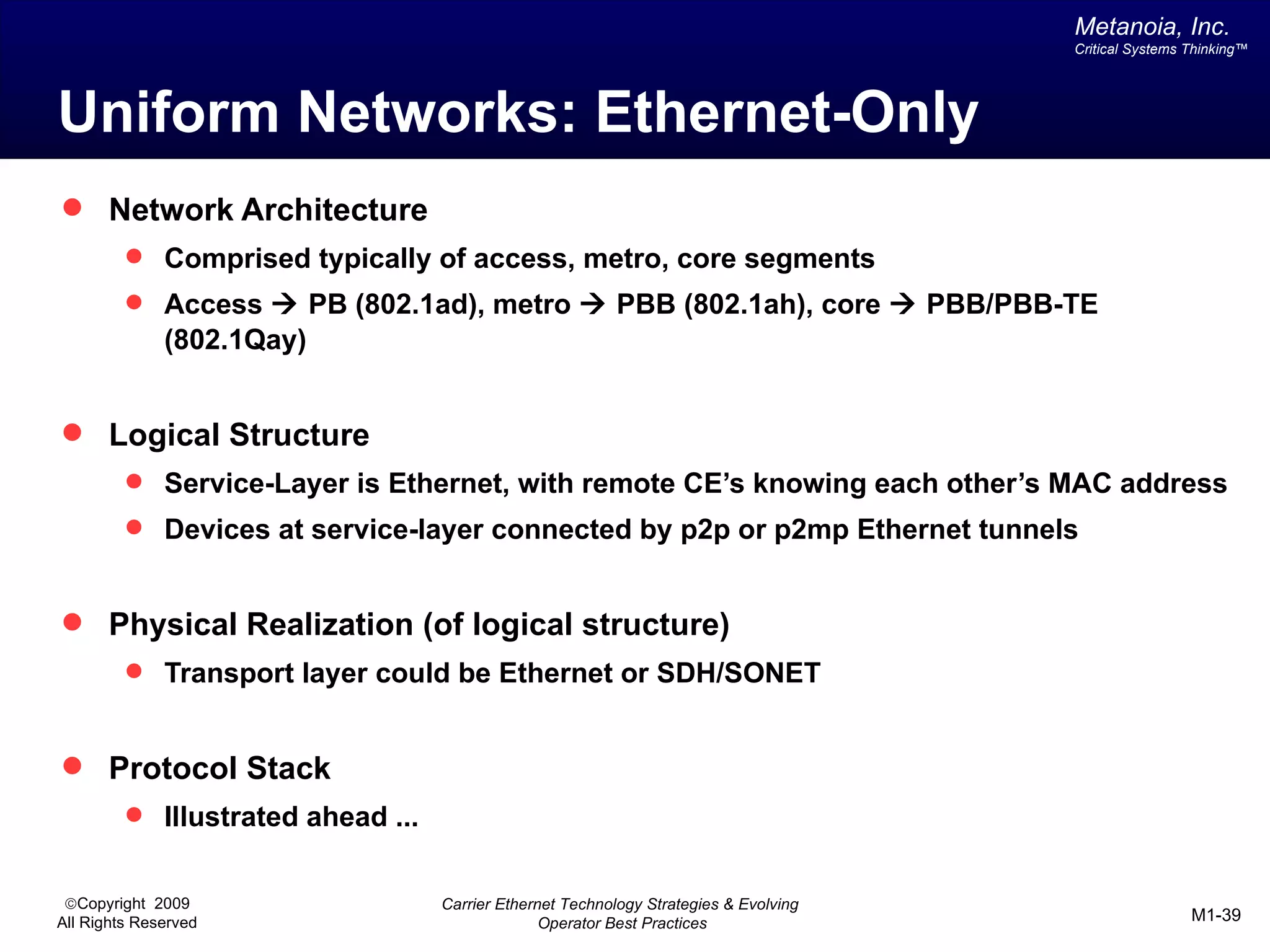
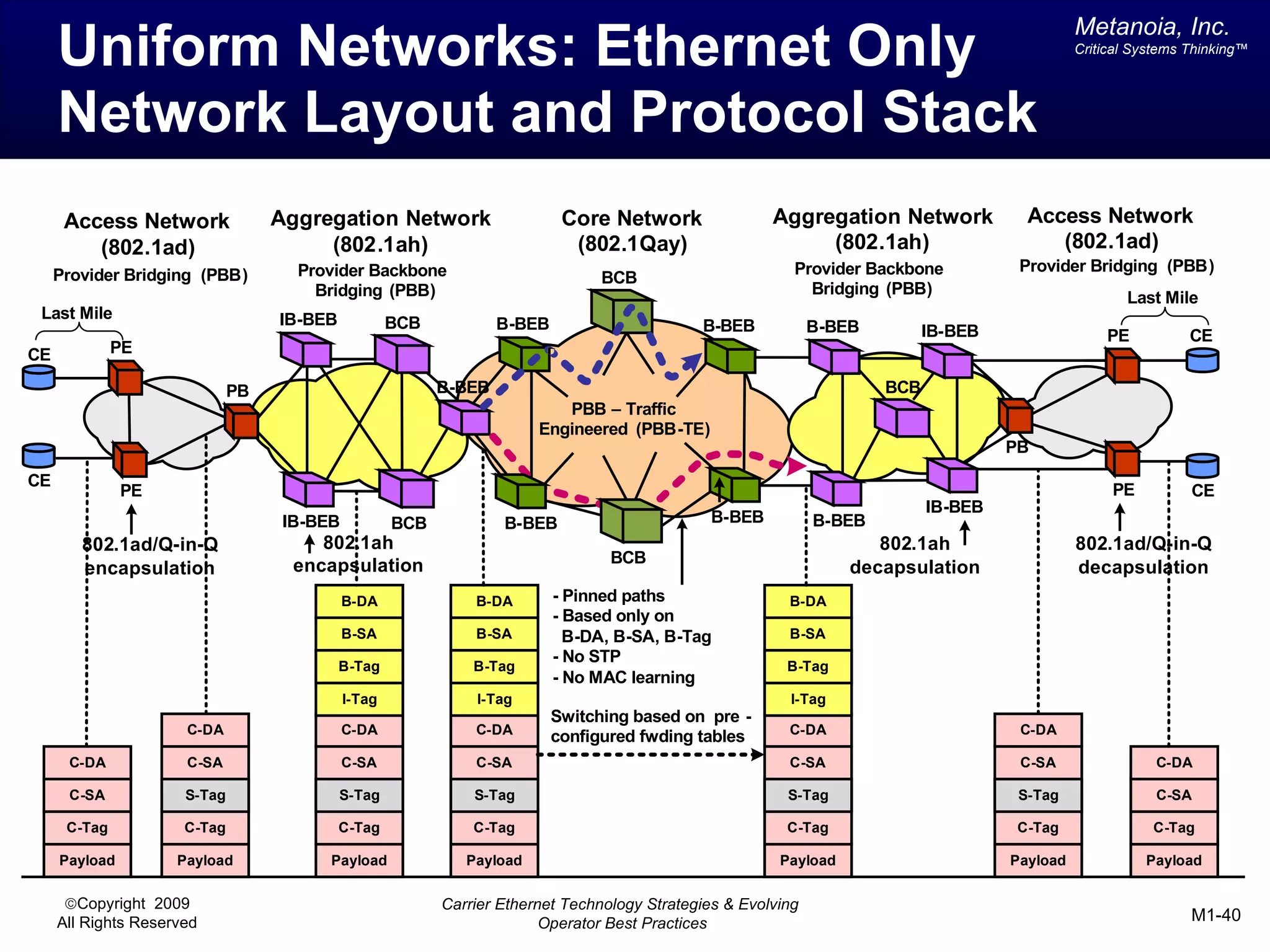
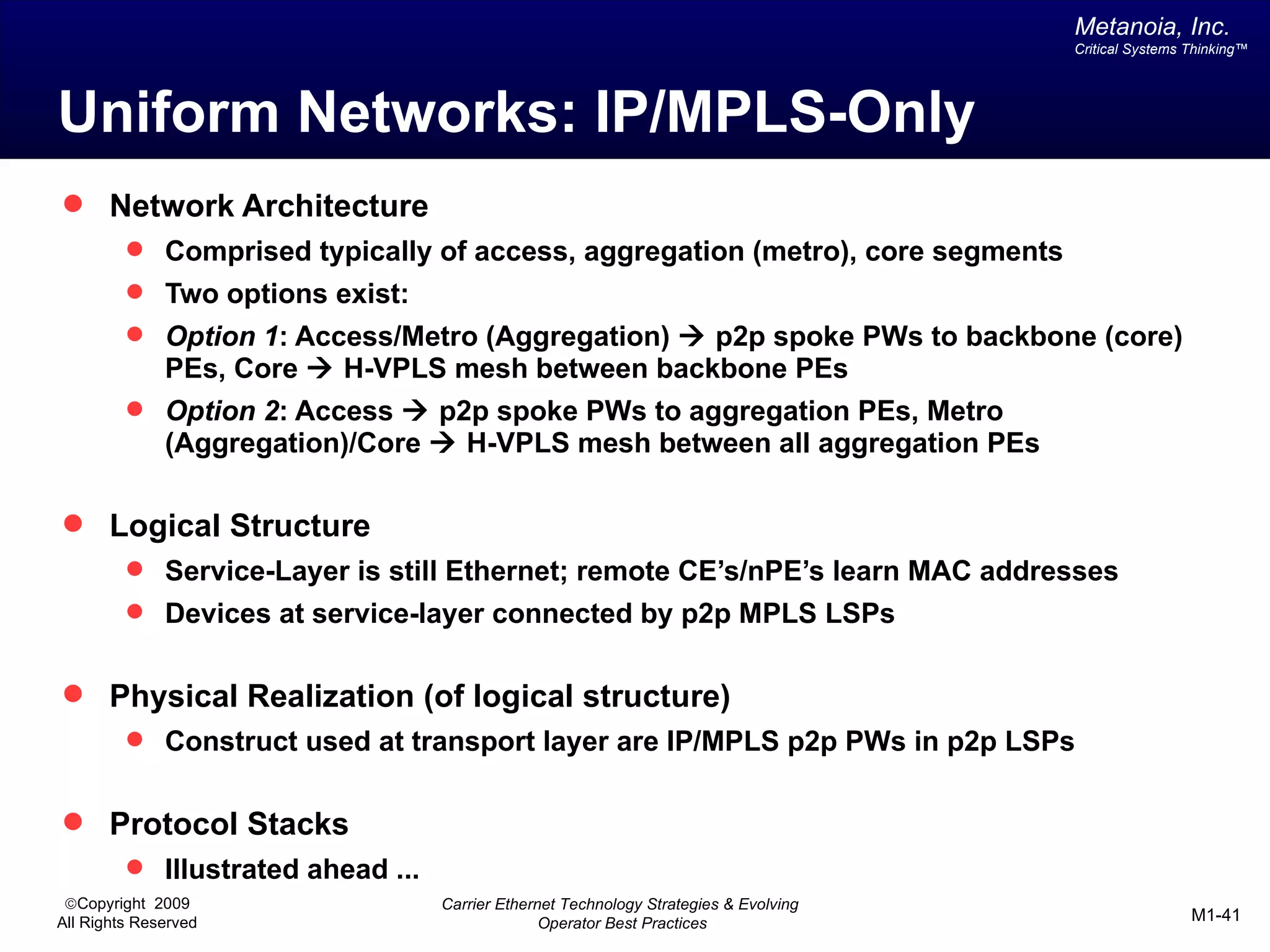
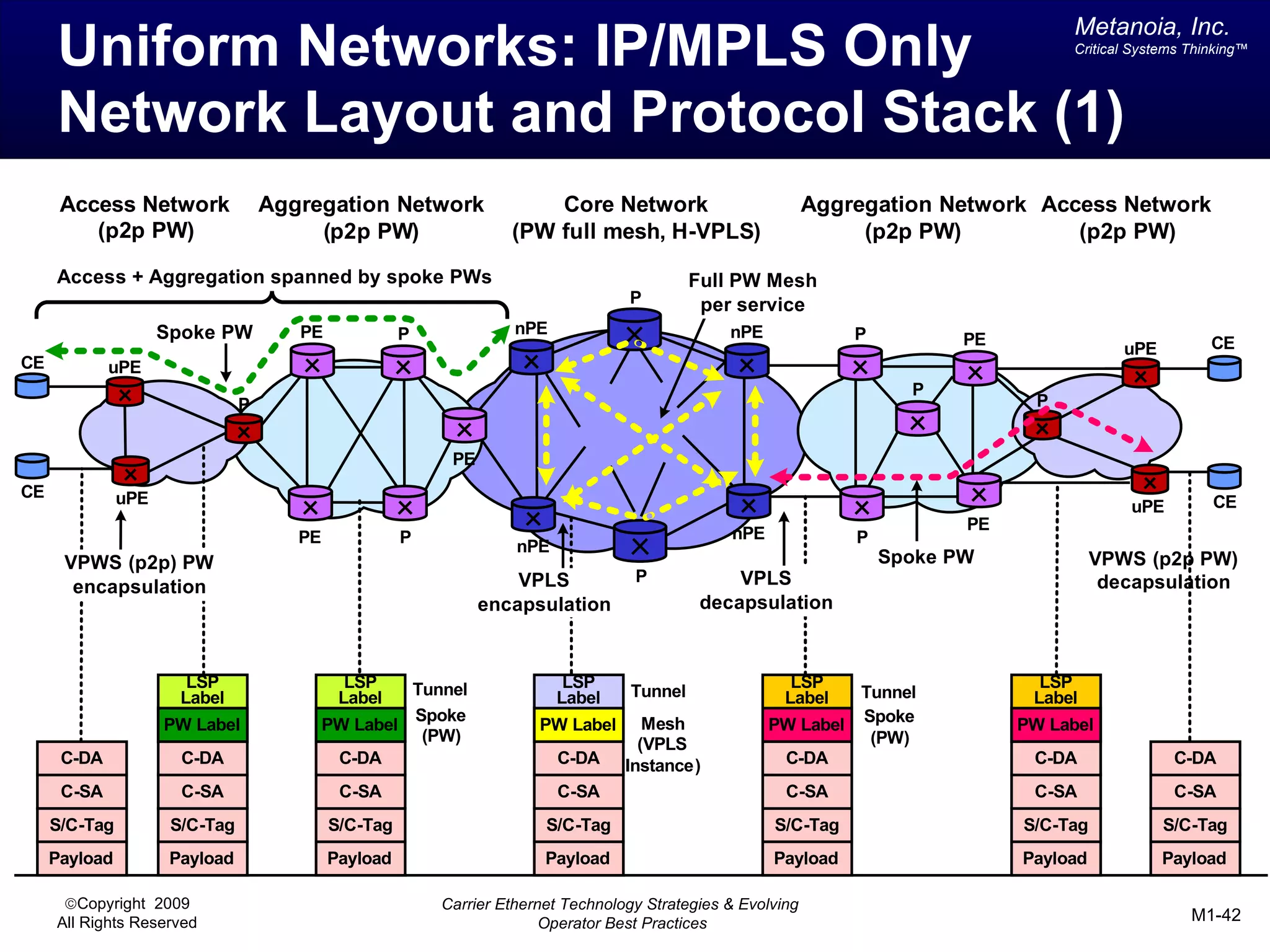
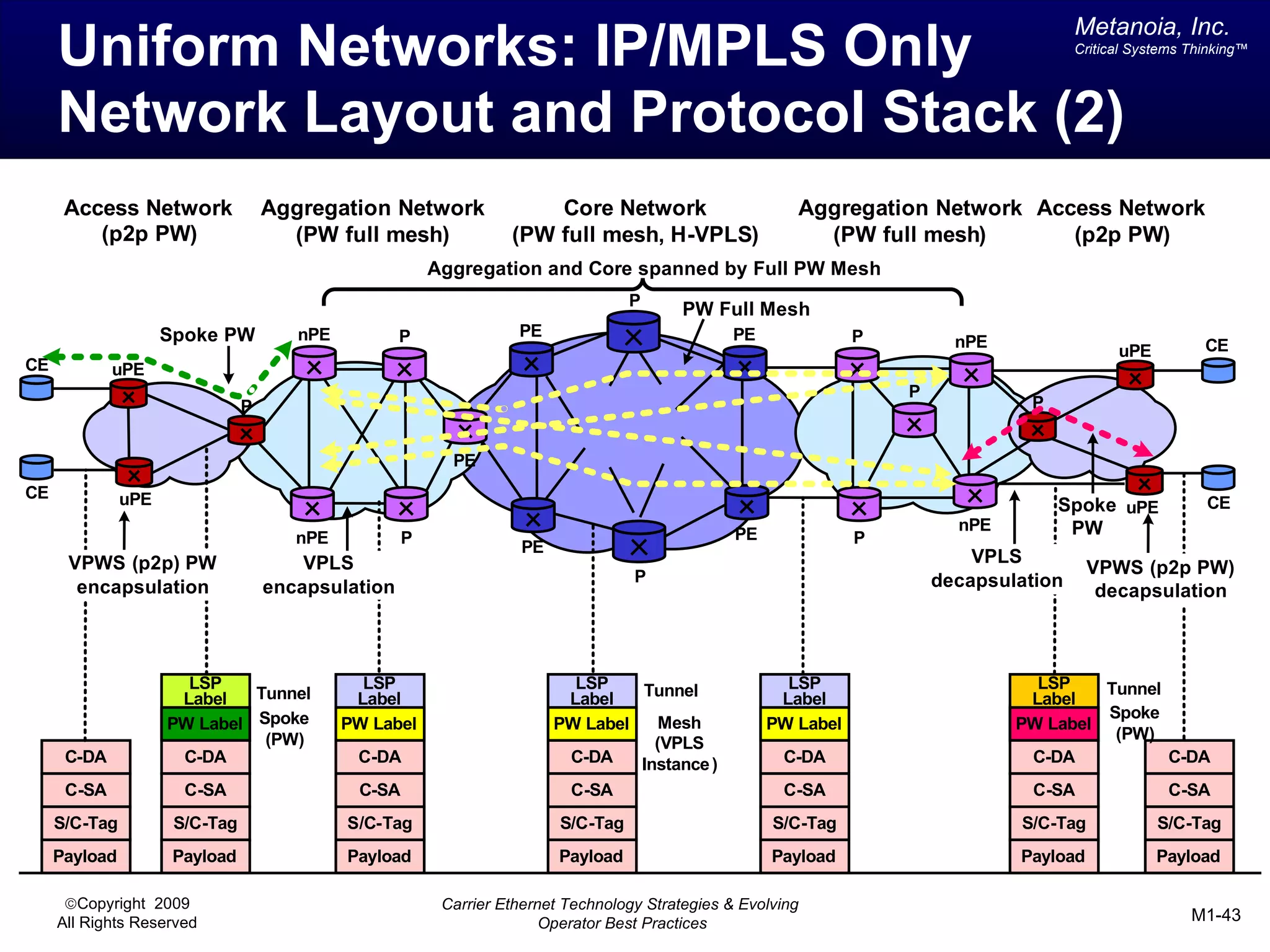
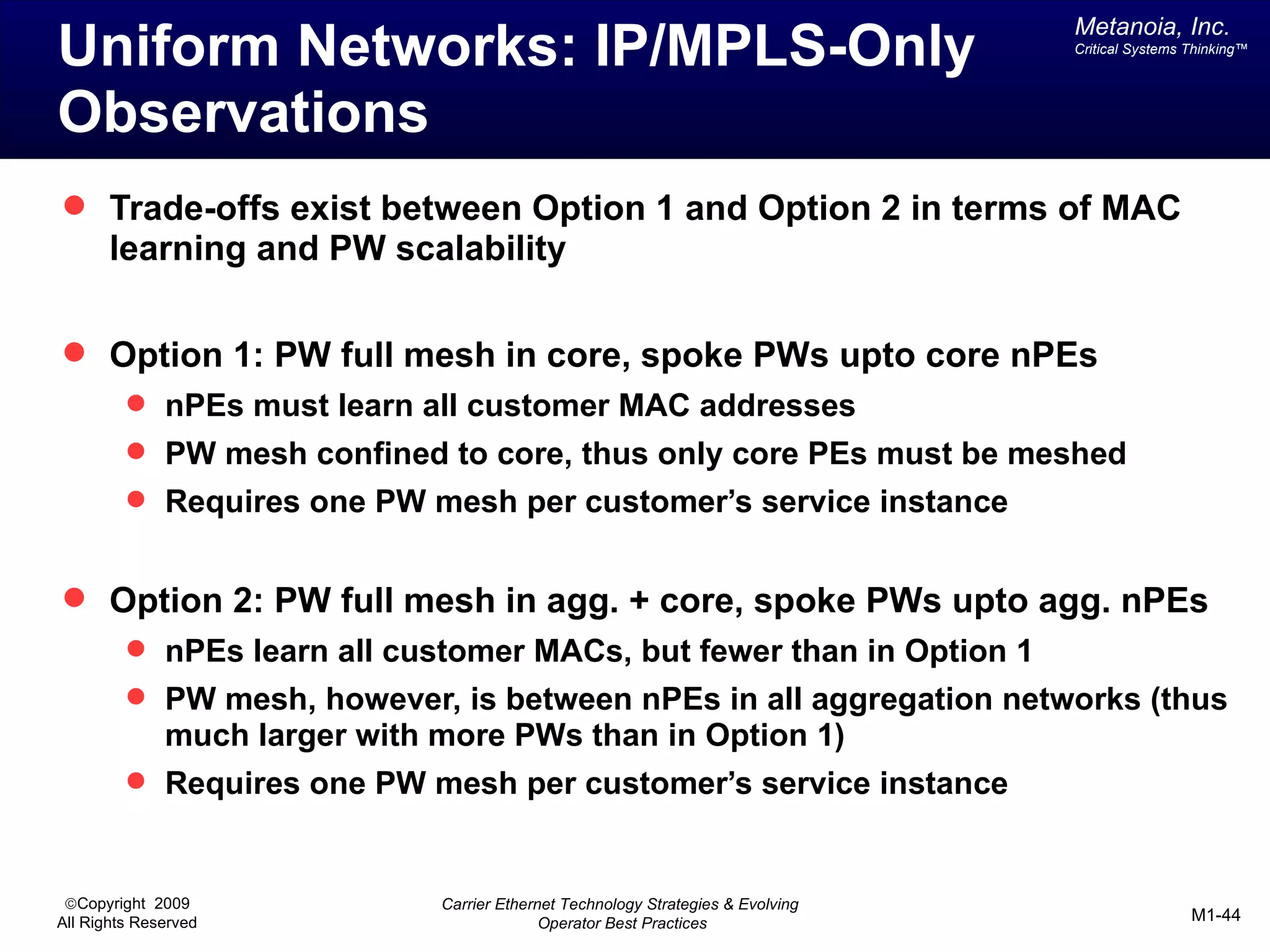
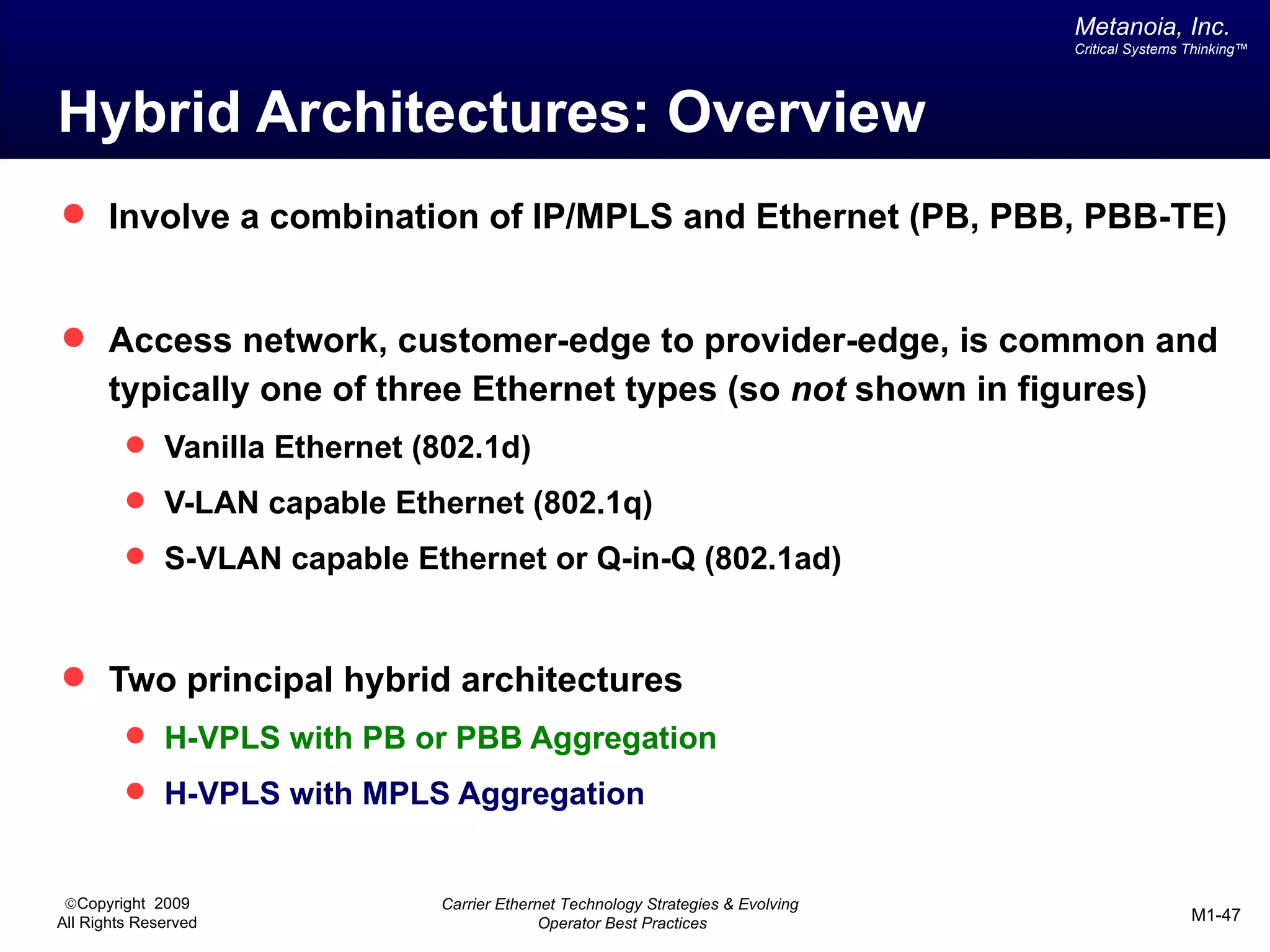
