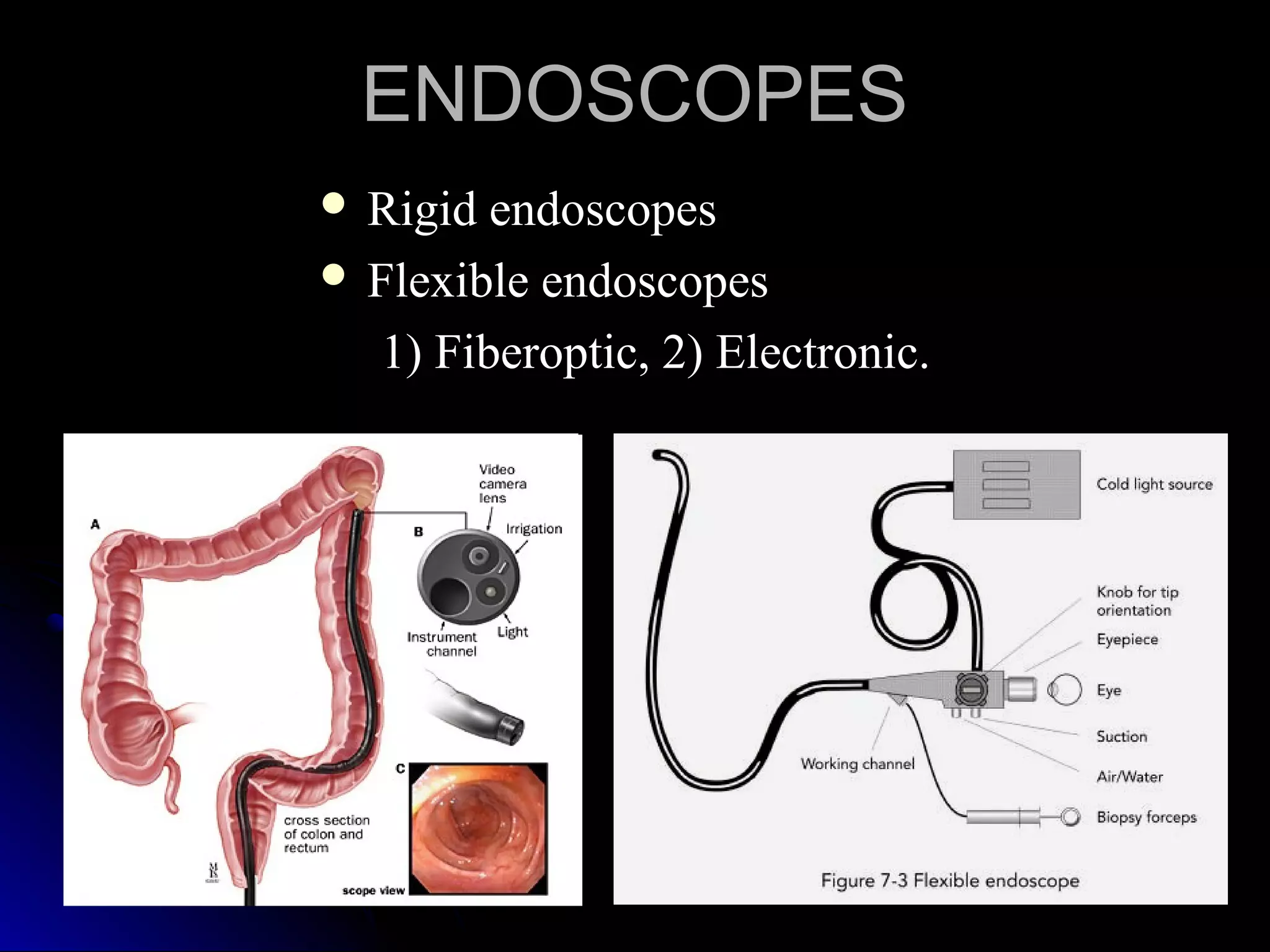
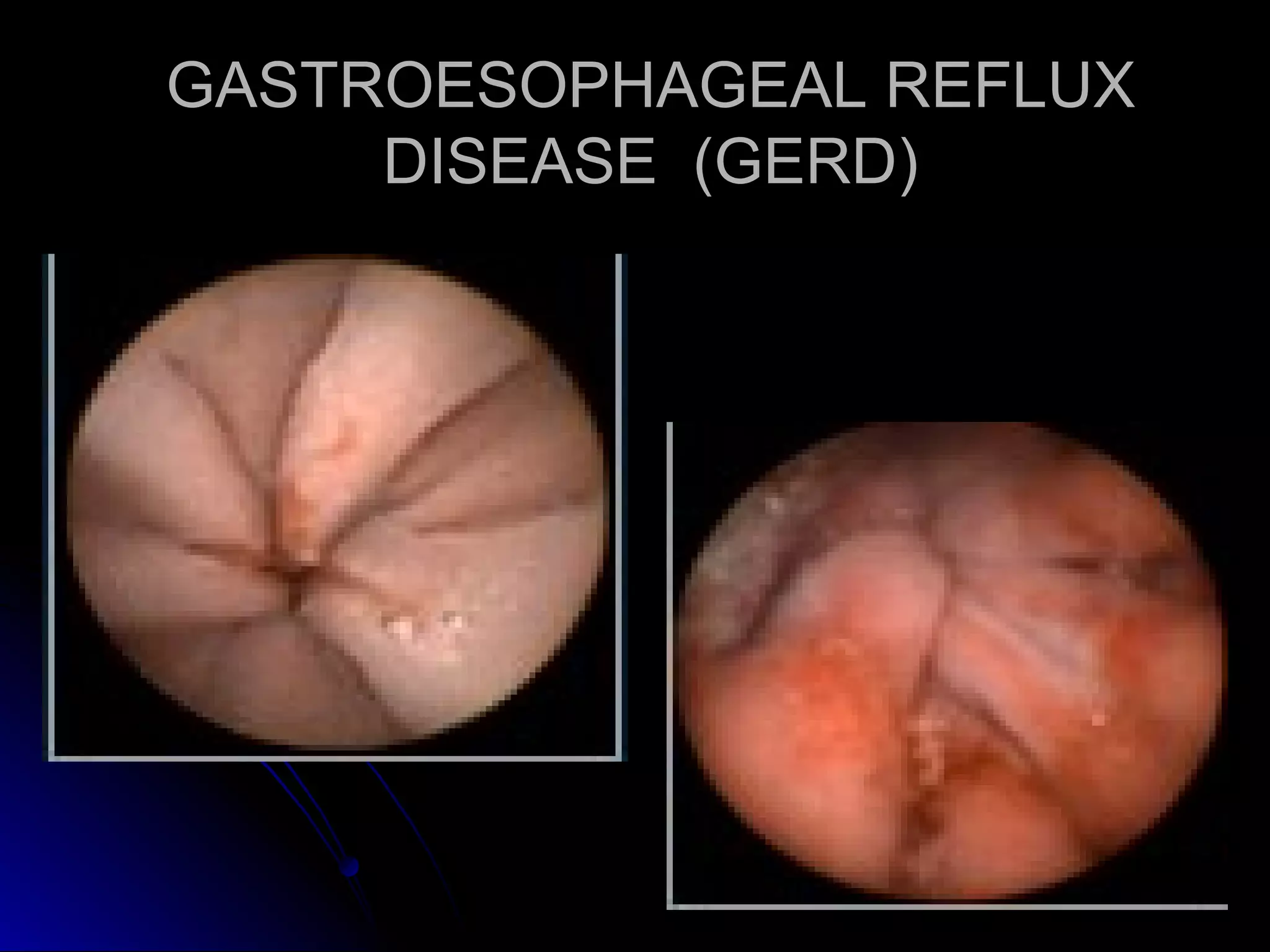
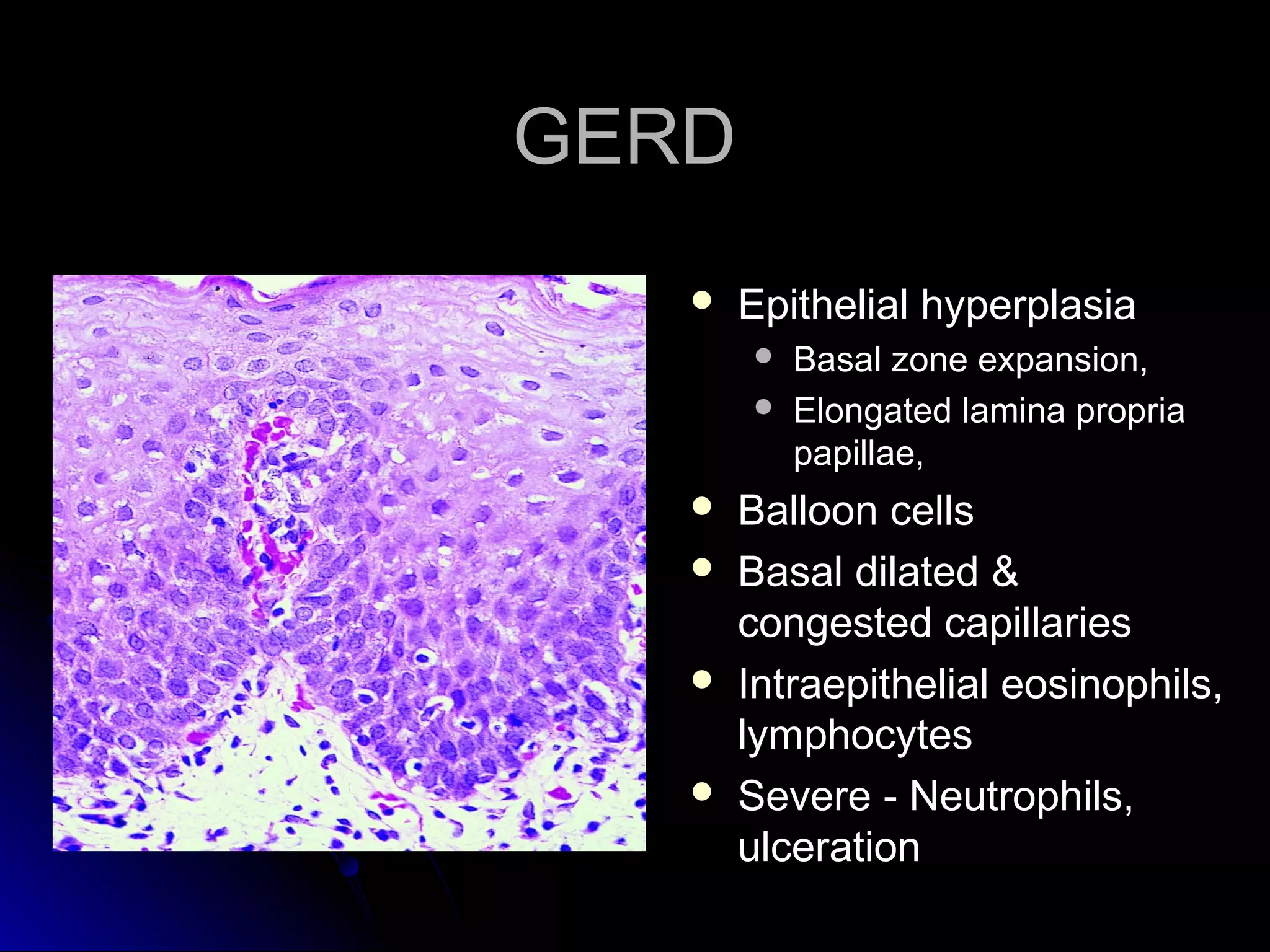
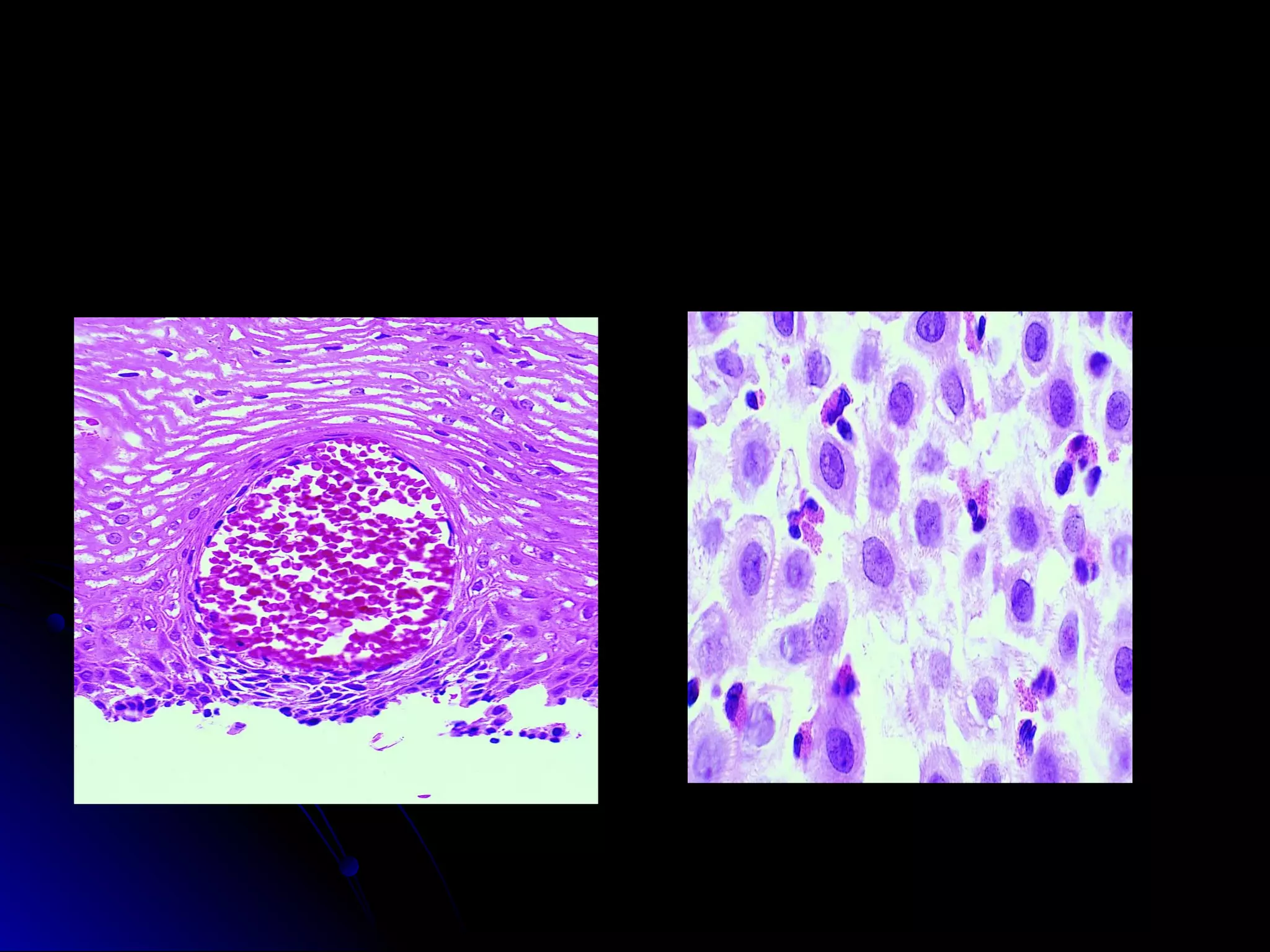
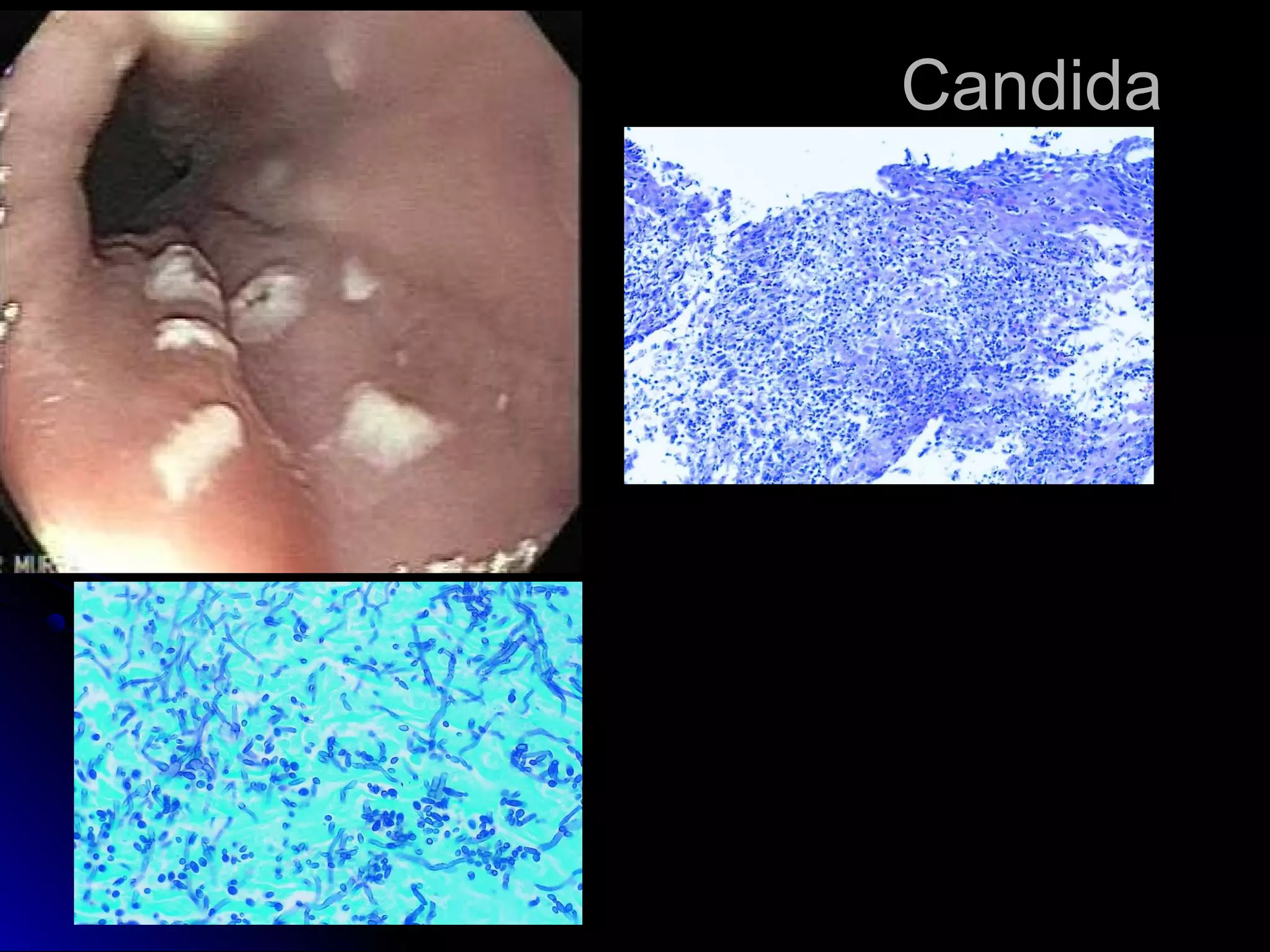
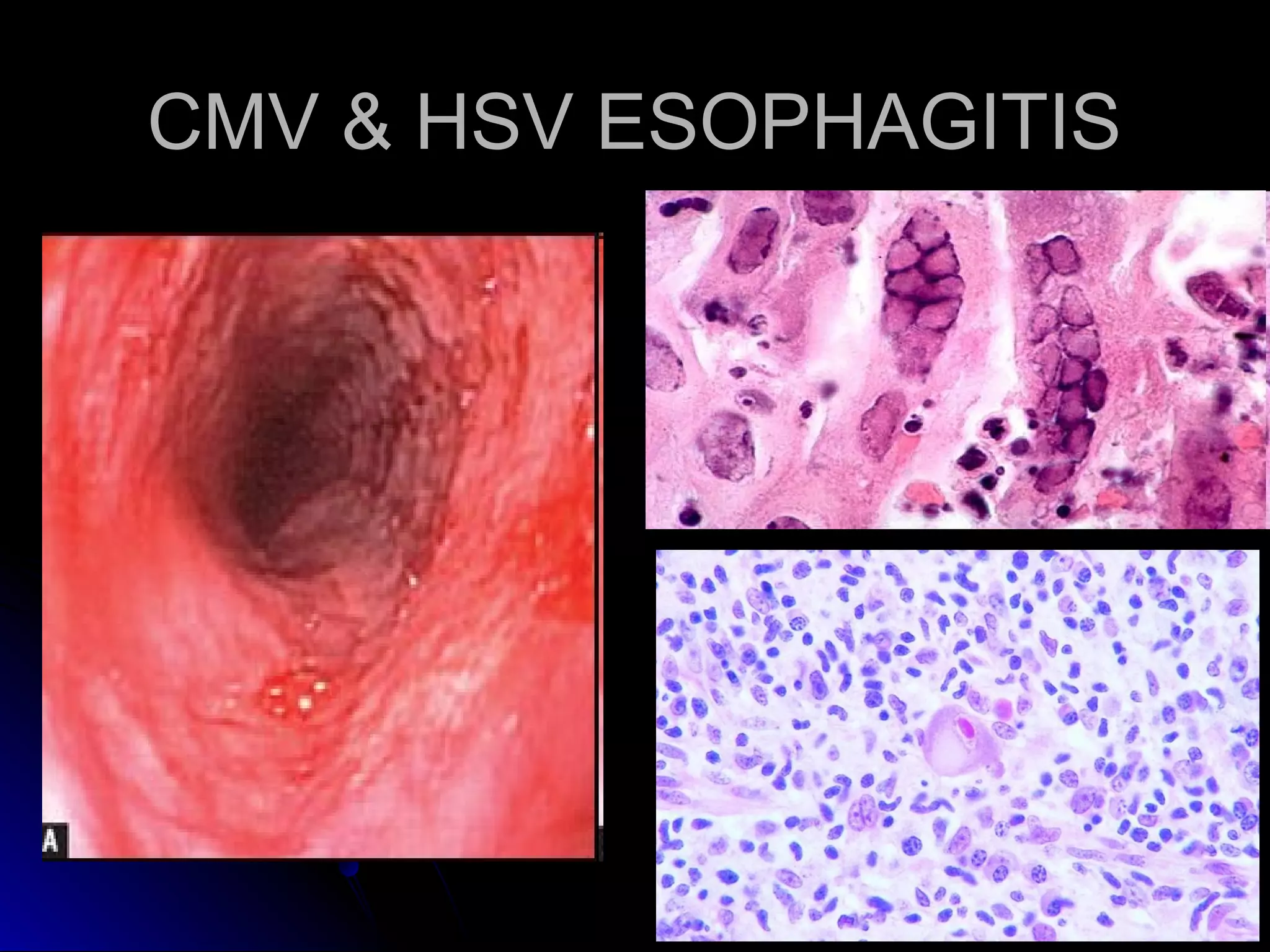
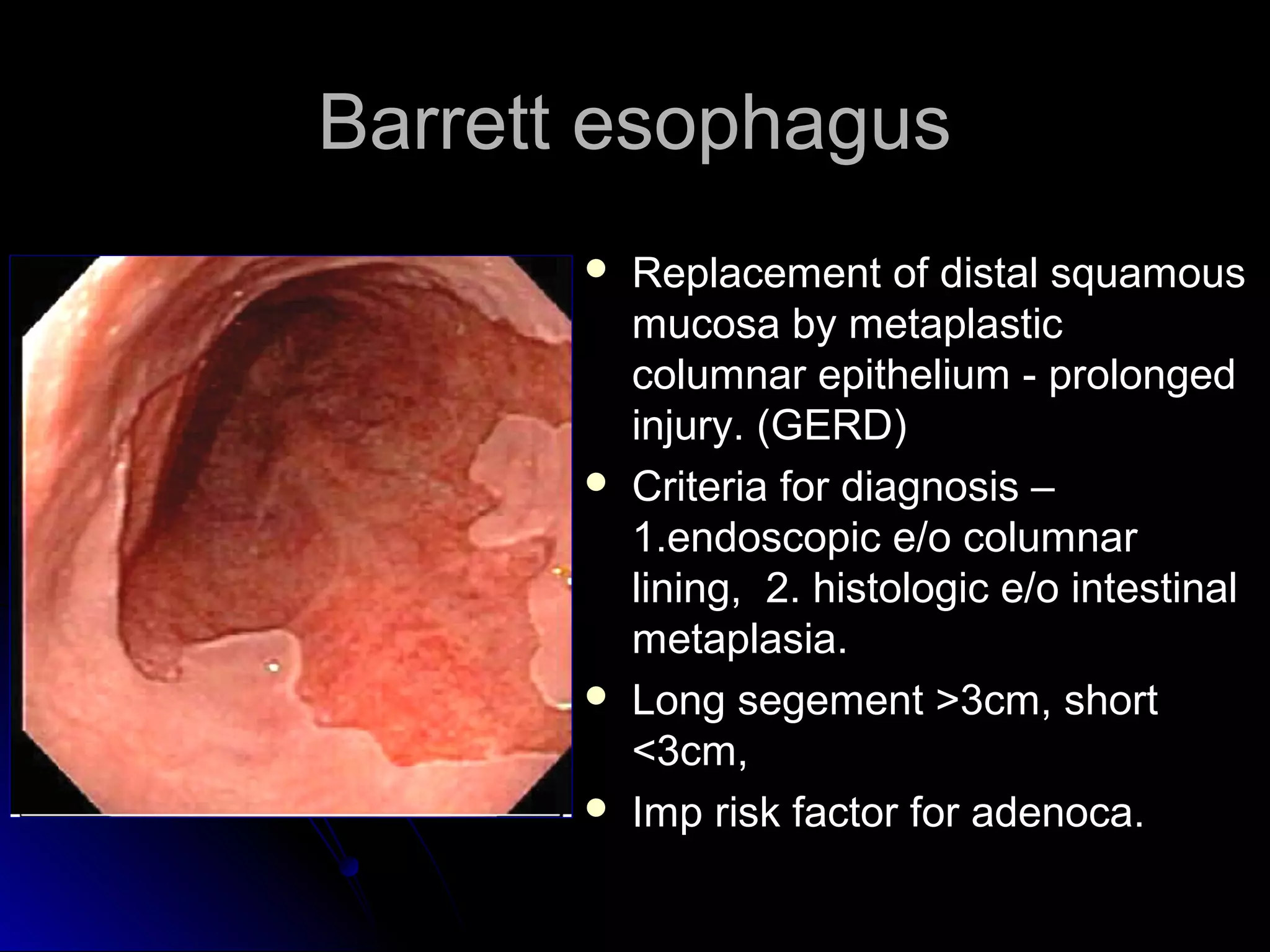
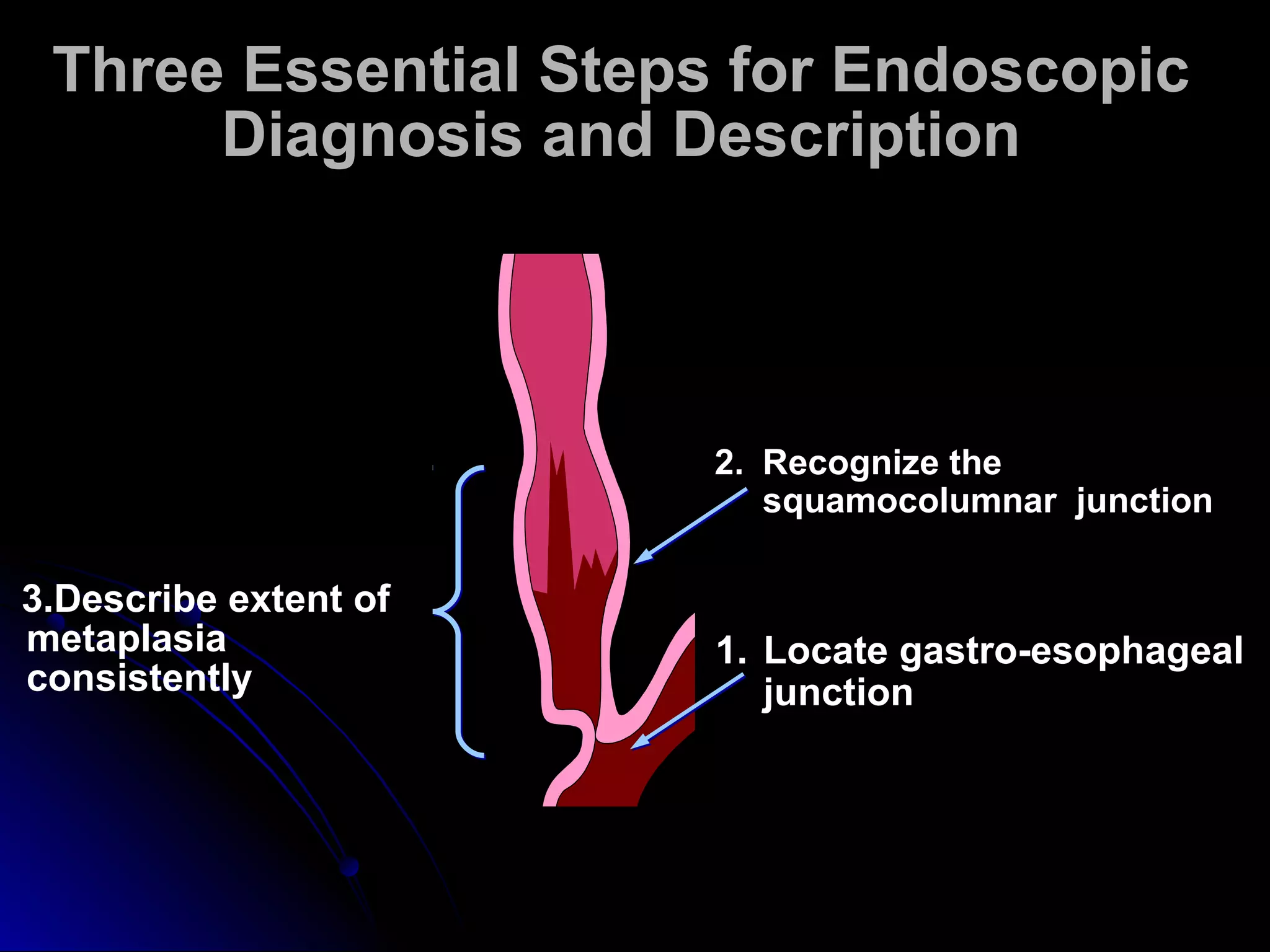
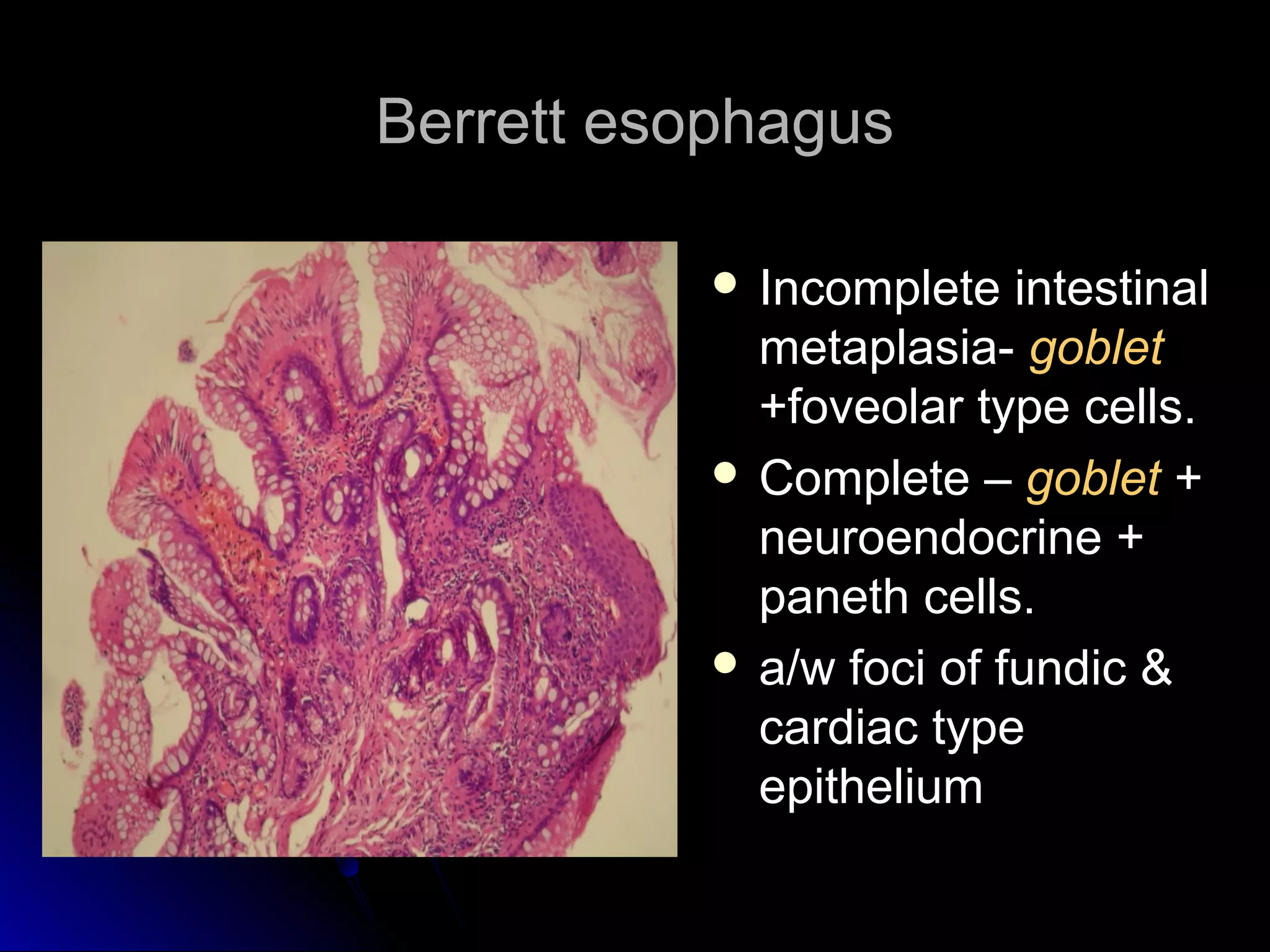
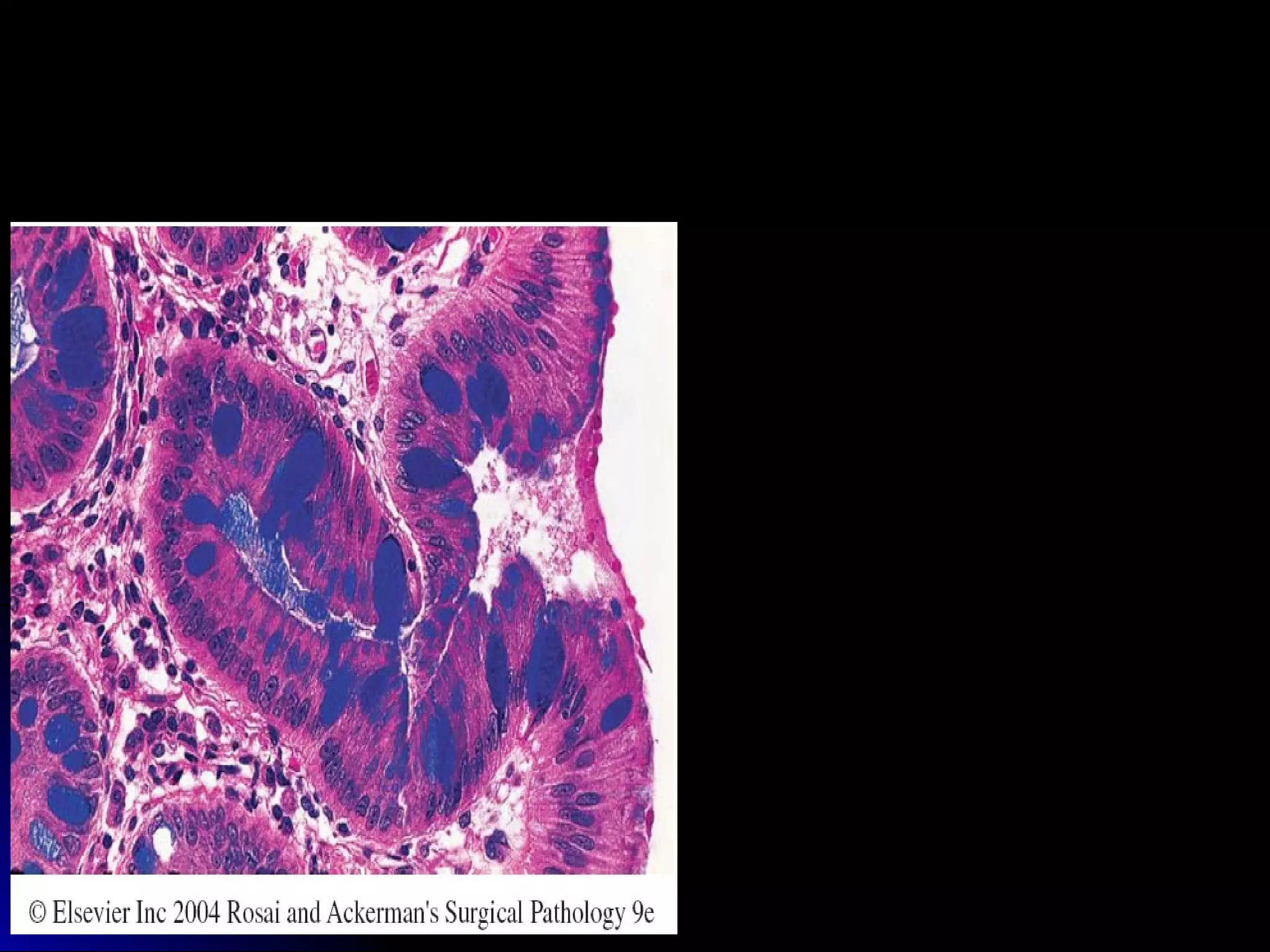
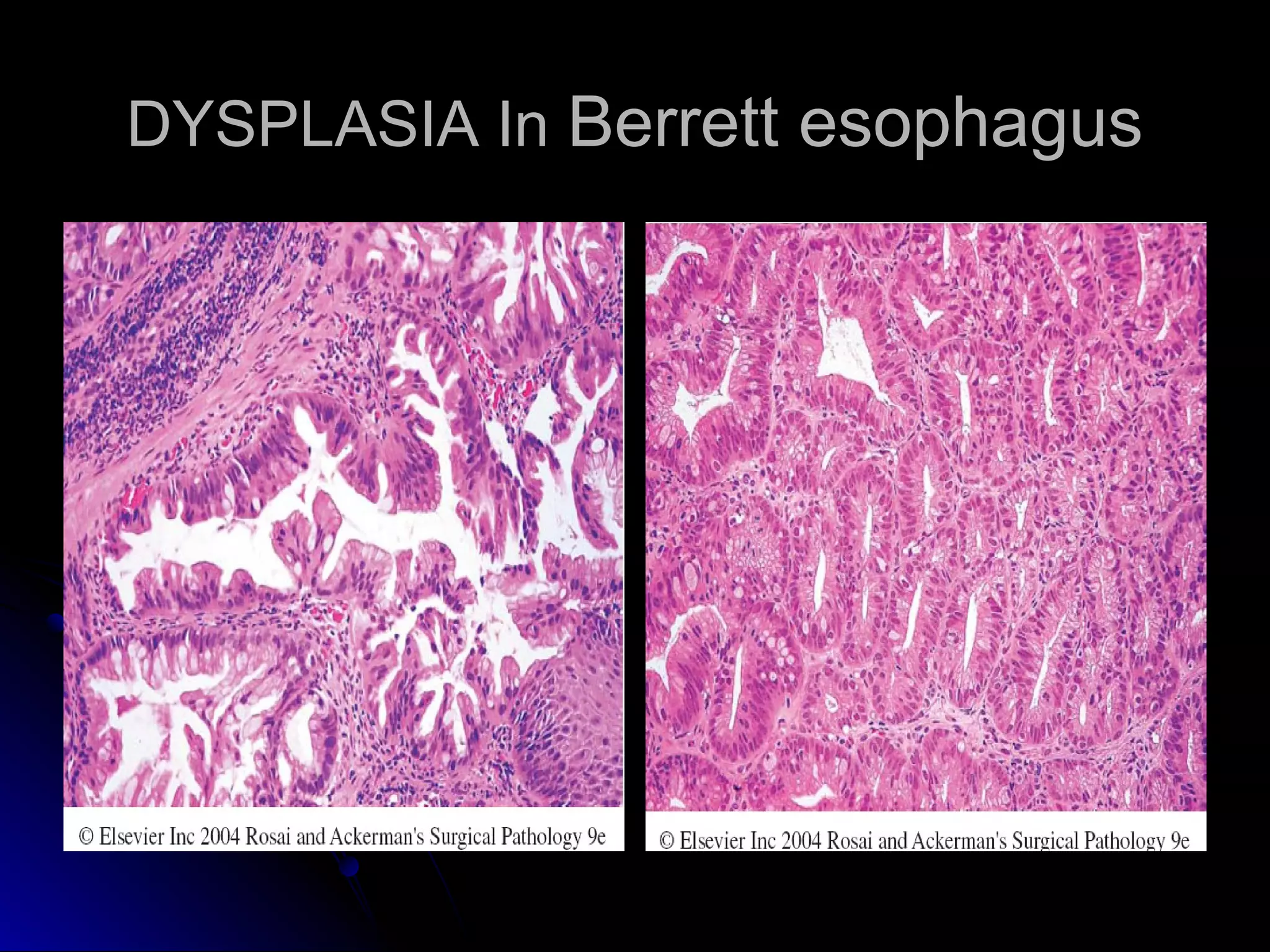
