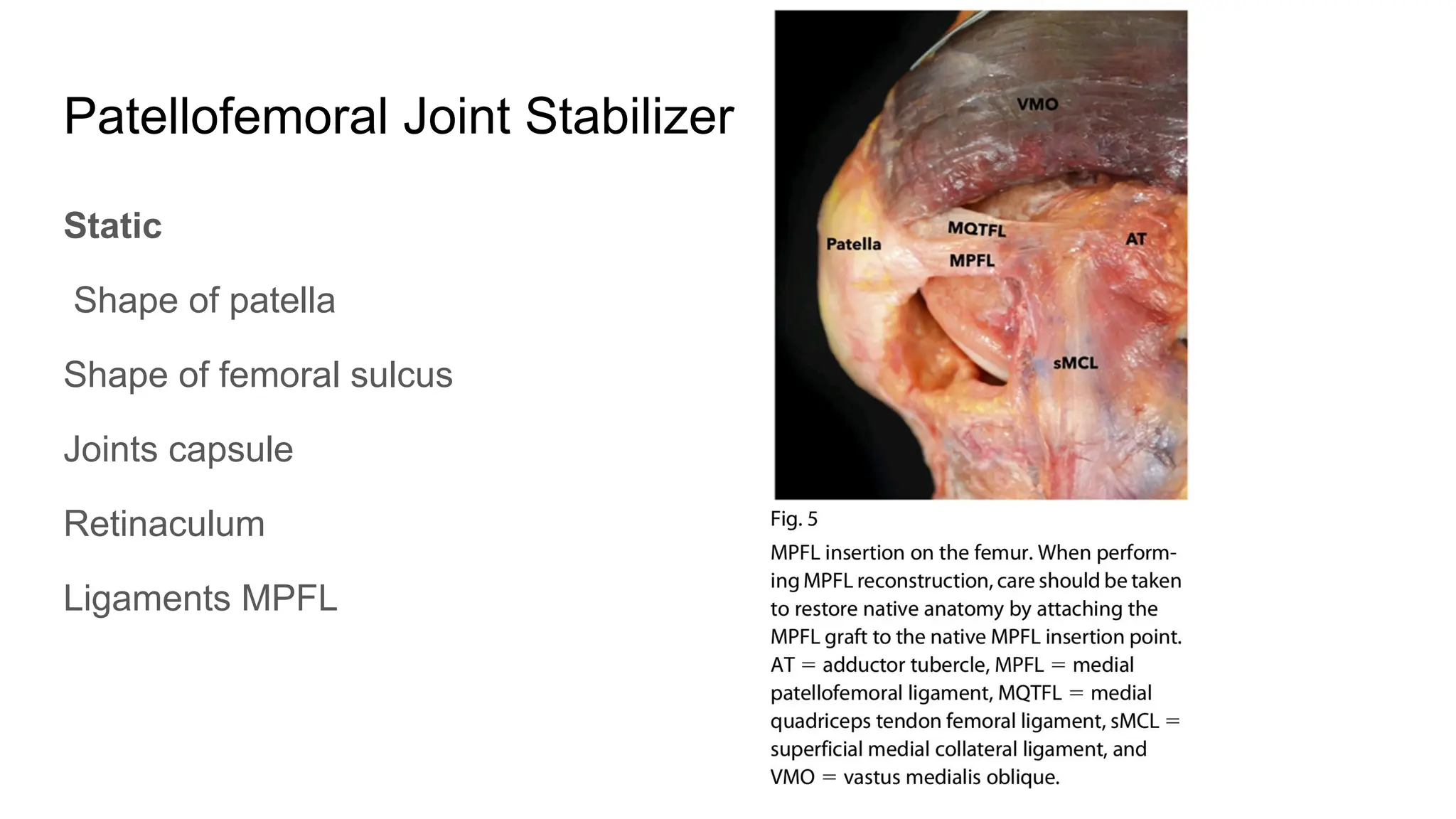