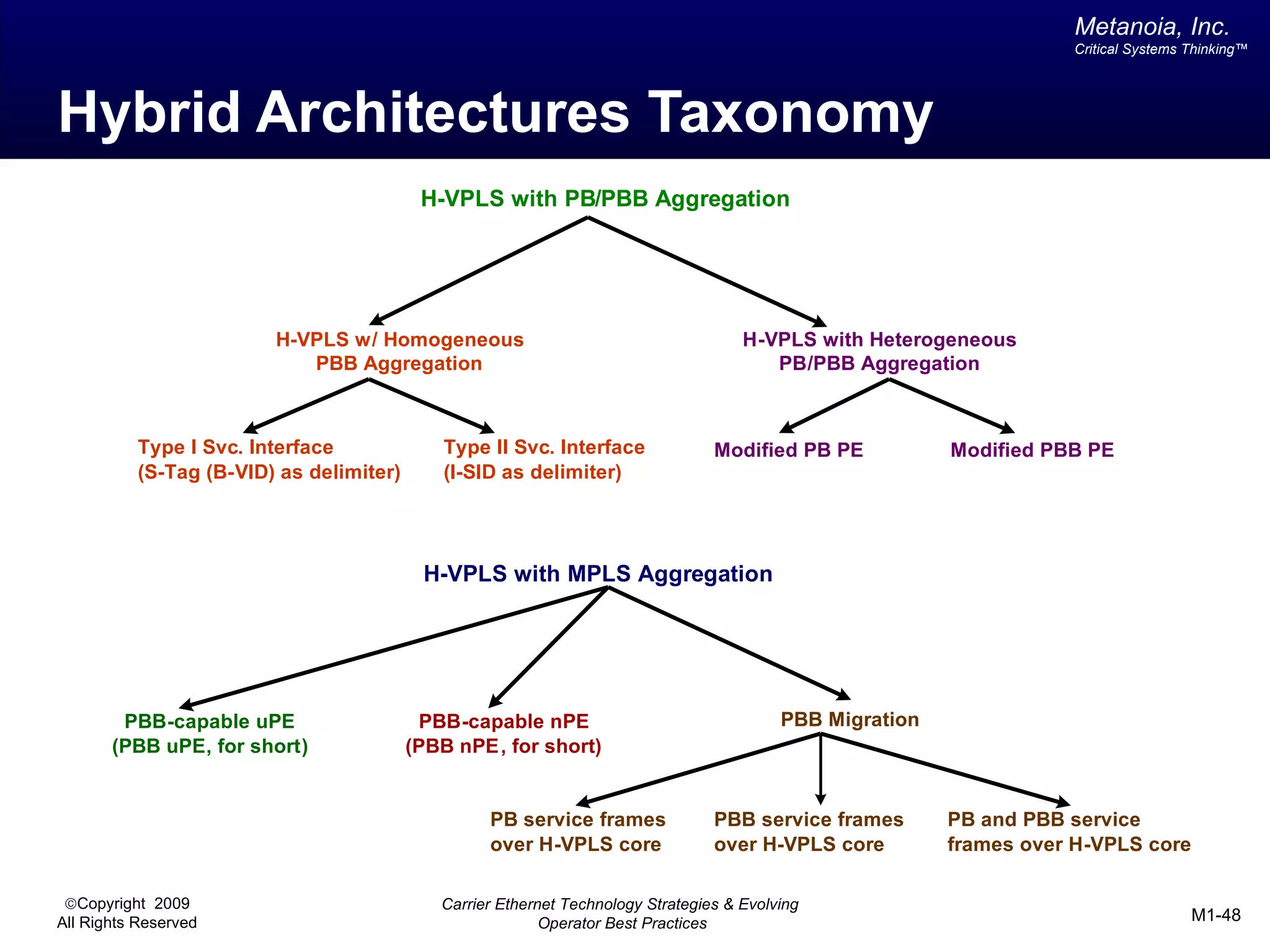
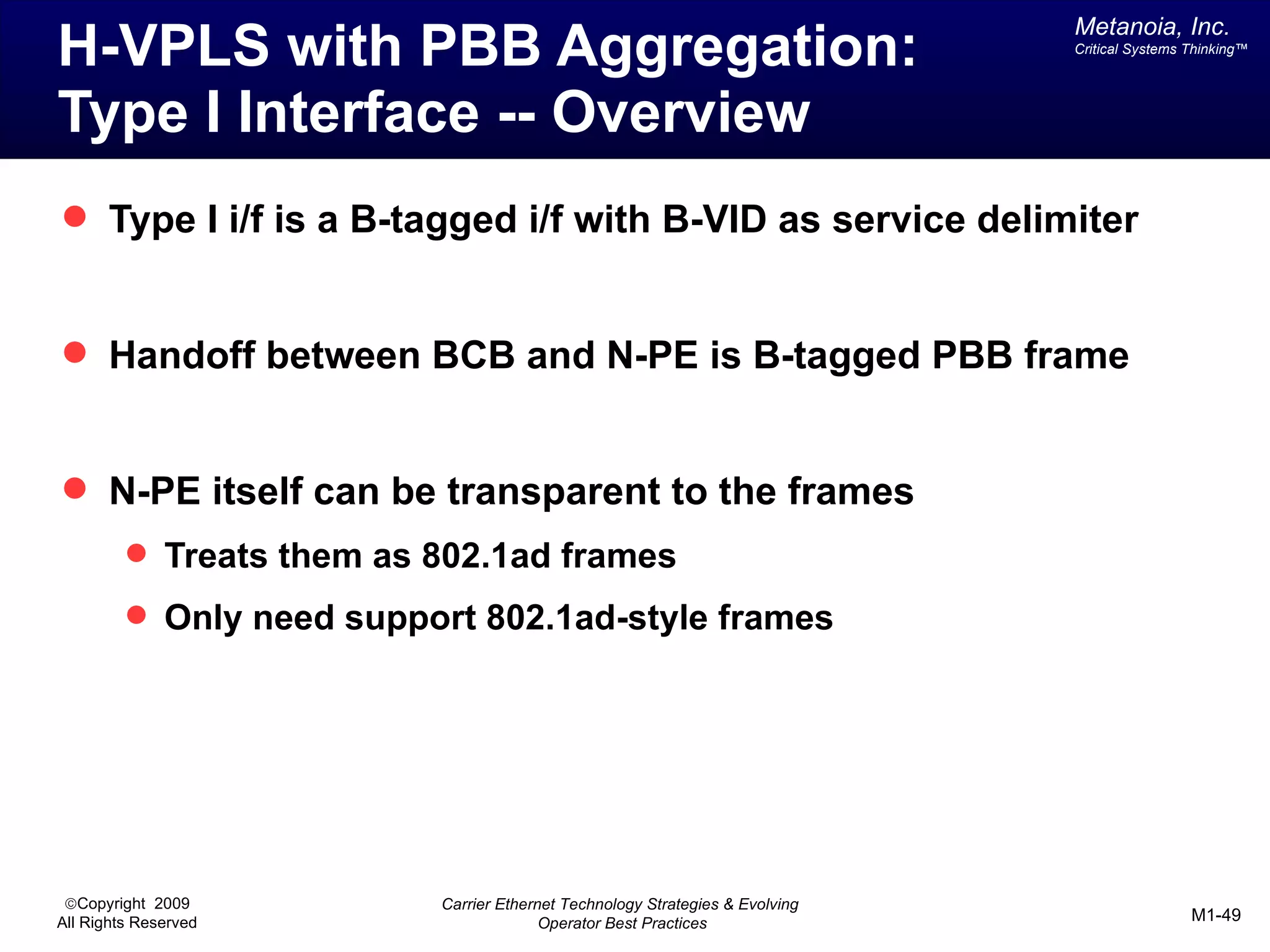
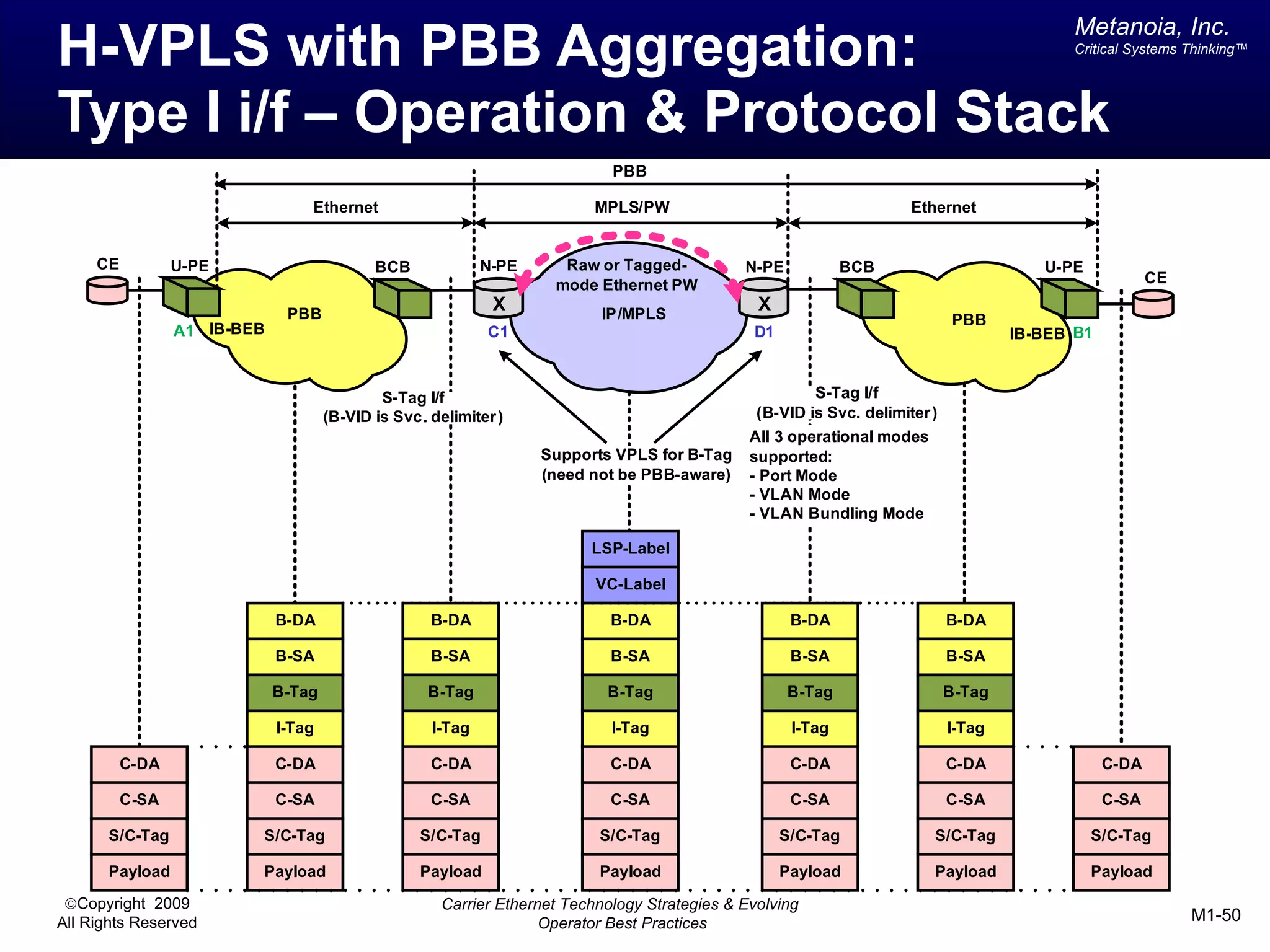
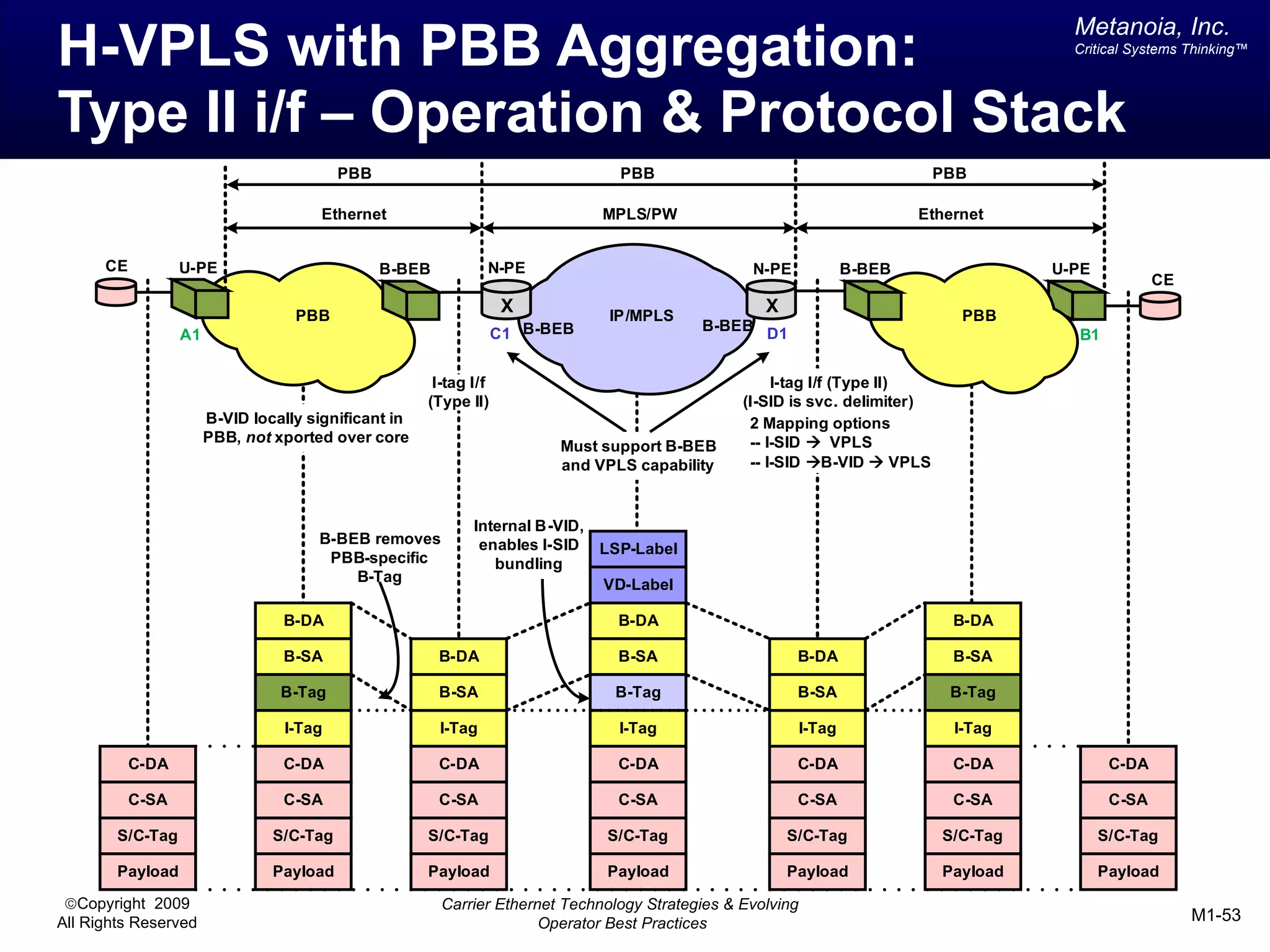
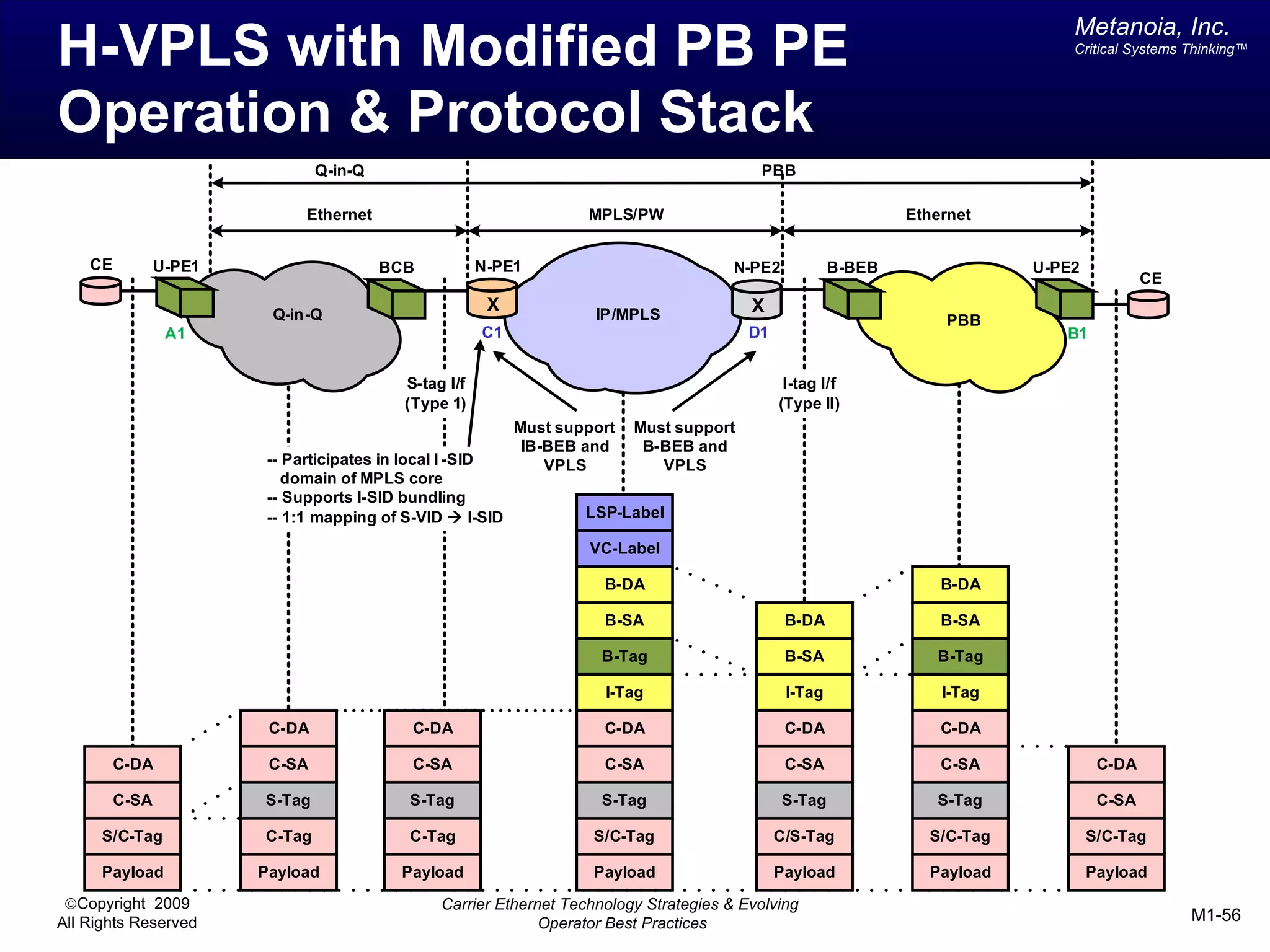
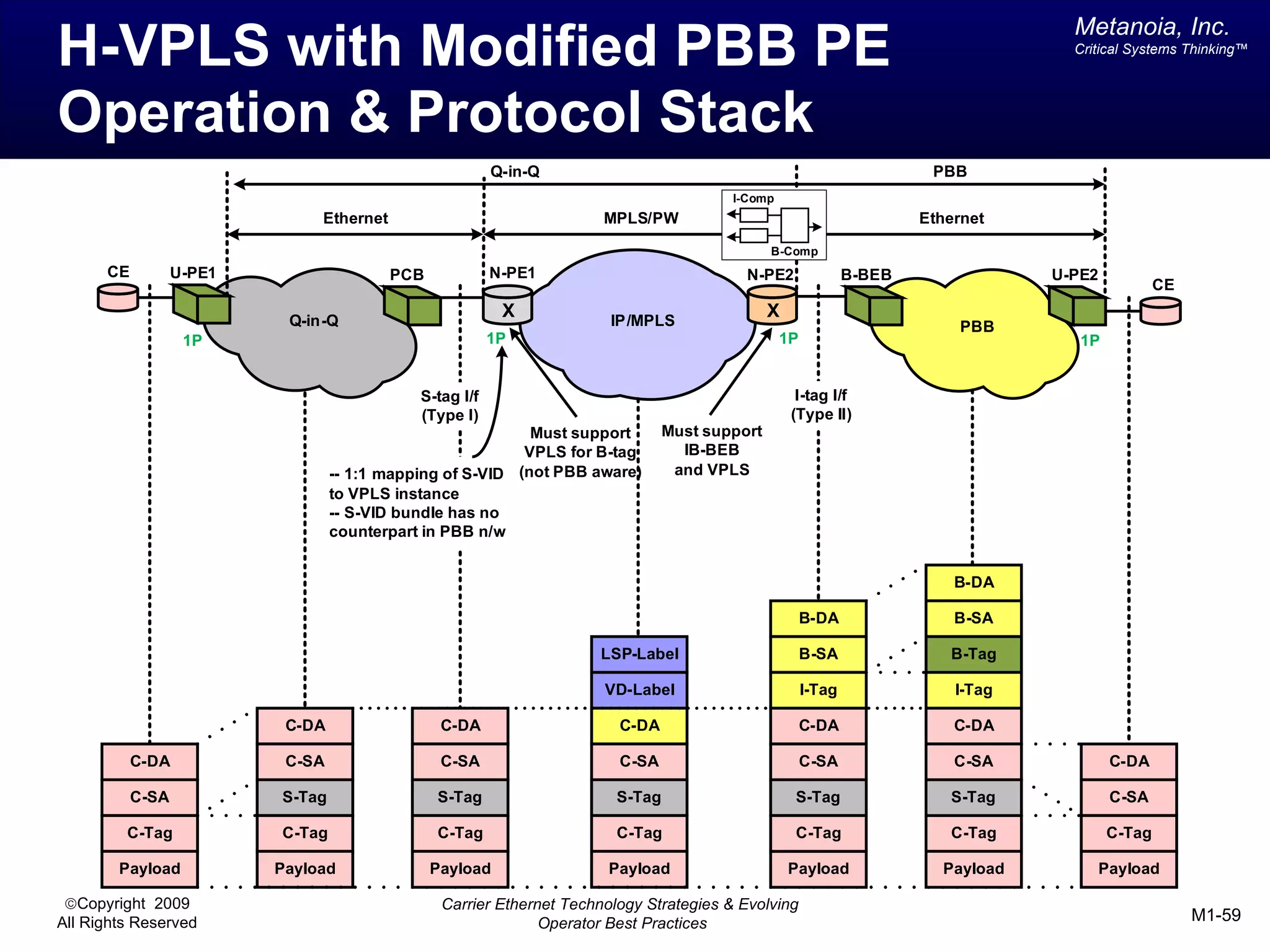