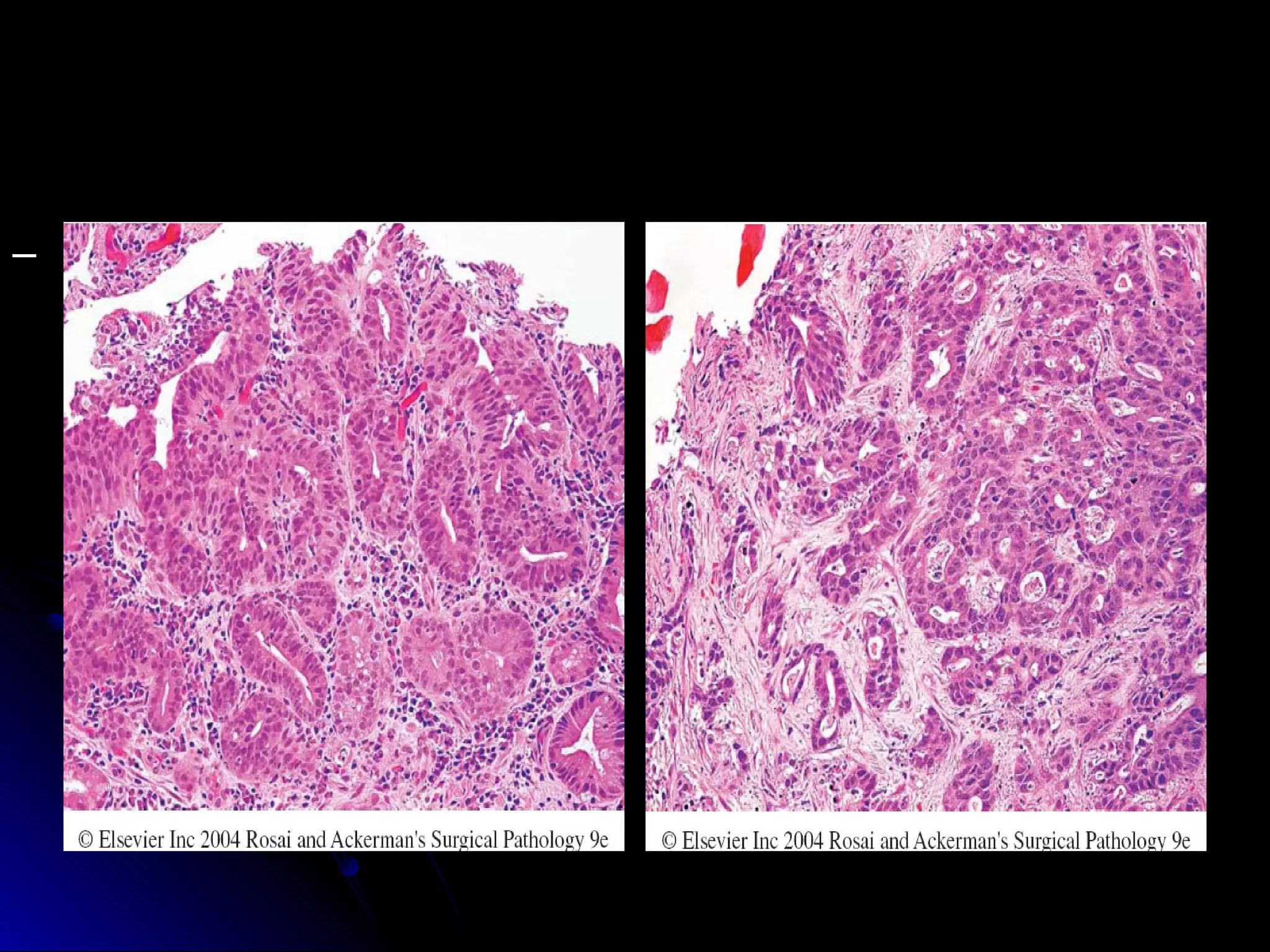
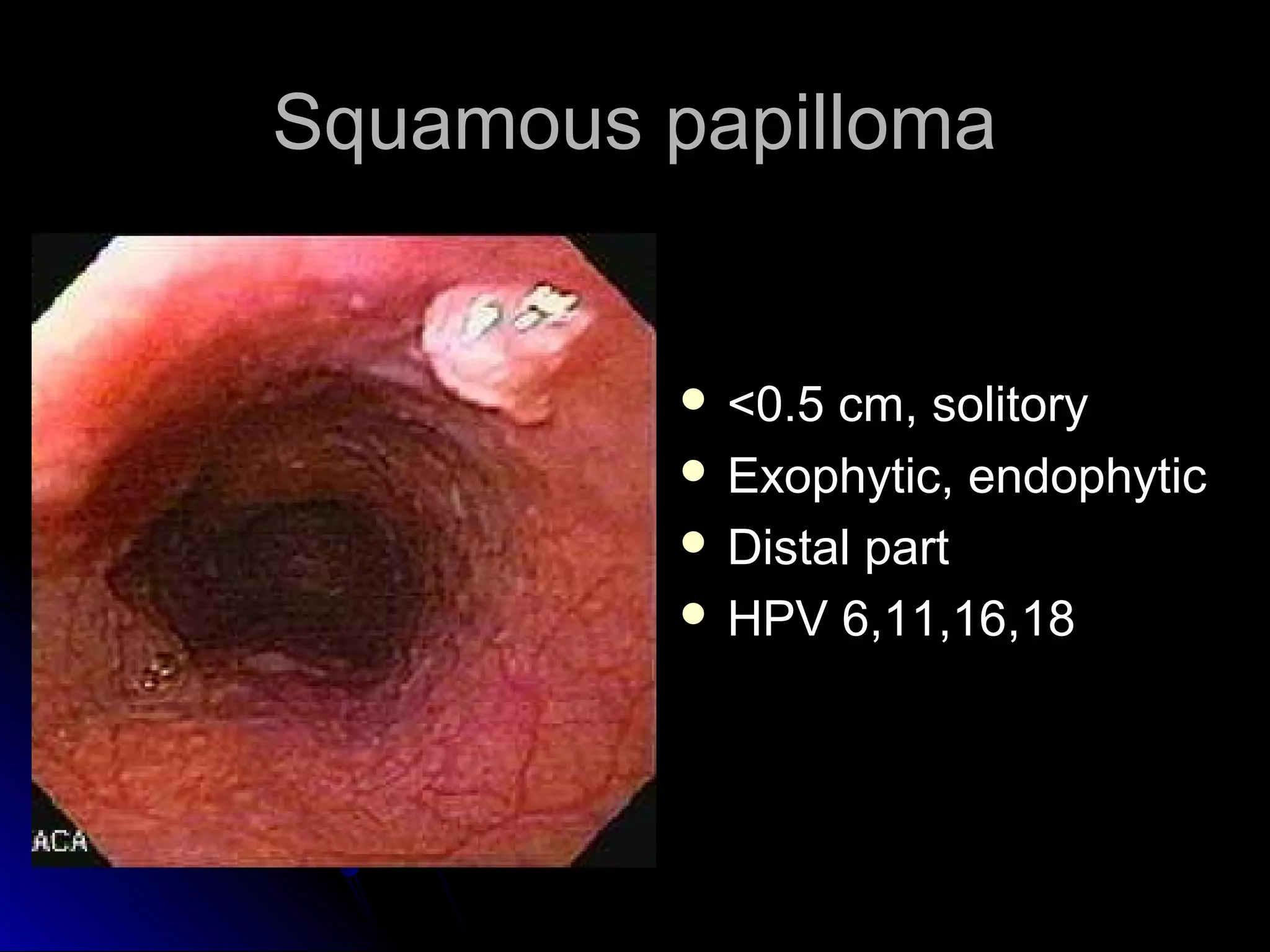
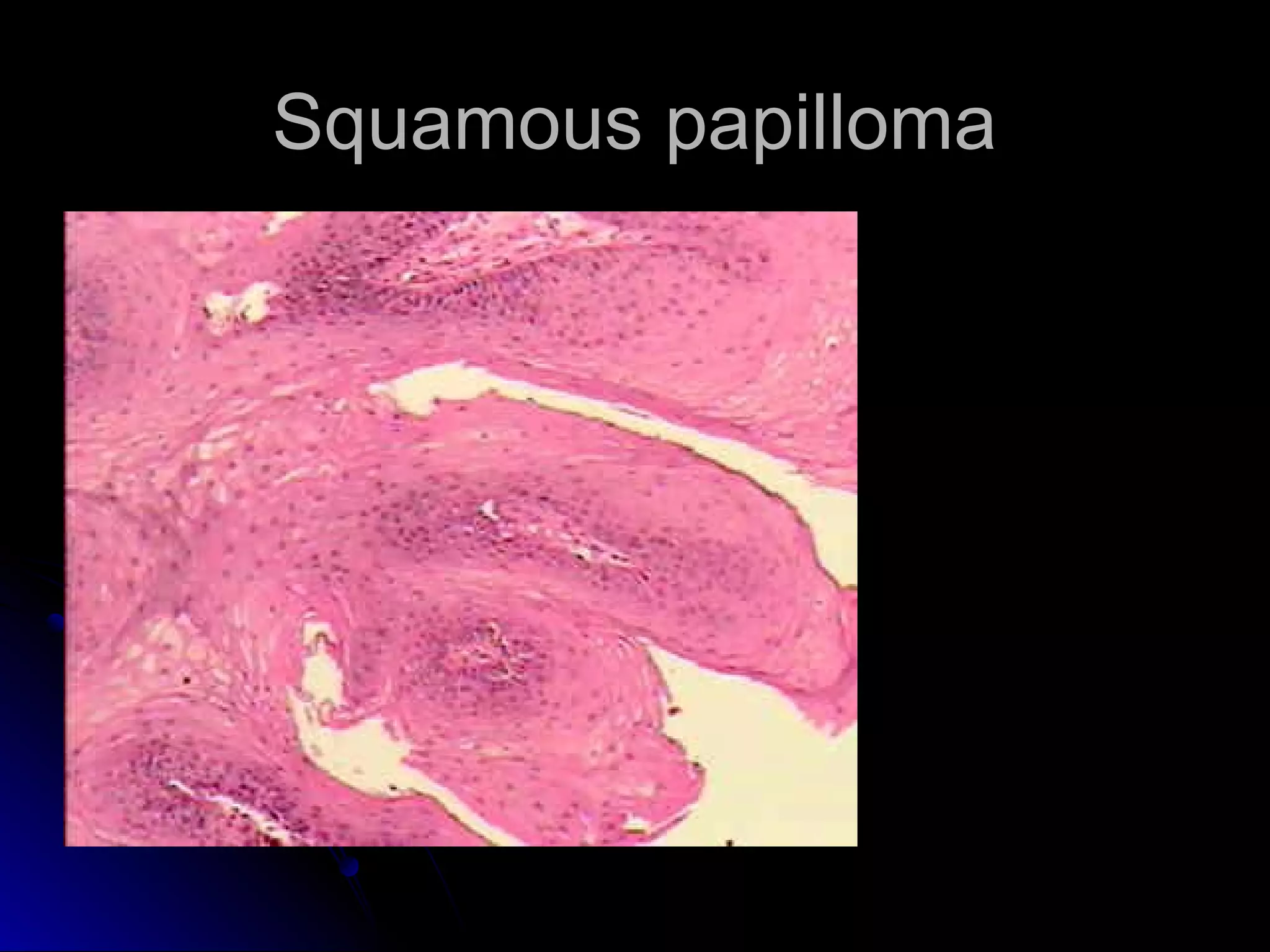
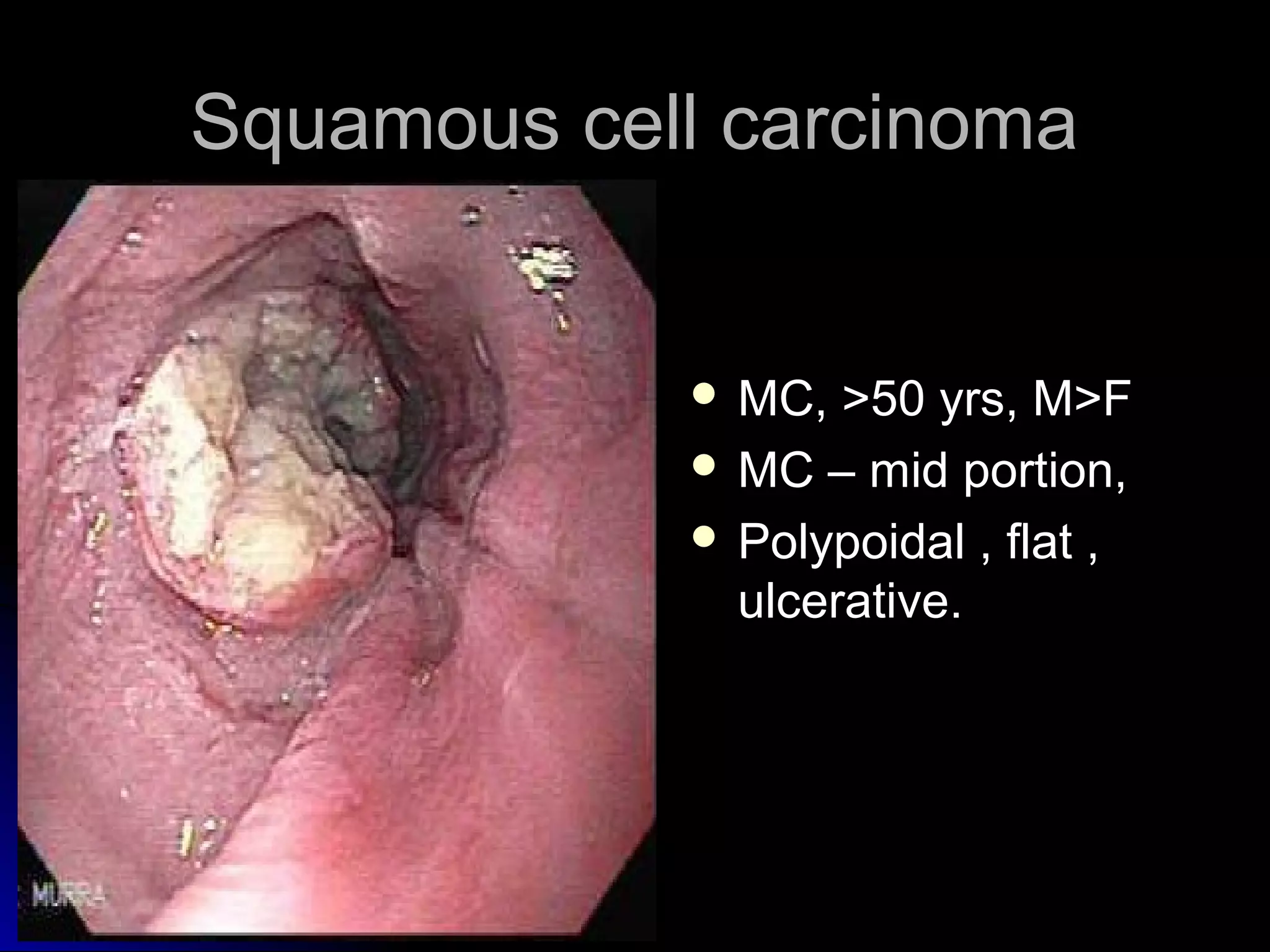
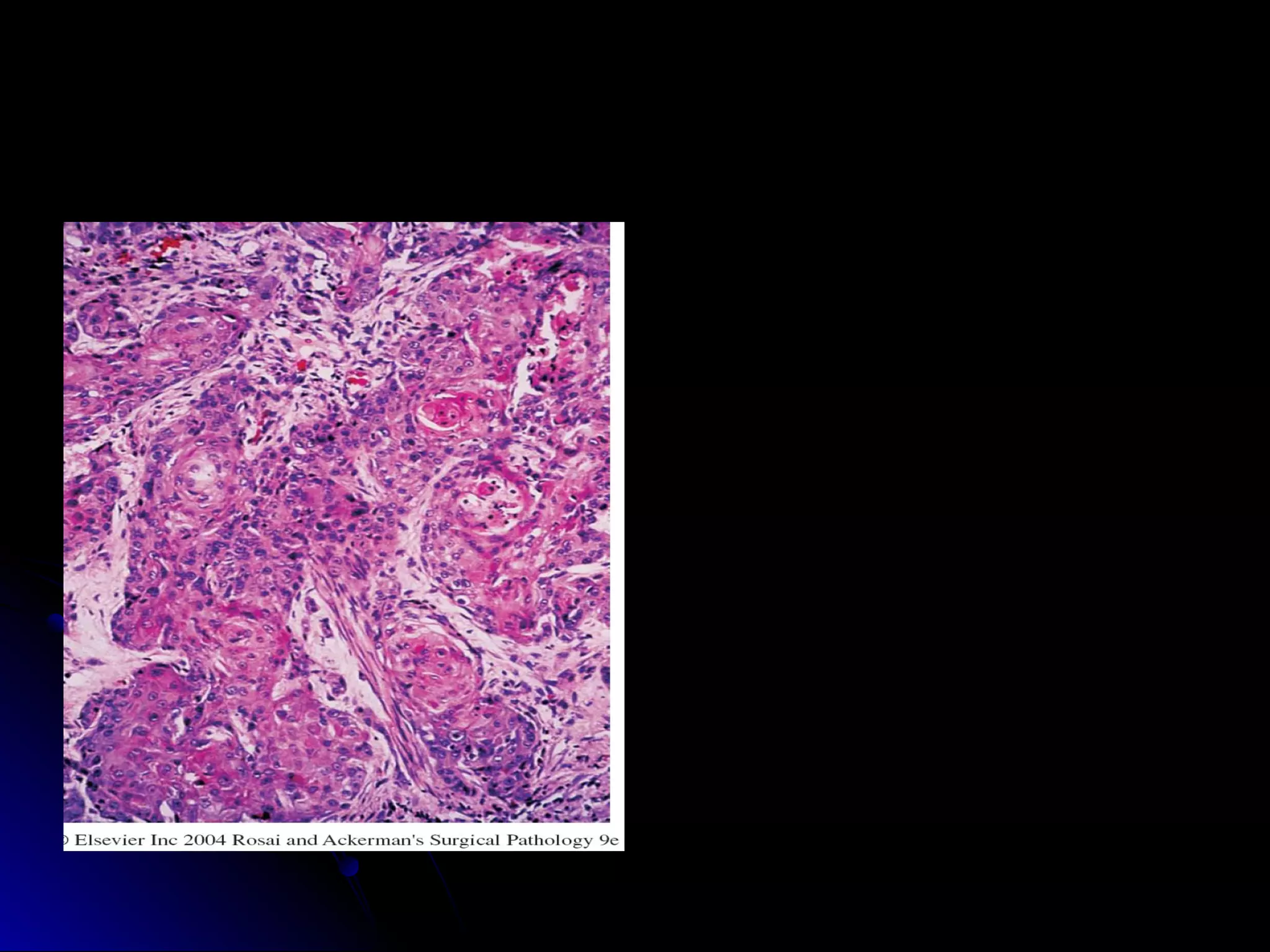
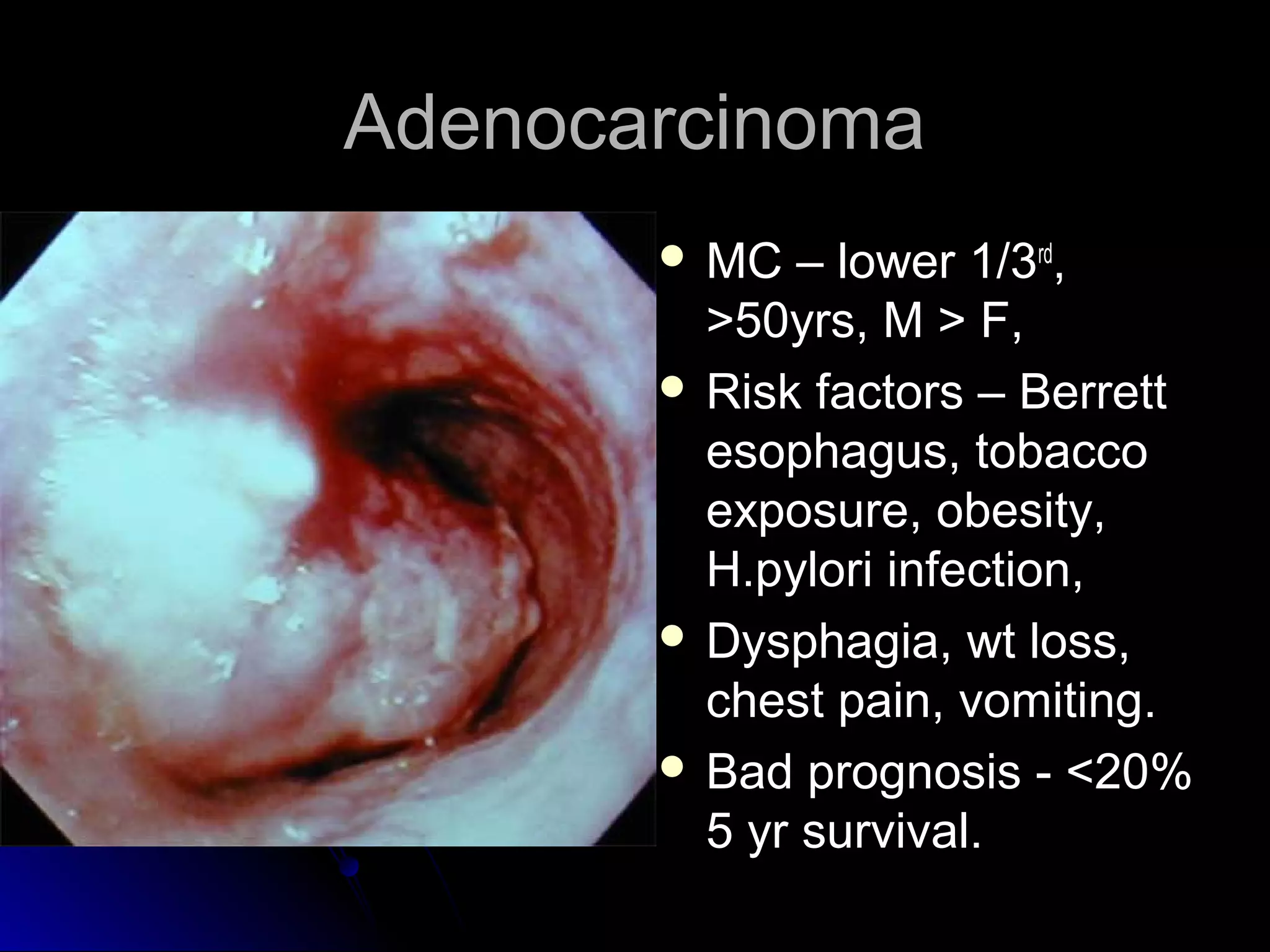
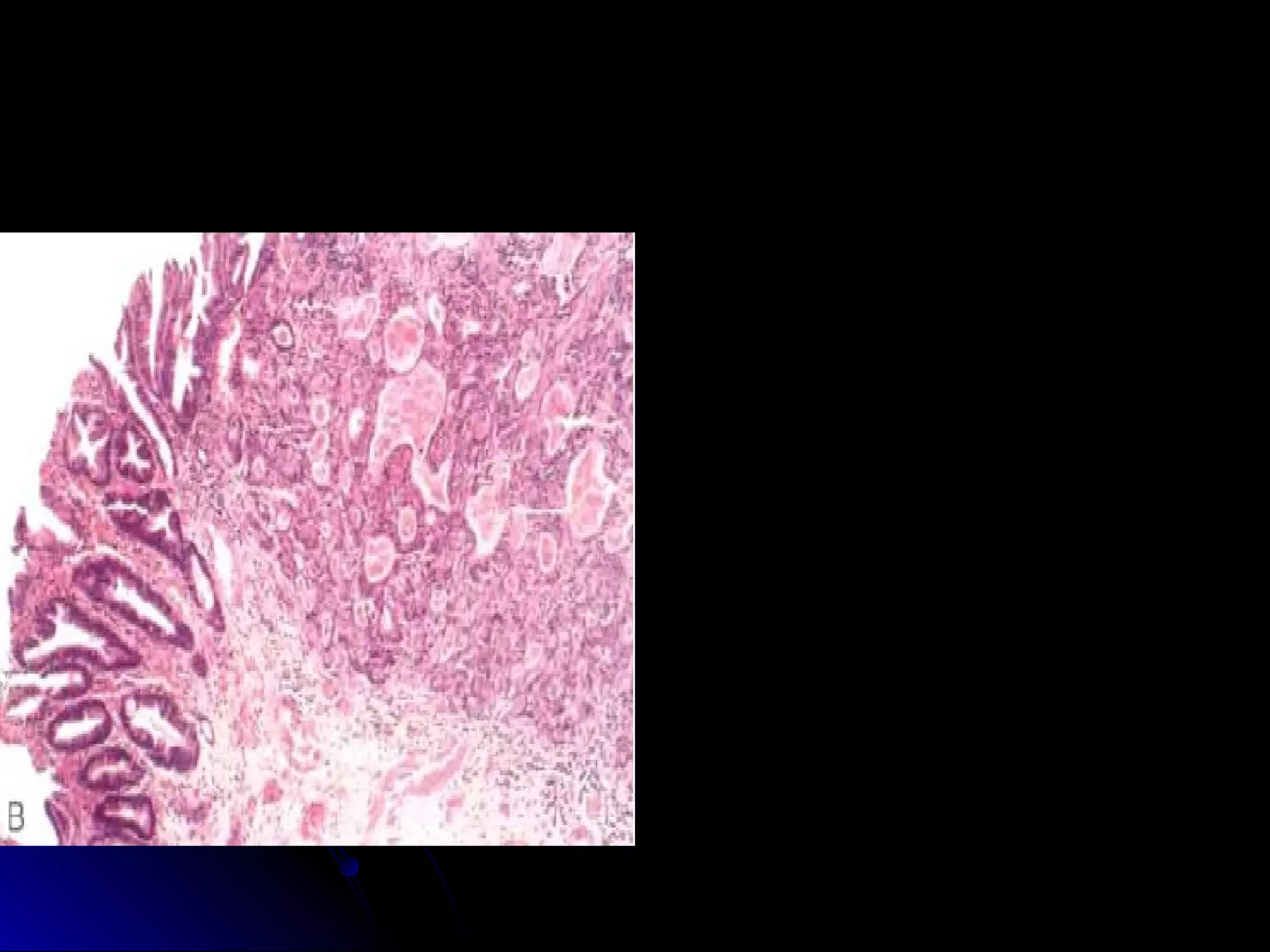
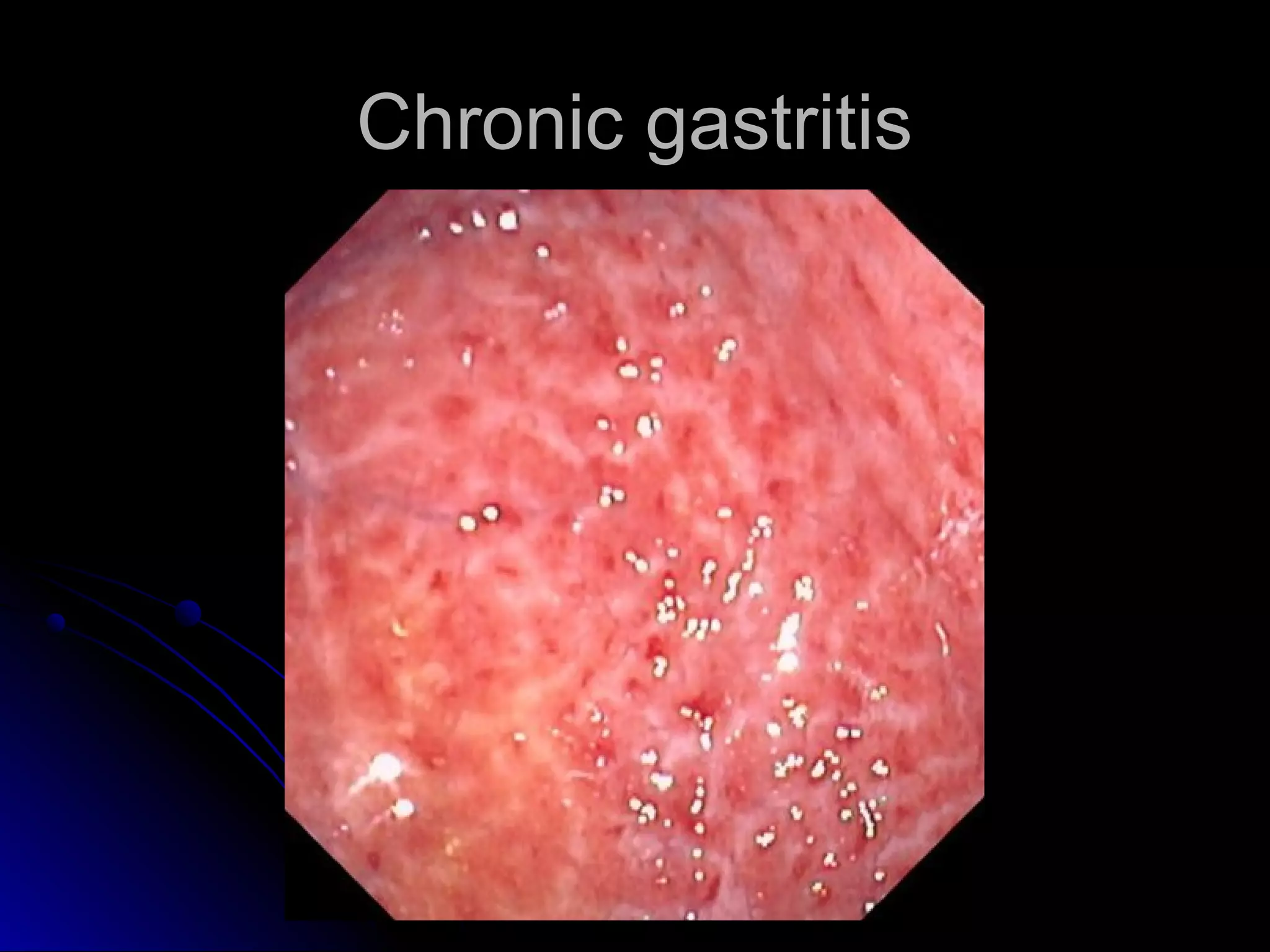
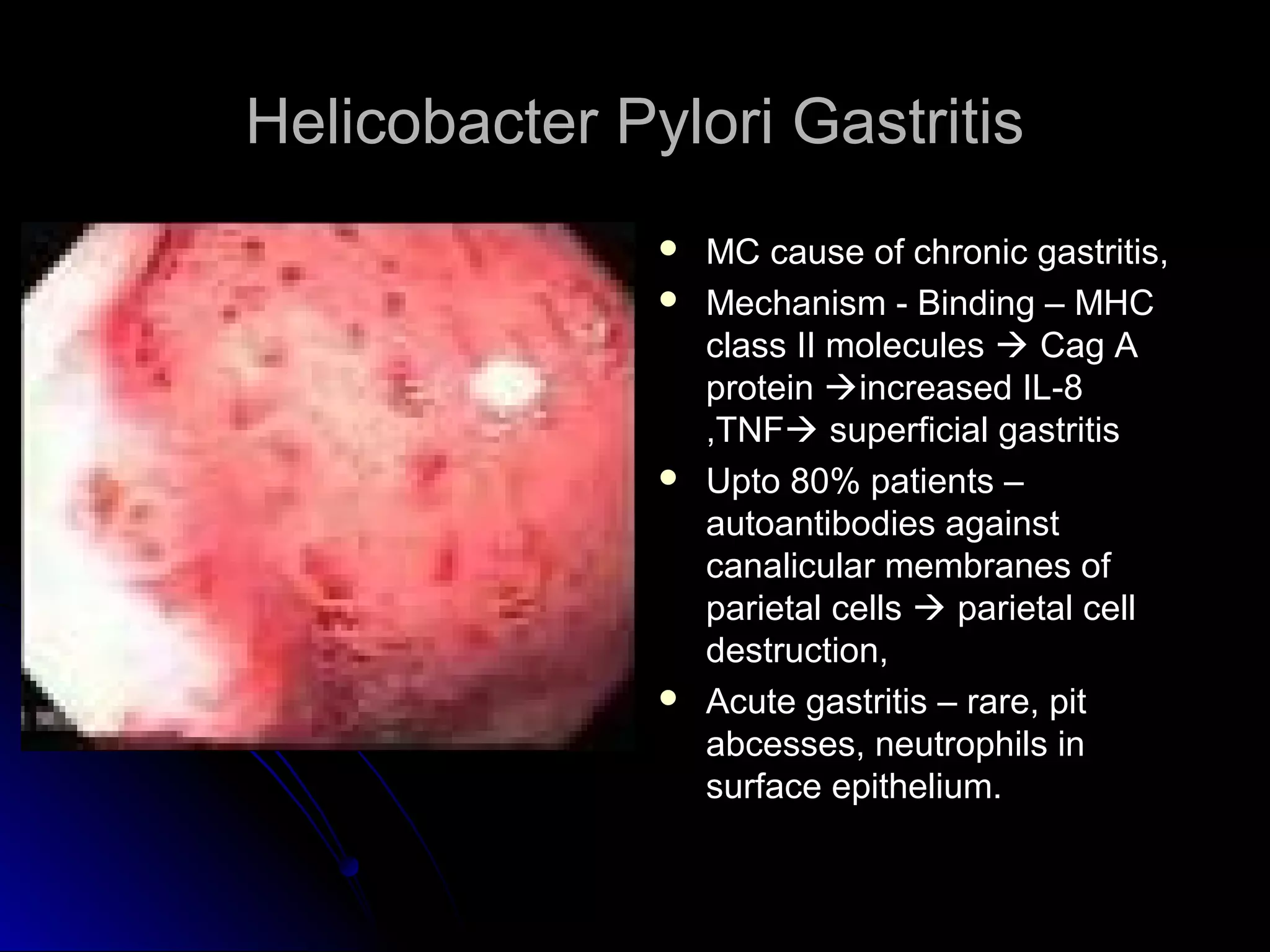
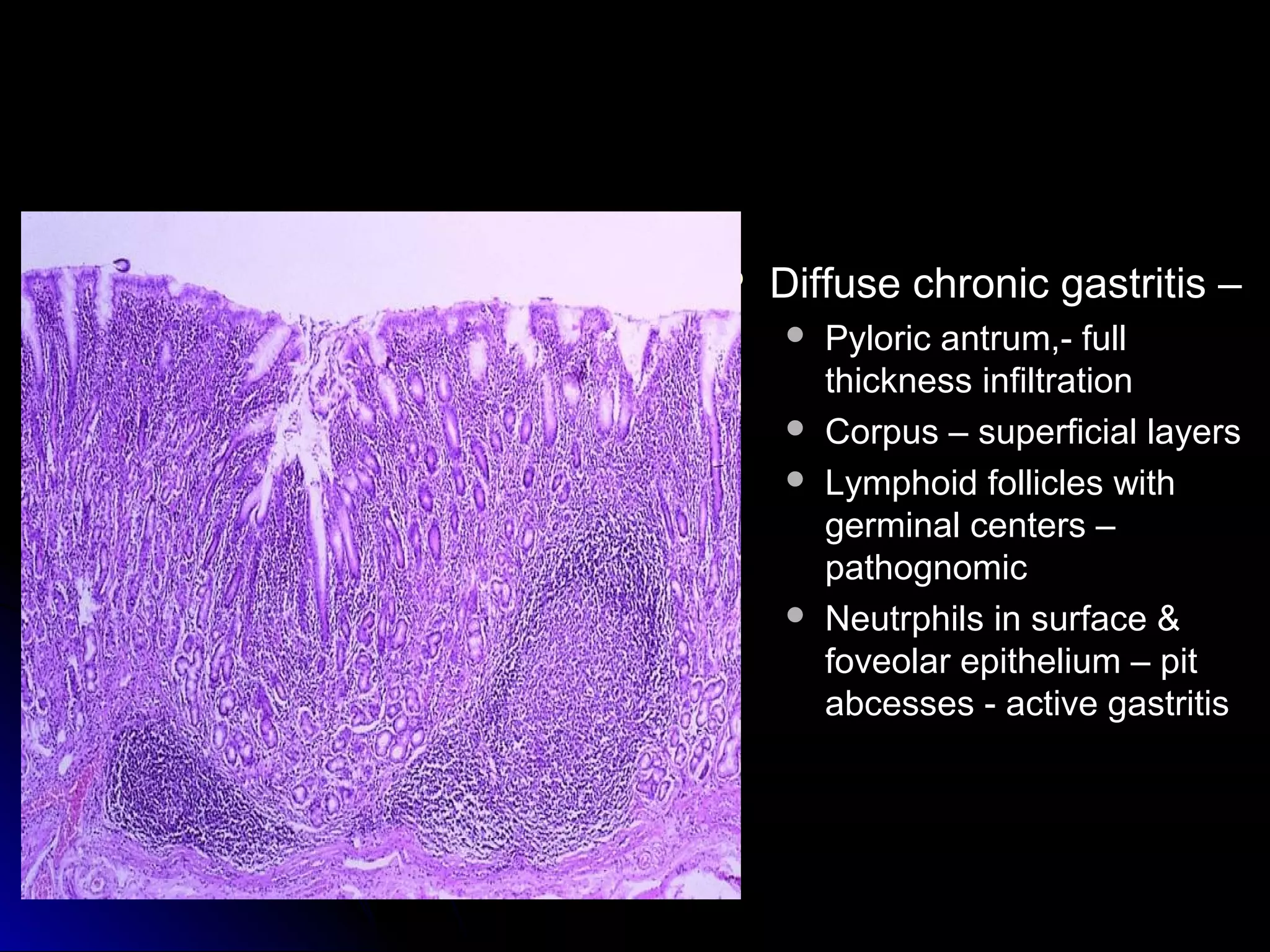