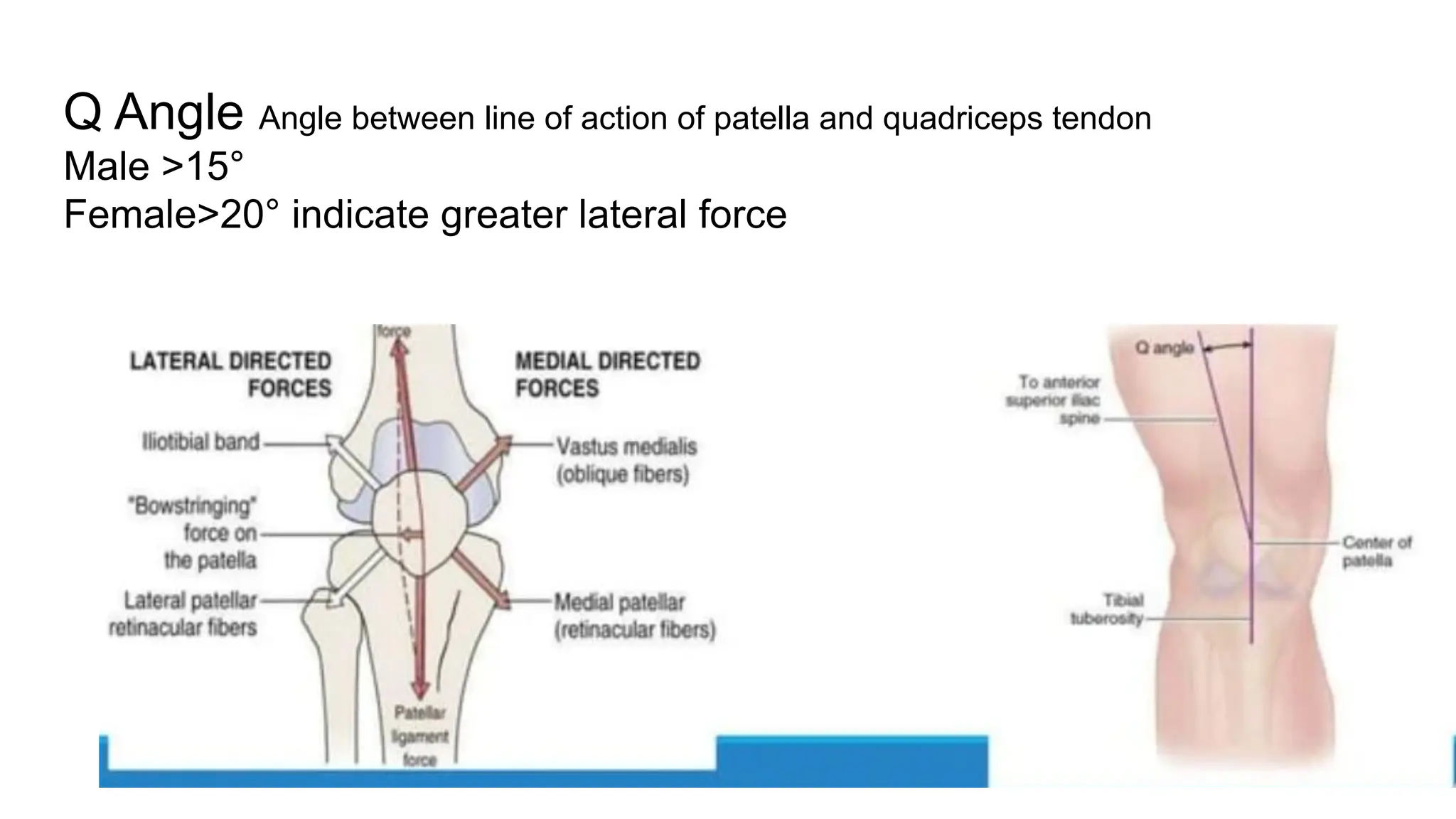