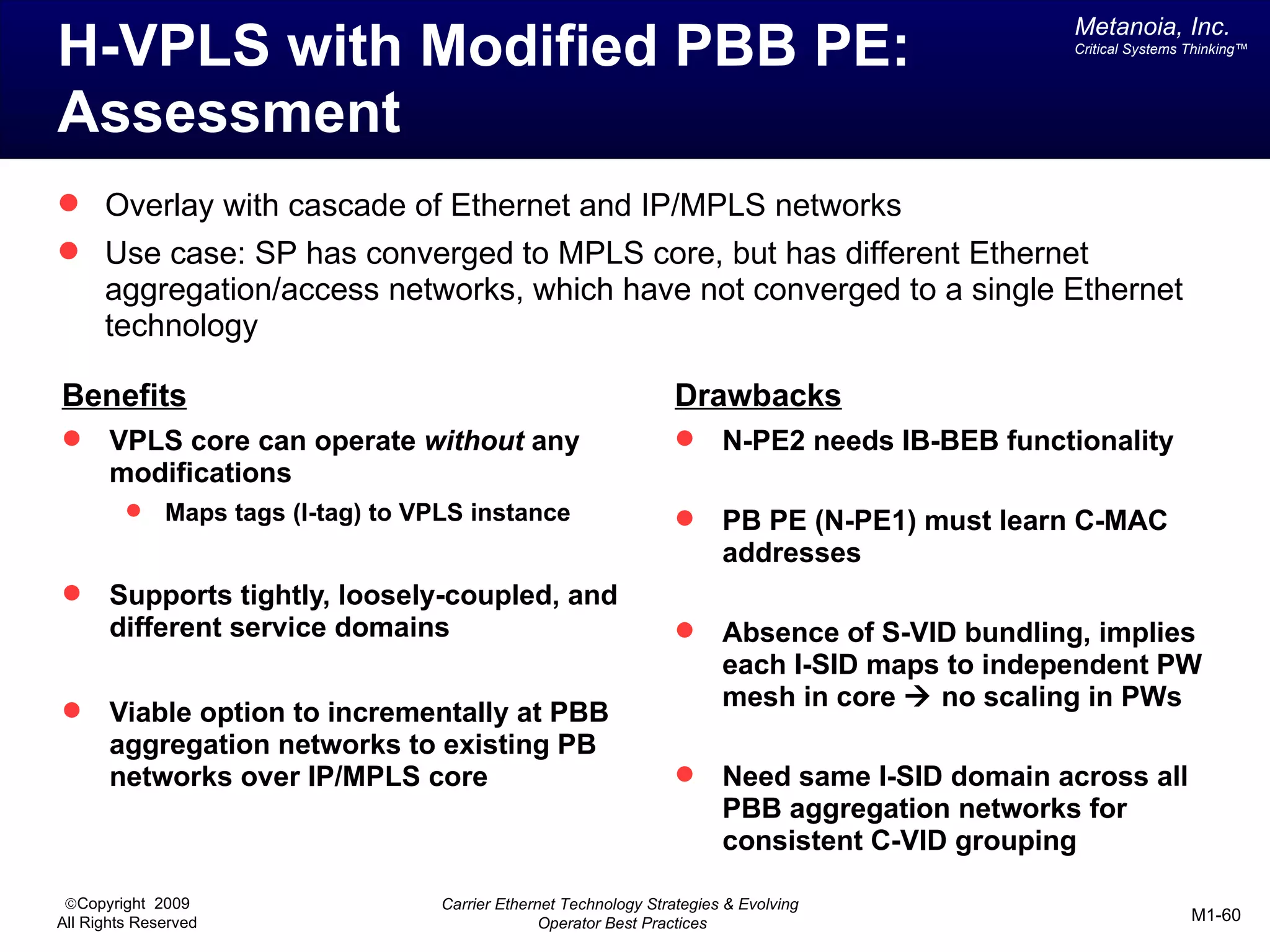
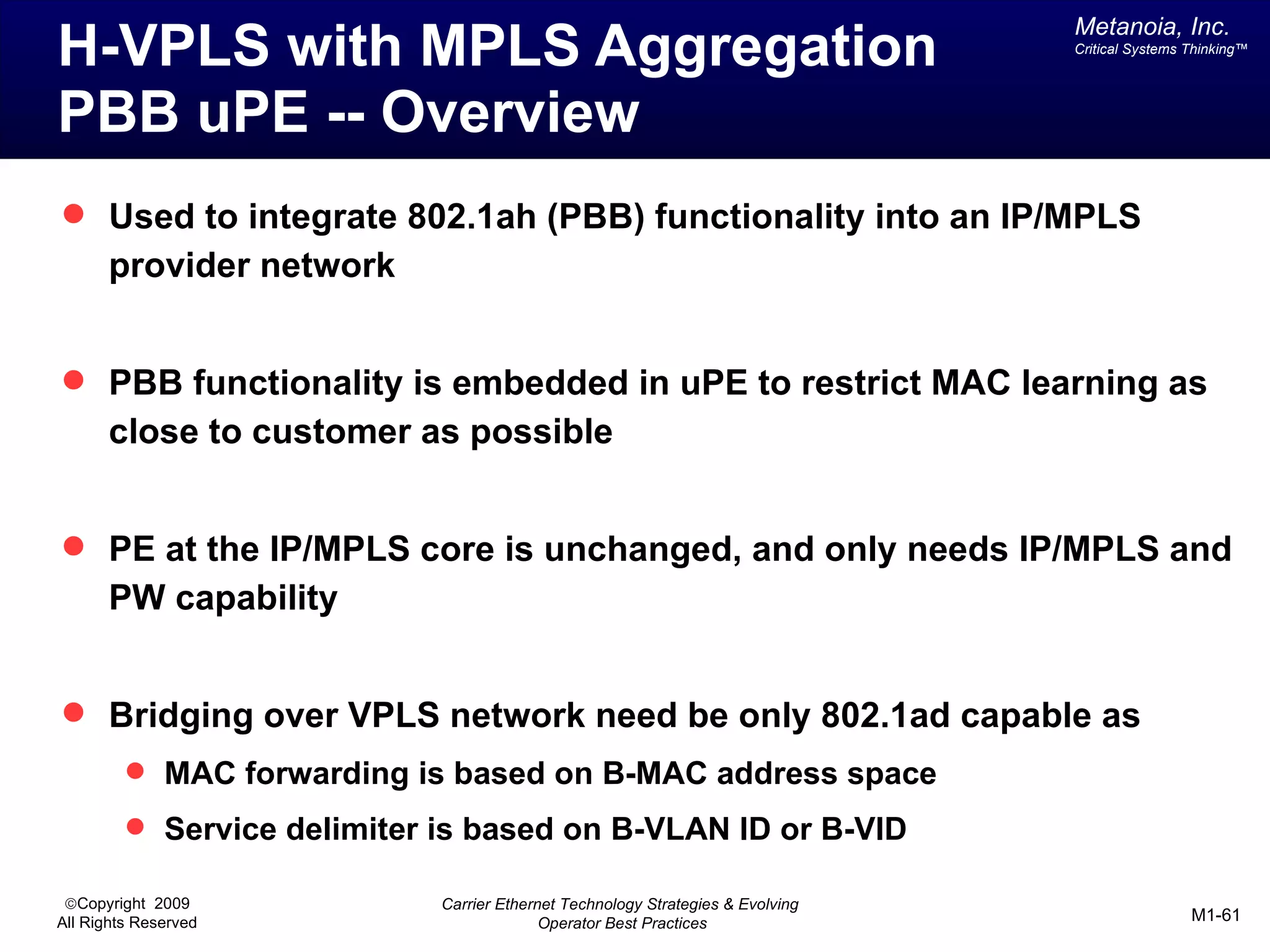
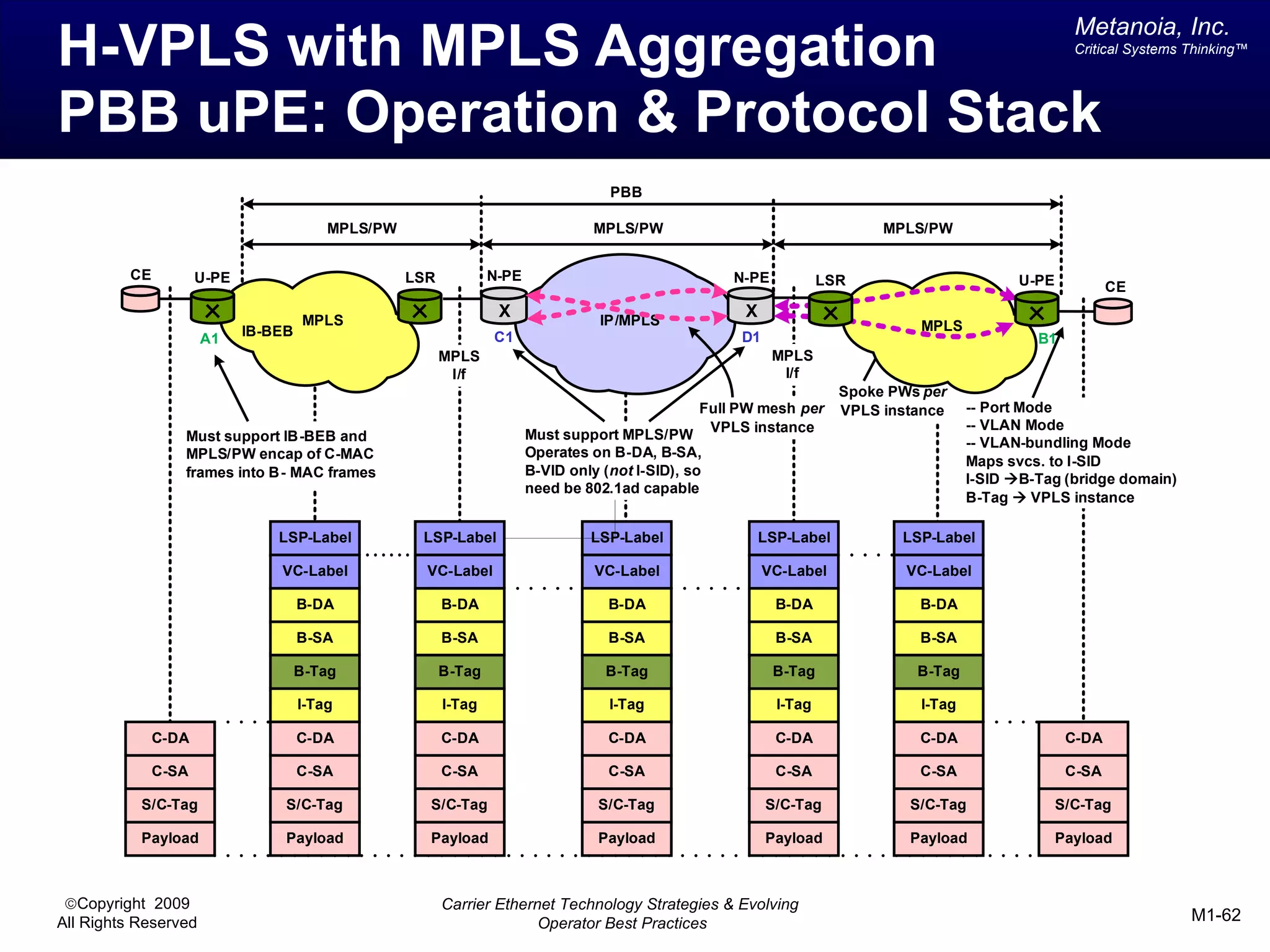
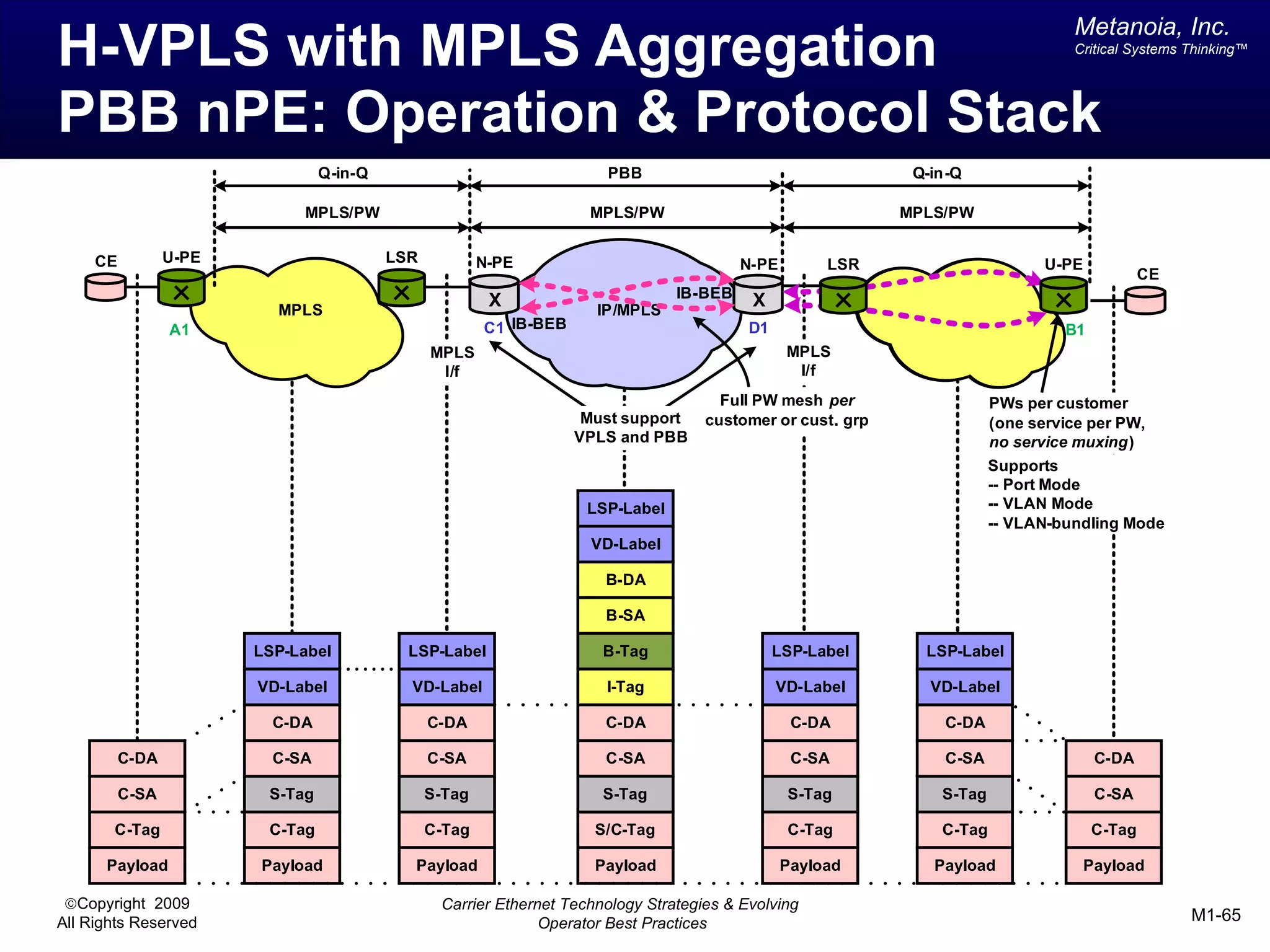
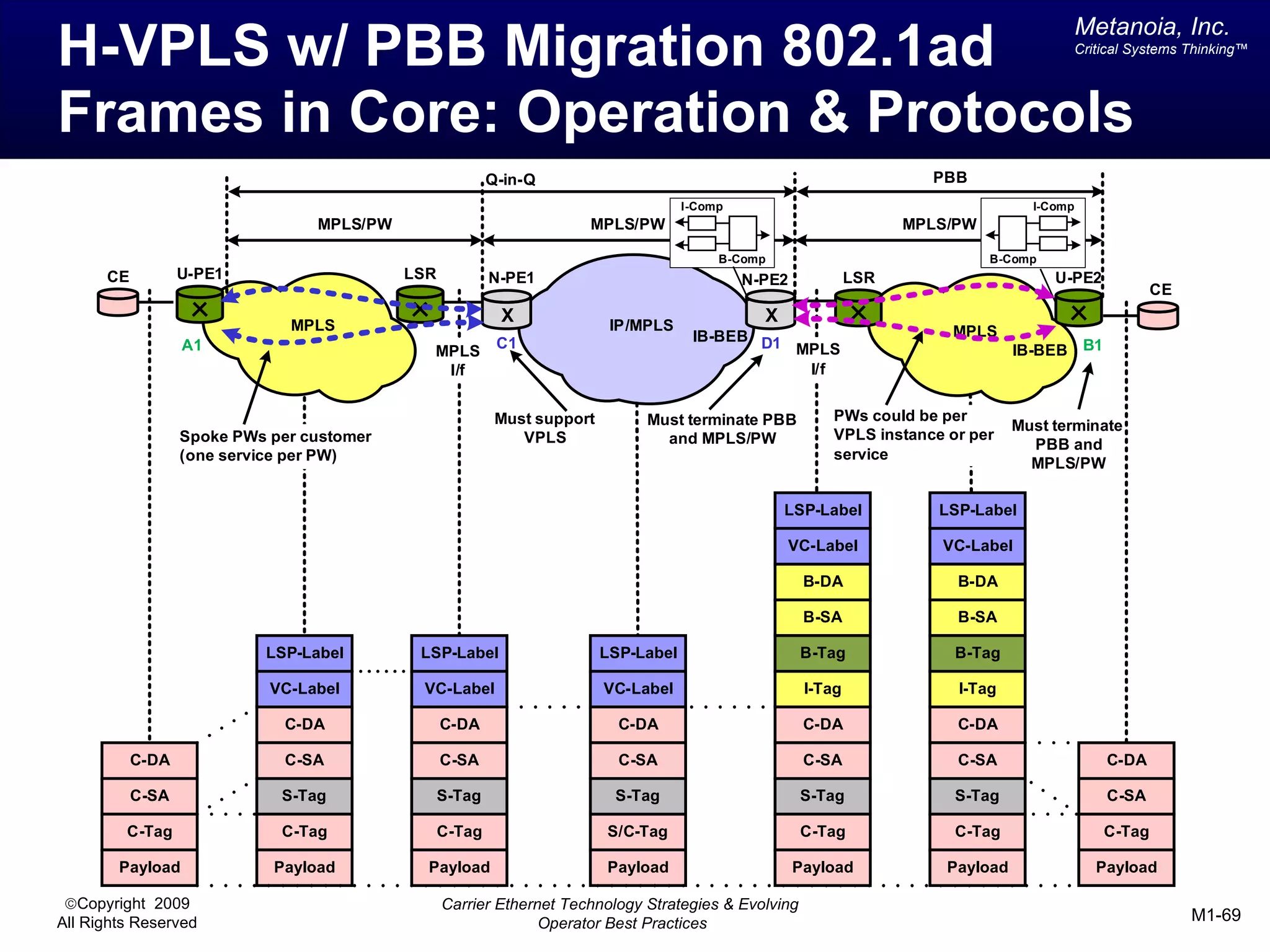
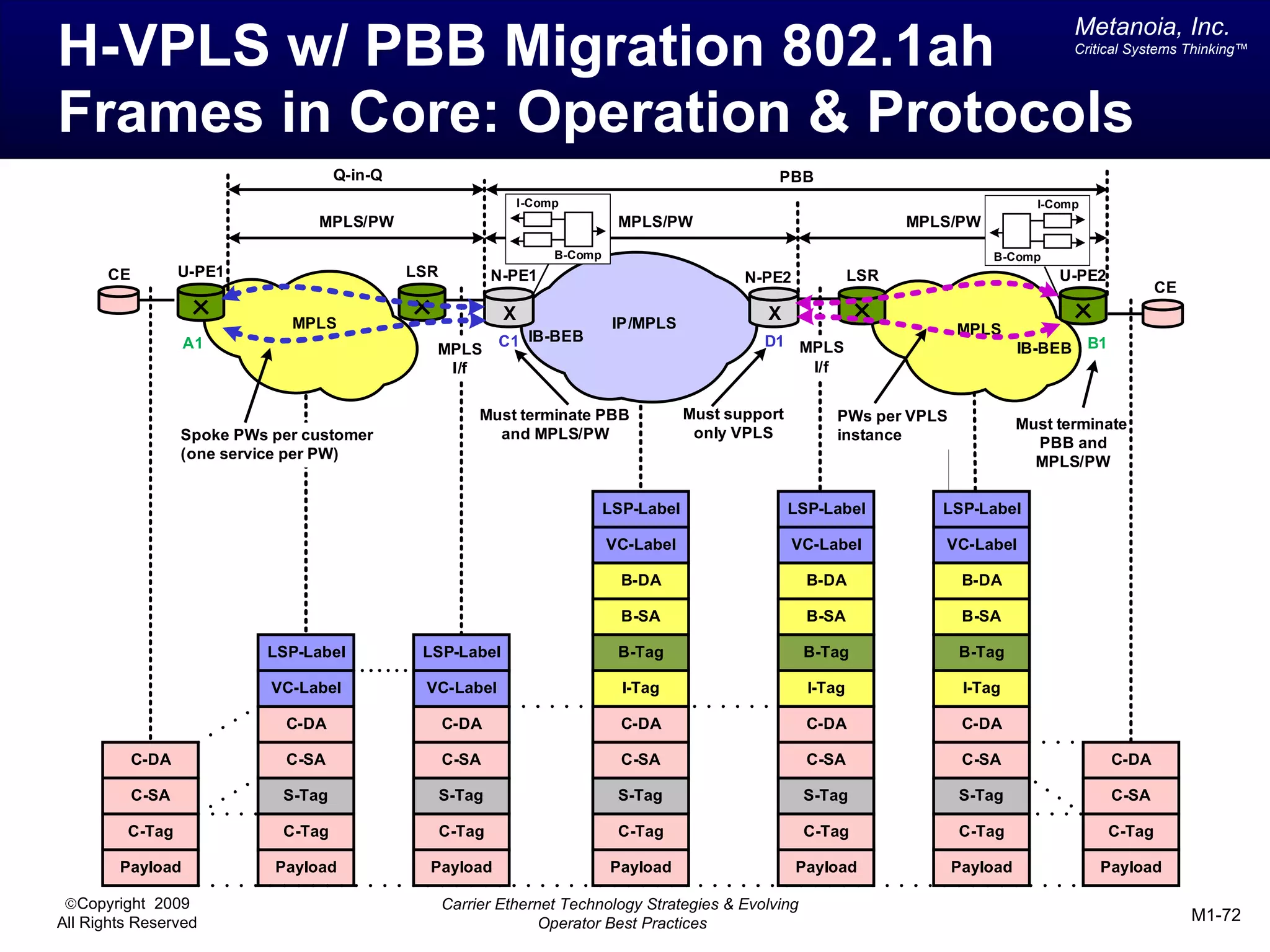
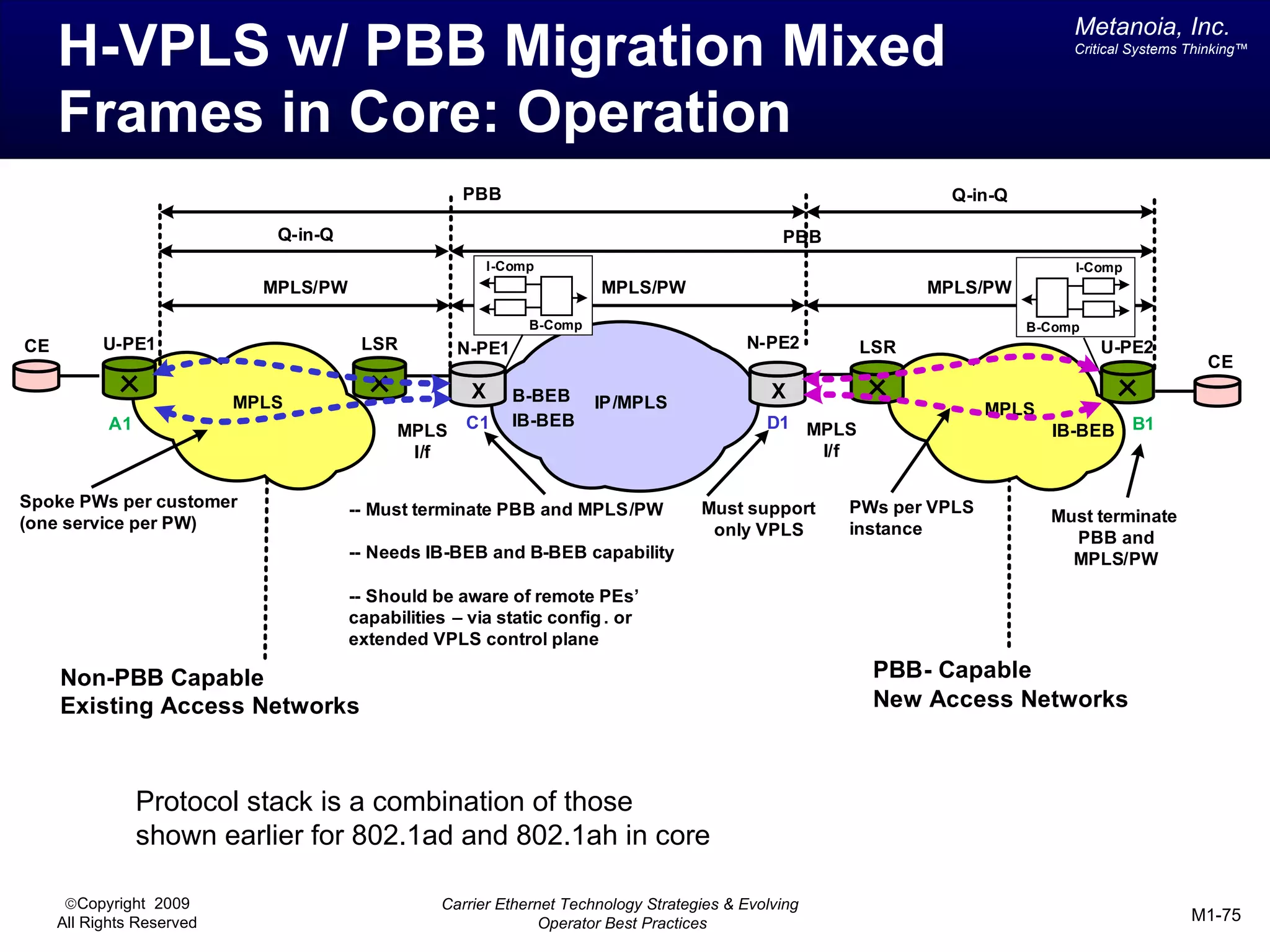