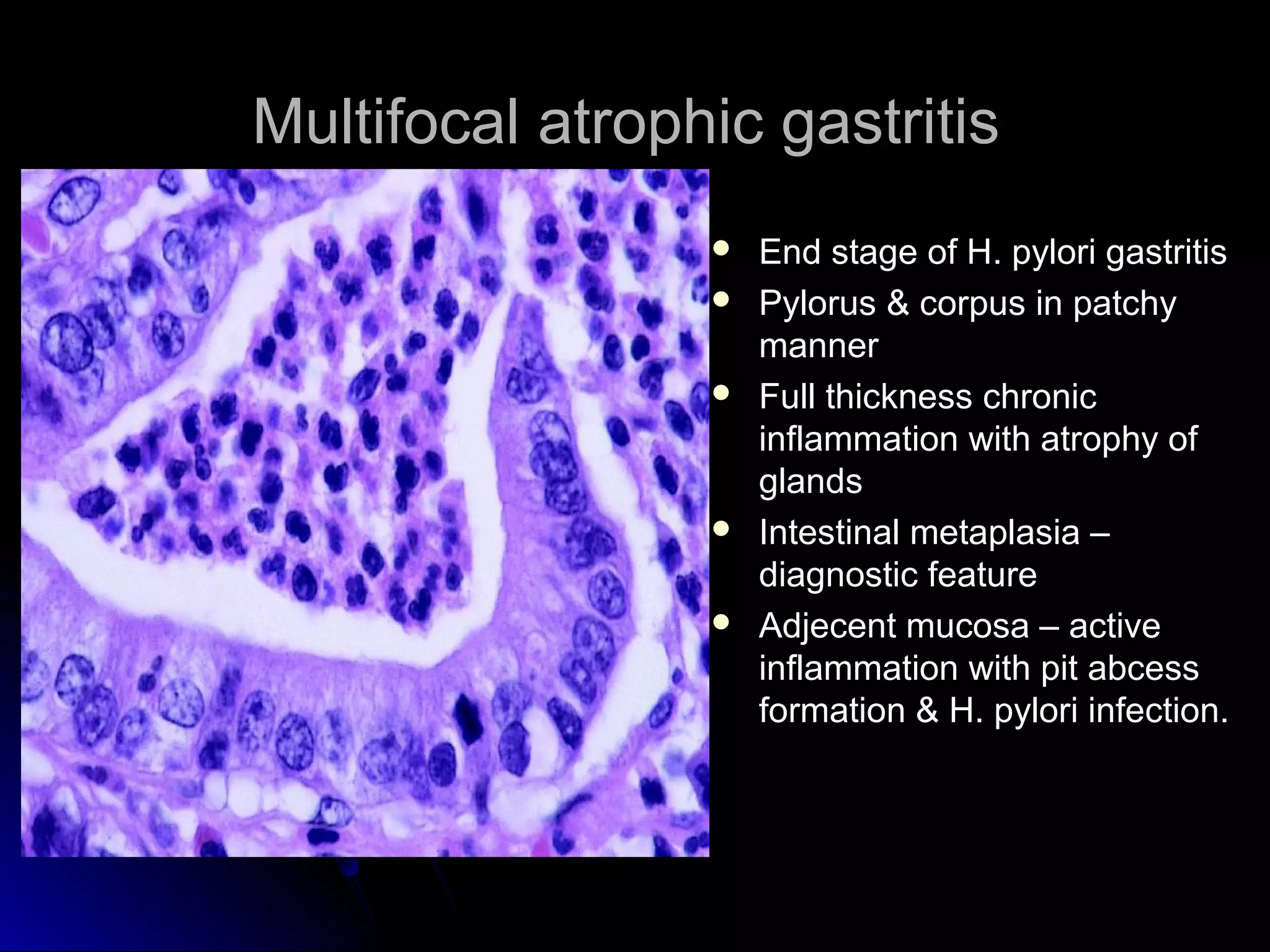
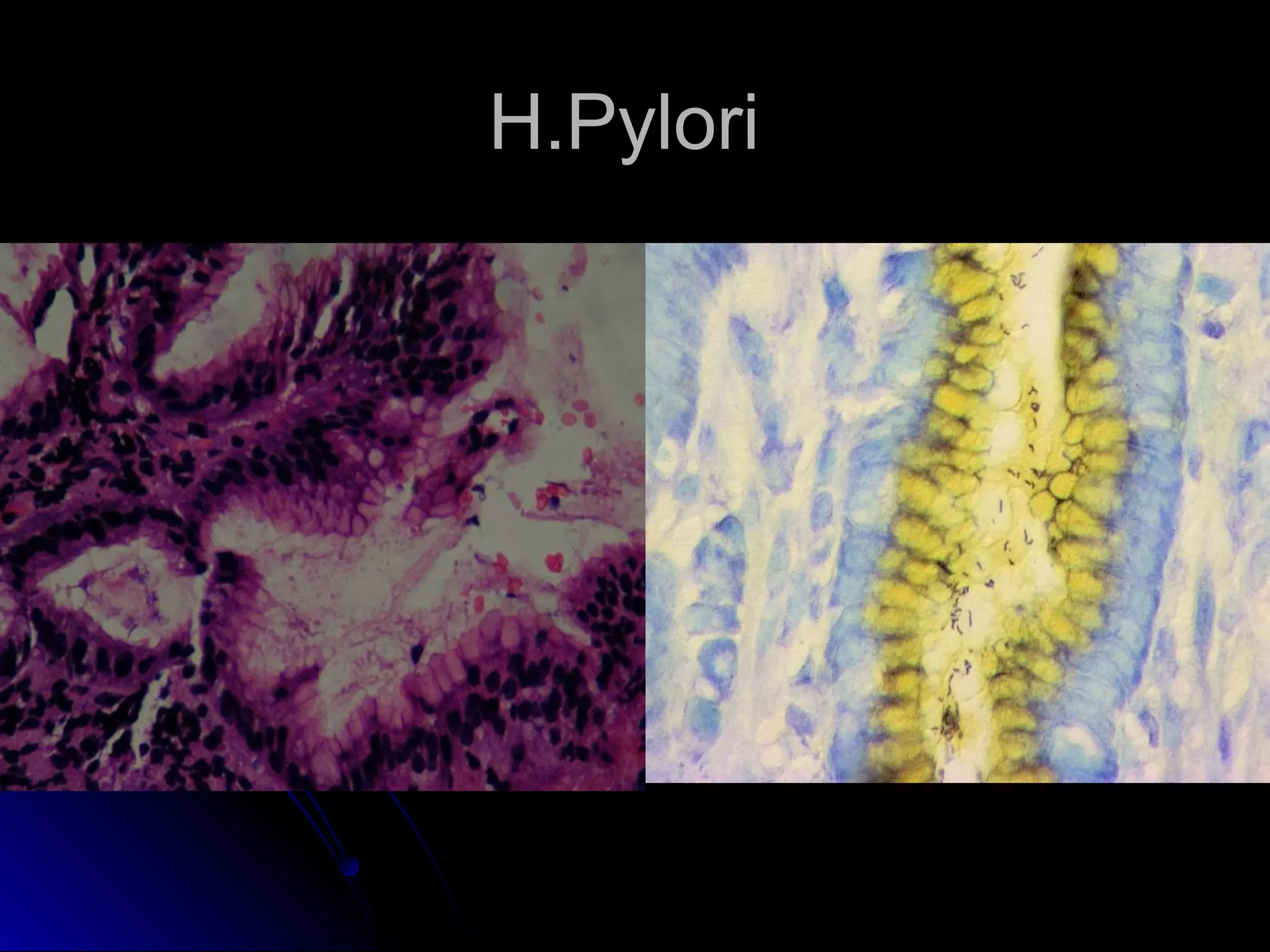
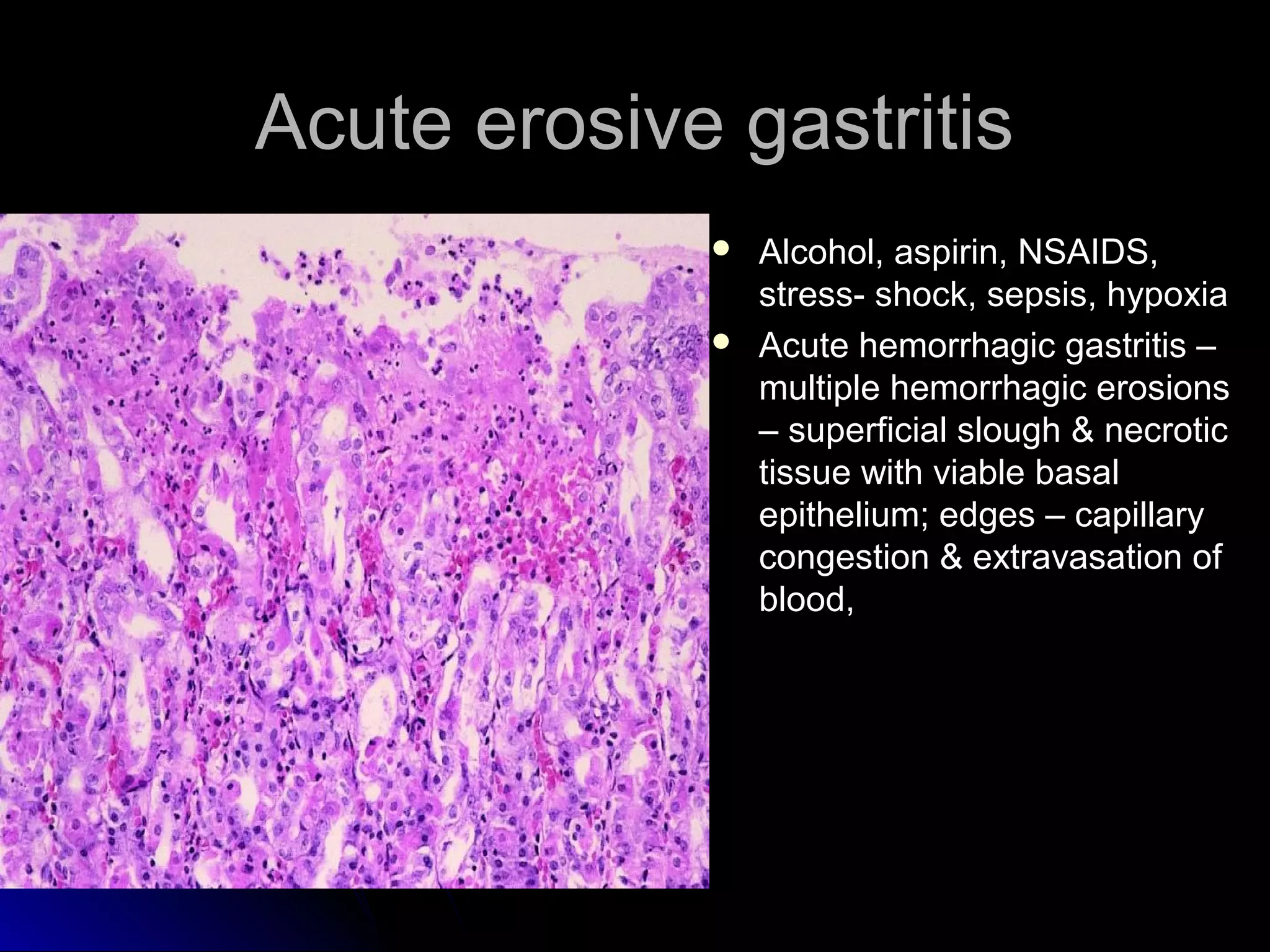
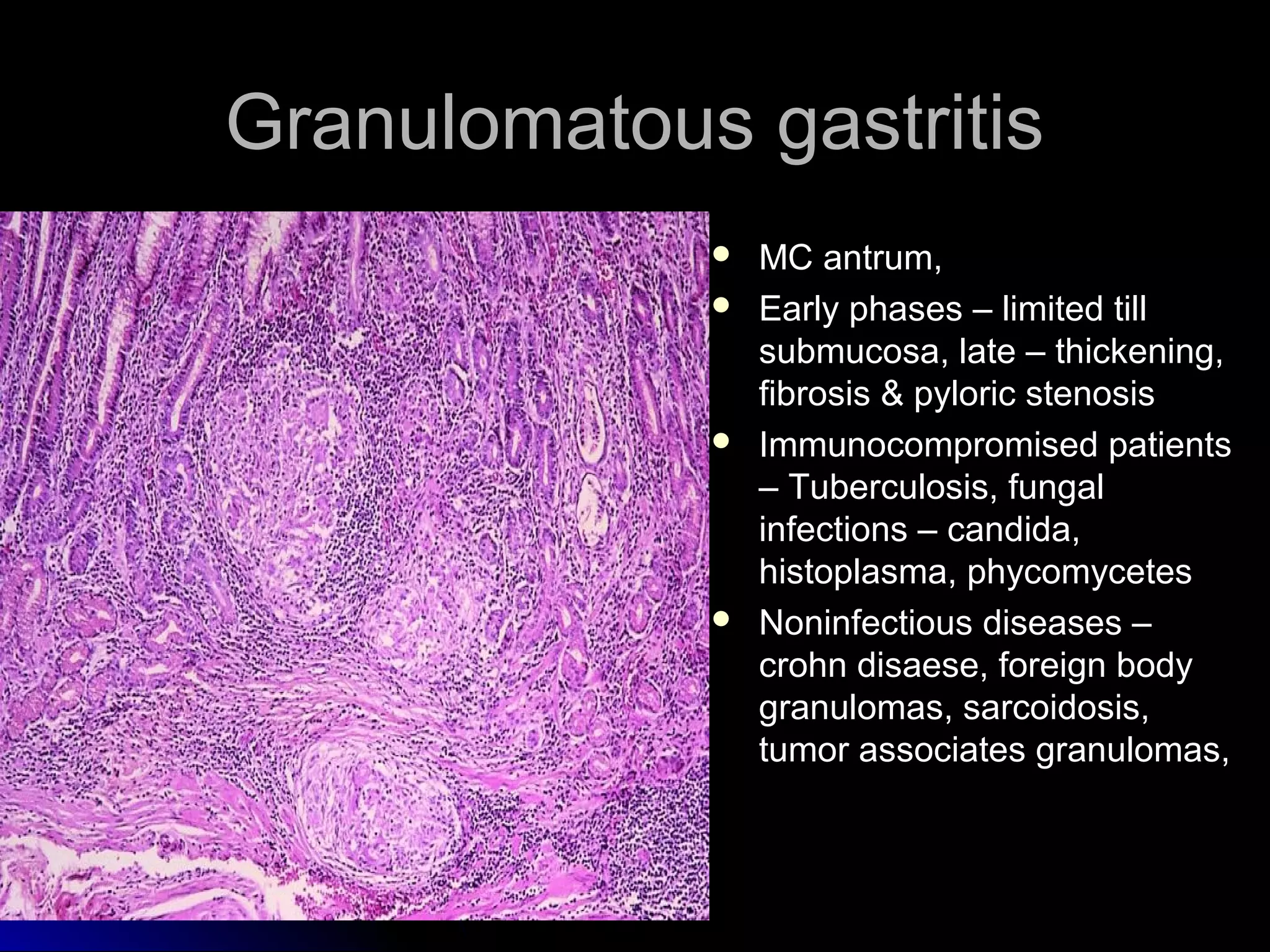
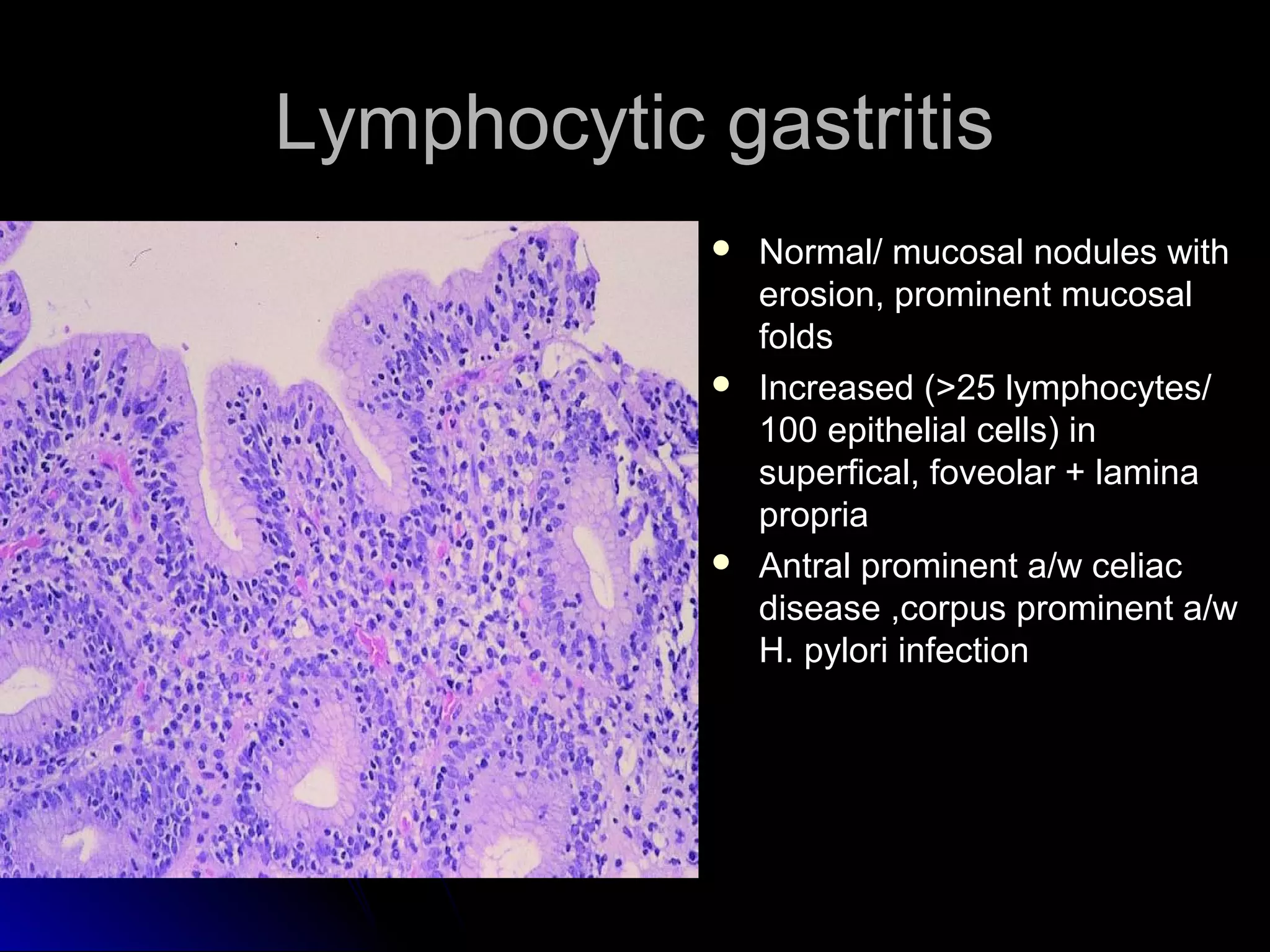
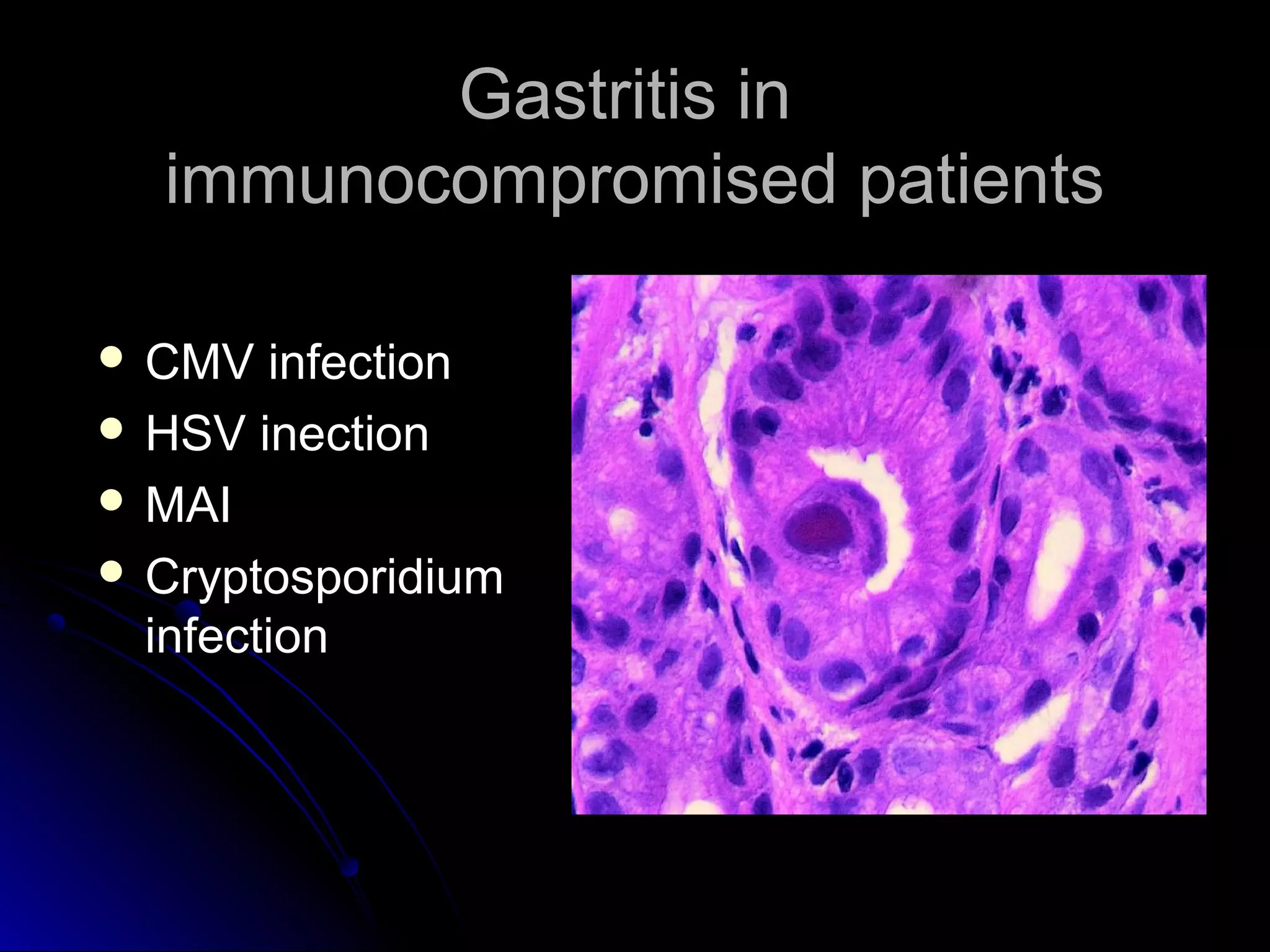
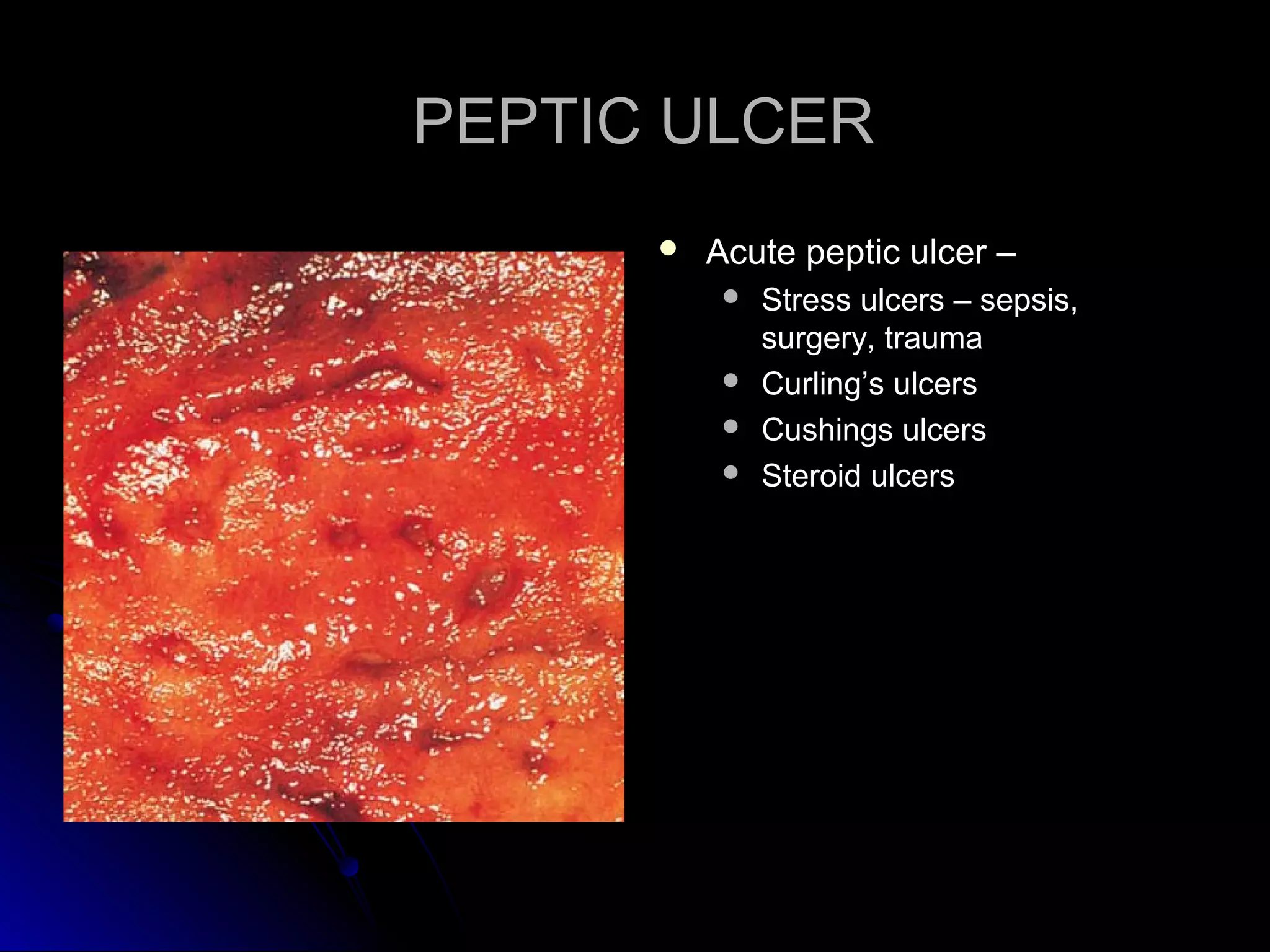
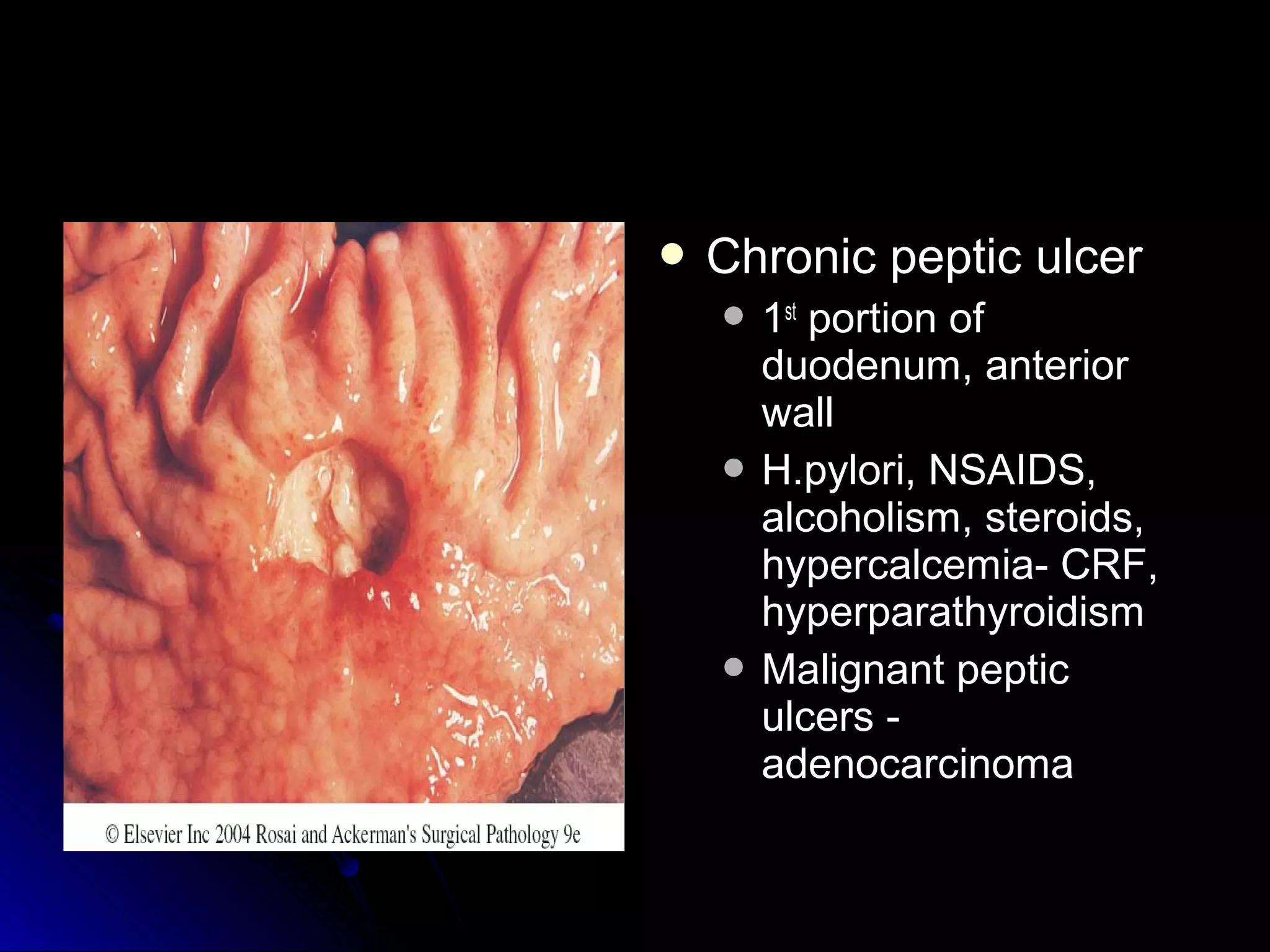
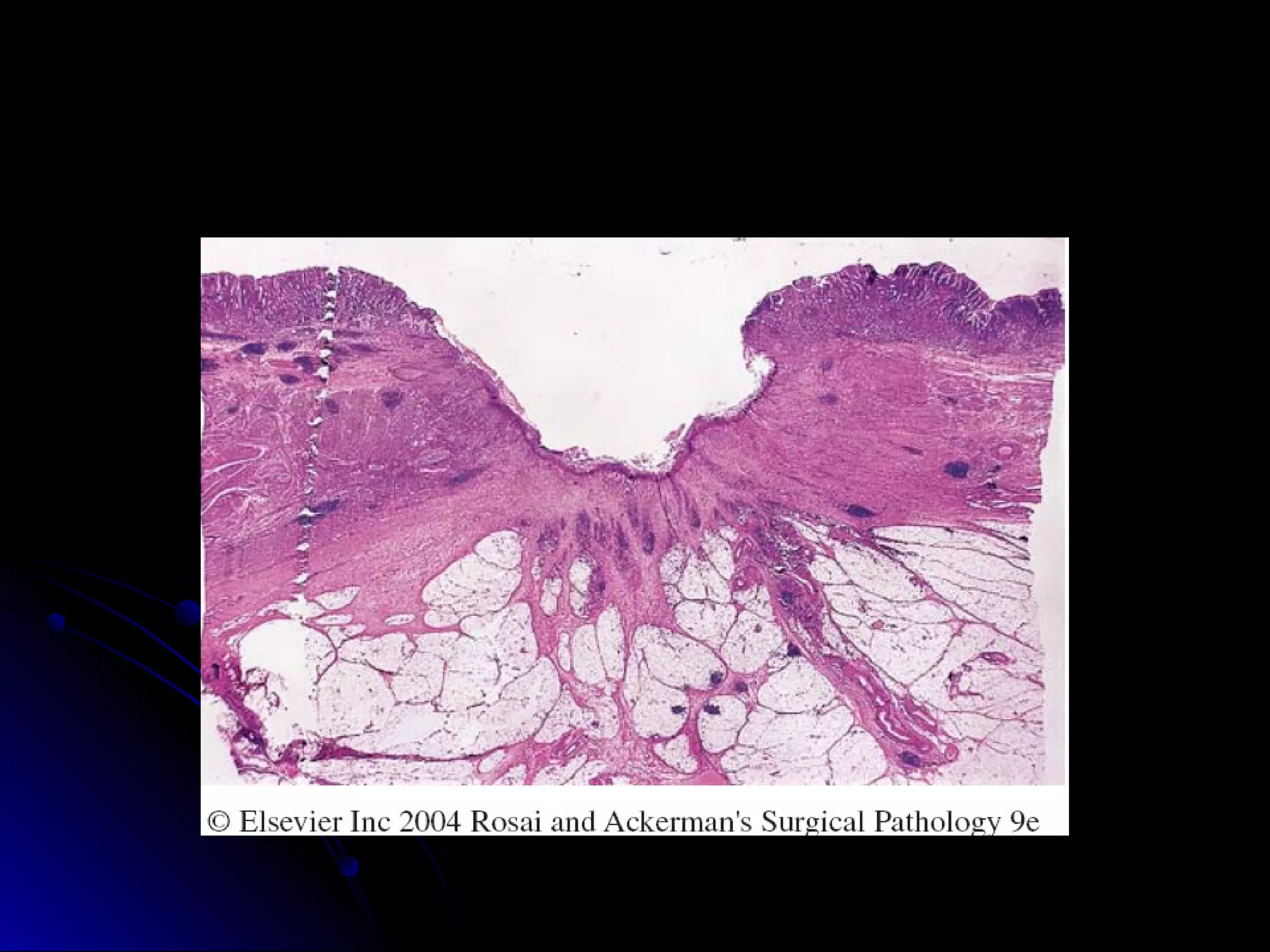
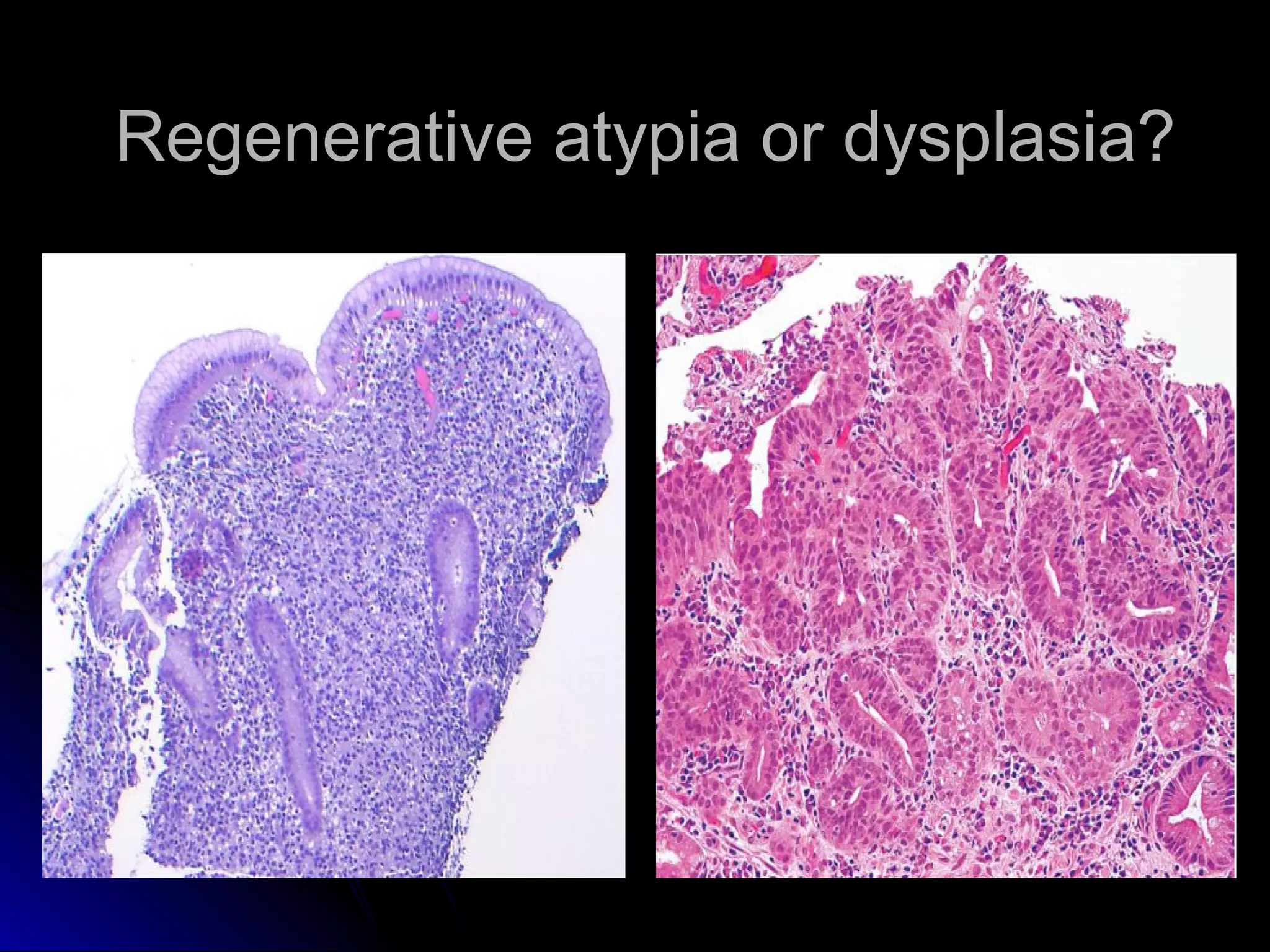
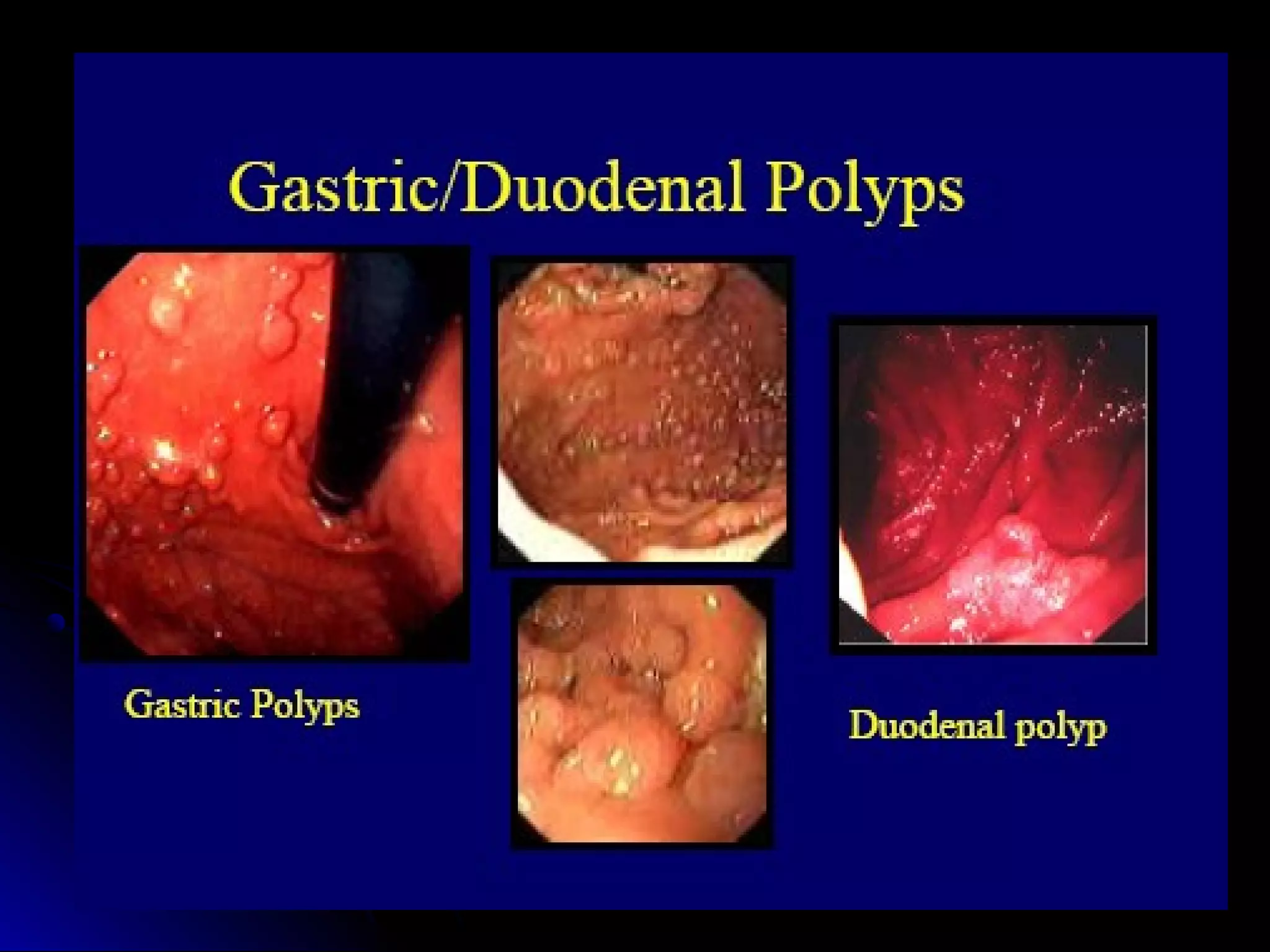
