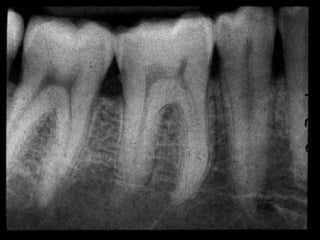
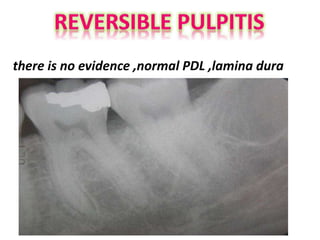
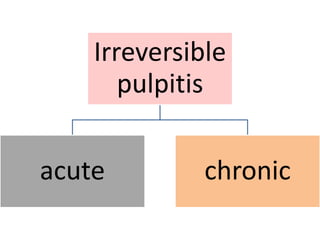
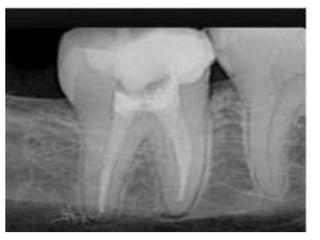
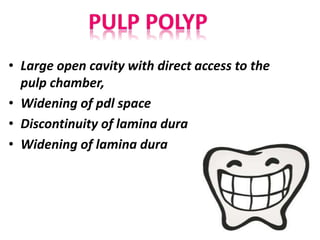
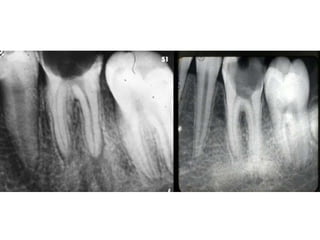
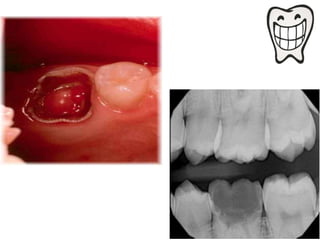
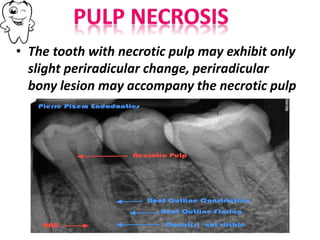
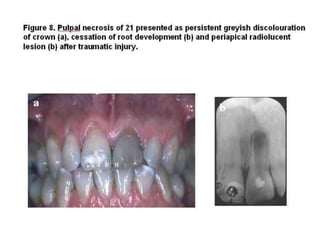
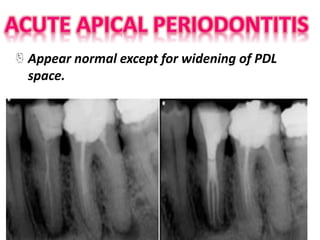
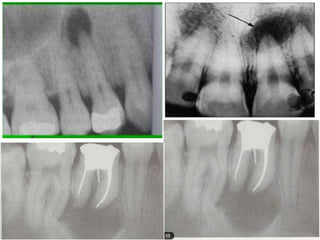
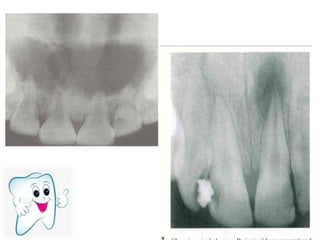
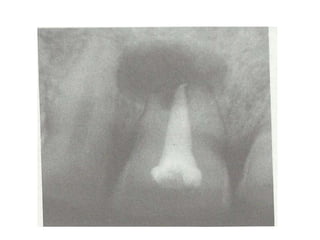
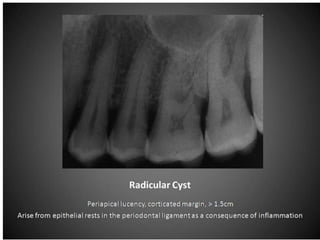
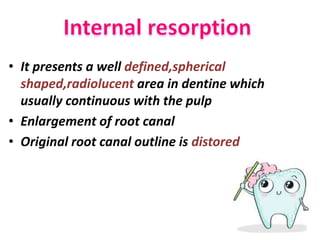
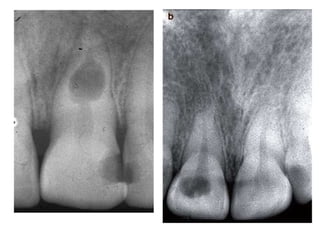
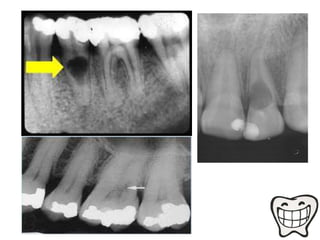
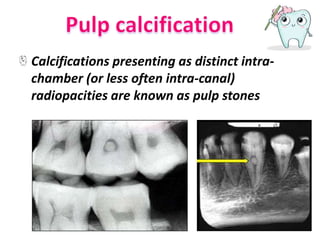
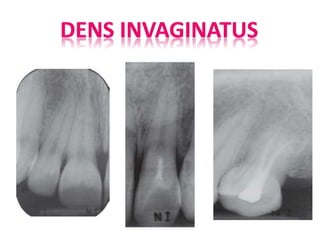
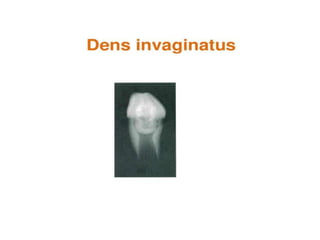
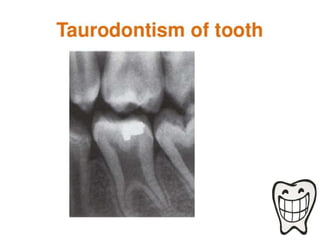
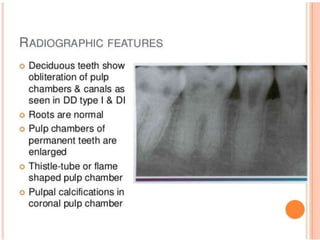
The document discusses various conditions that can affect the tooth pulp and surrounding structures. It describes the normal anatomy of the pulp and defines different types of pulpitis. It then outlines several pathological conditions such as pulp necrosis, pulp polyps, periapical abscess, granuloma, and cysts. For each condition, it provides details on clinical features and radiographic appearances seen on dental imaging.