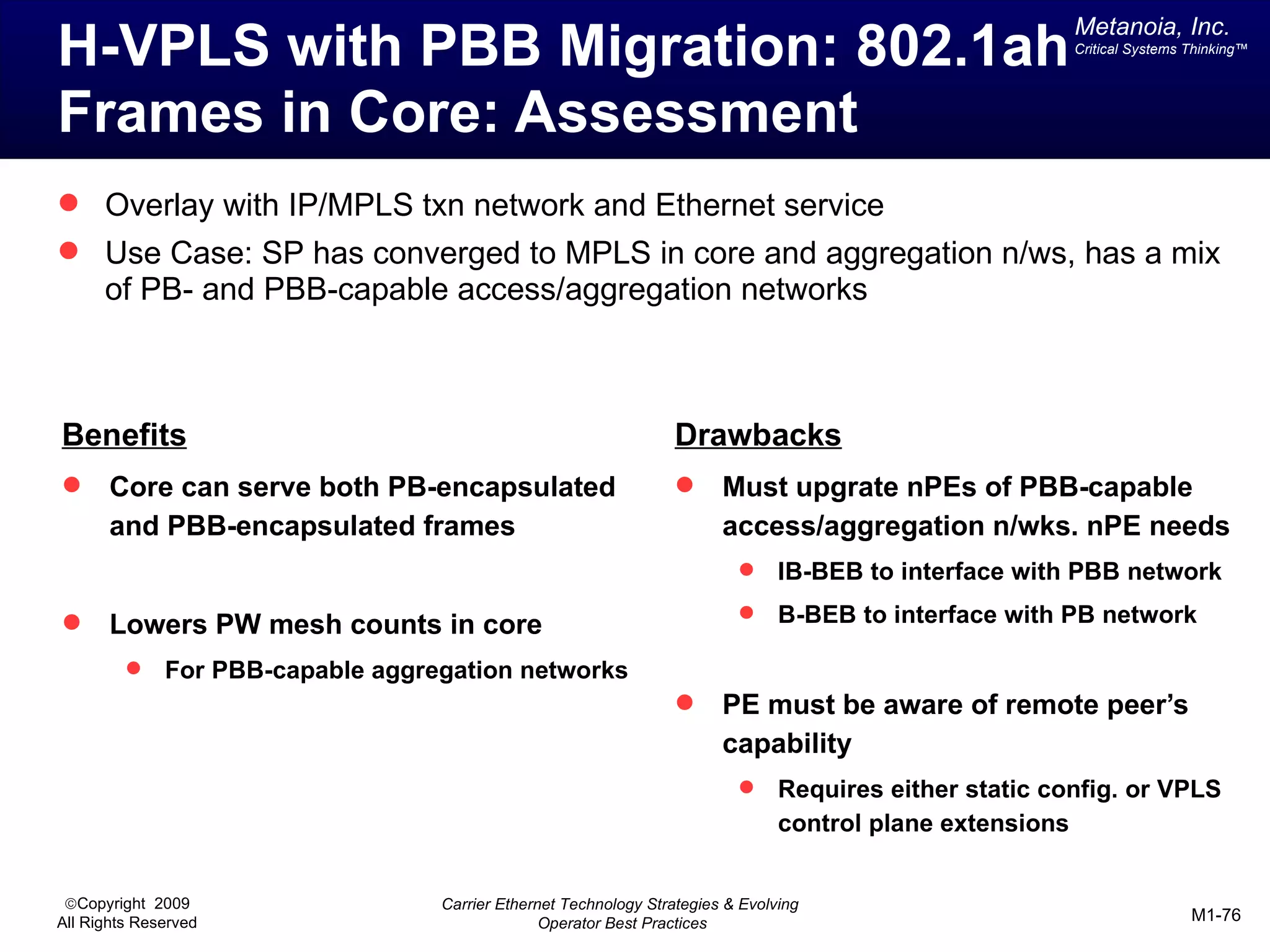
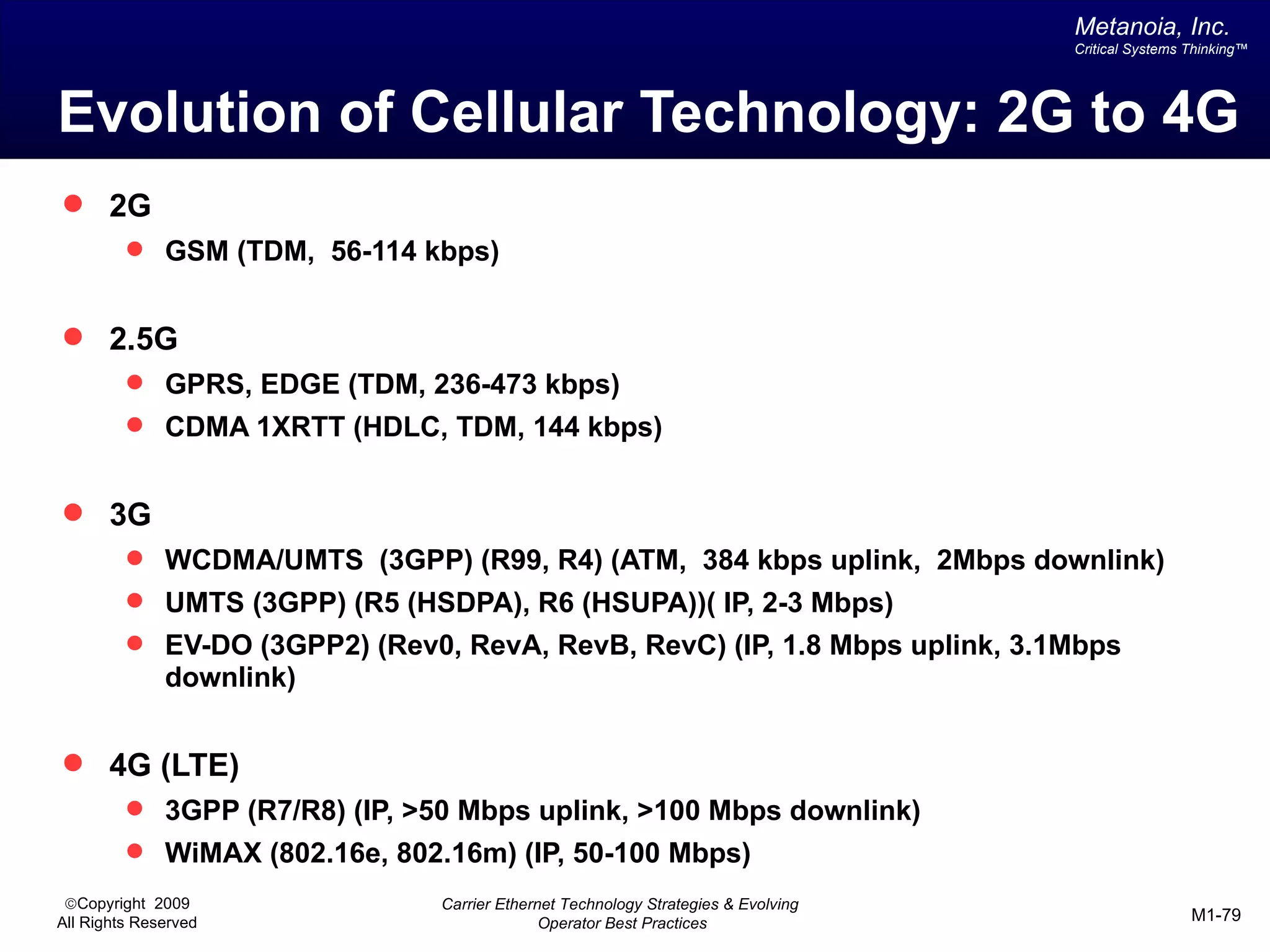
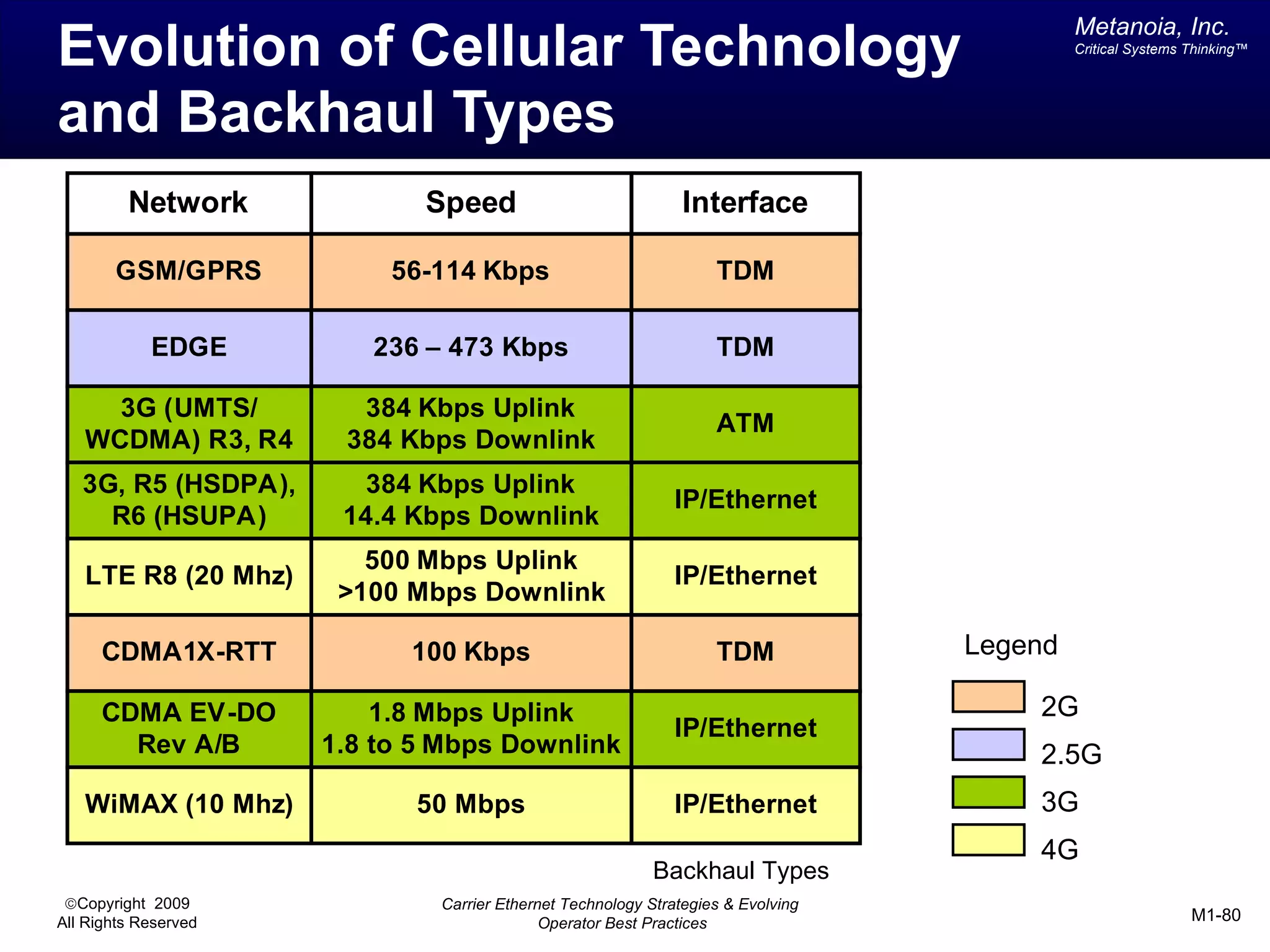
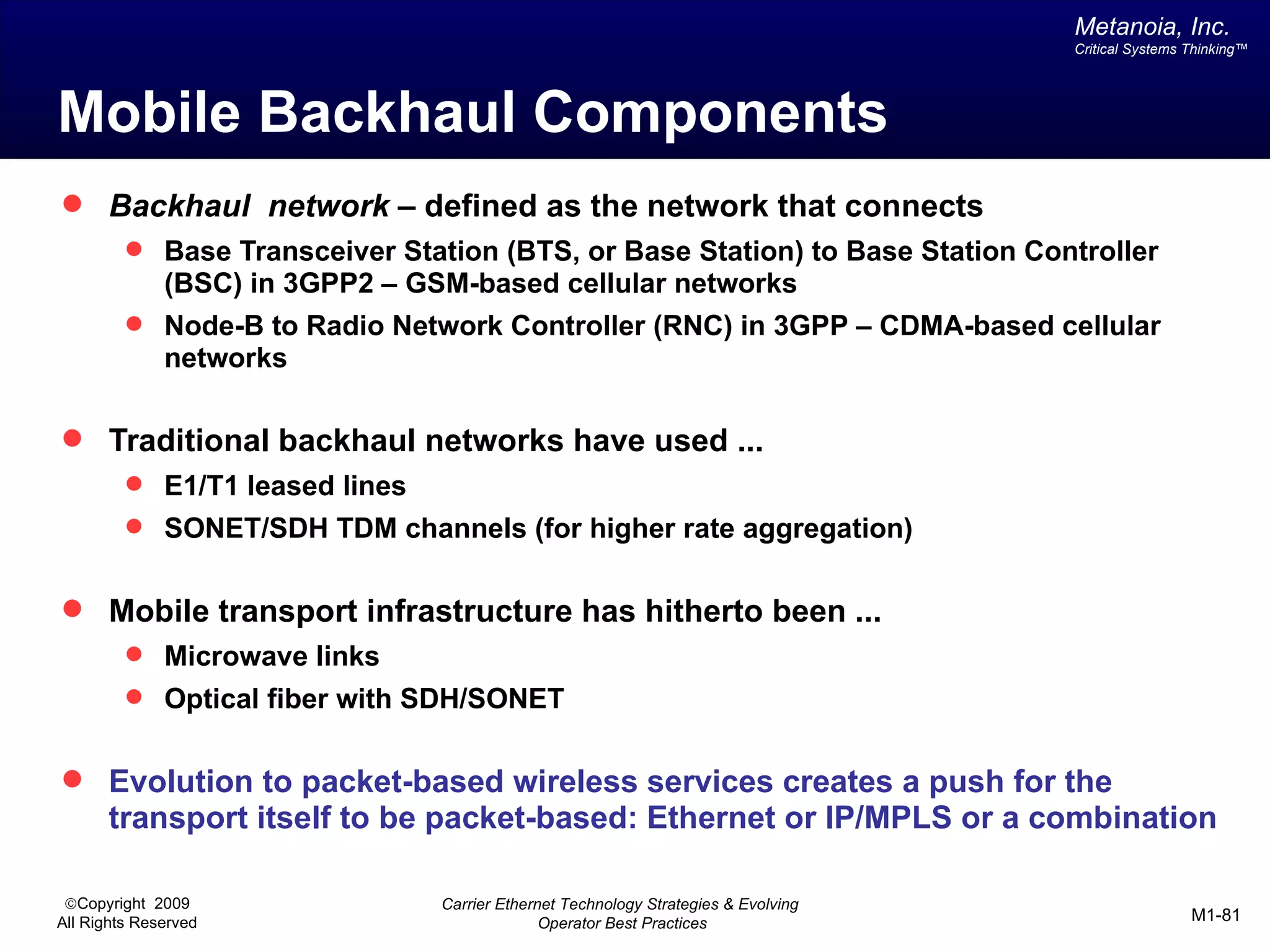
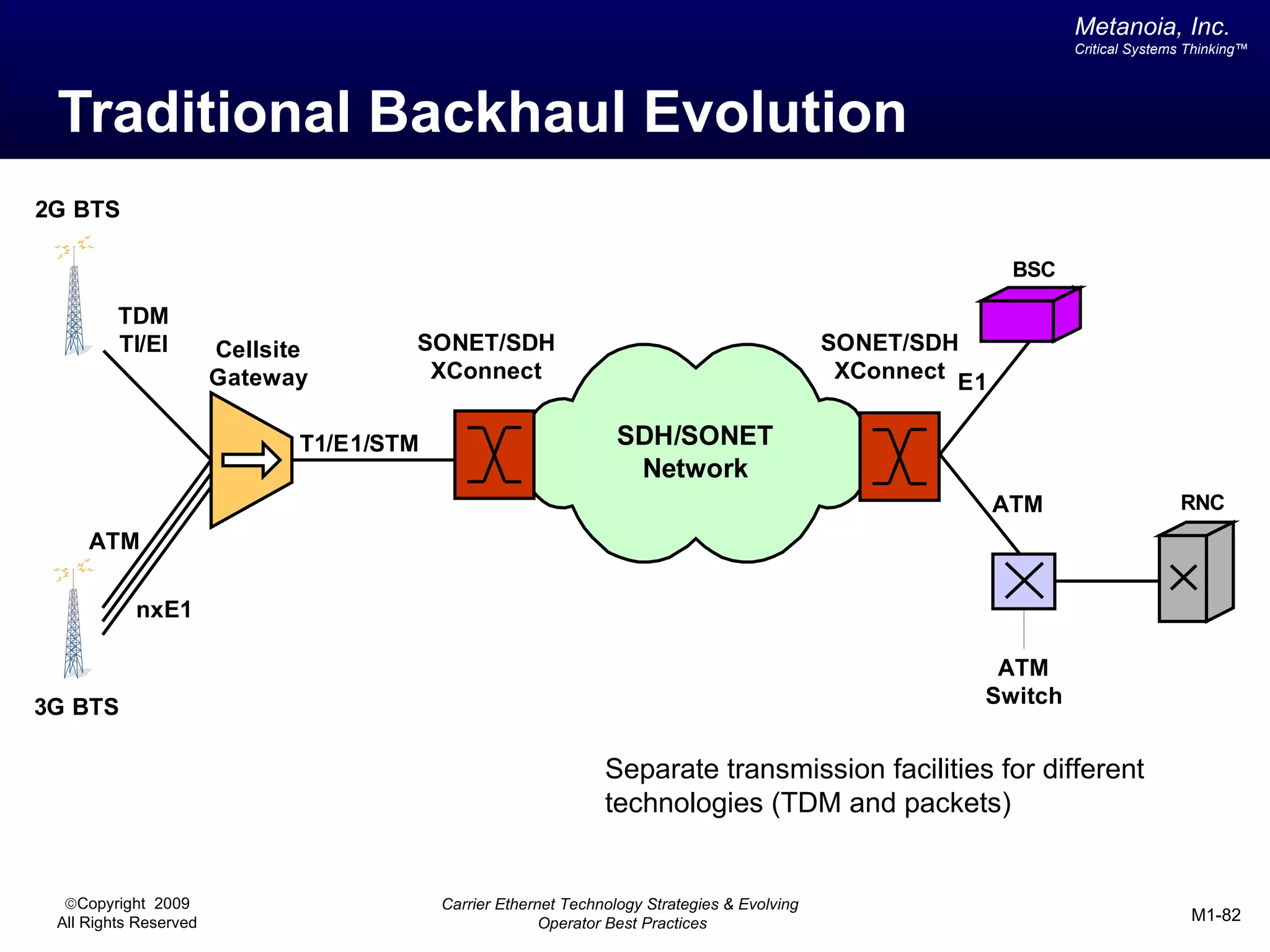
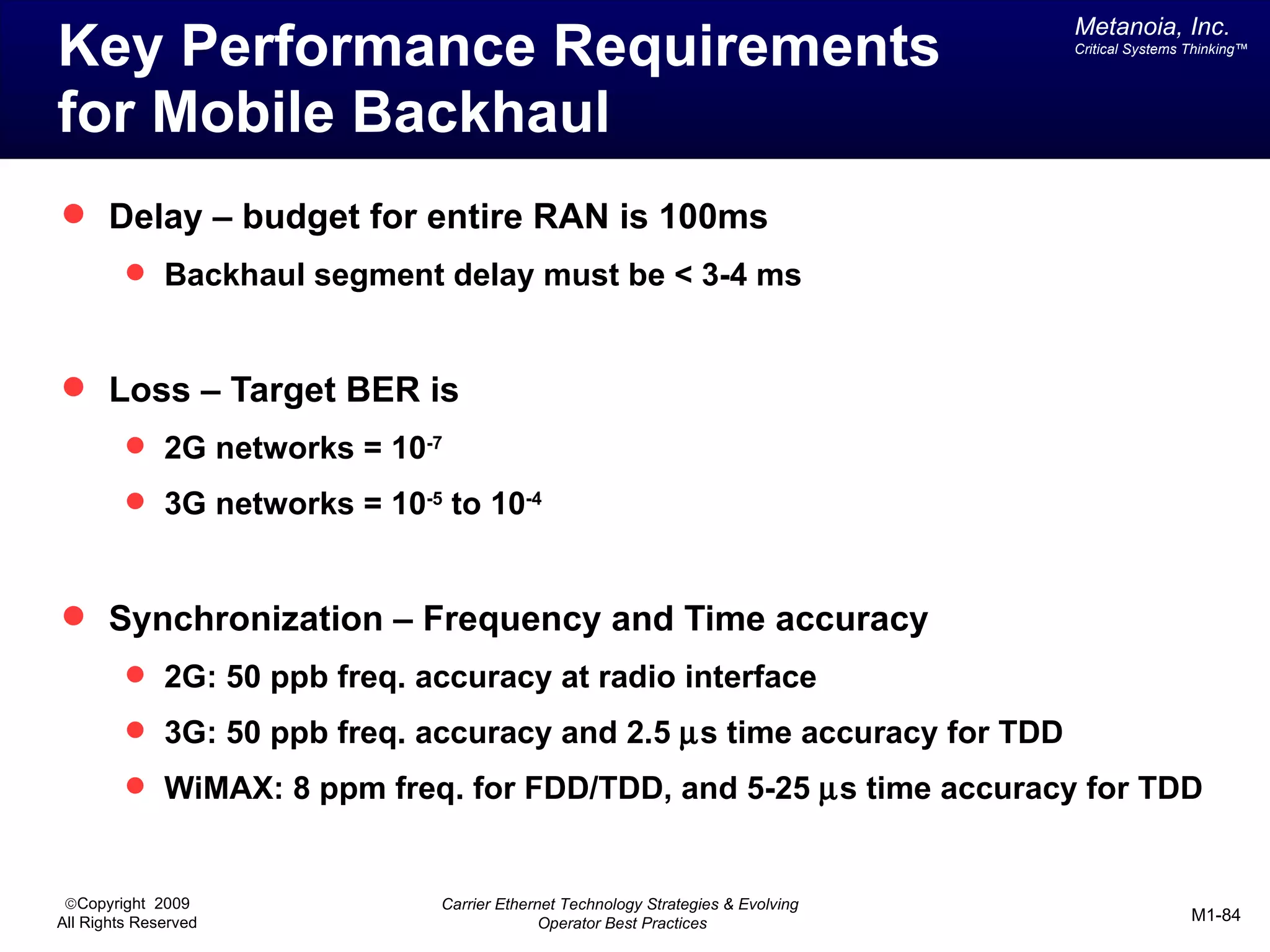
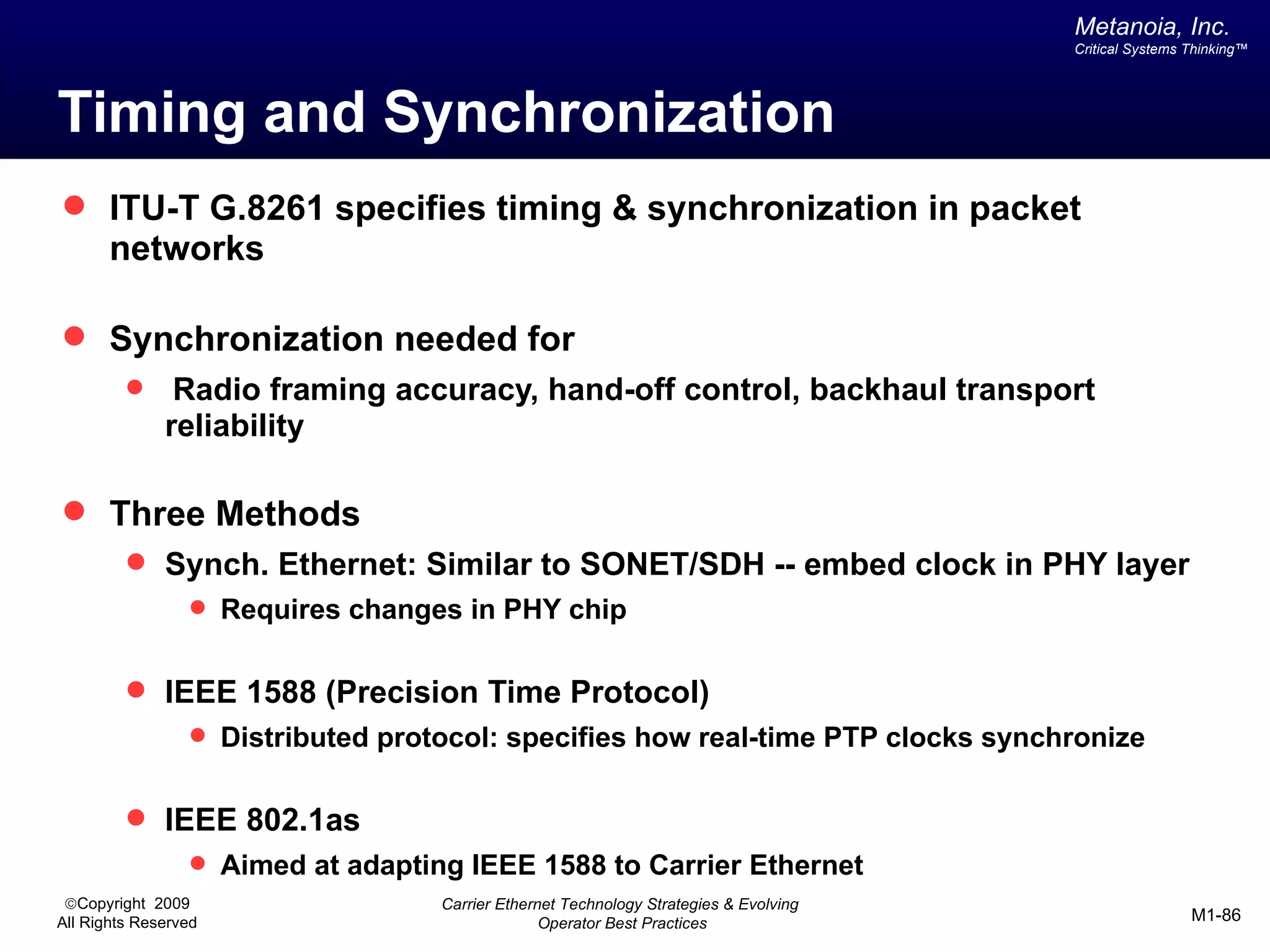