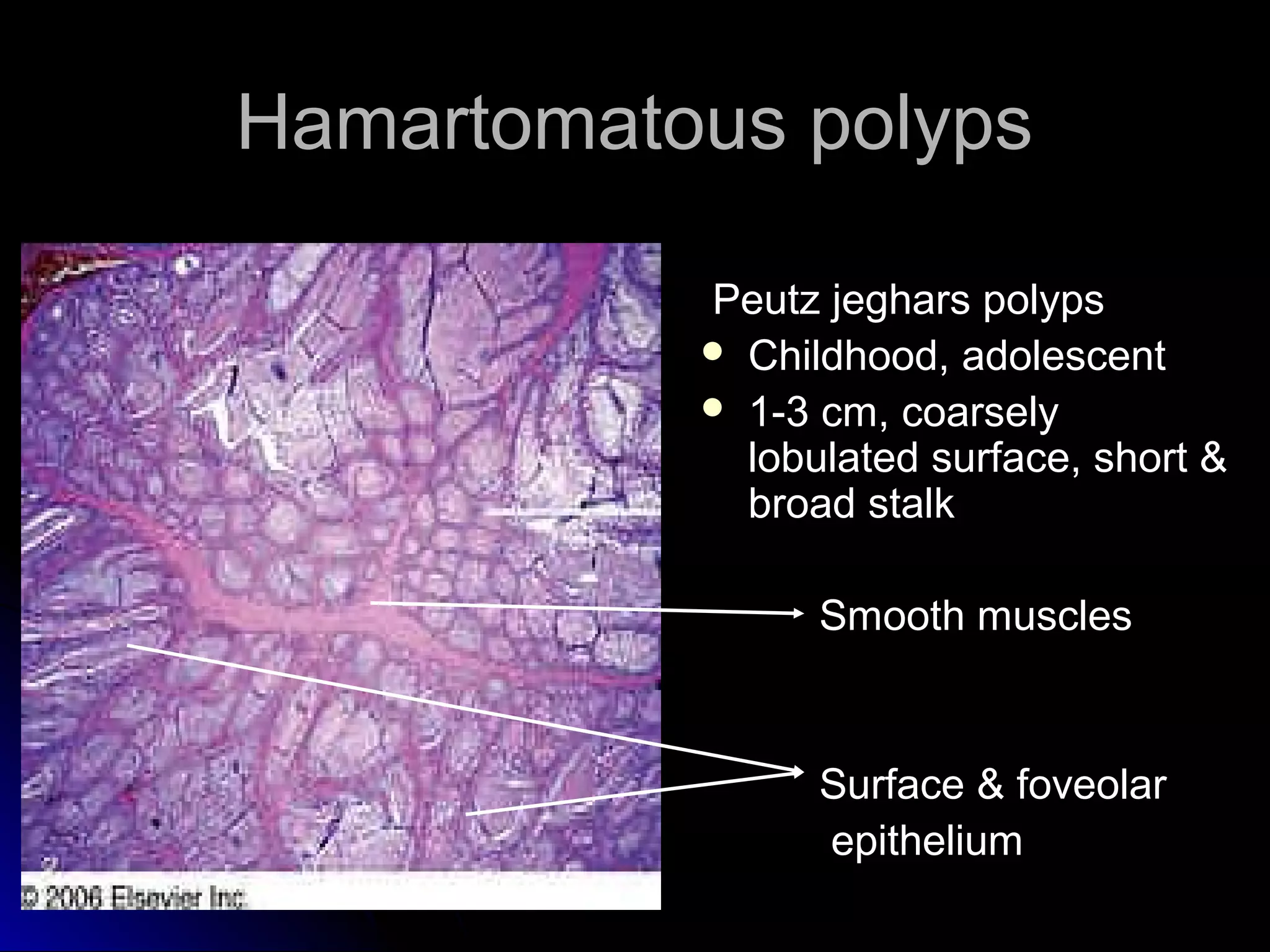
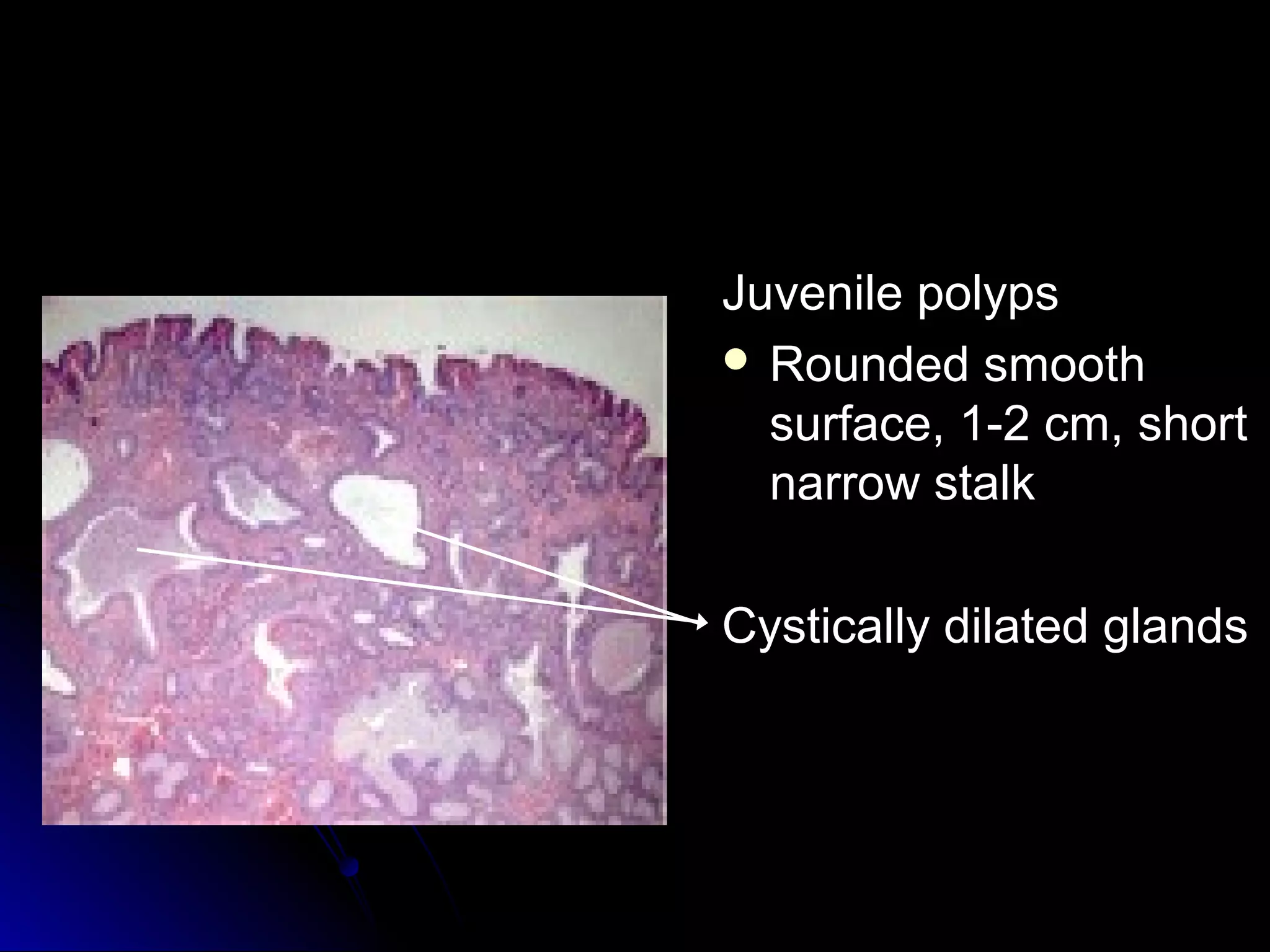
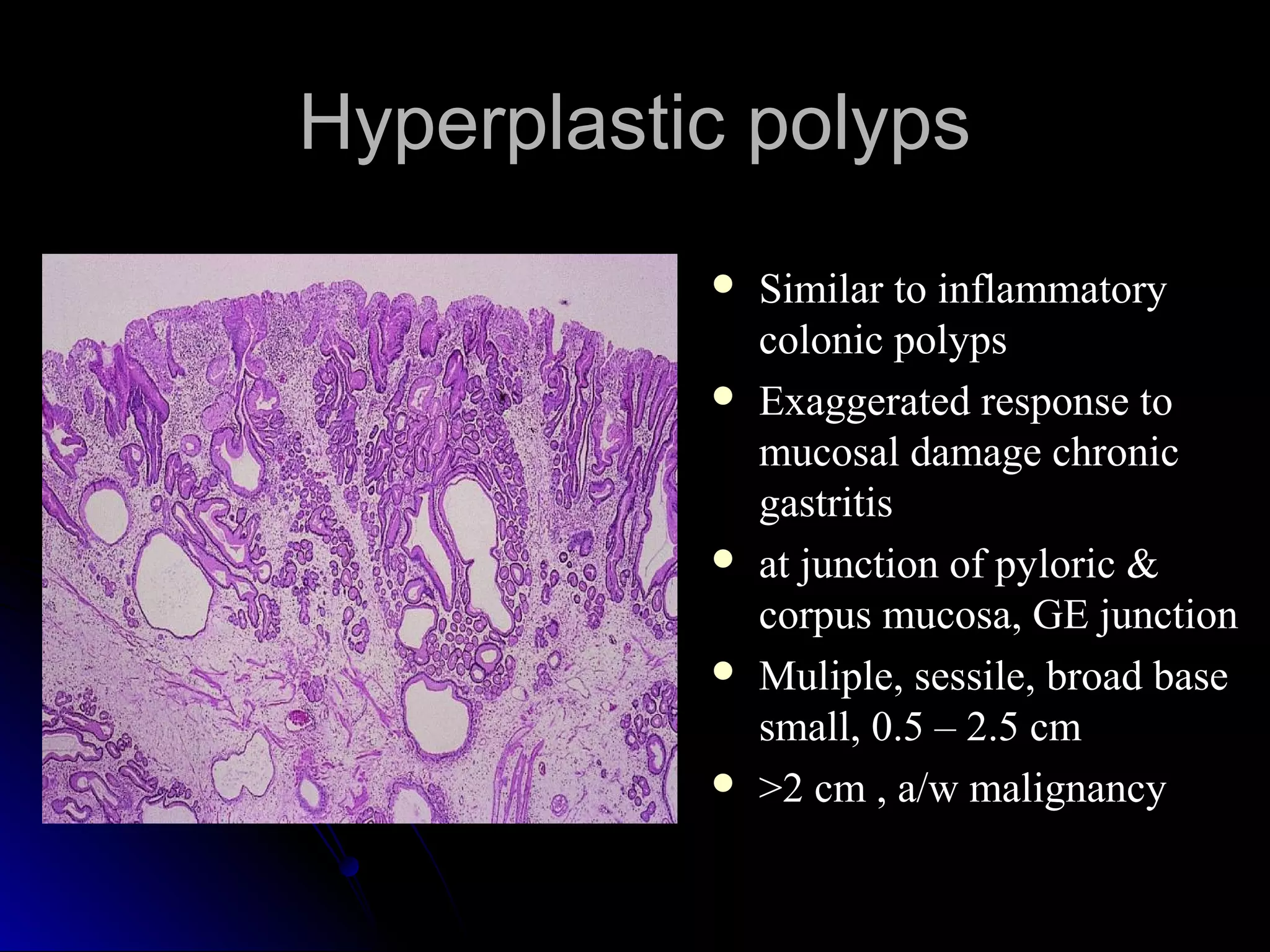
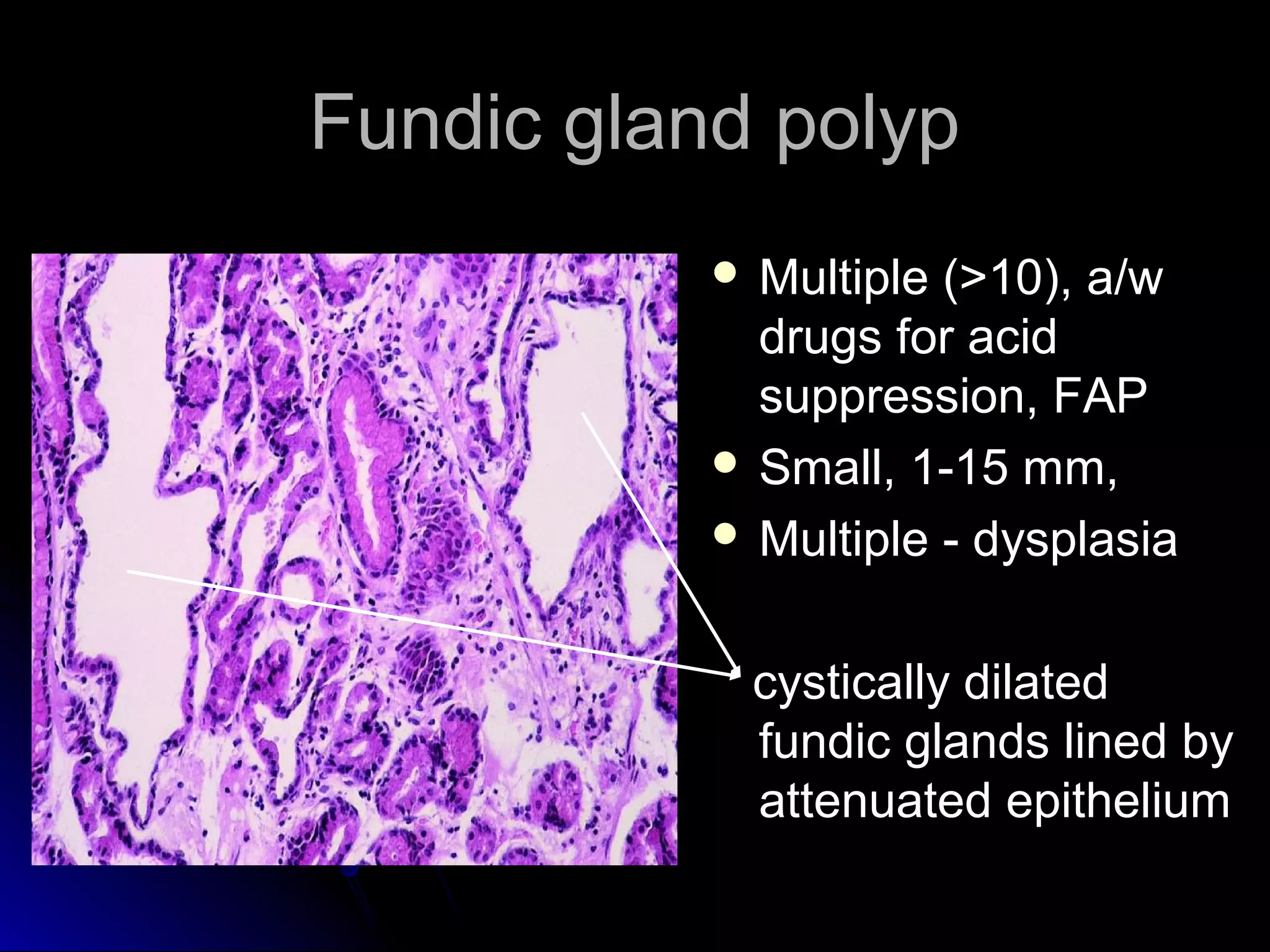
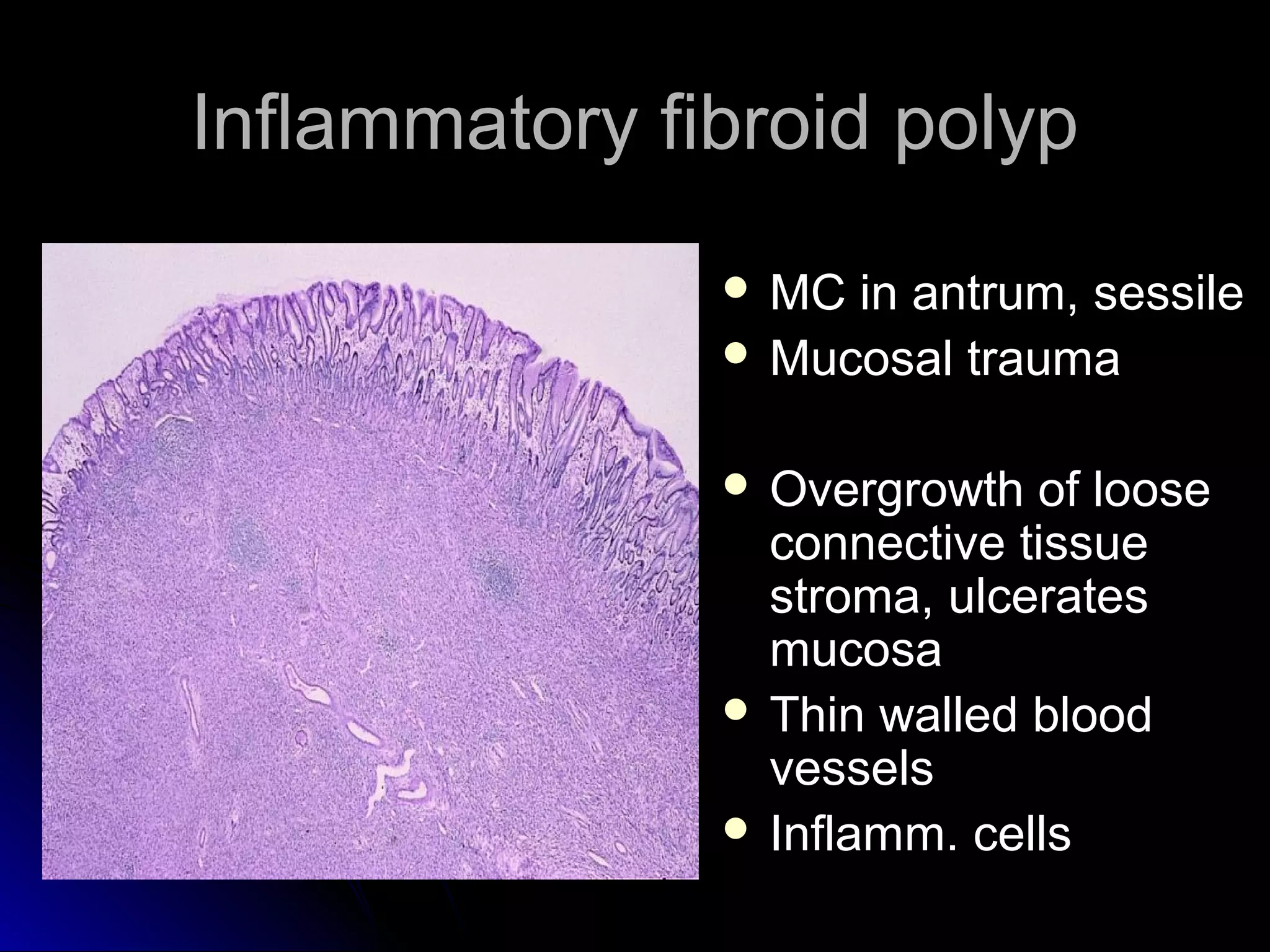
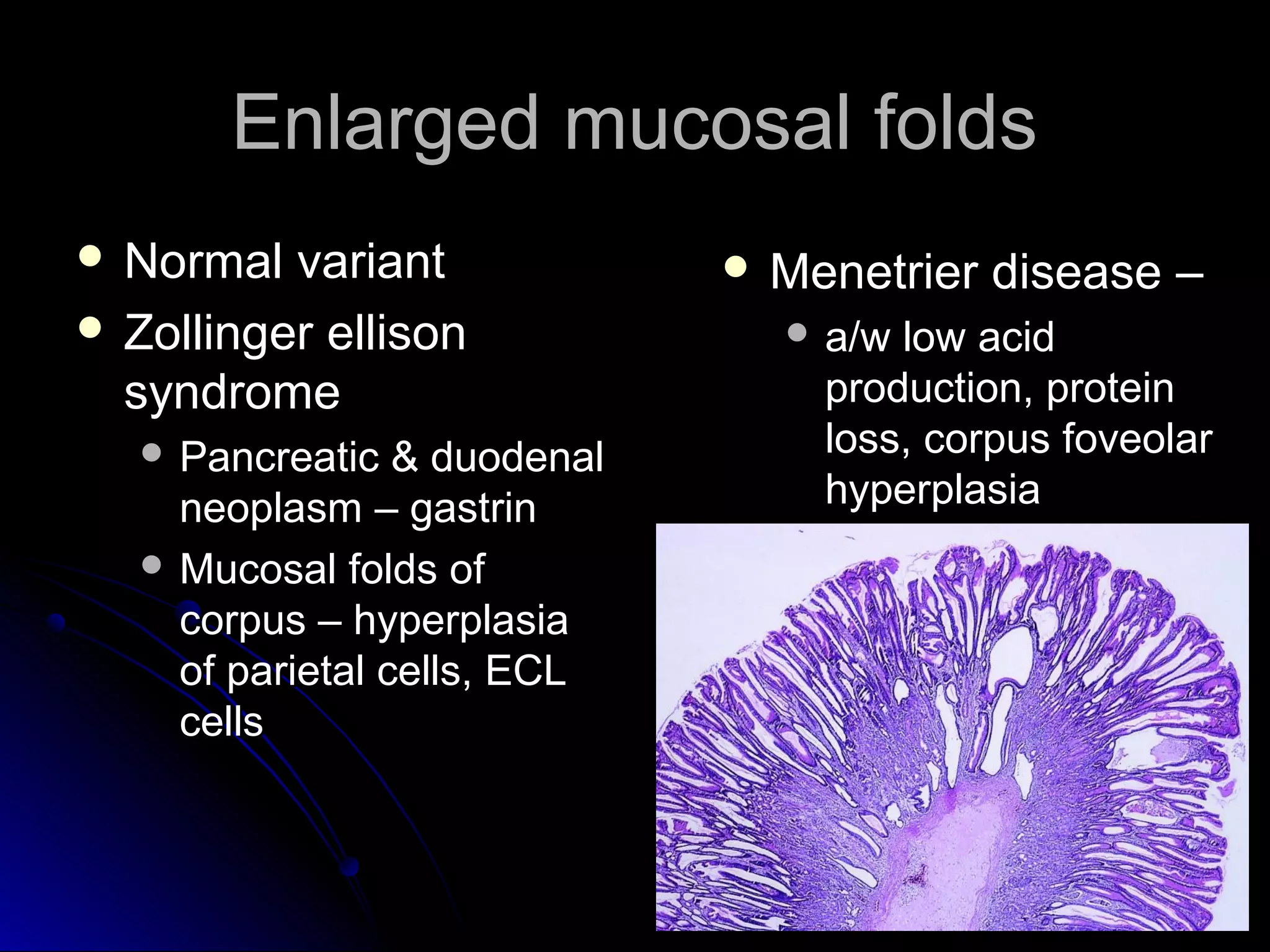
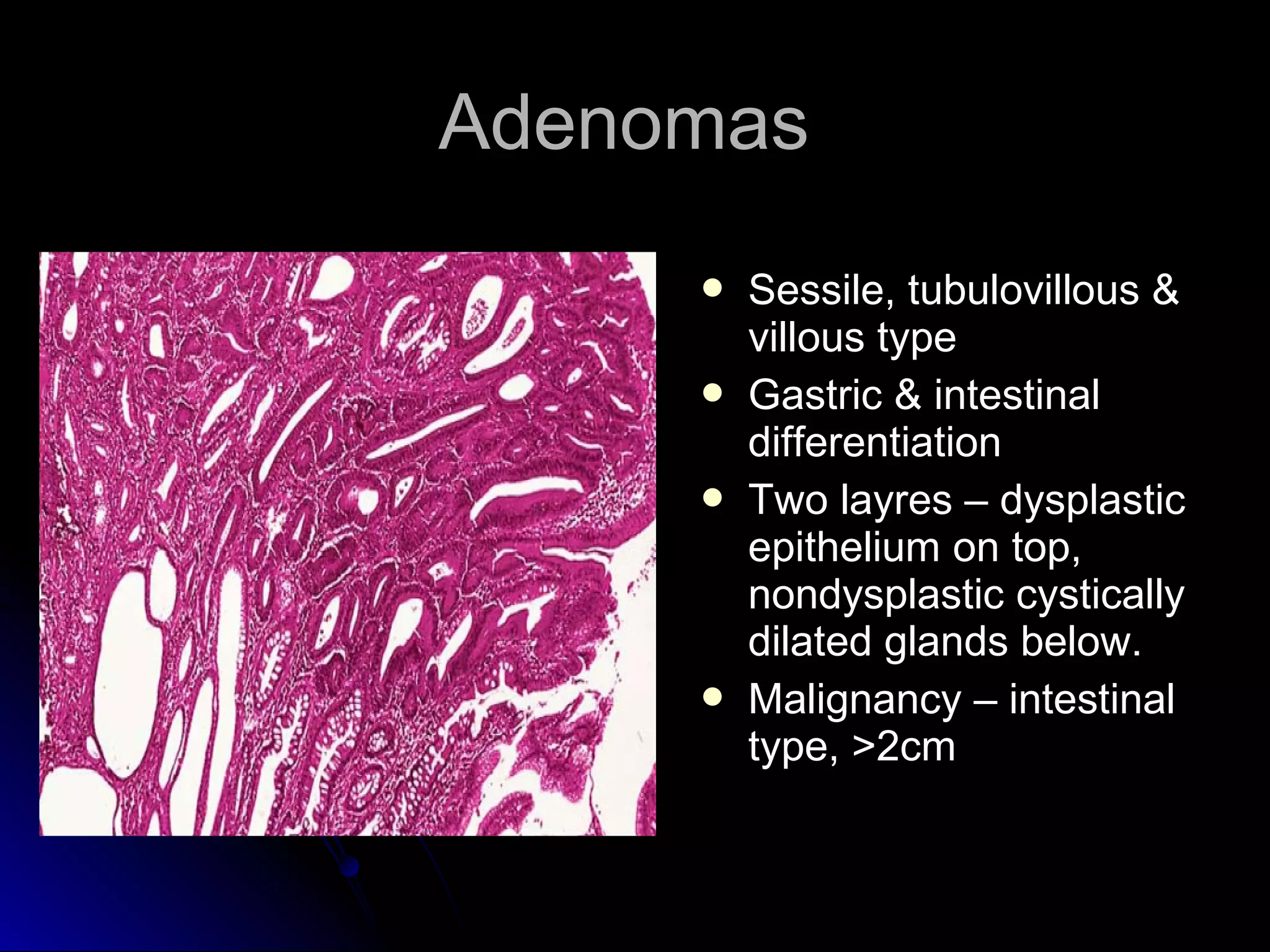
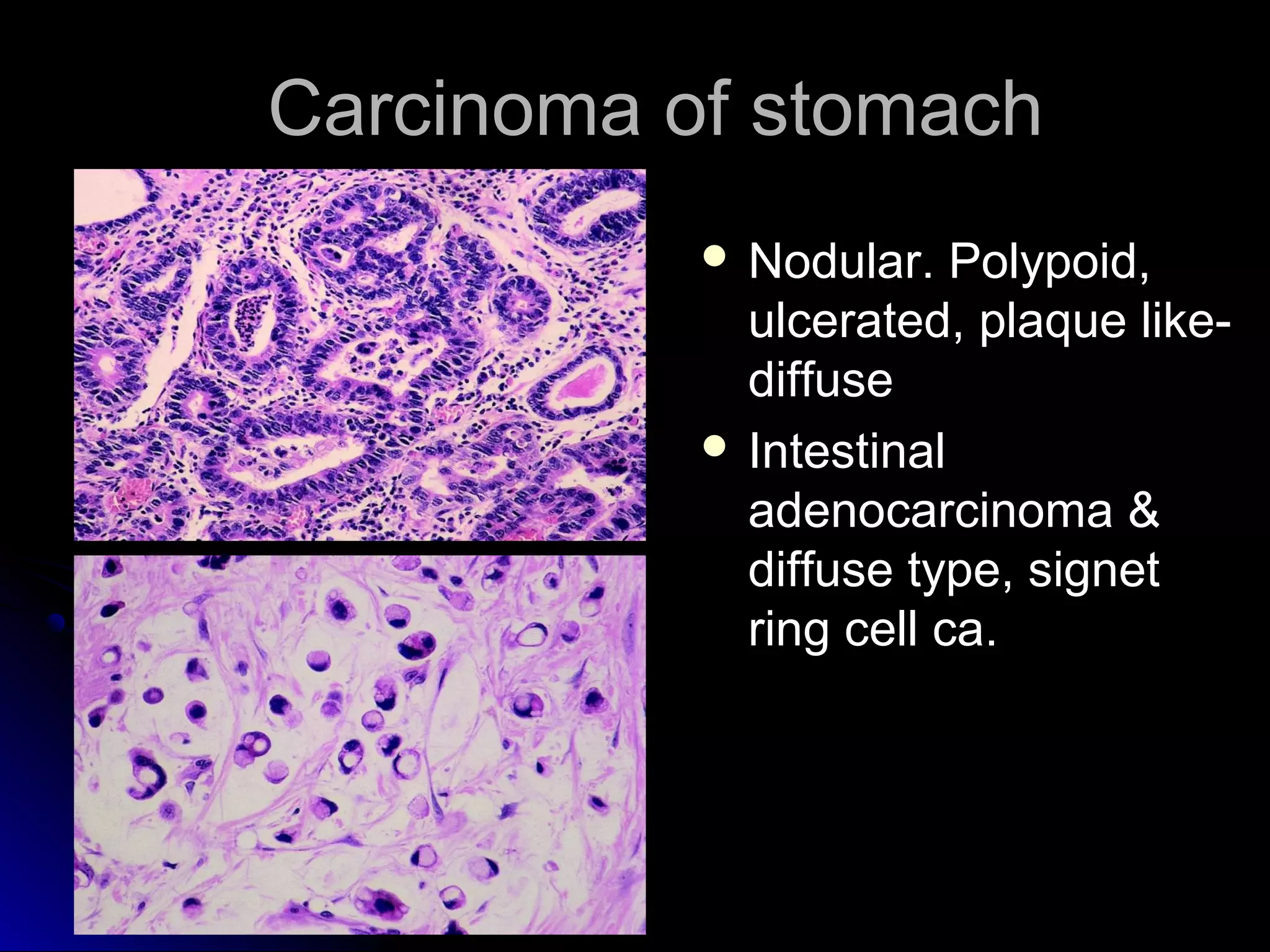
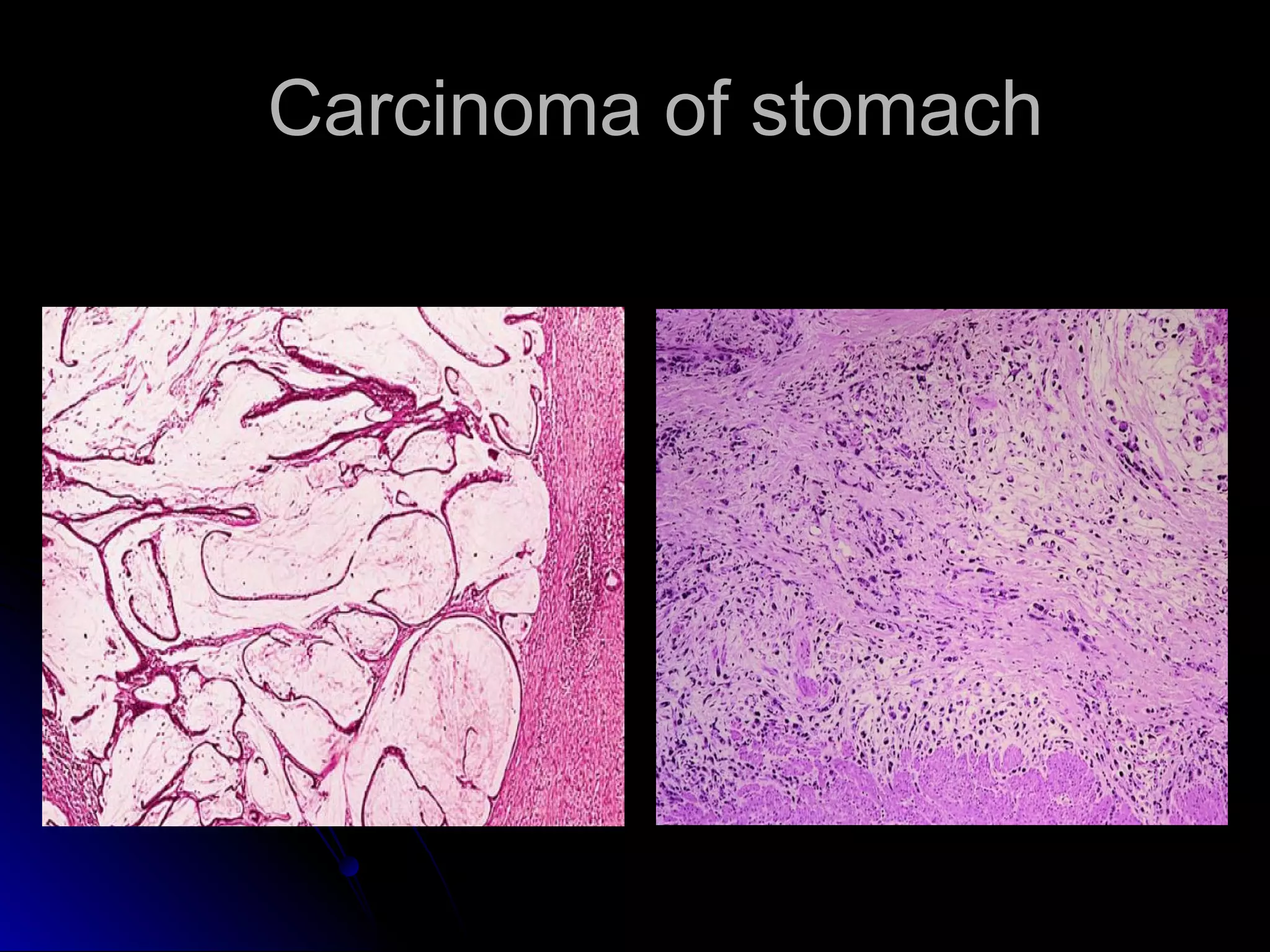
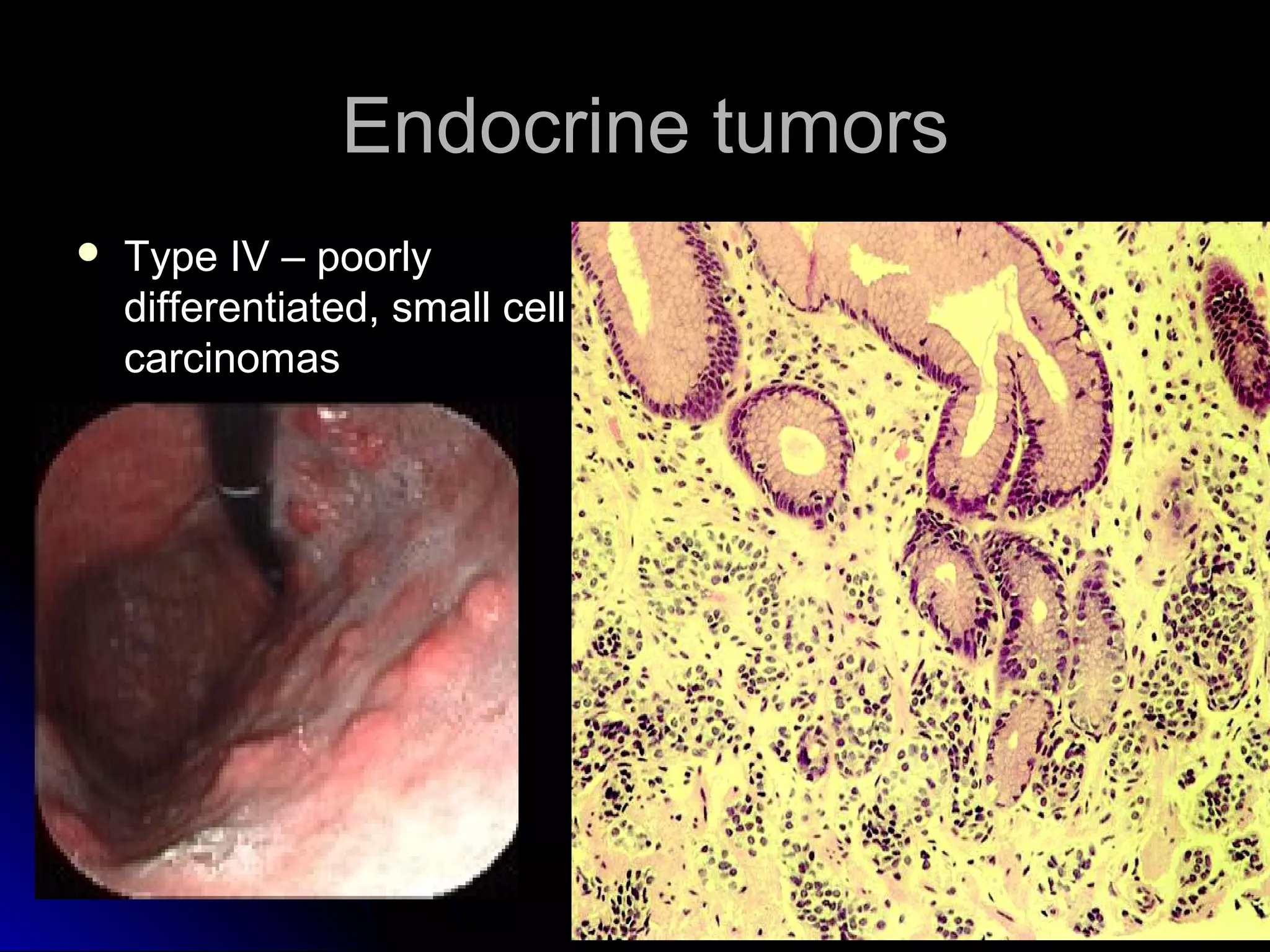
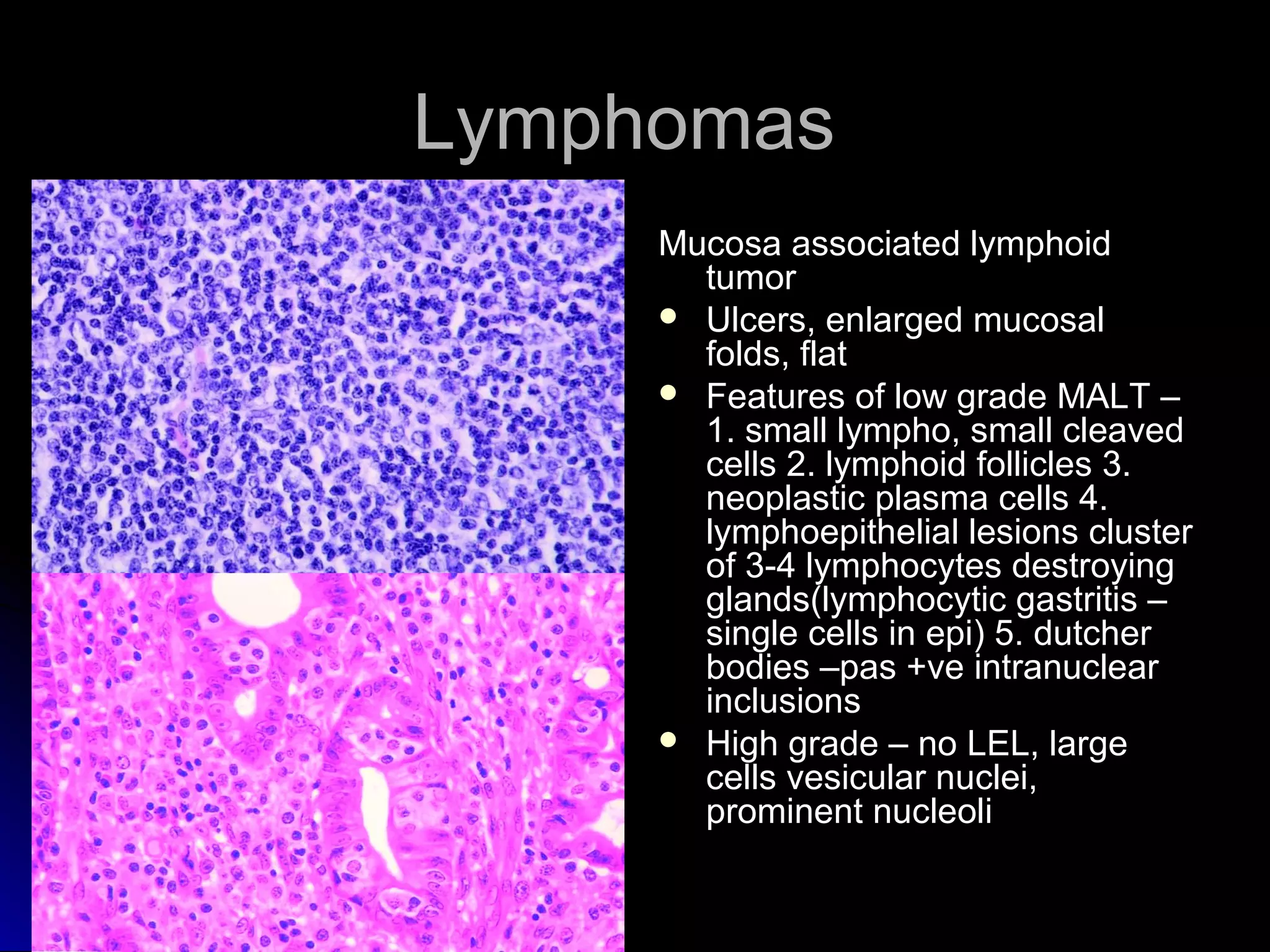