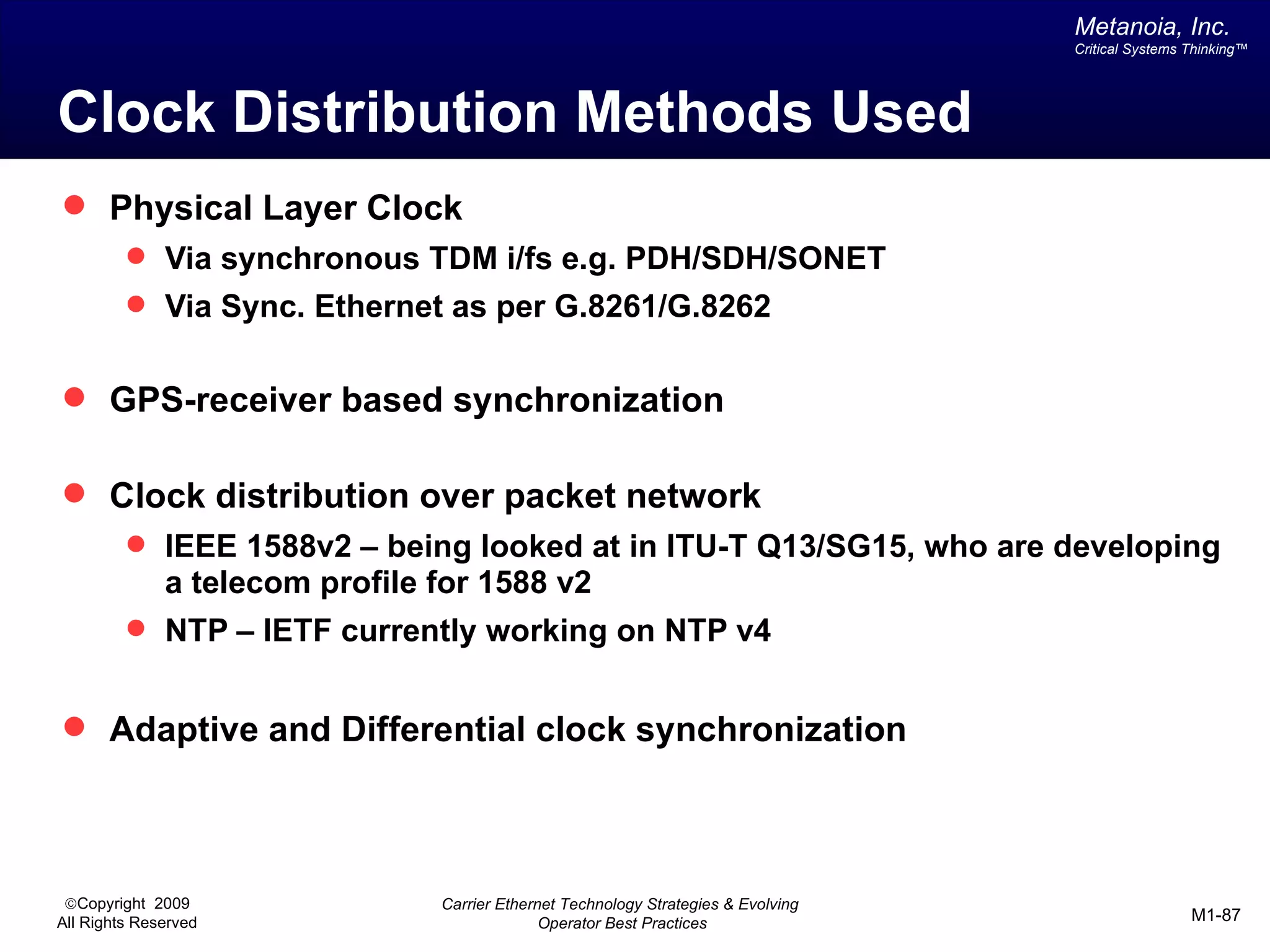
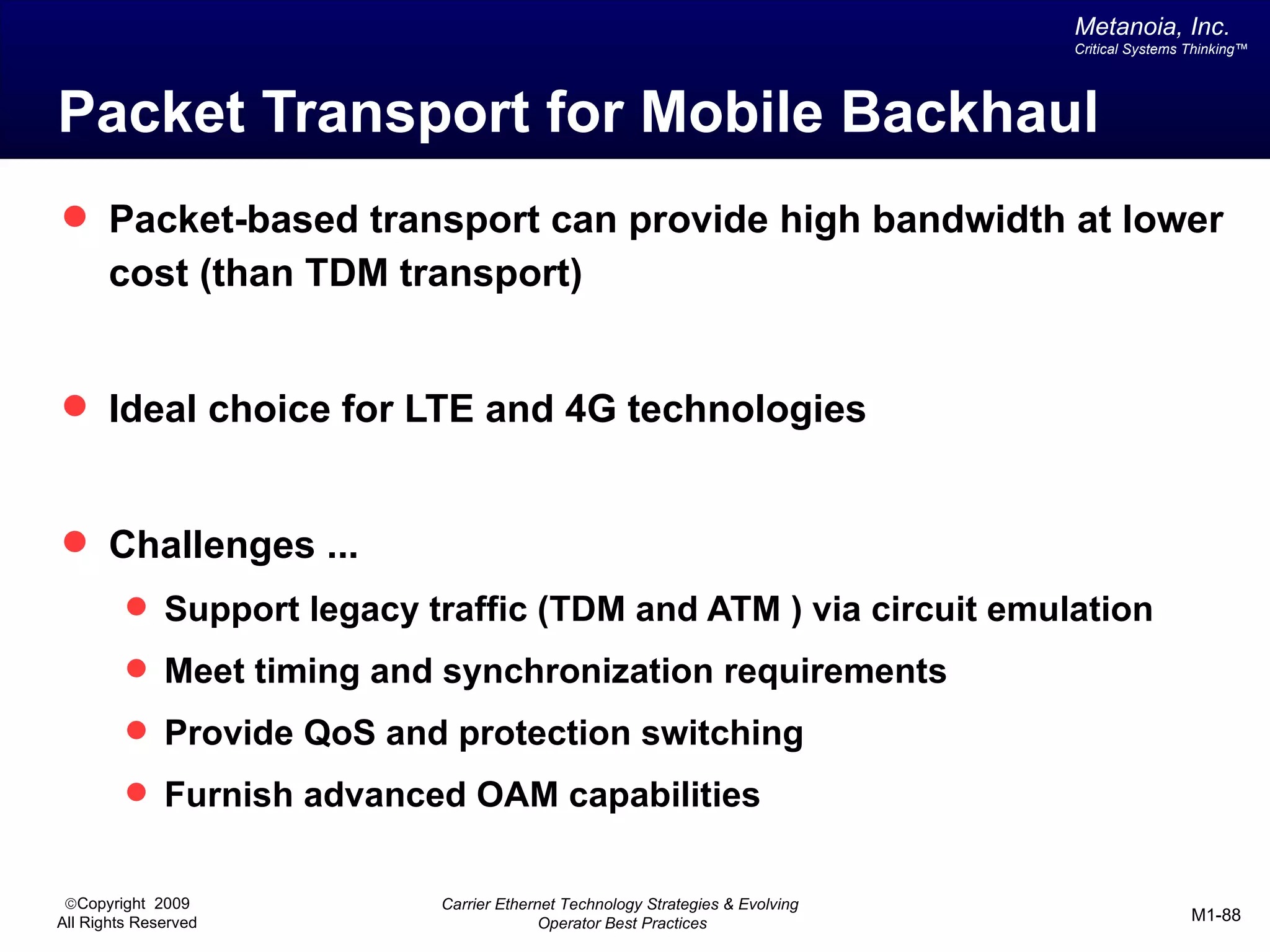
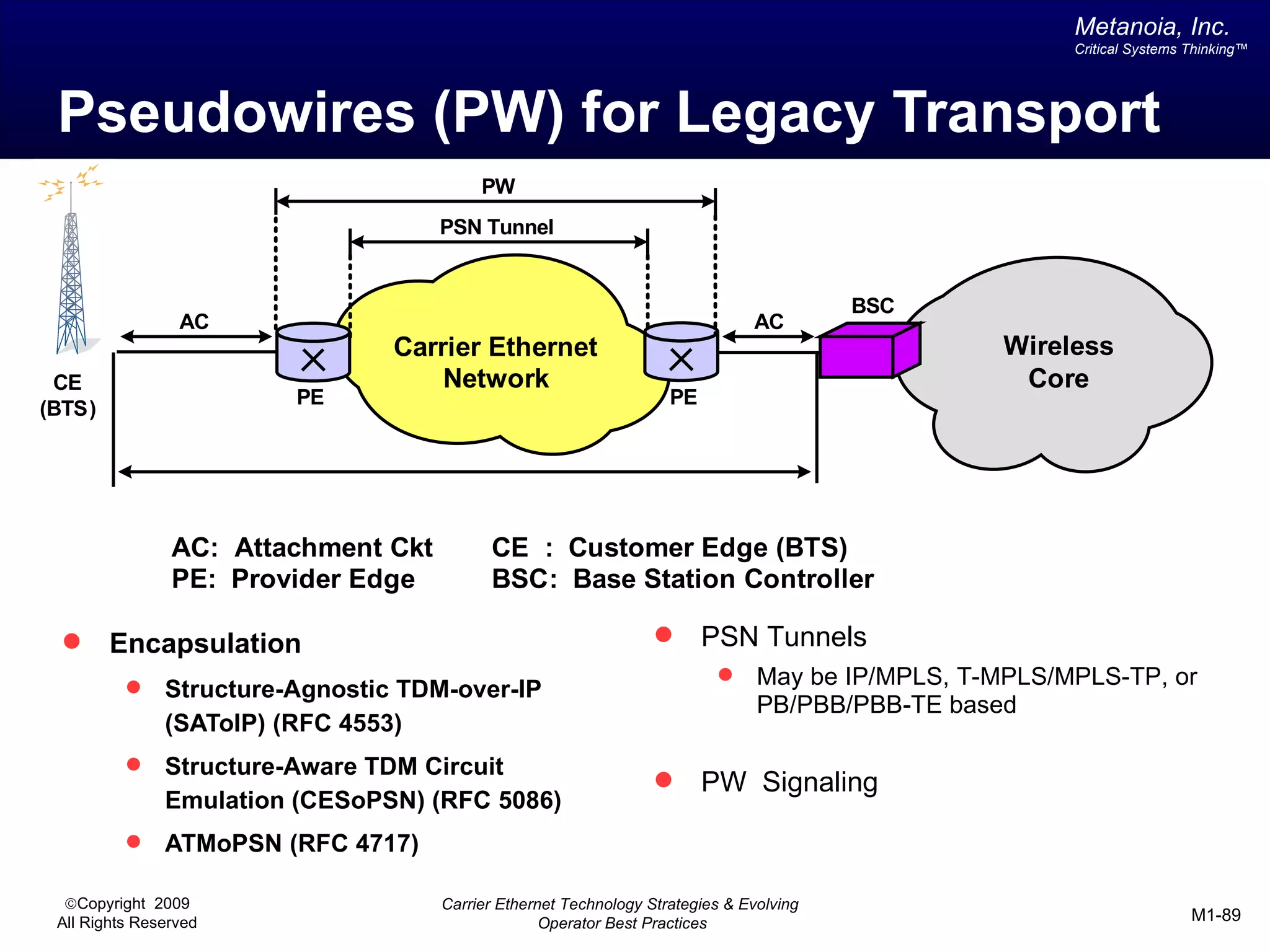
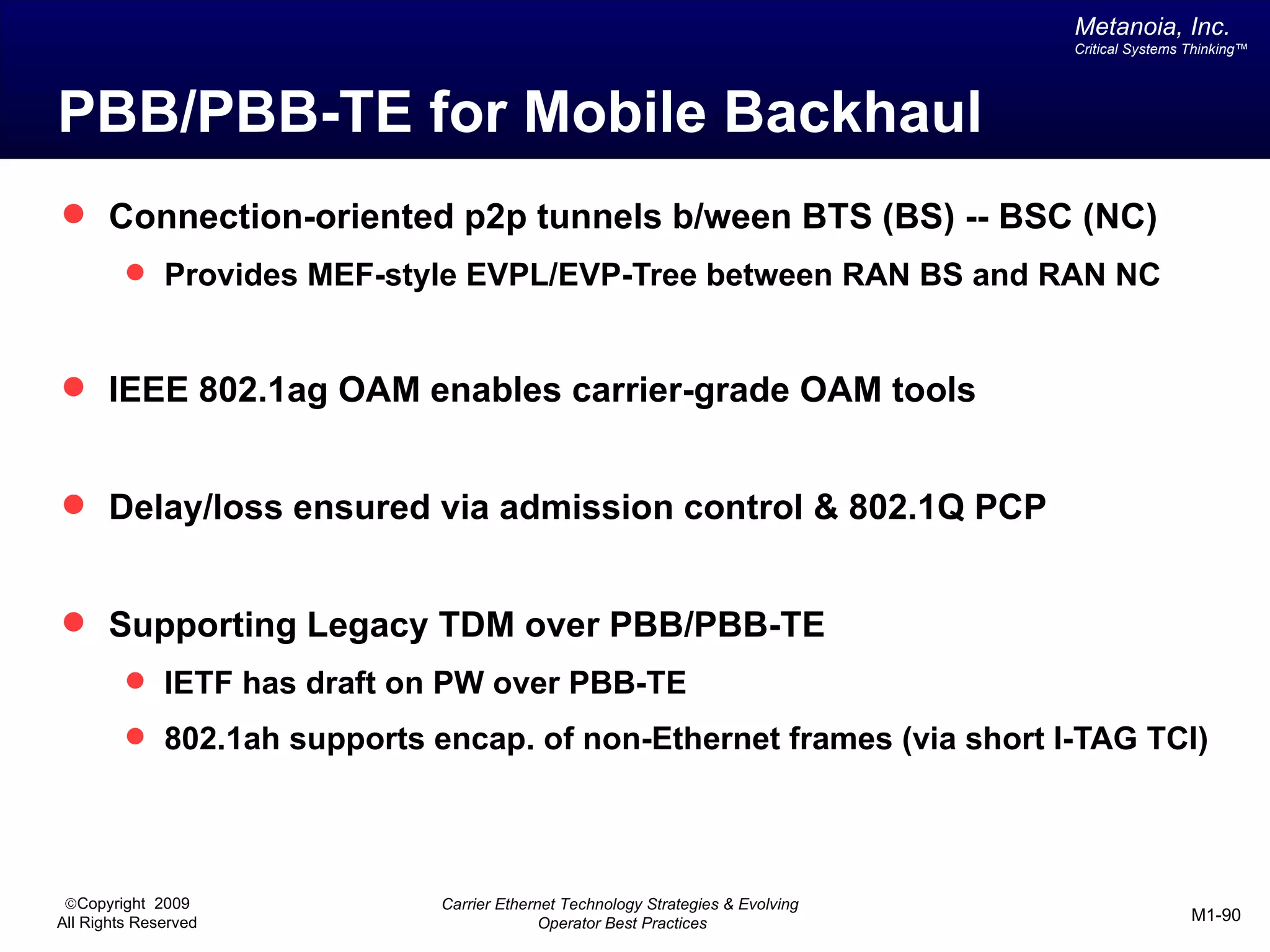
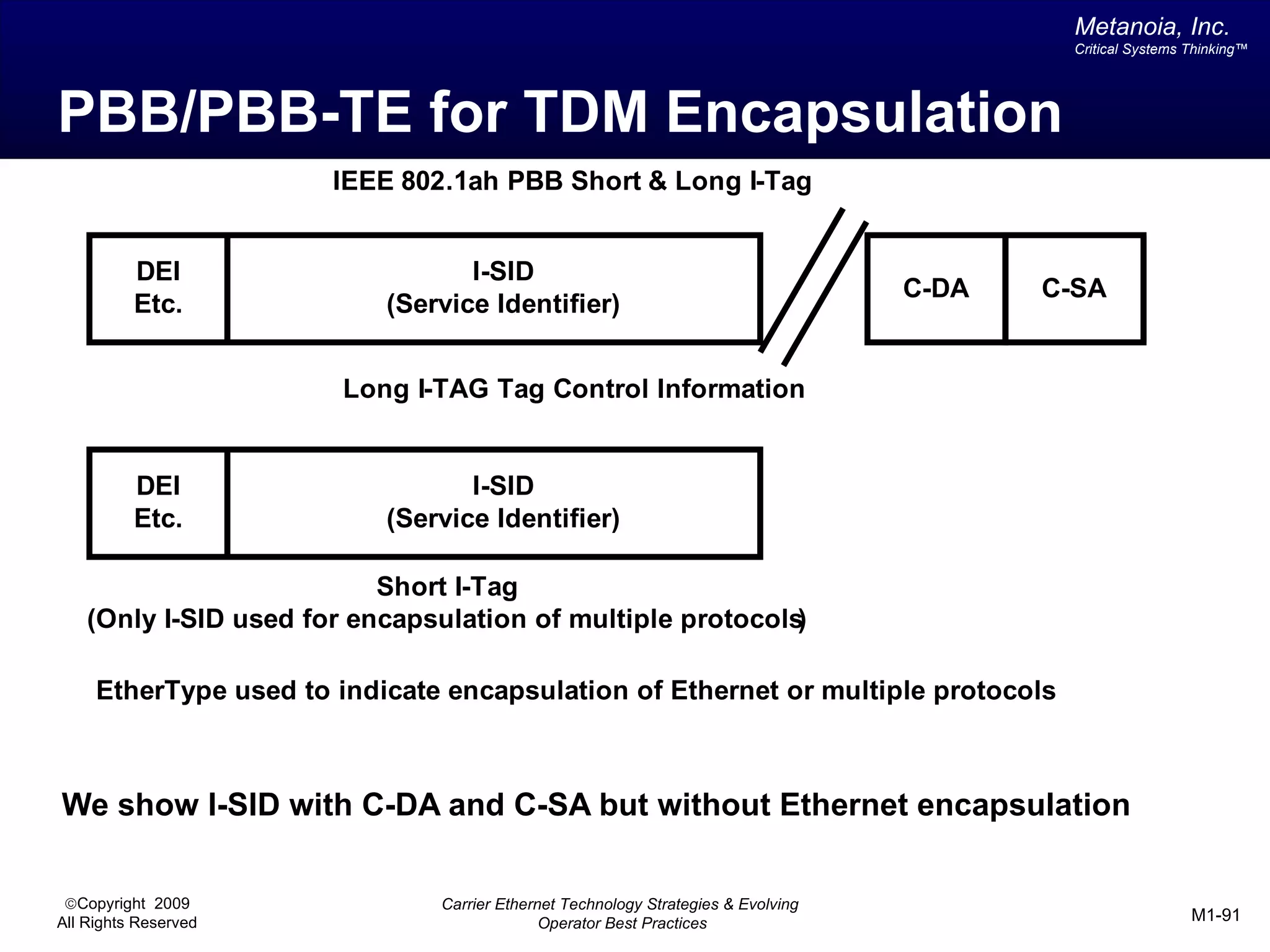
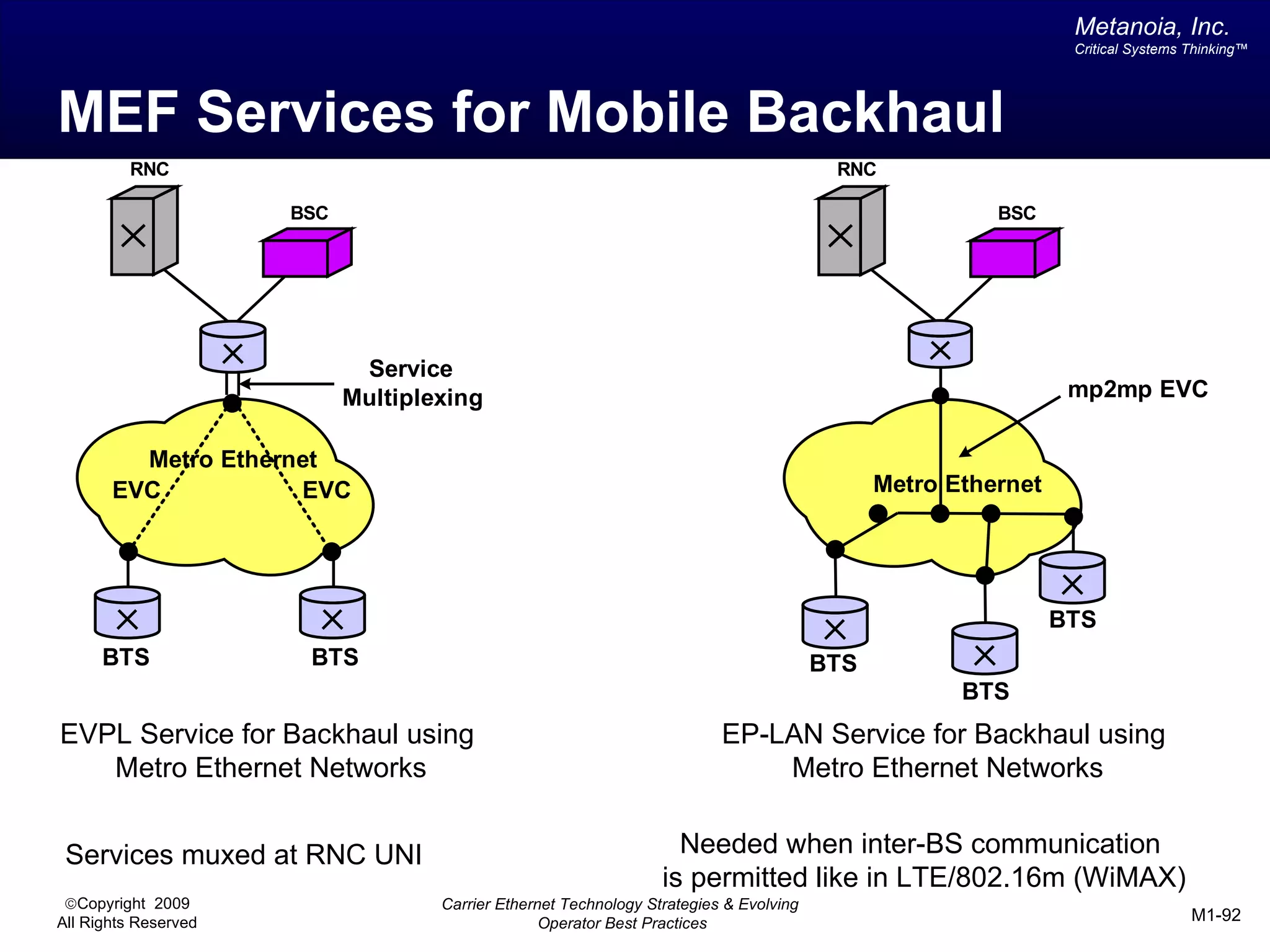
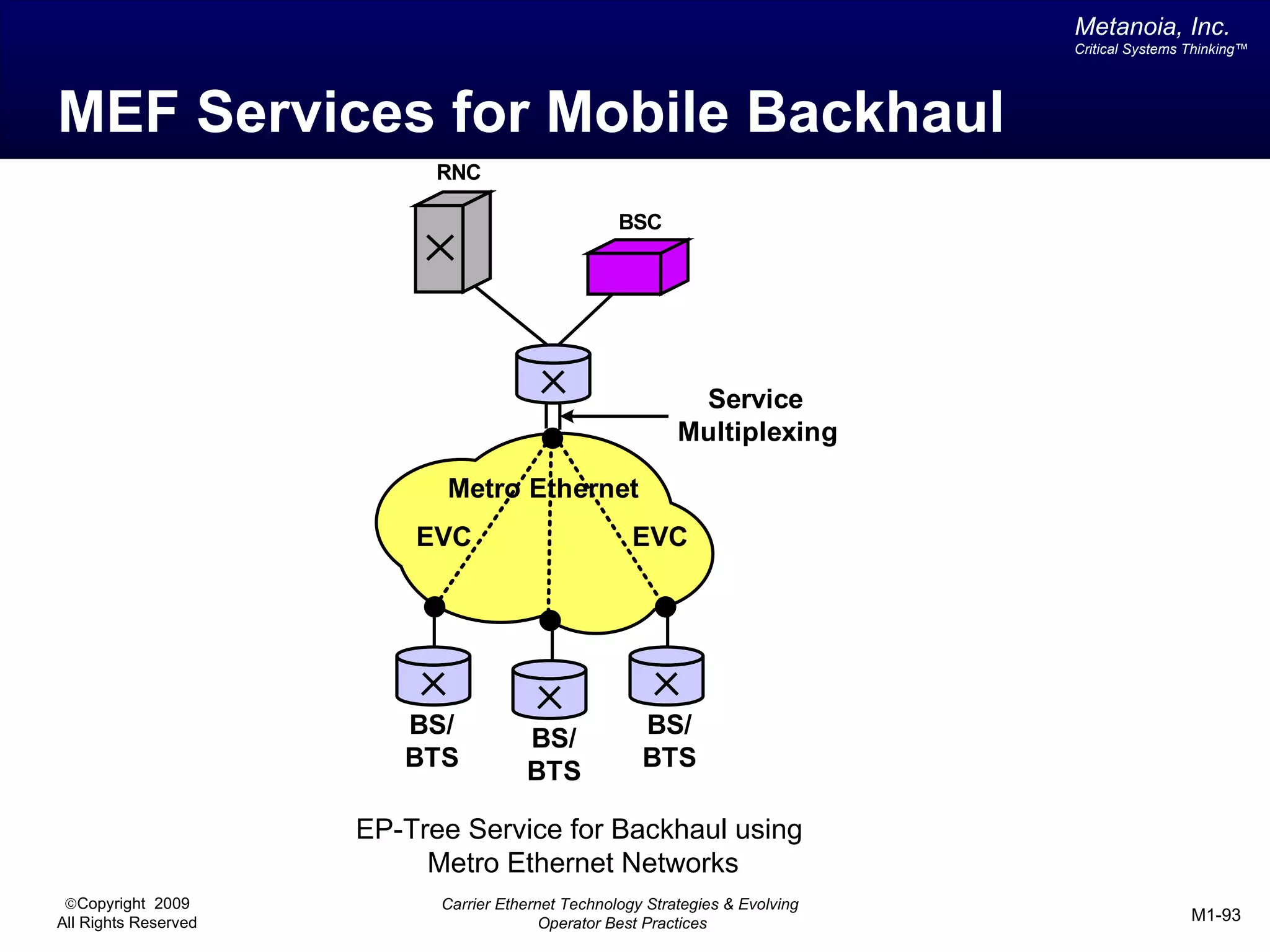