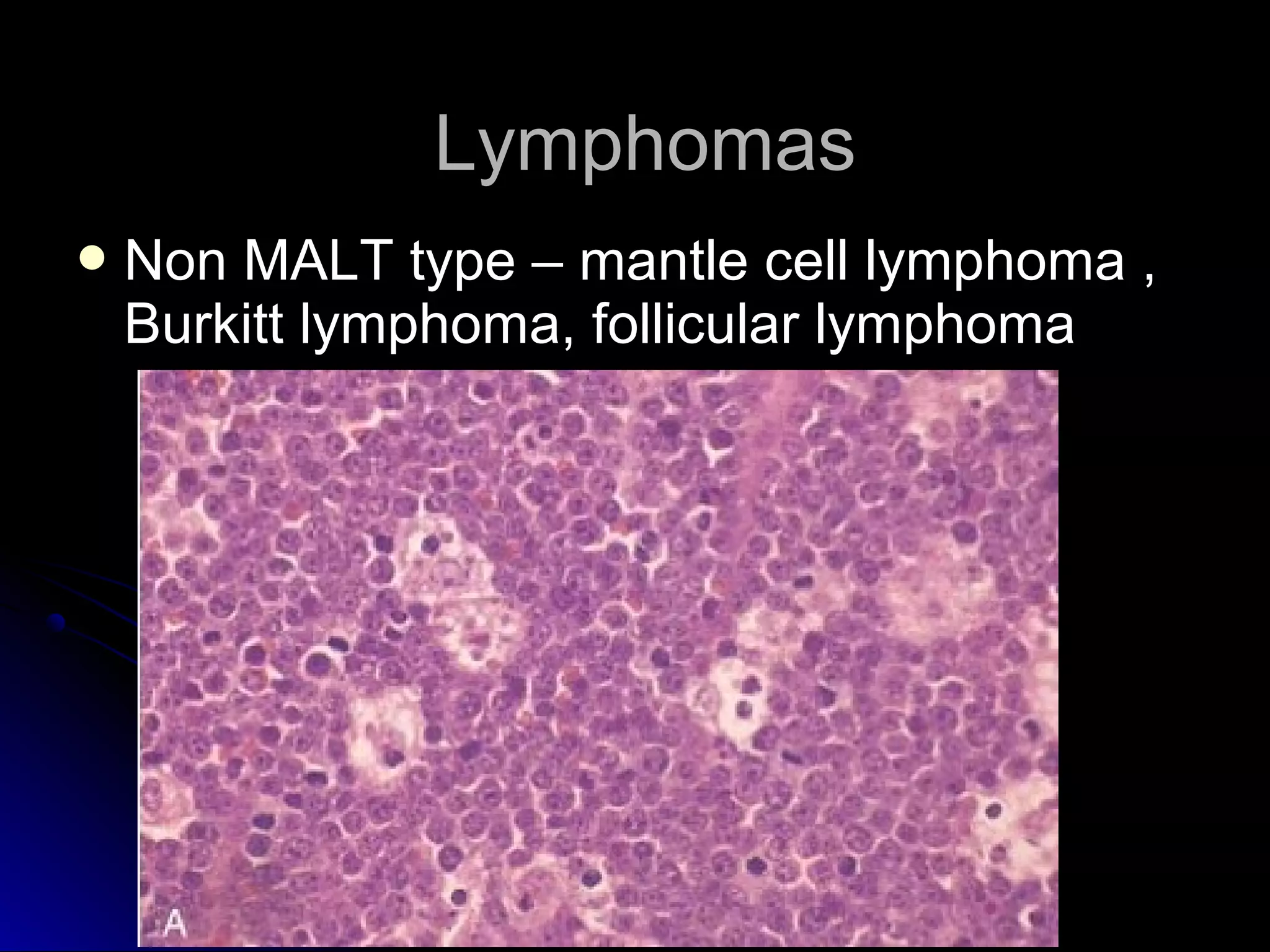
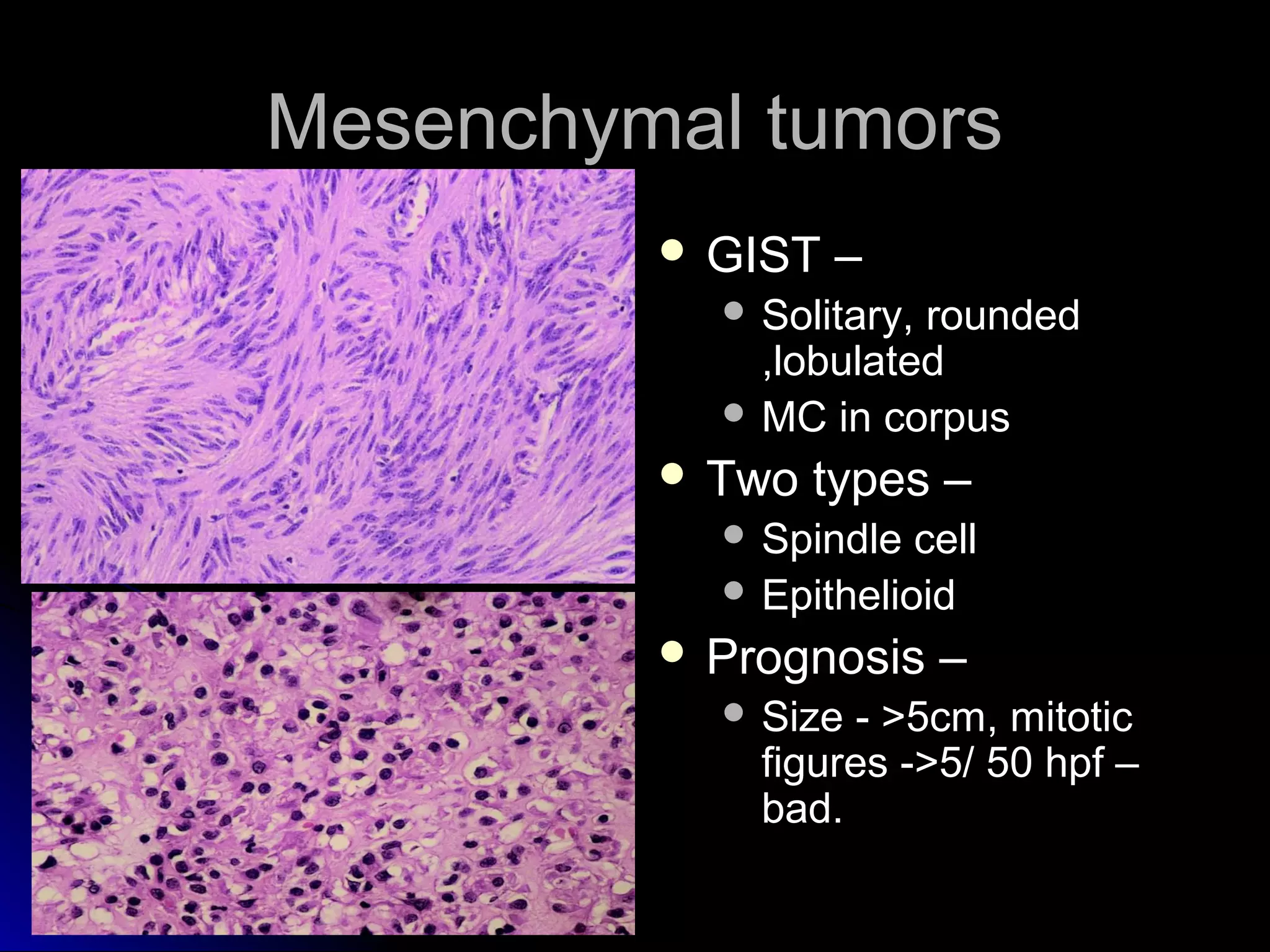
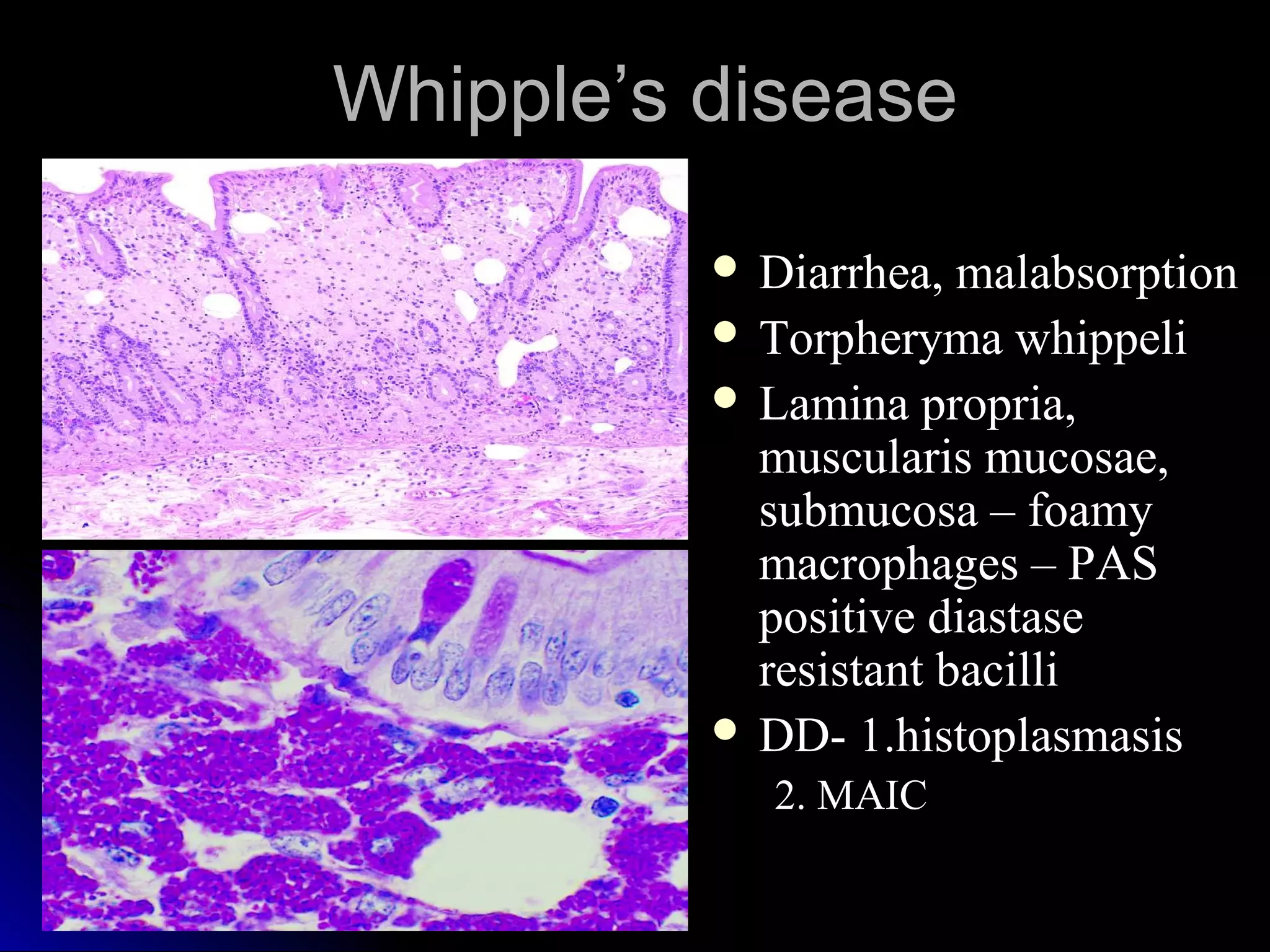
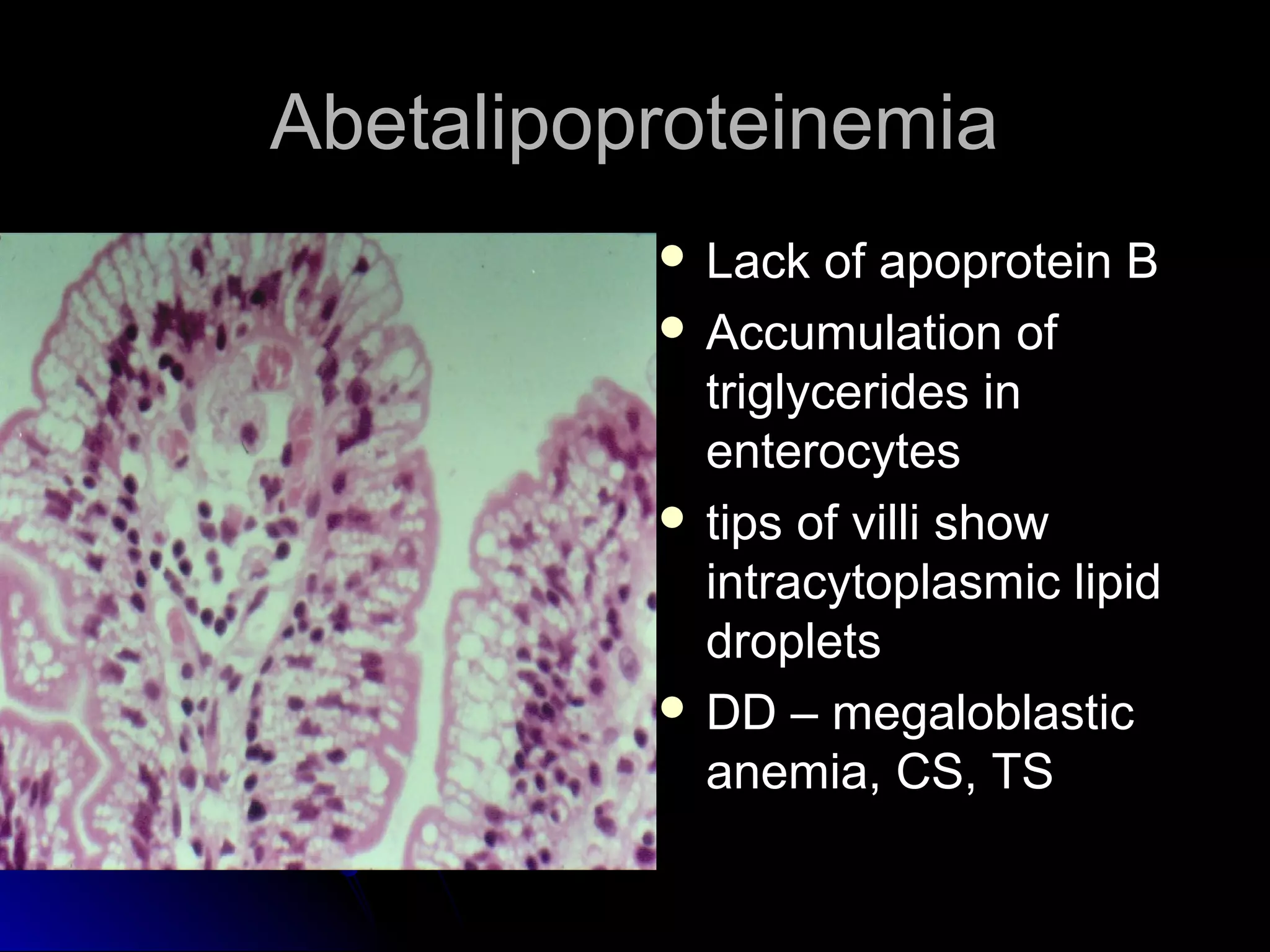
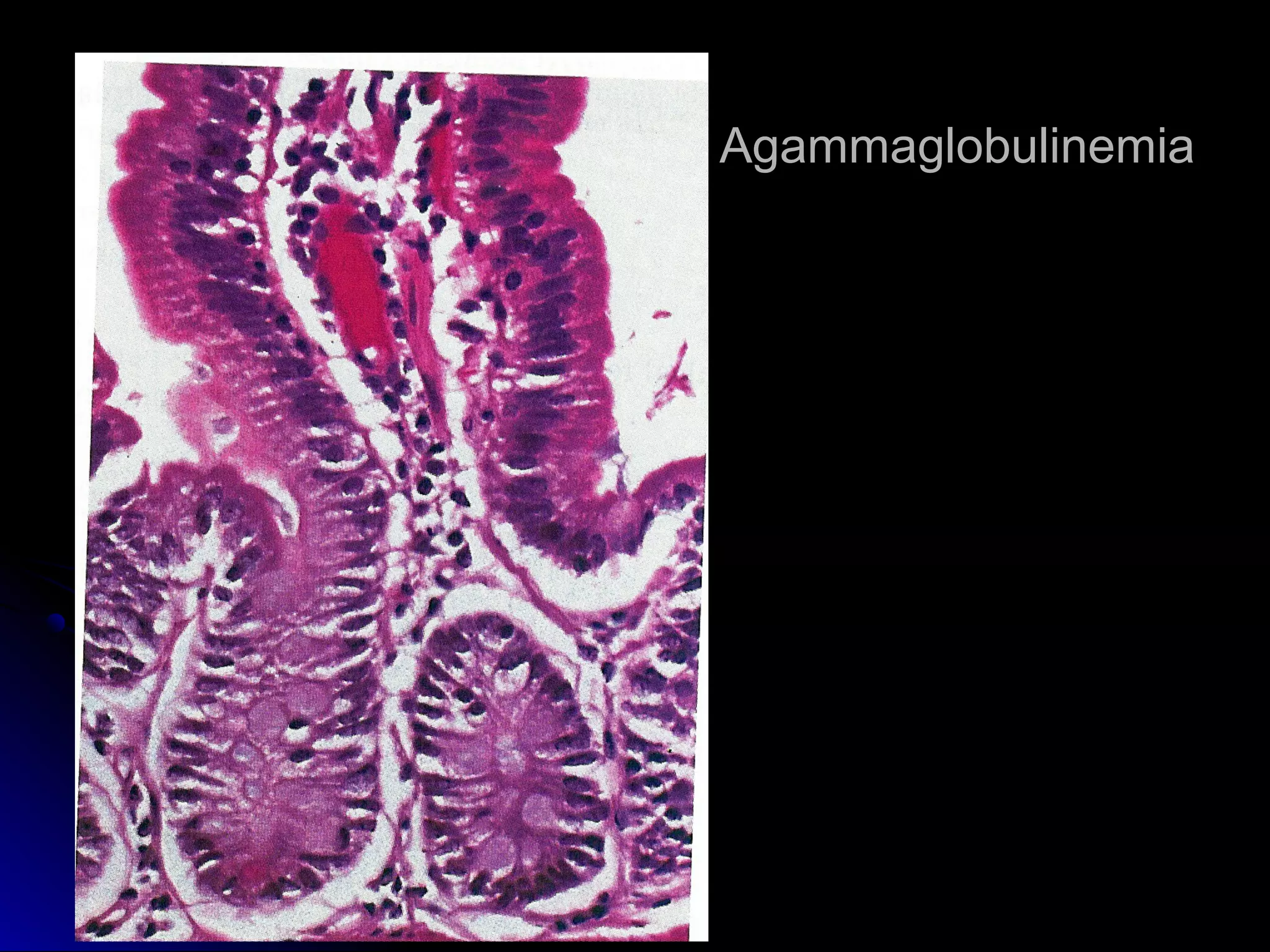
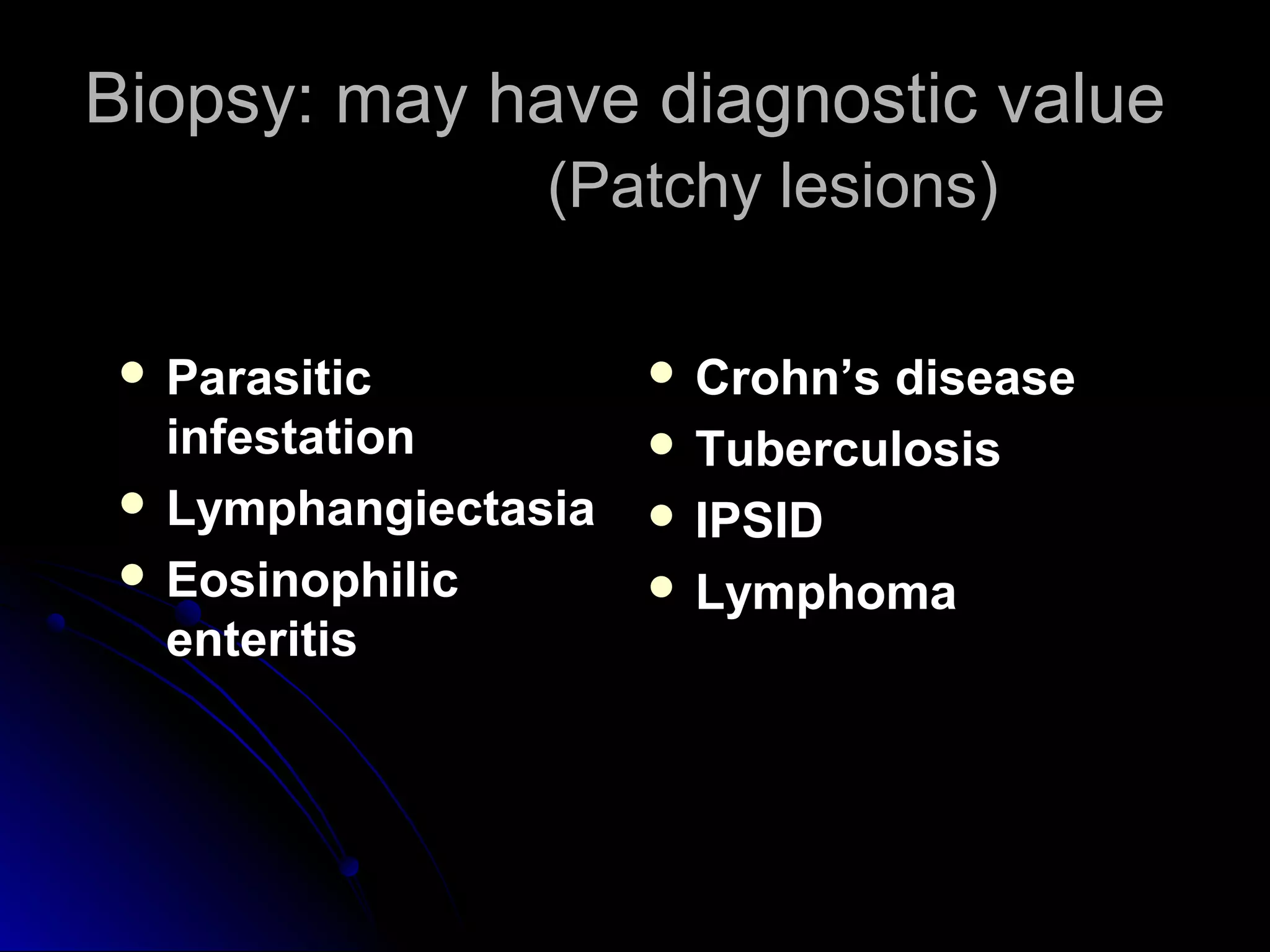
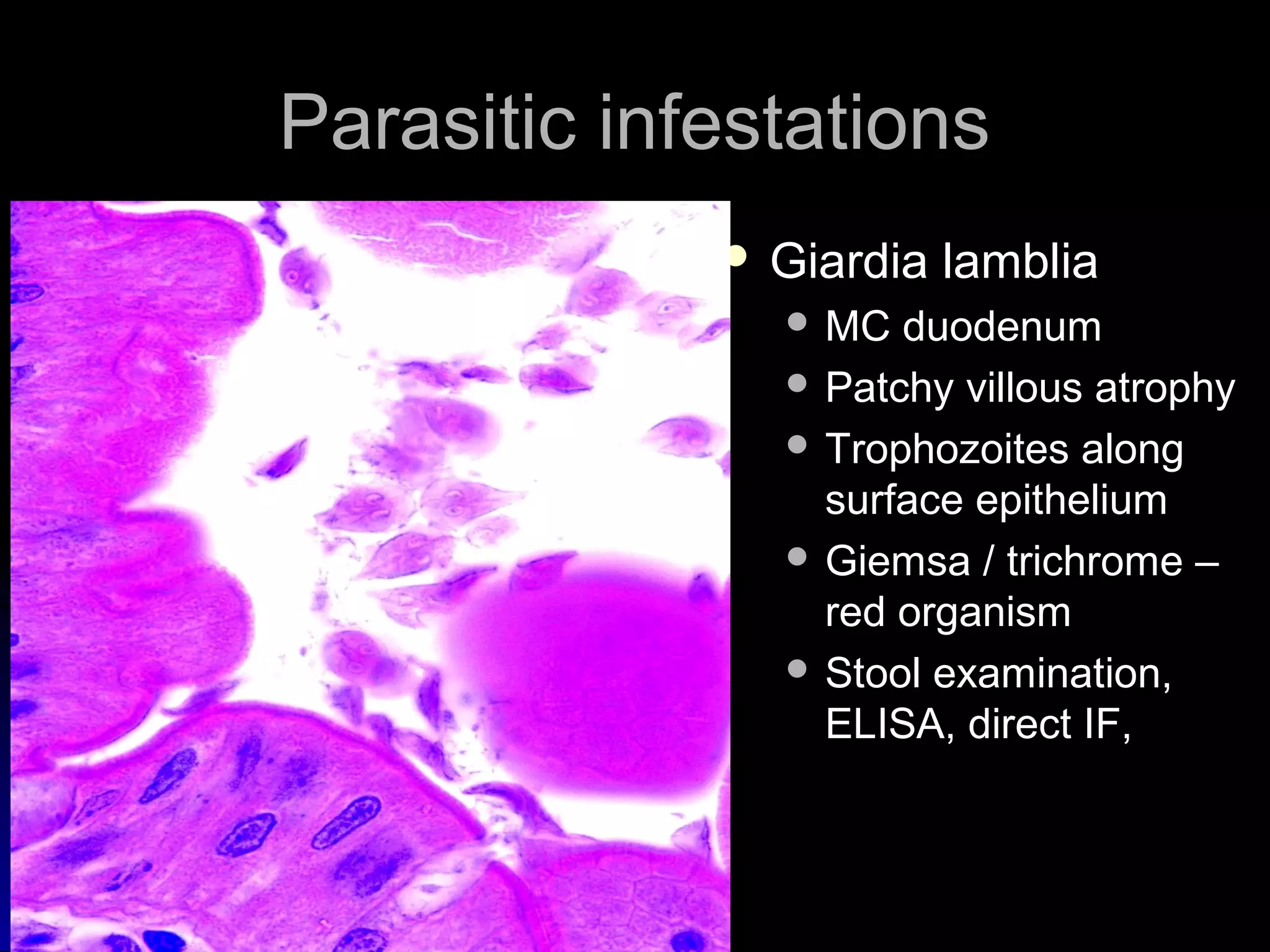
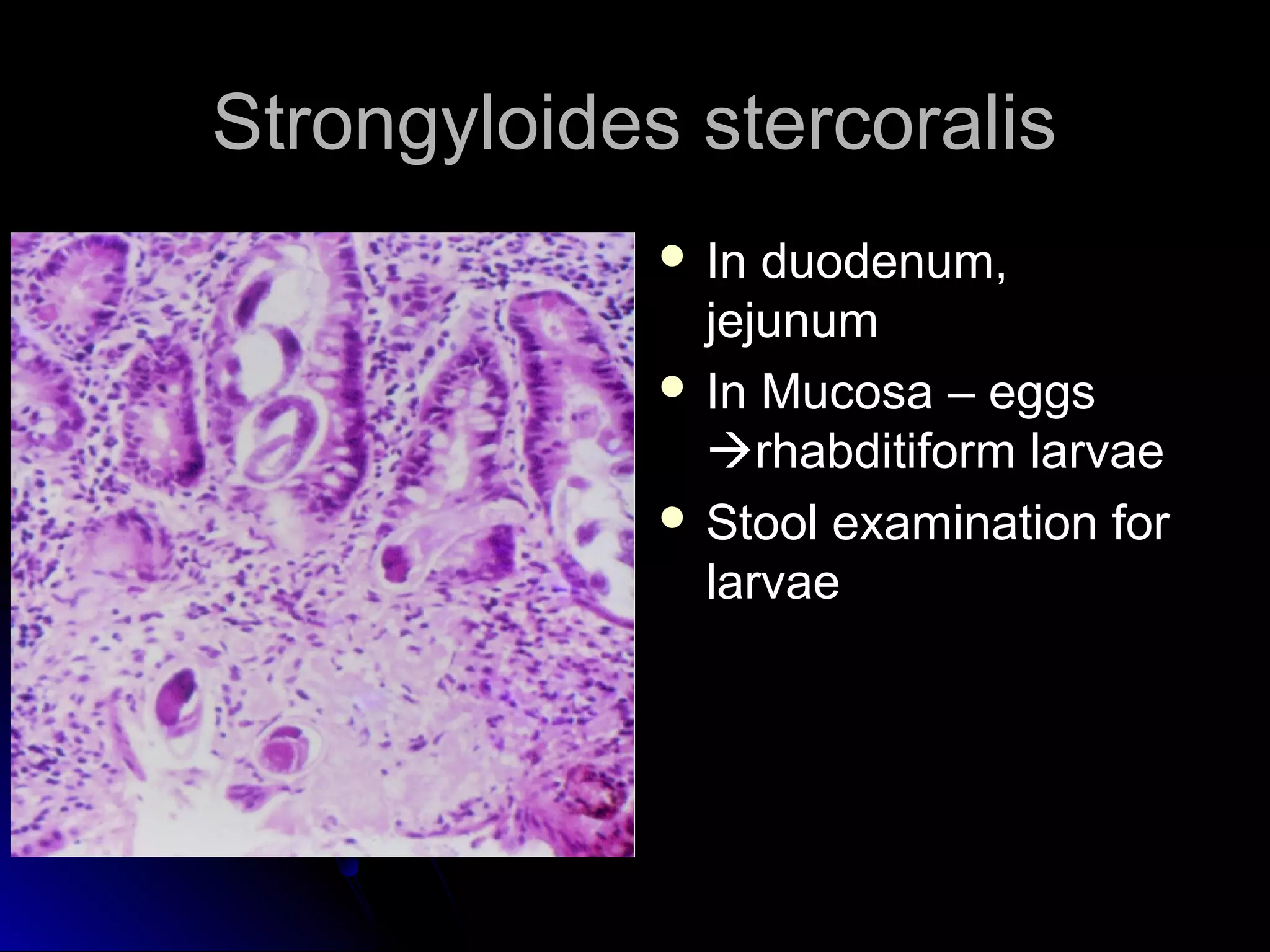
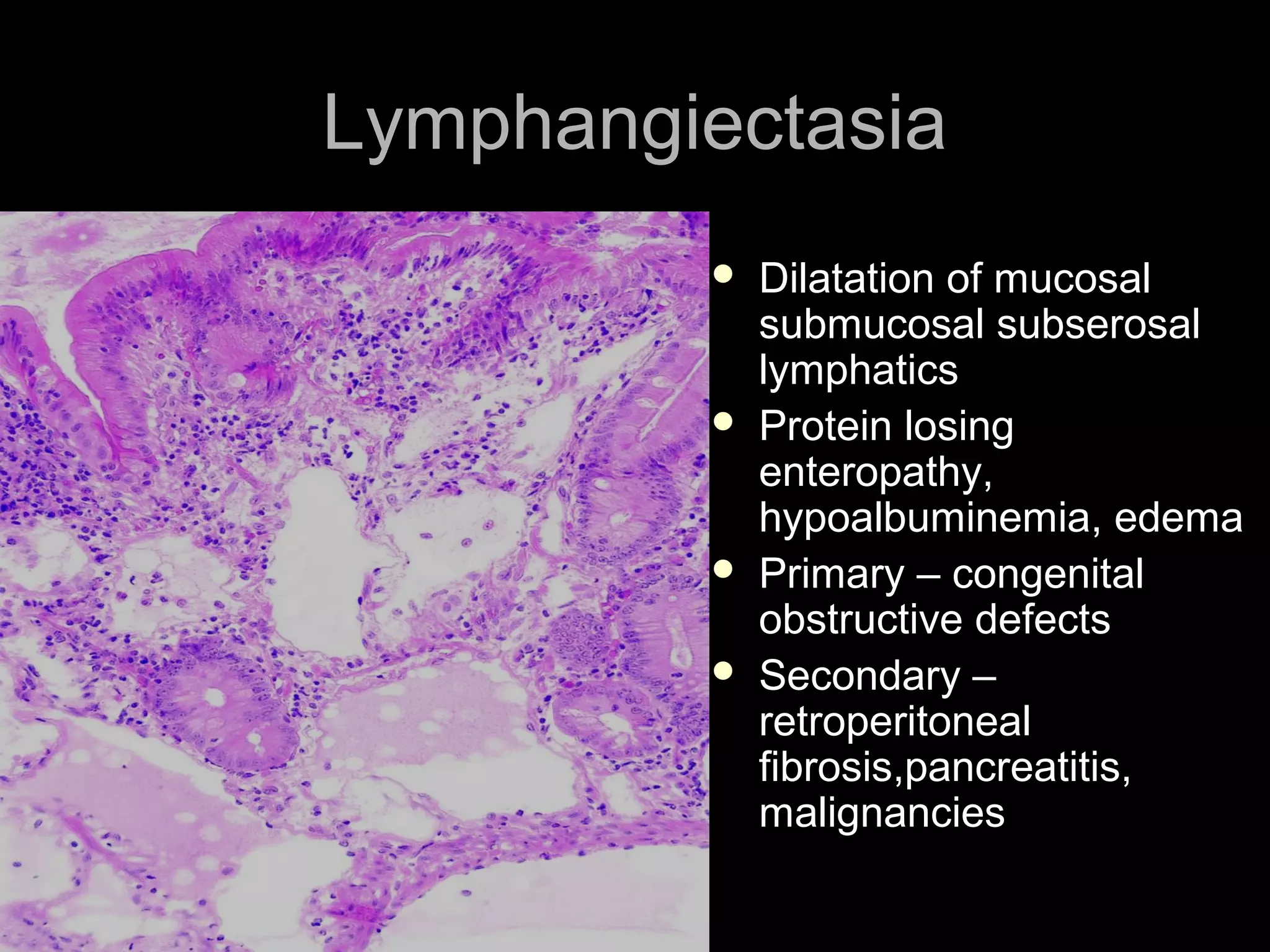
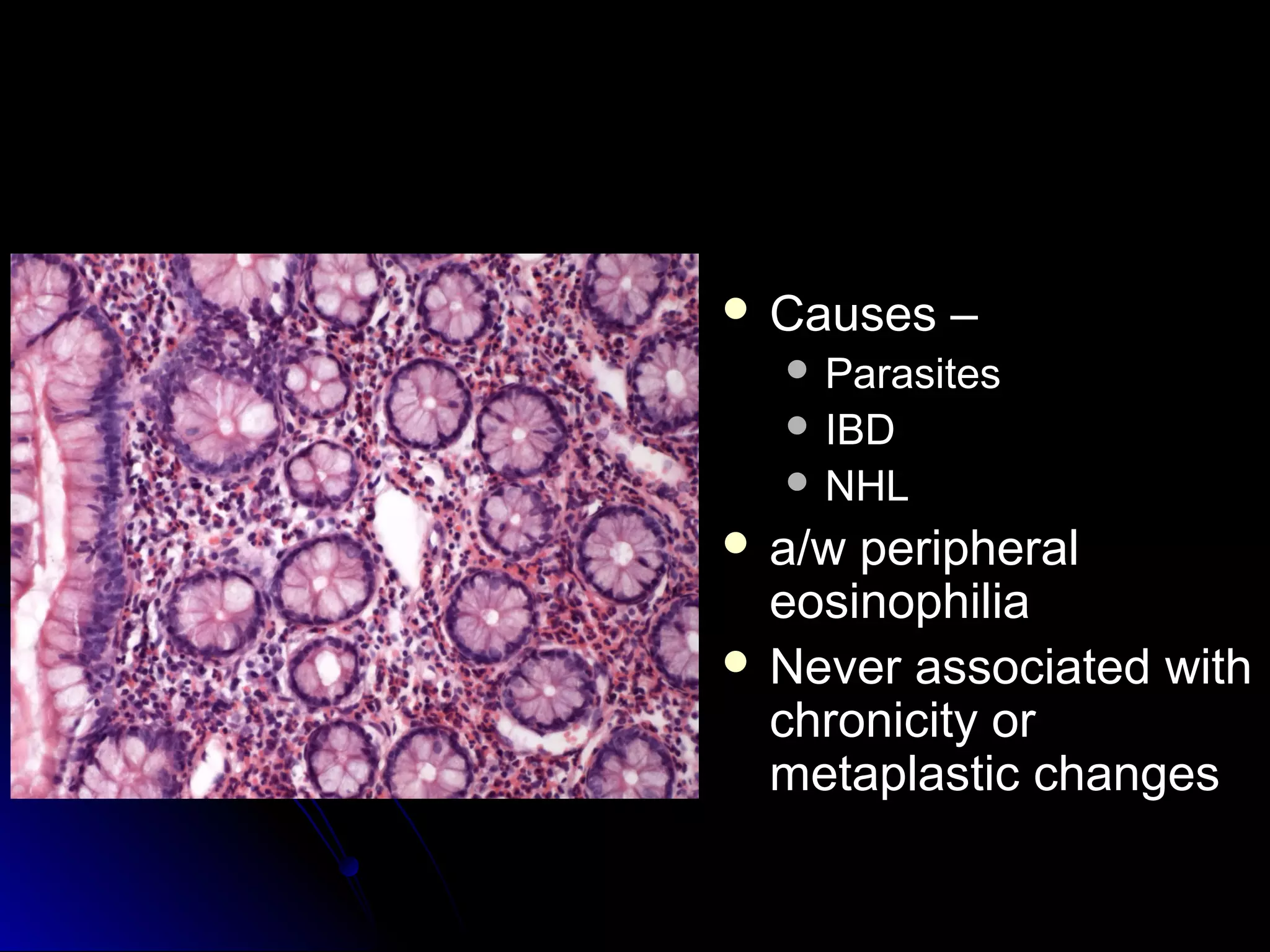
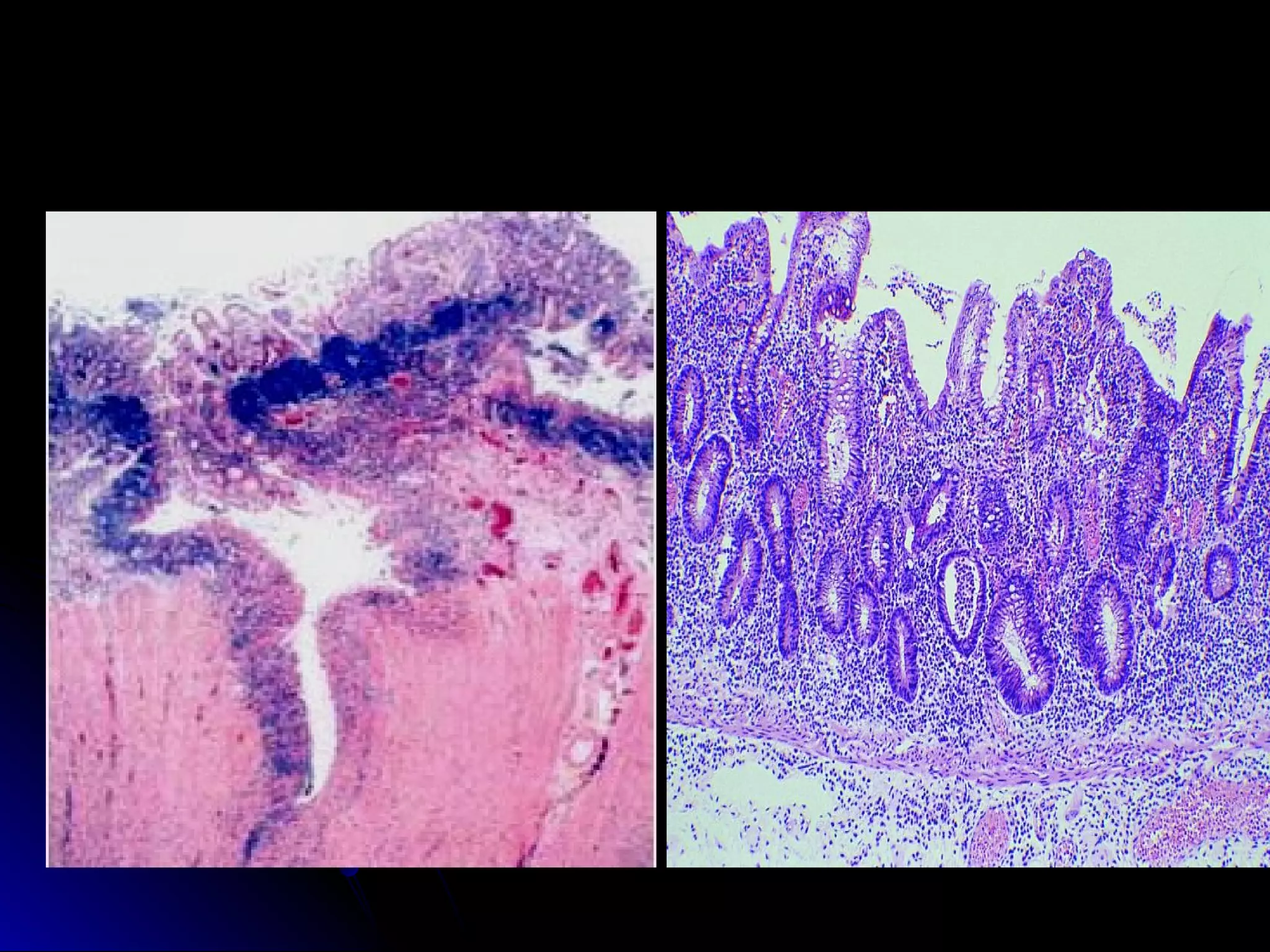
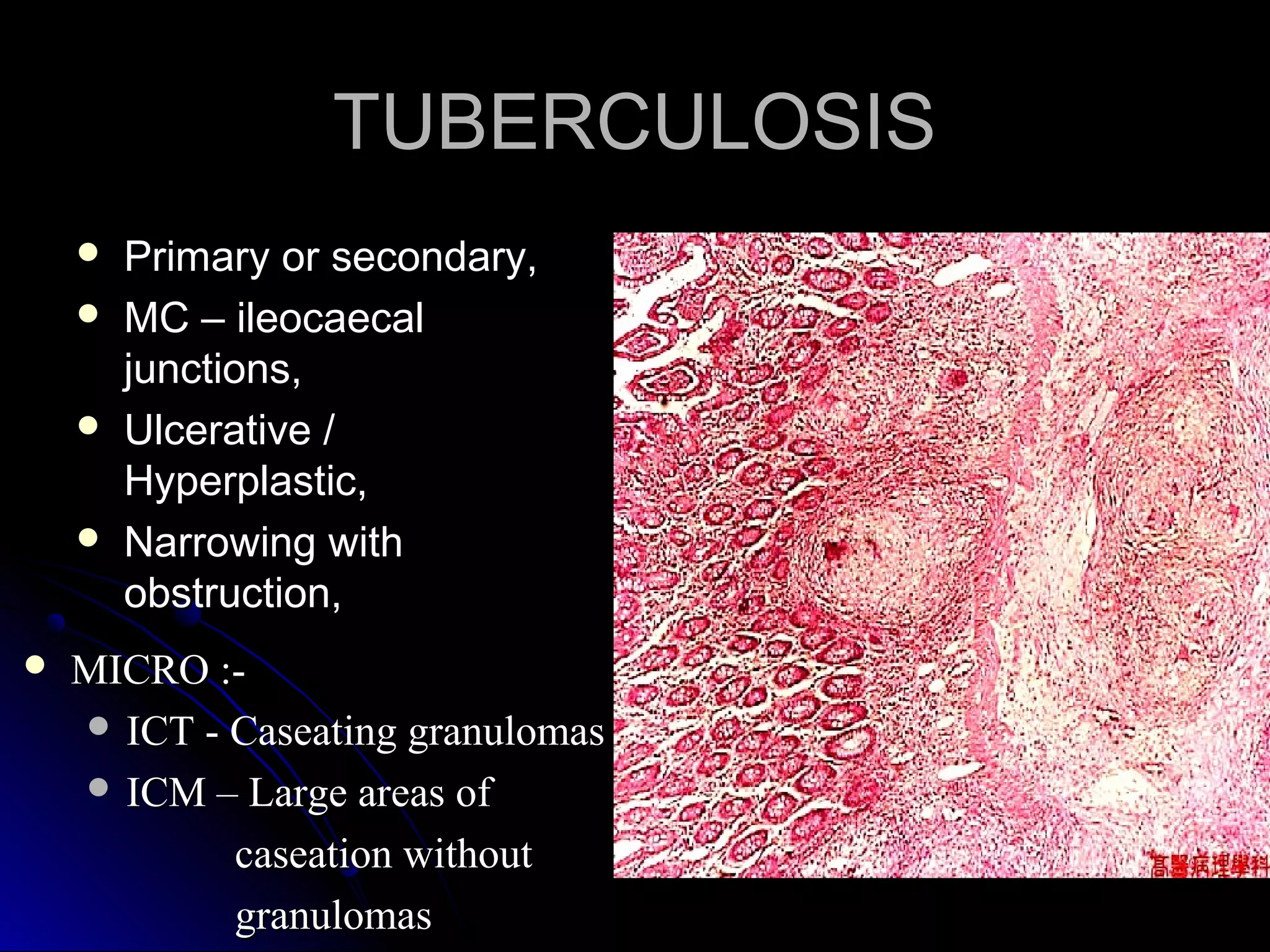
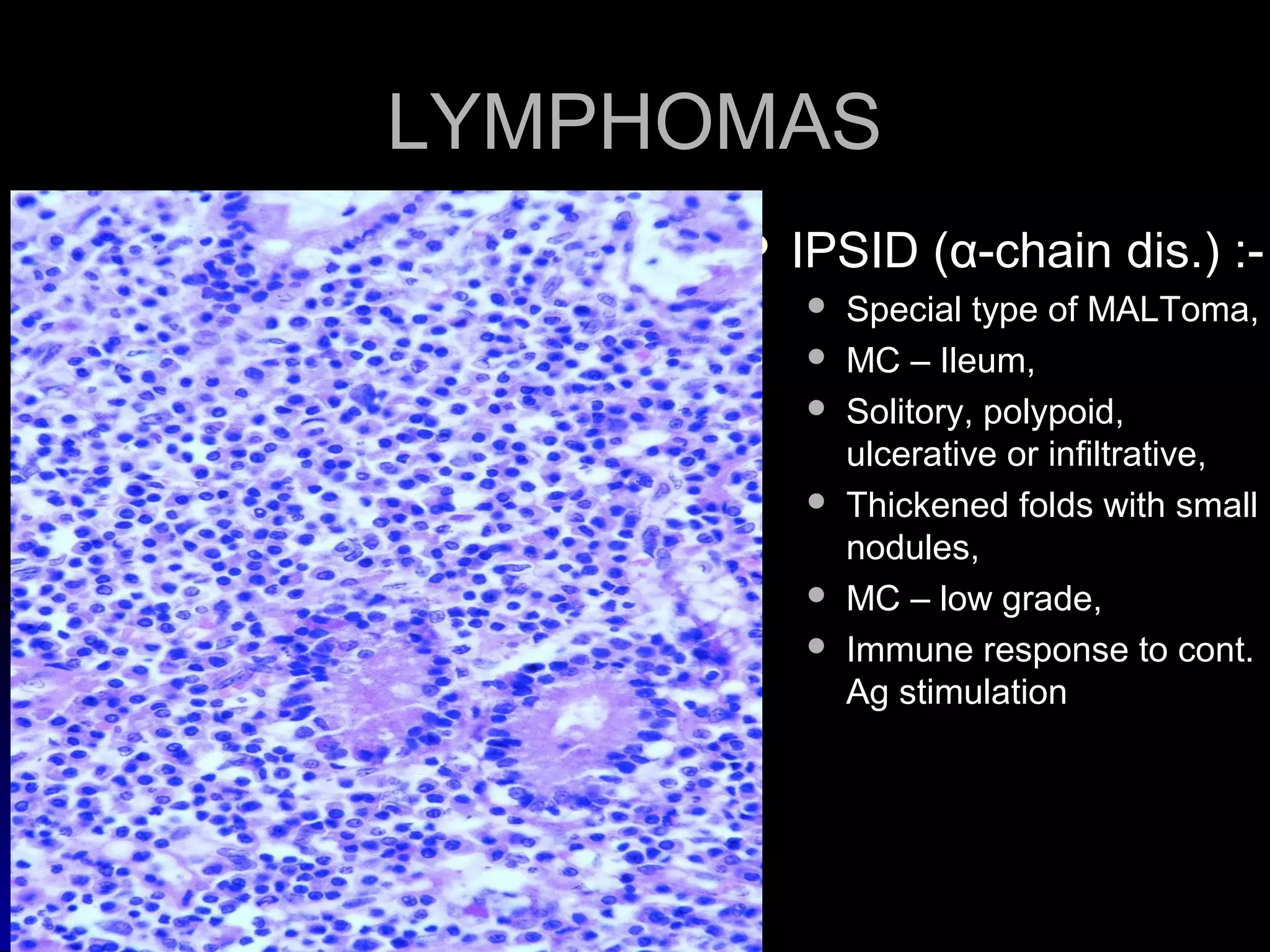
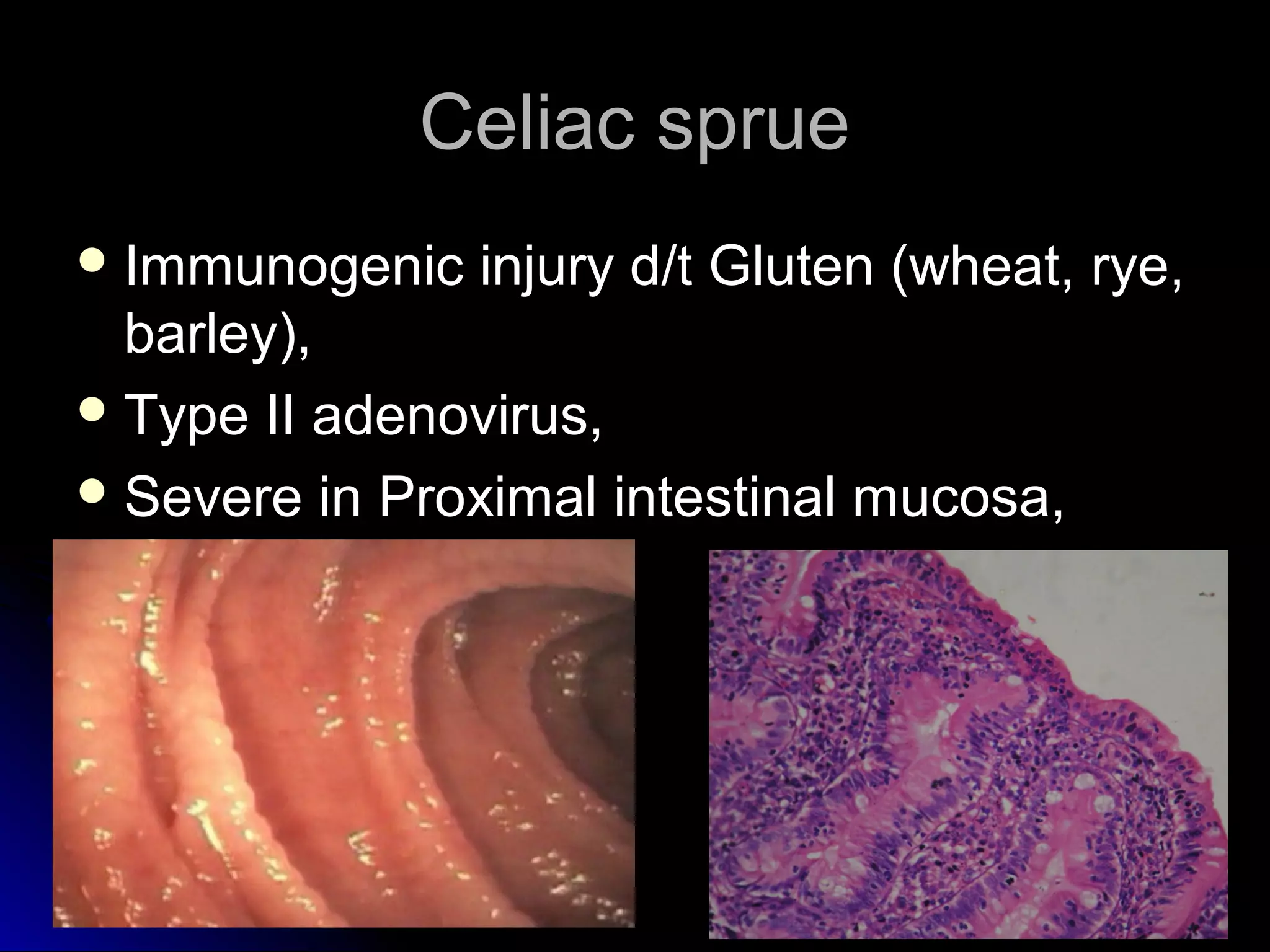
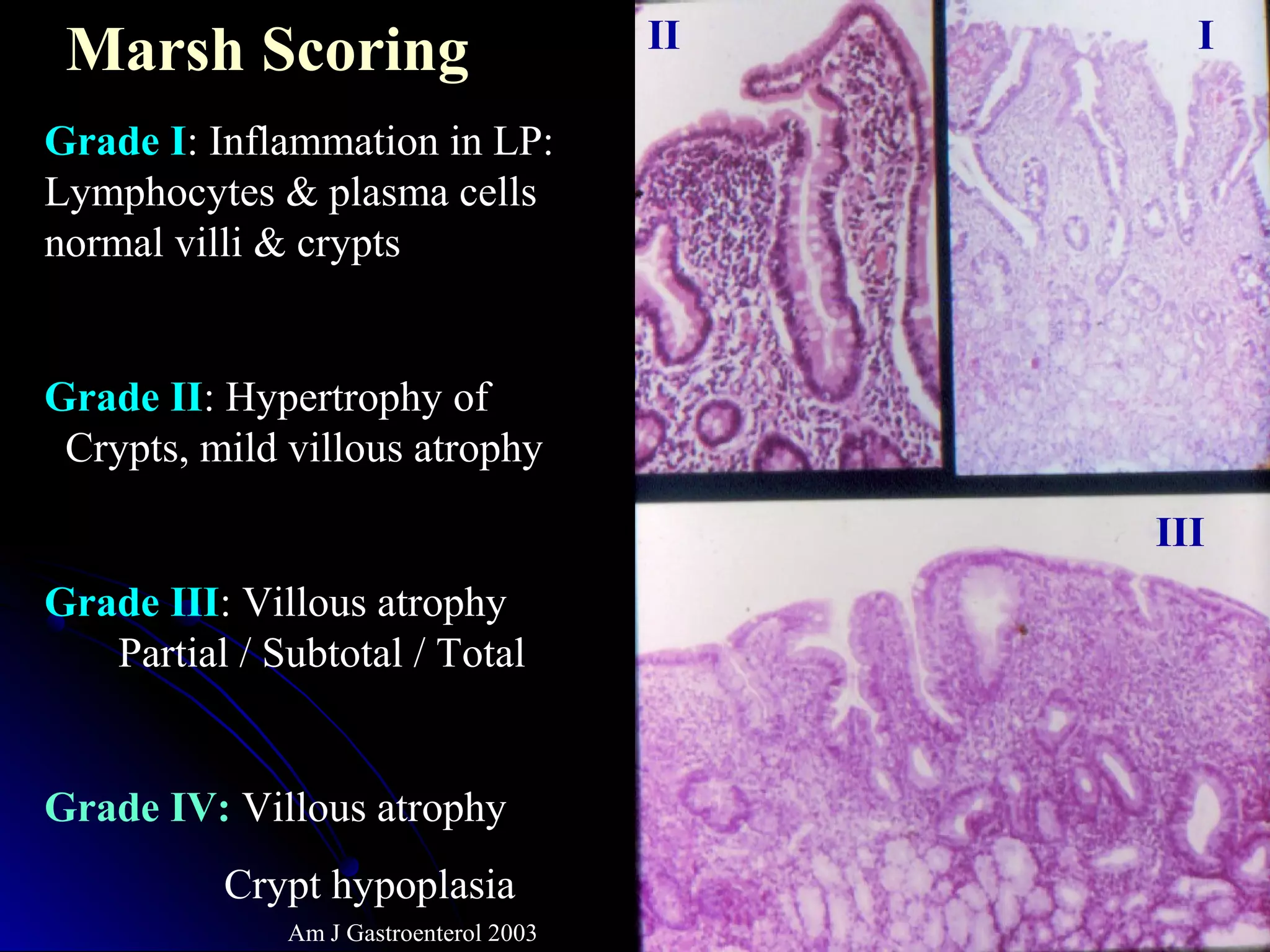
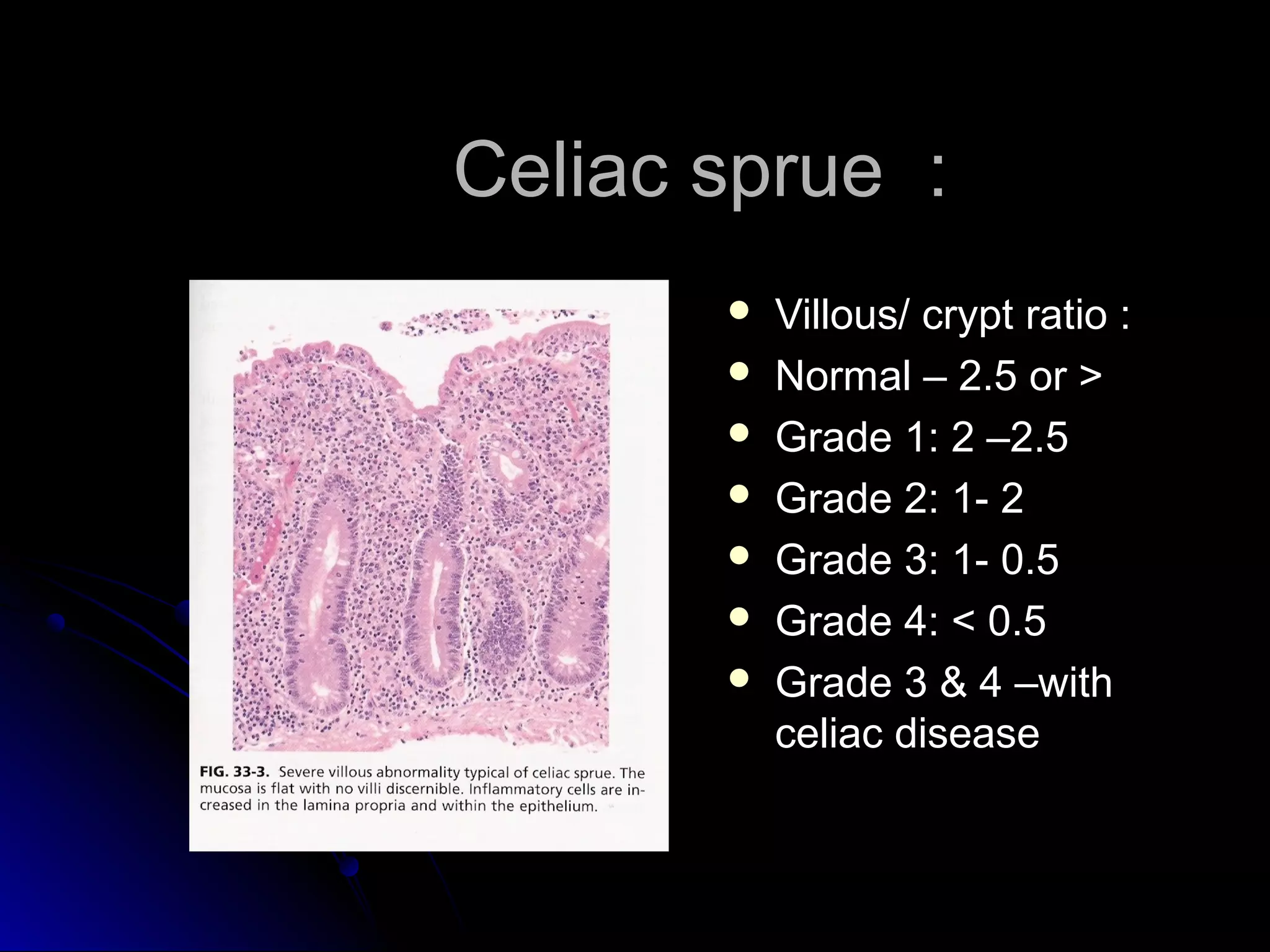
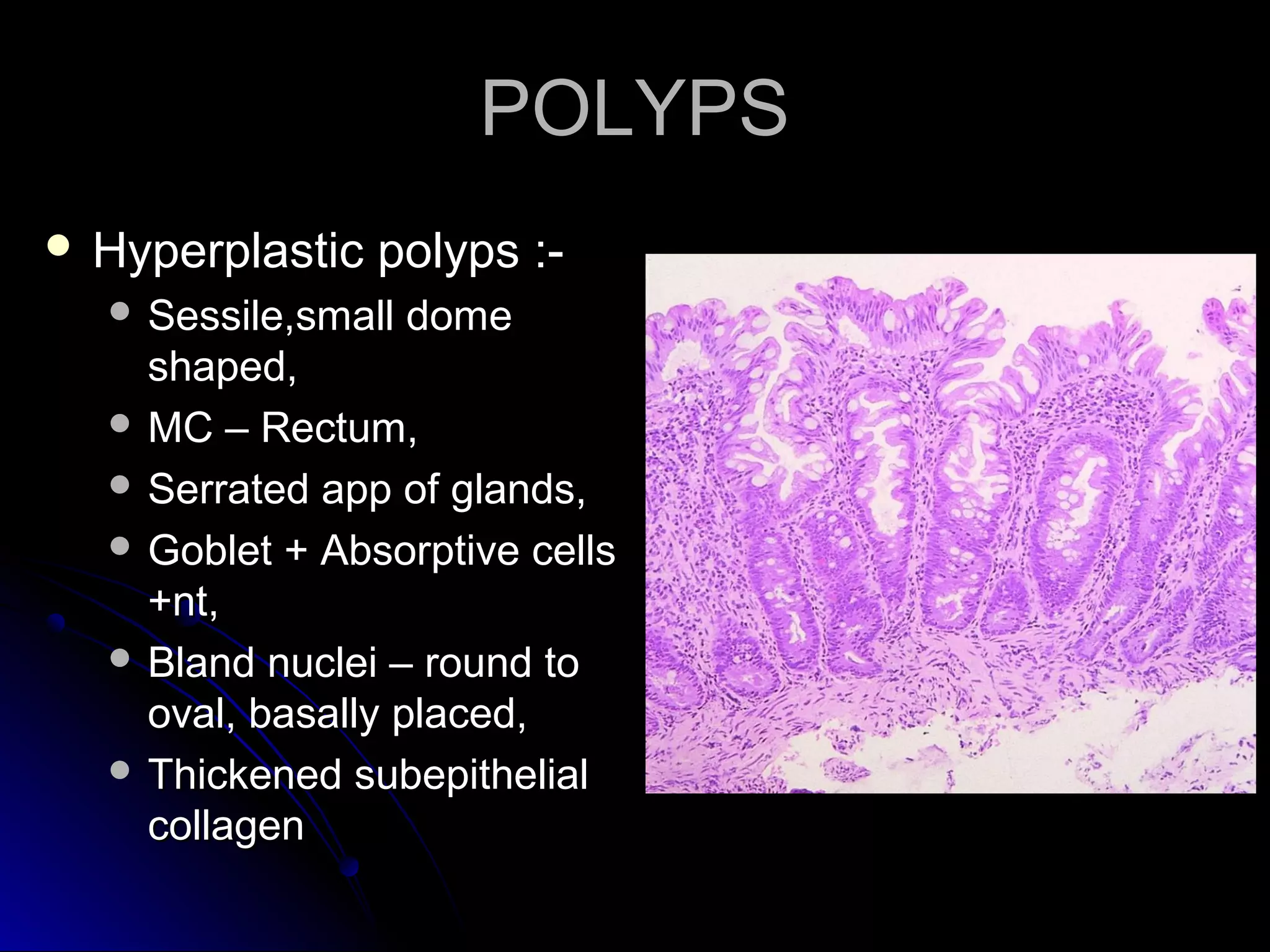
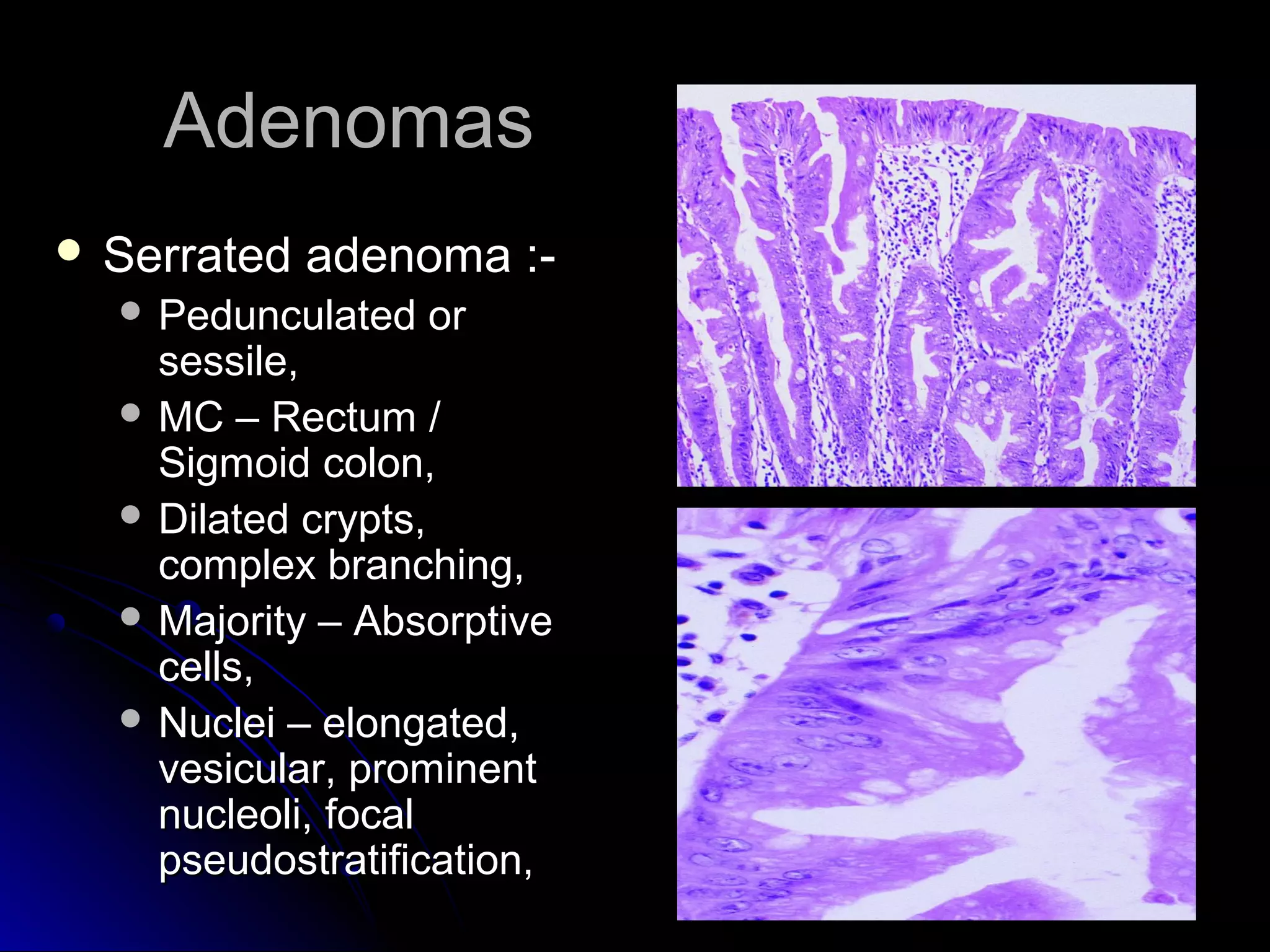
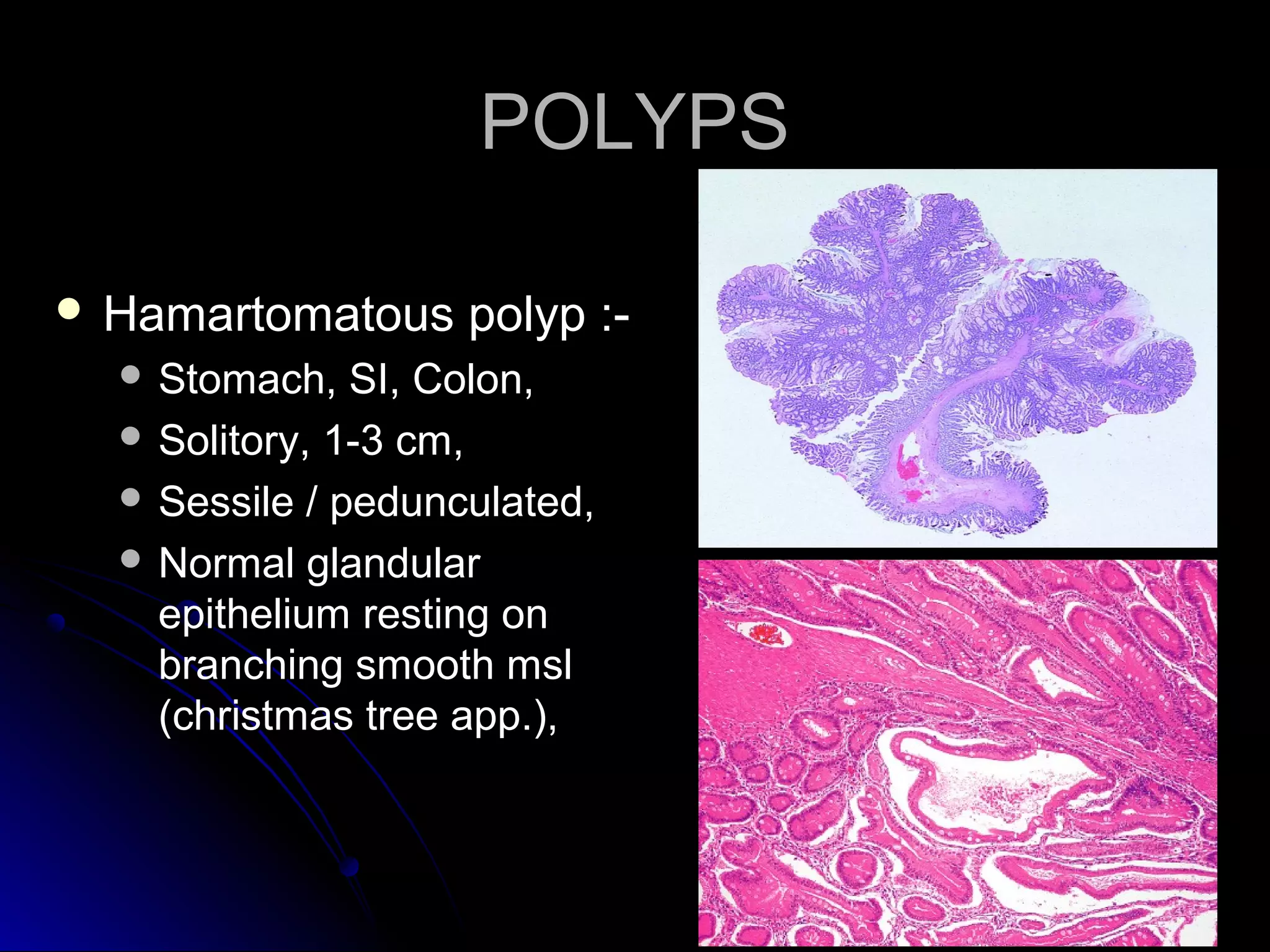
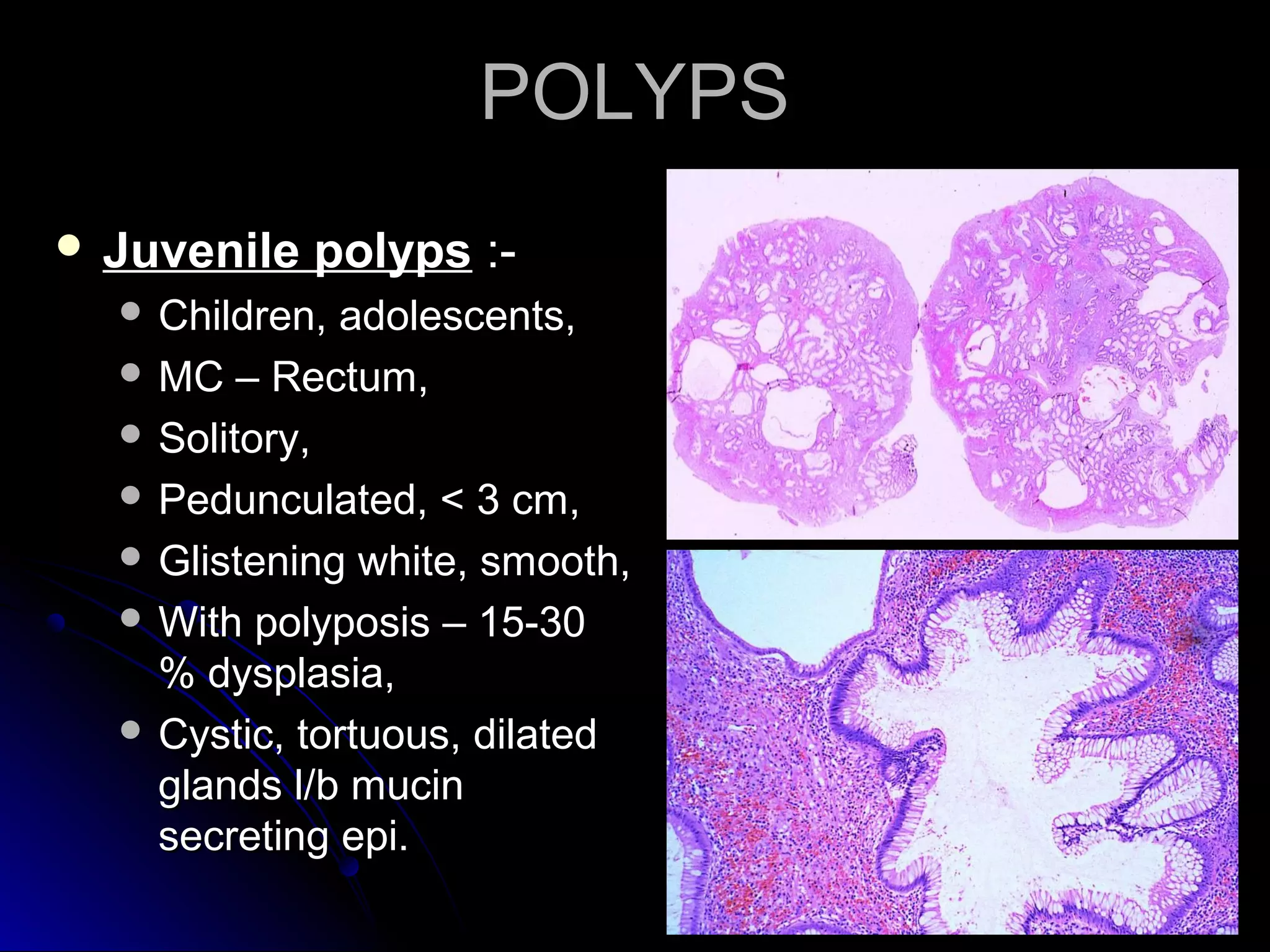
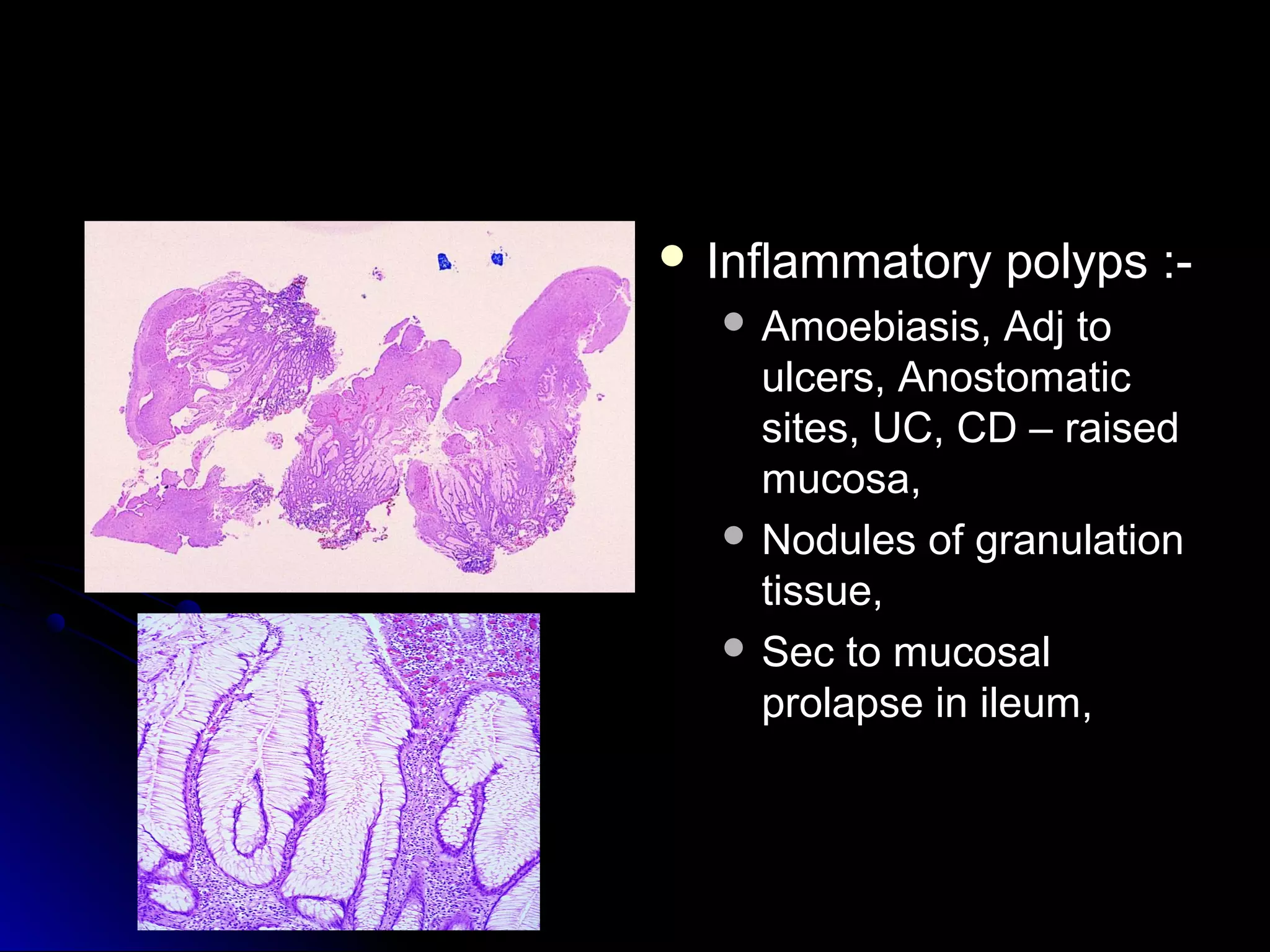