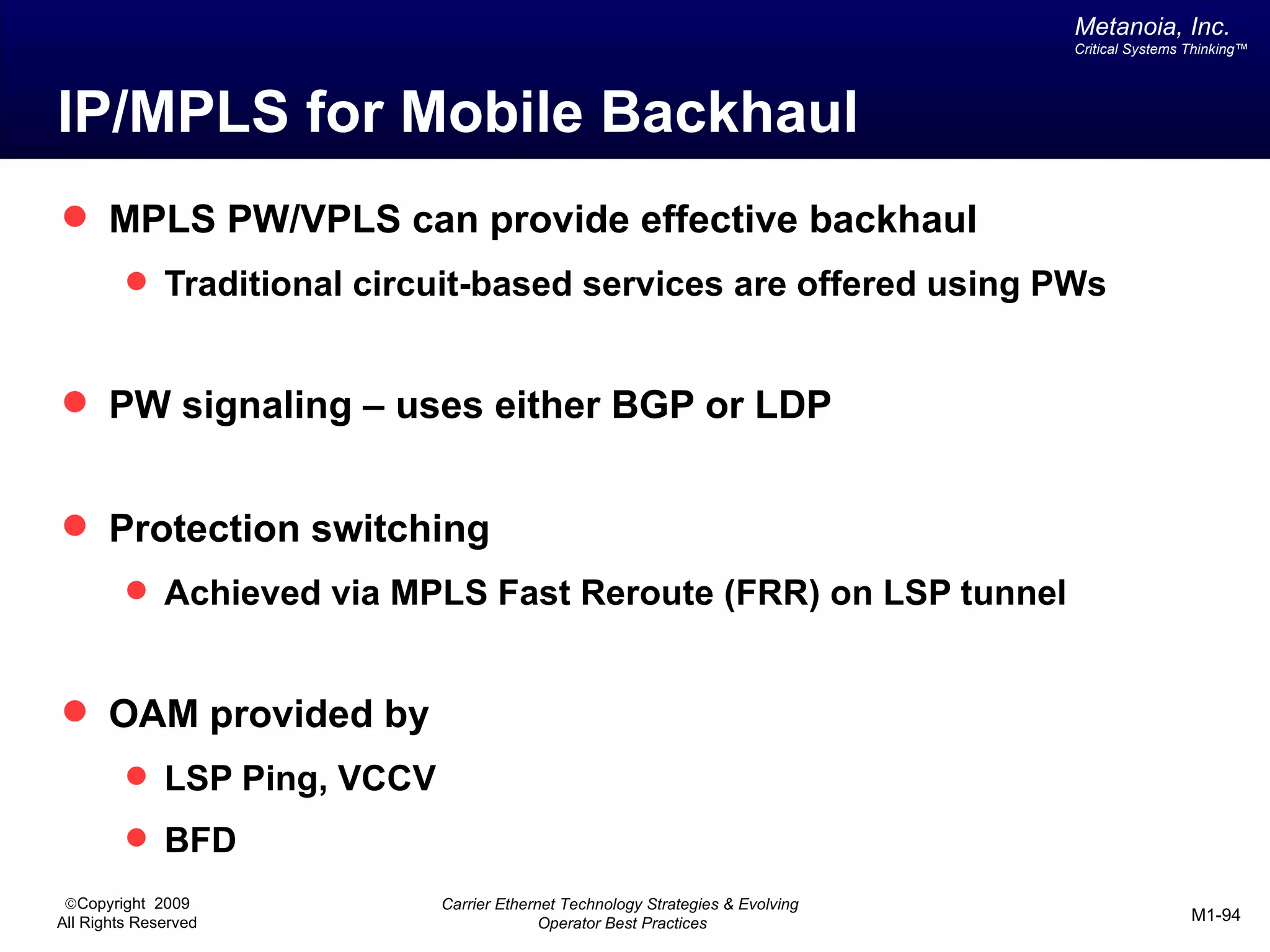
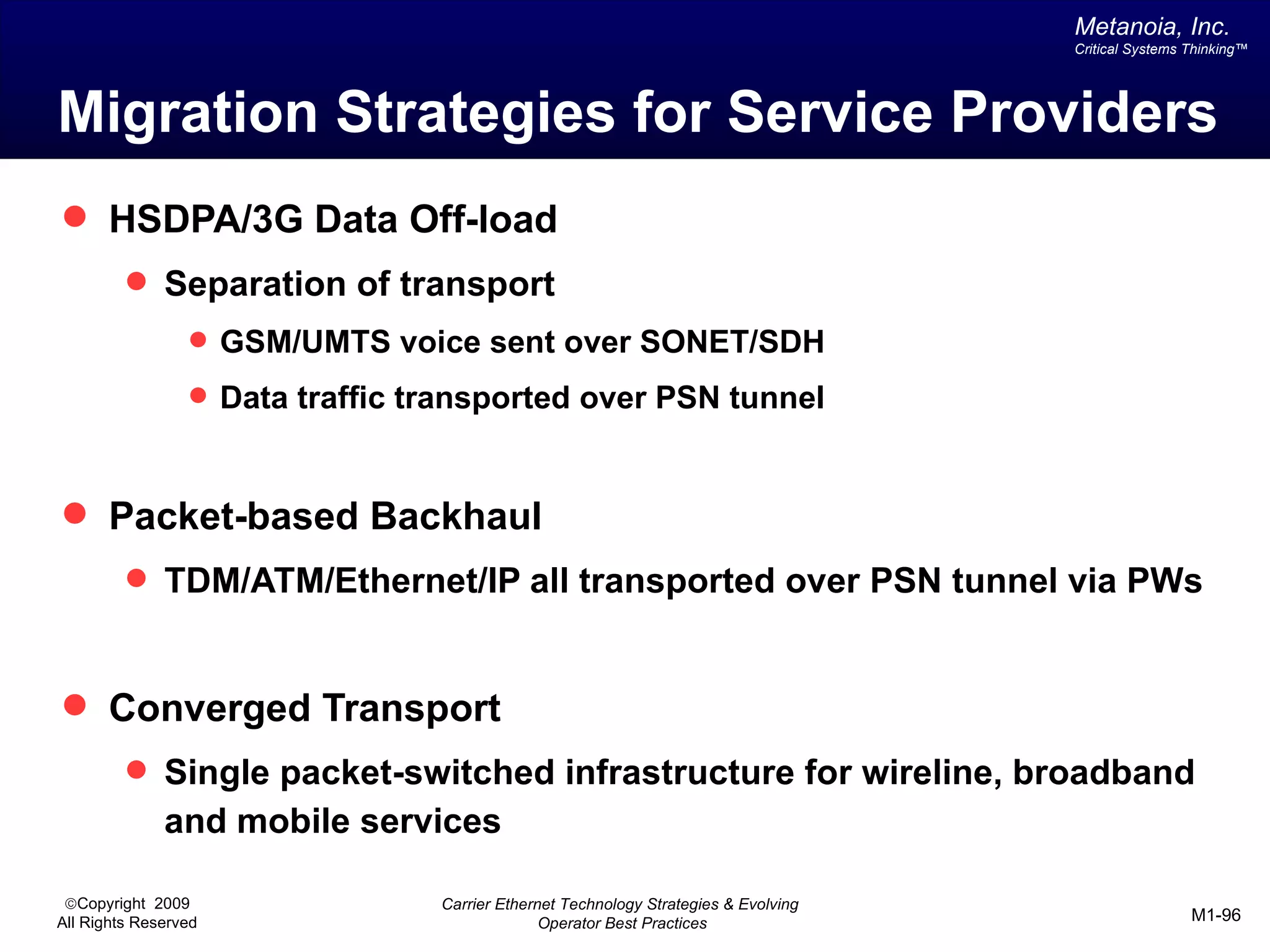
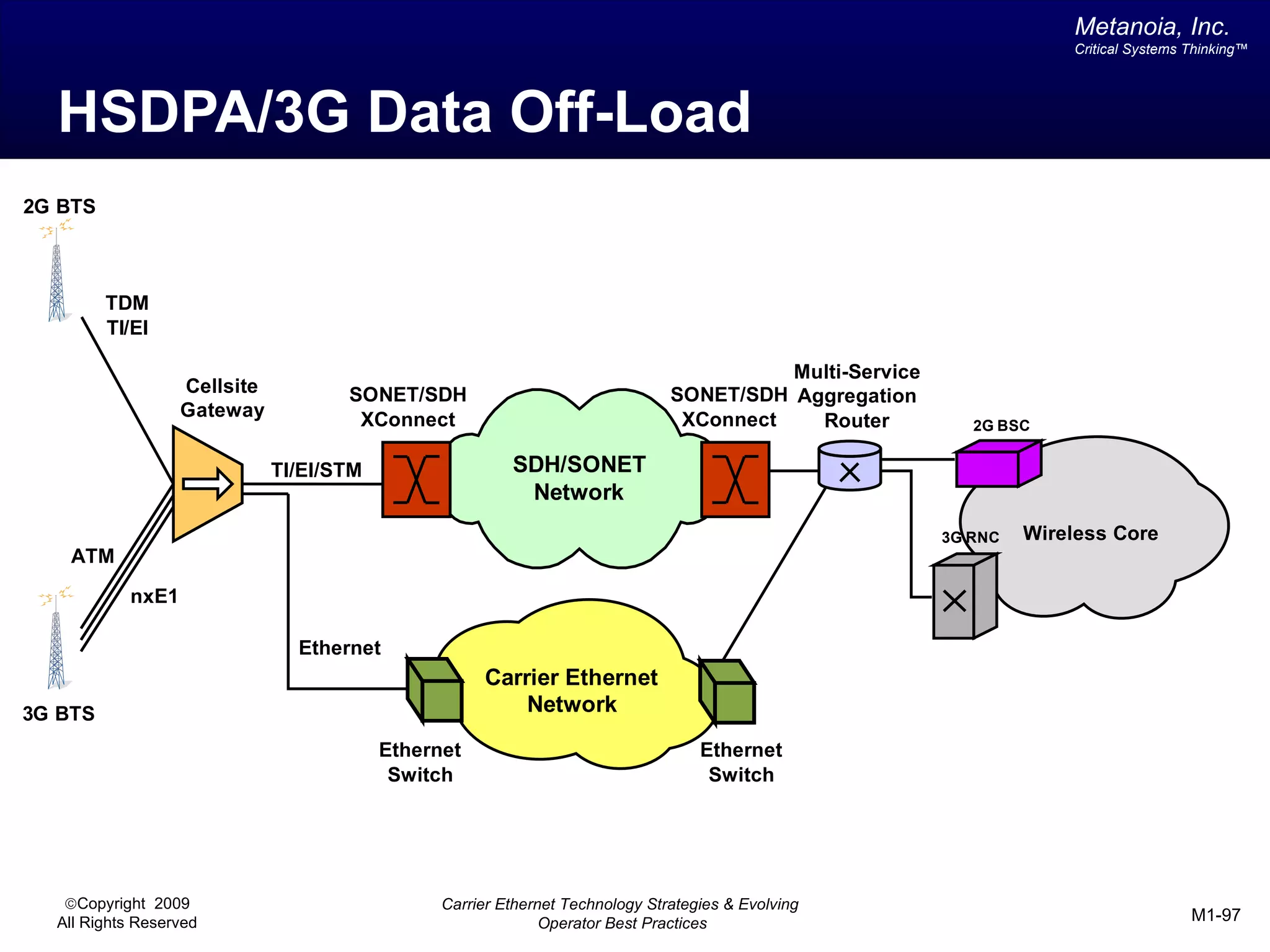
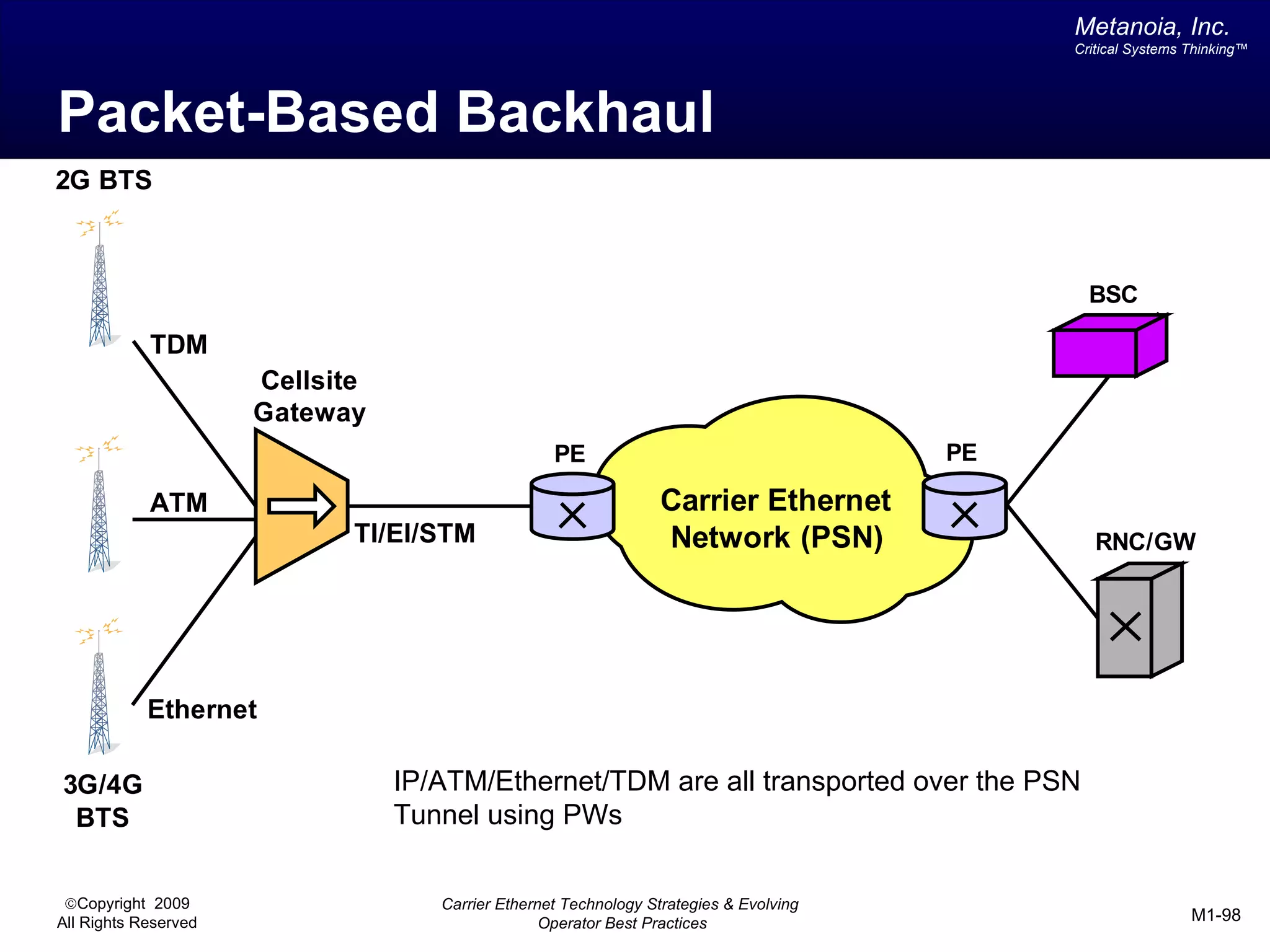
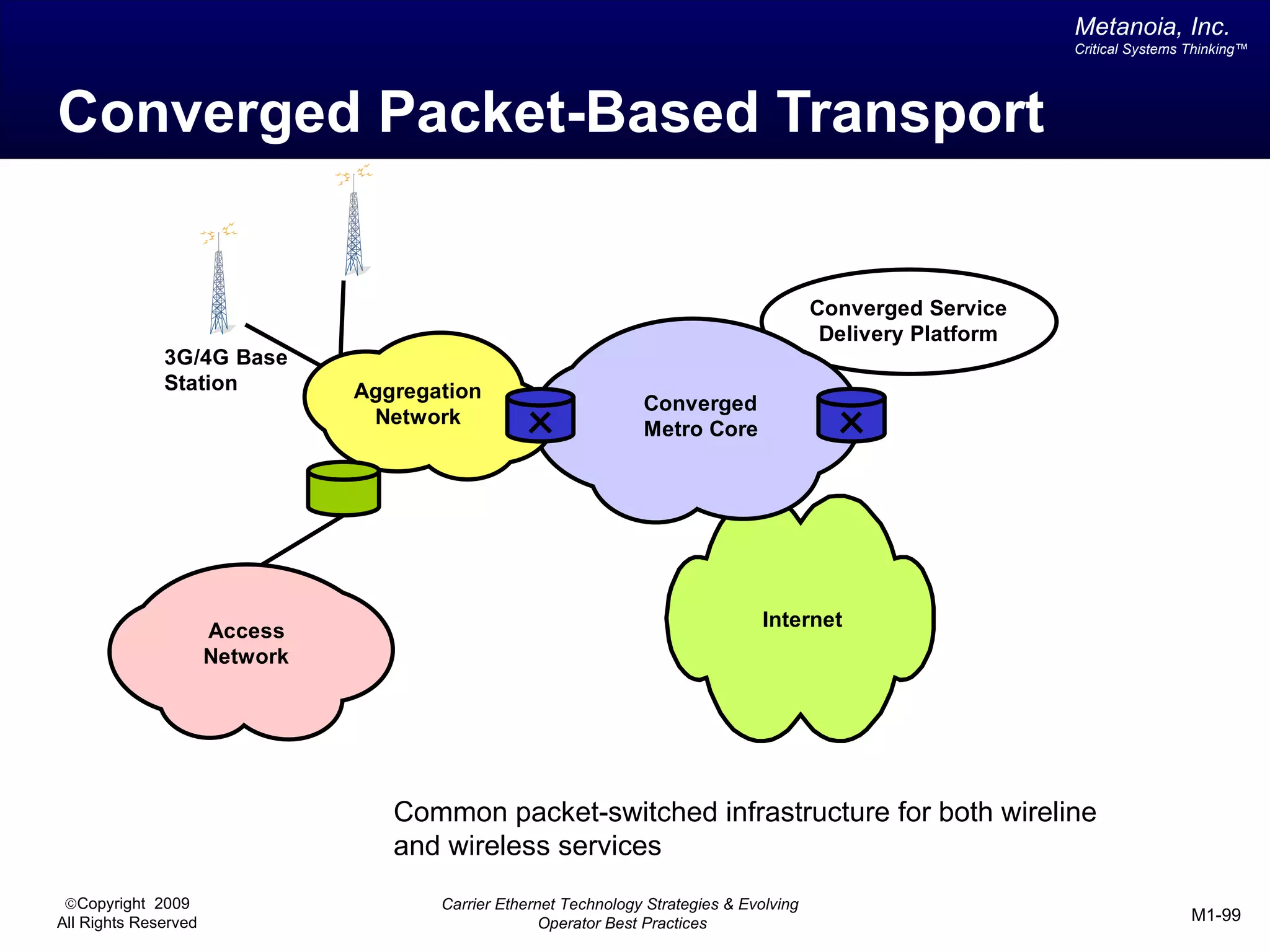
The document outlines various architectural options for metro carrier-ethernet network buildouts, focusing on the applicability of key technologies and analysis of basic architecture types such as parallel, overlay, uniform, and hybrid networks. It also includes a comparative assessment of technologies suited for metro access, aggregation, and core segments, utilizing a rating scale for their effectiveness in those contexts. The analysis further elaborates on the practical considerations of each architectural choice in terms of capital and operational expenses, flexibility, and management complexity.