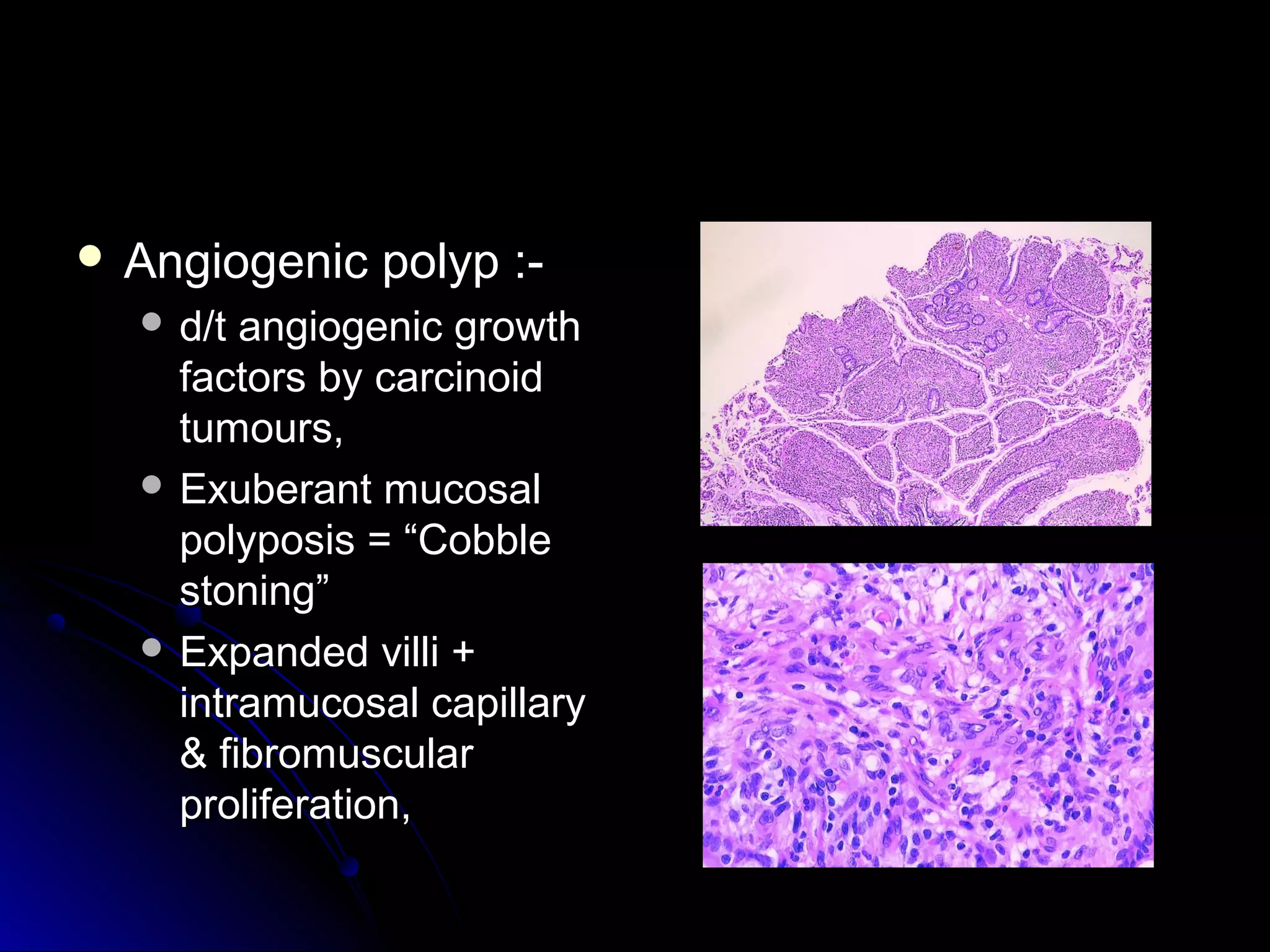
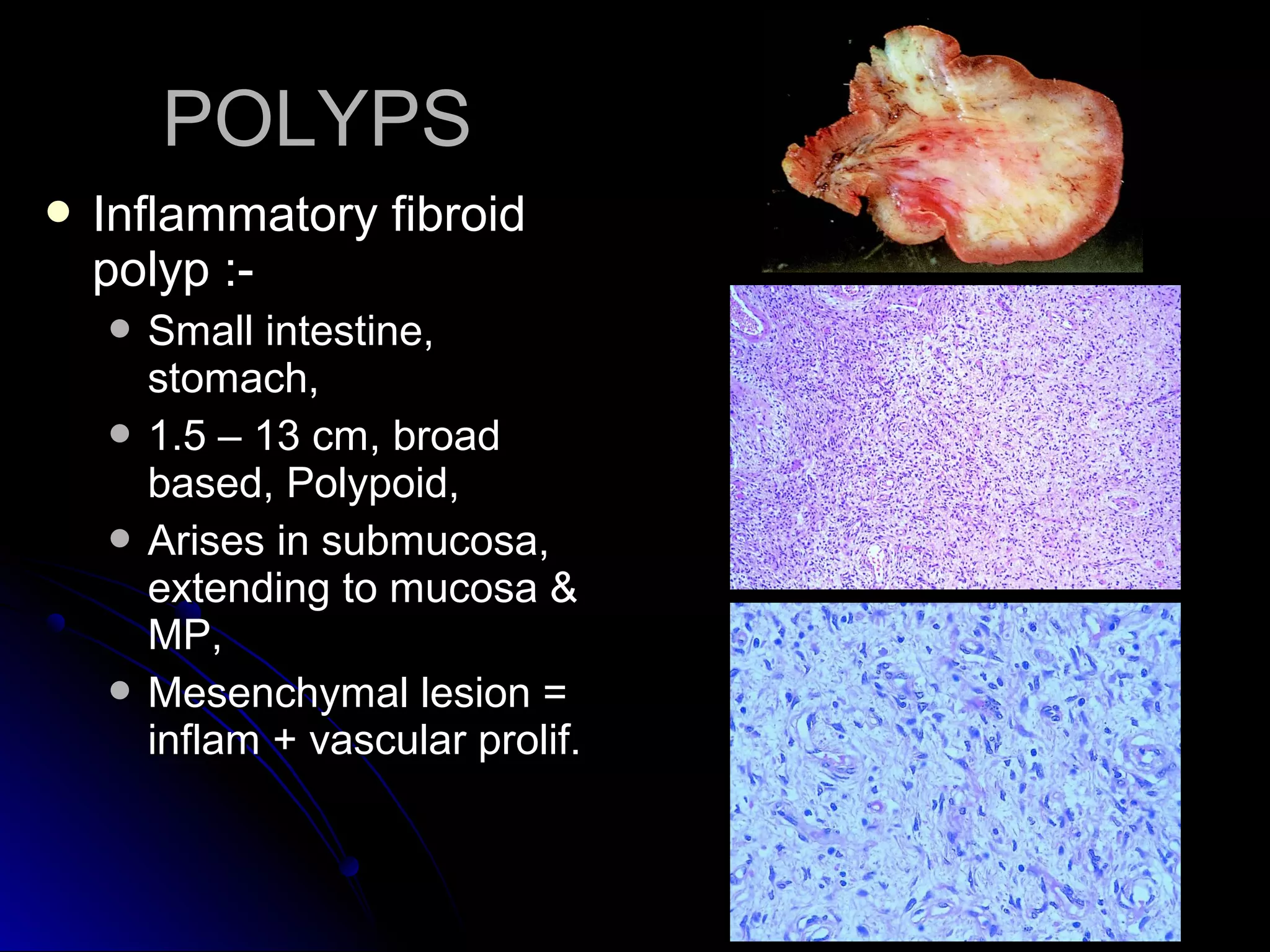
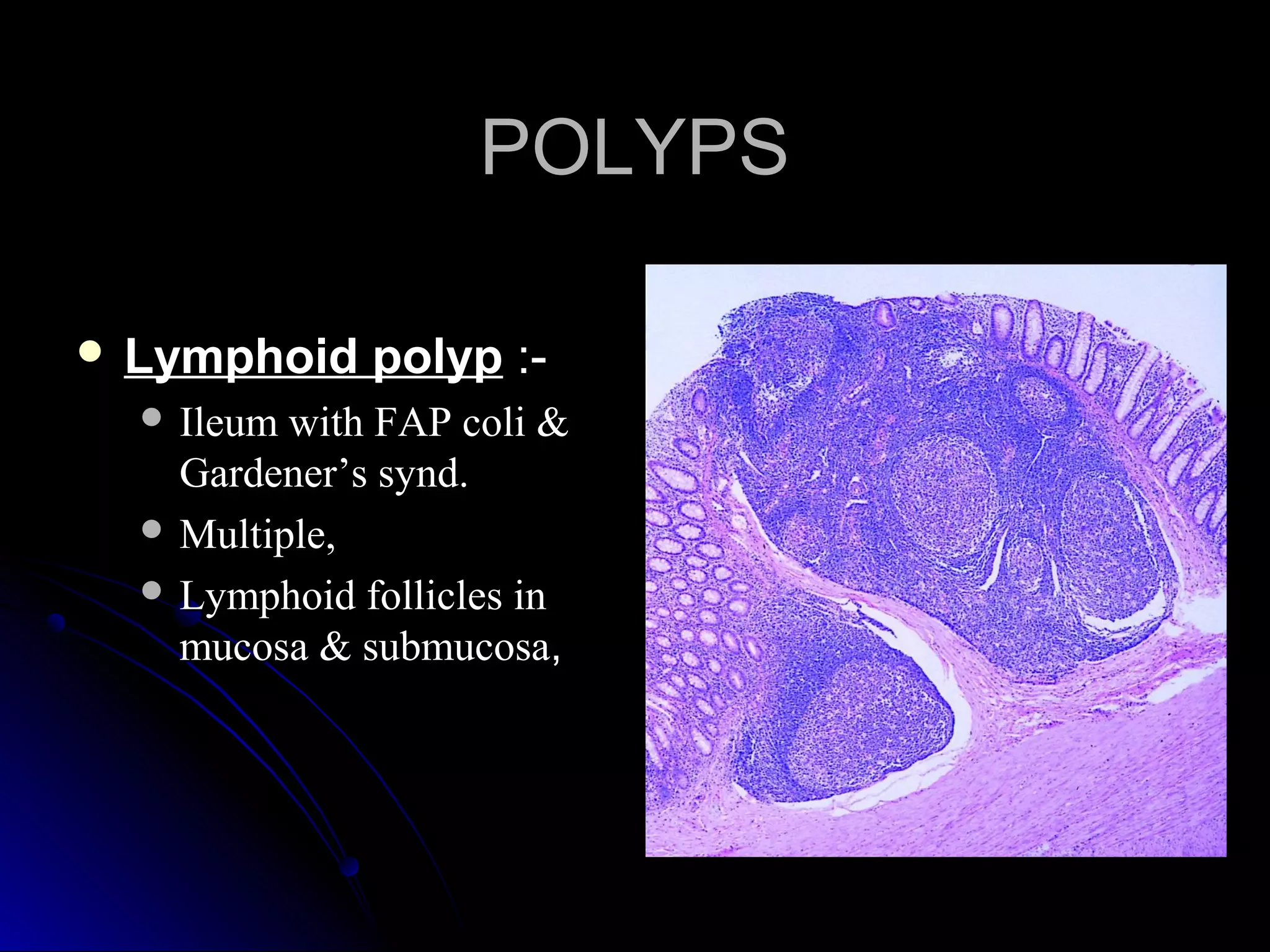
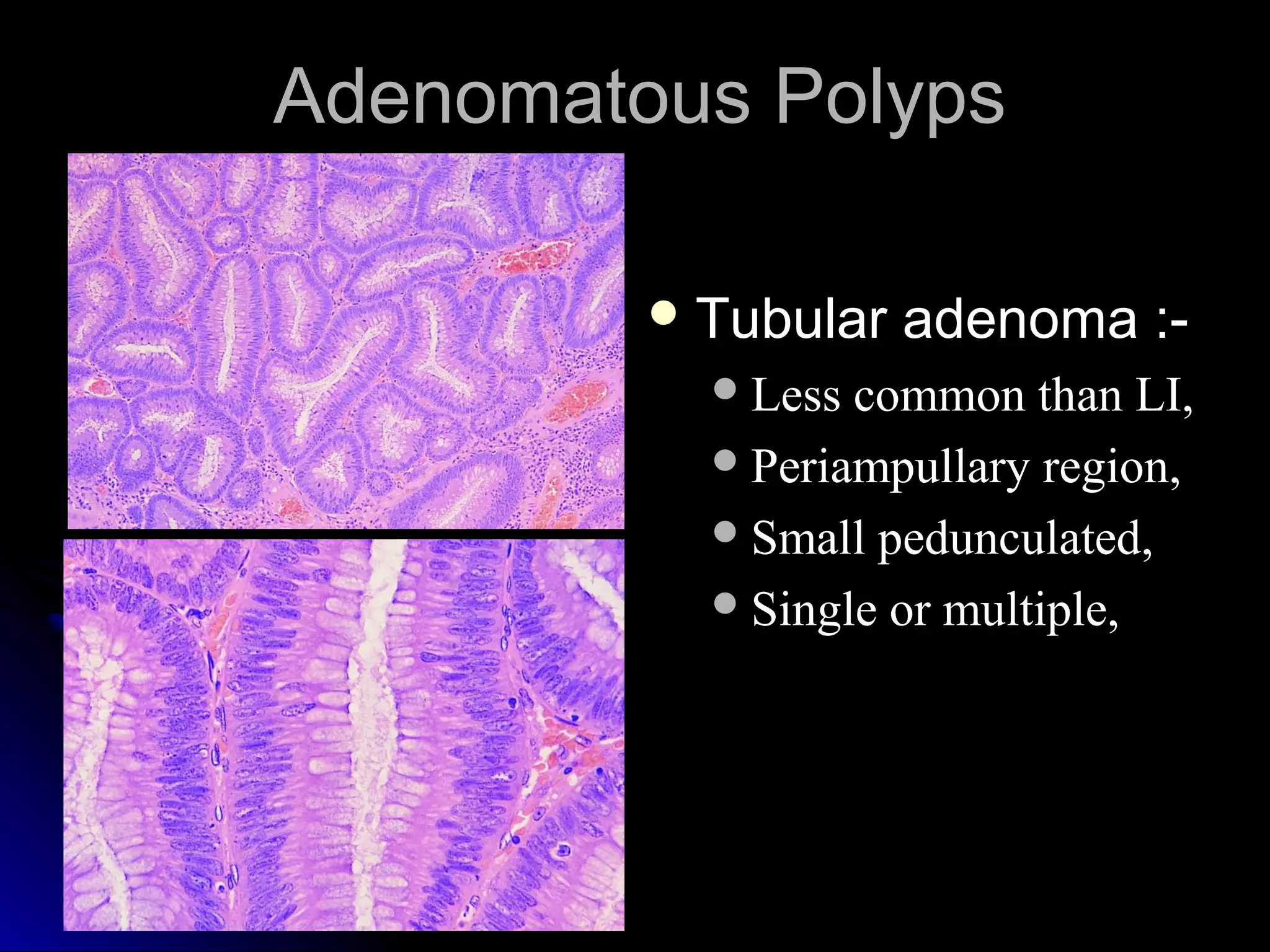
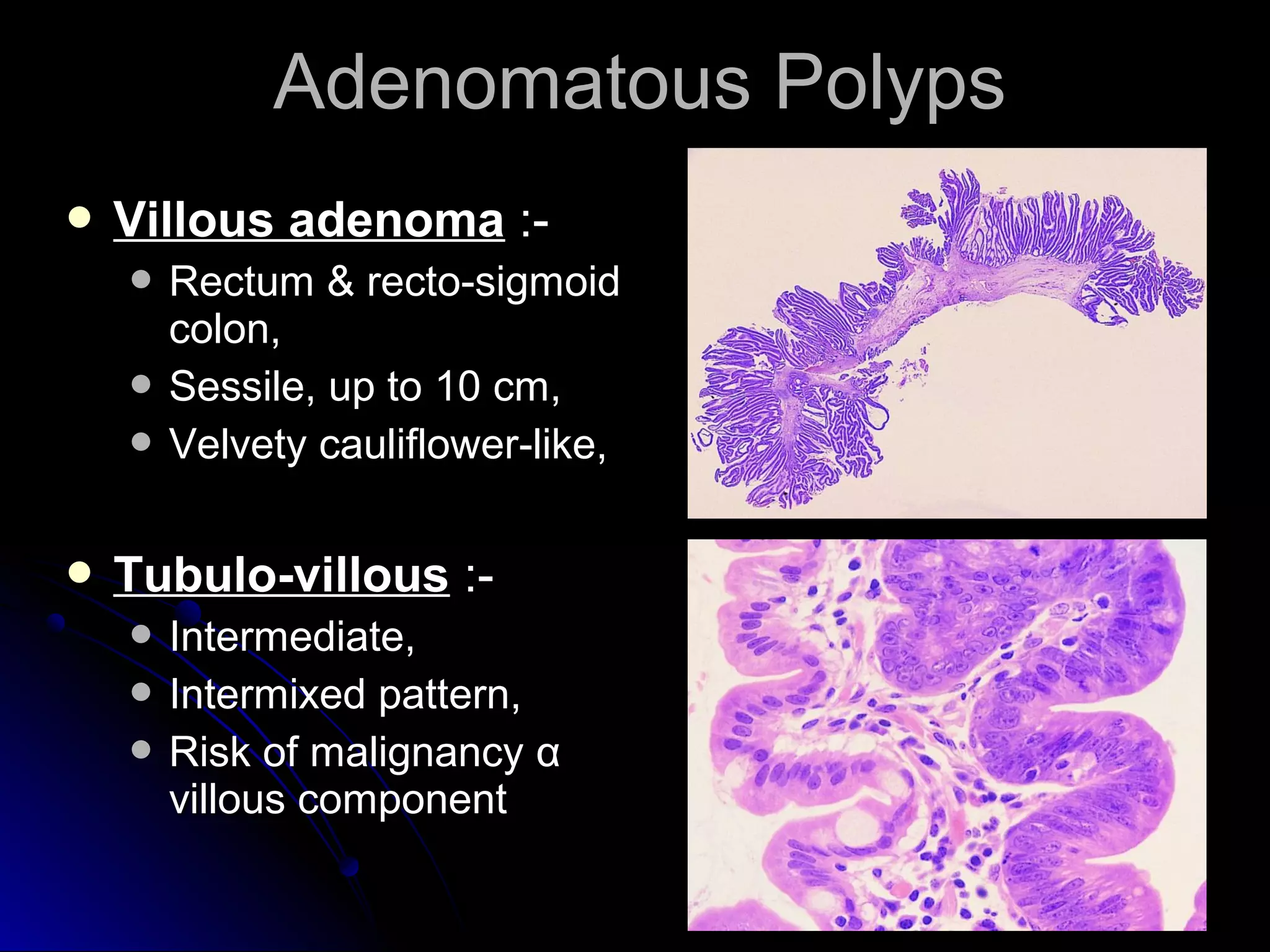
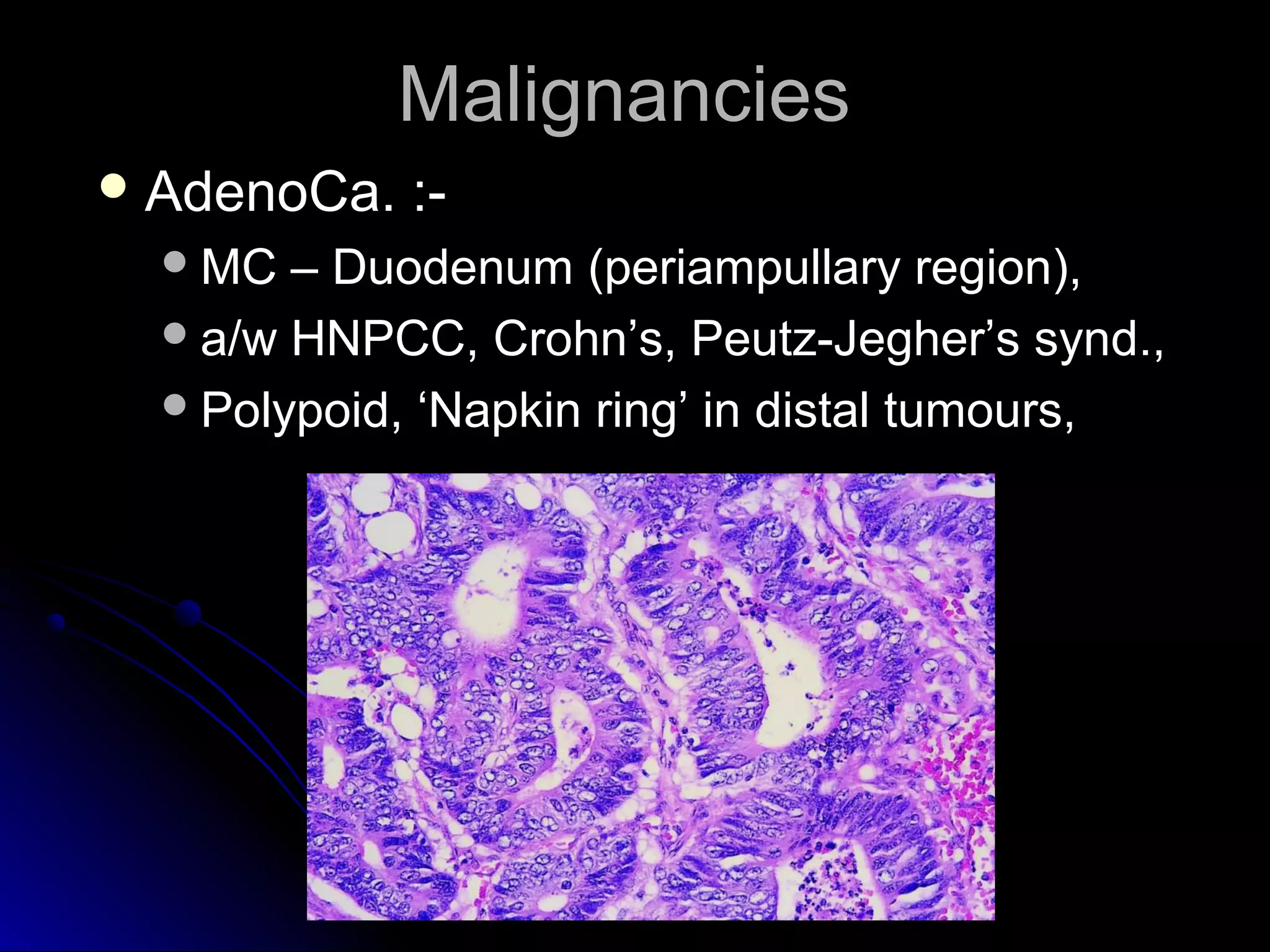
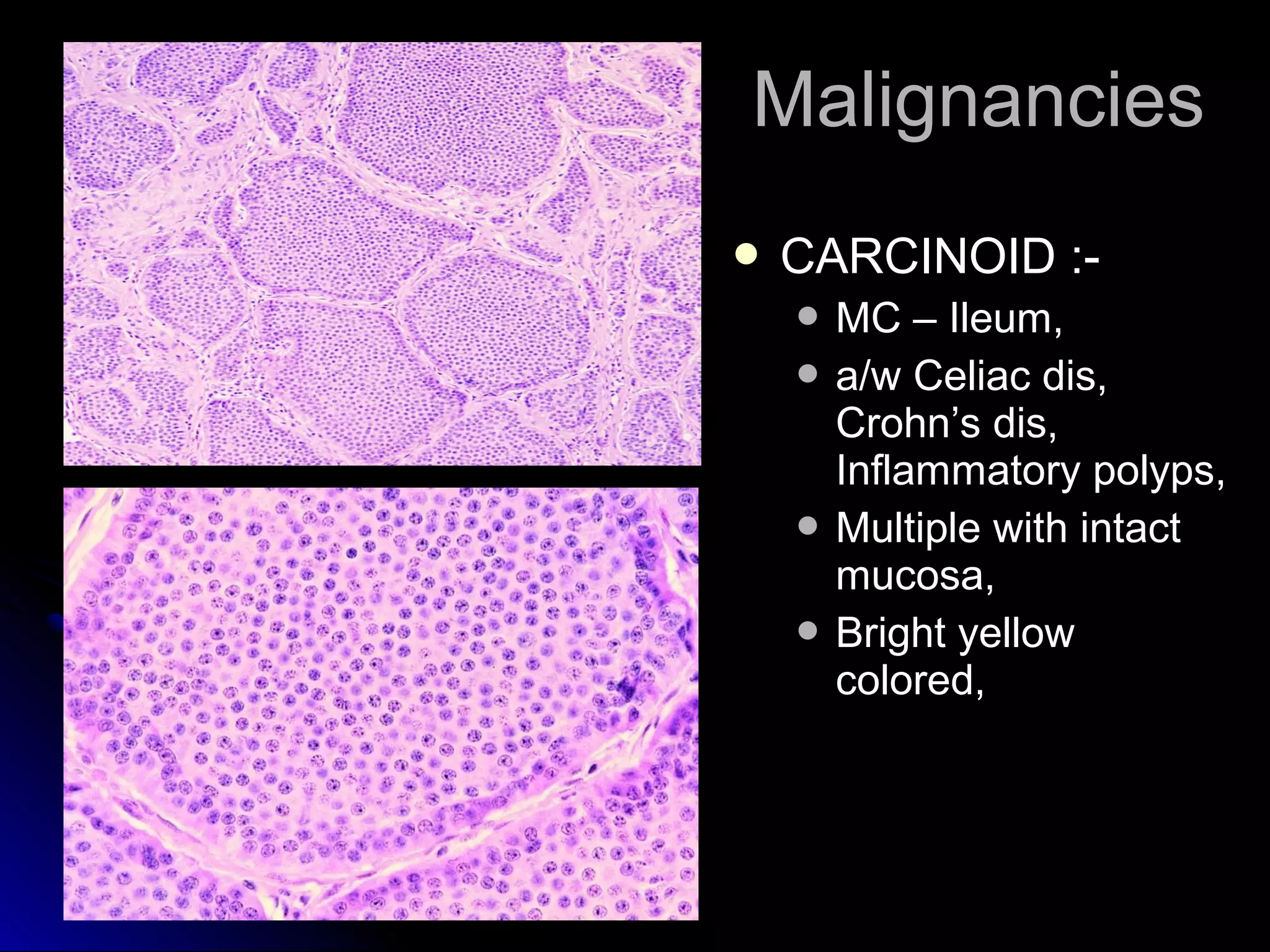
This document provides information on endoscopic gastrointestinal biopsies and their interpretation. It discusses endoscopy techniques and tools used to visualize the gastrointestinal tract and obtain biopsies. Key points include types of endoscopes, handling of biopsy specimens, processing for histological examination, common indications for endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract, and histological findings and interpretations for conditions of the esophagus and stomach, including chronic gastritis, Helicobacter pylori infection, Barrett's esophagus, and polypoid lesions.