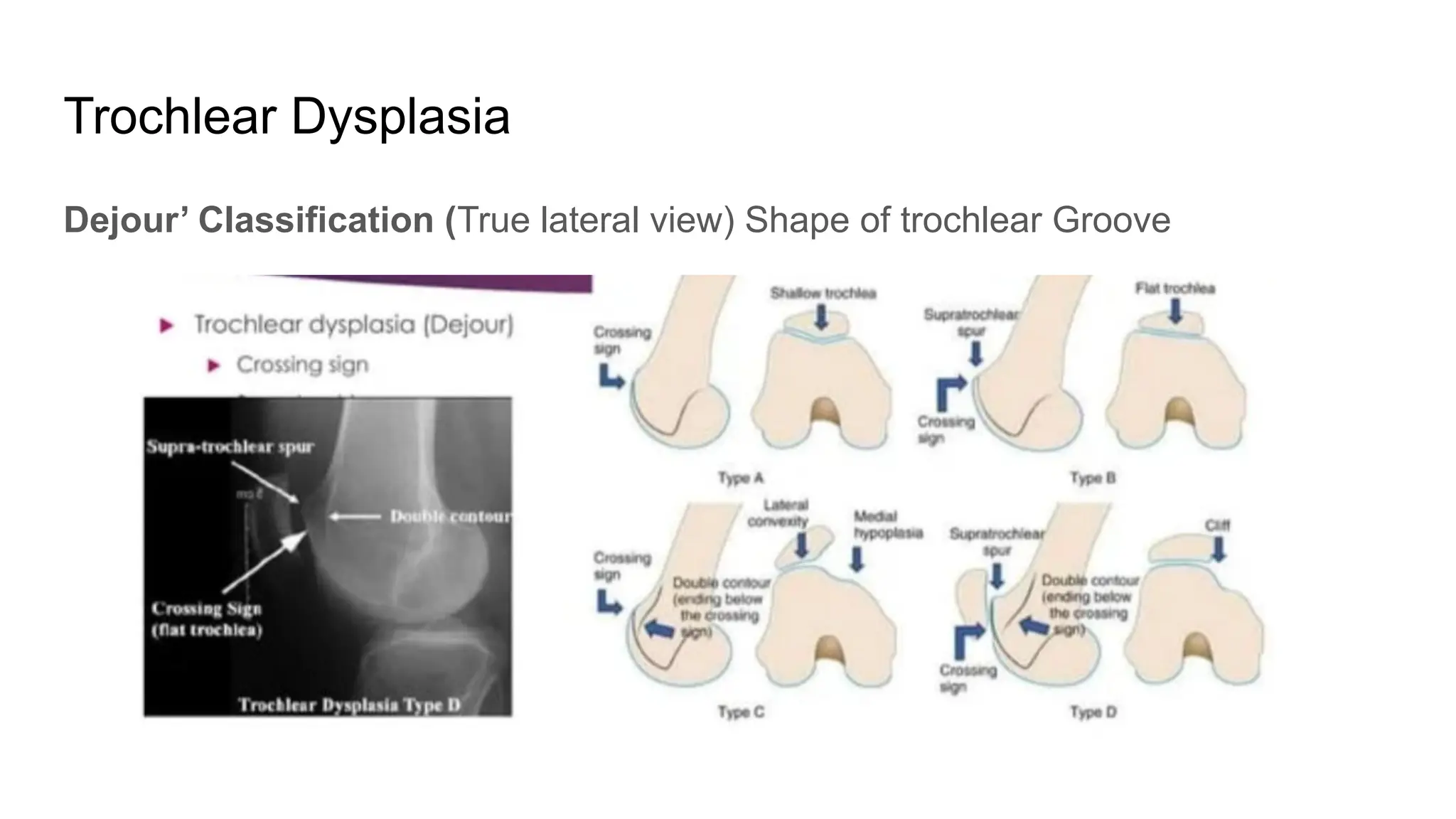
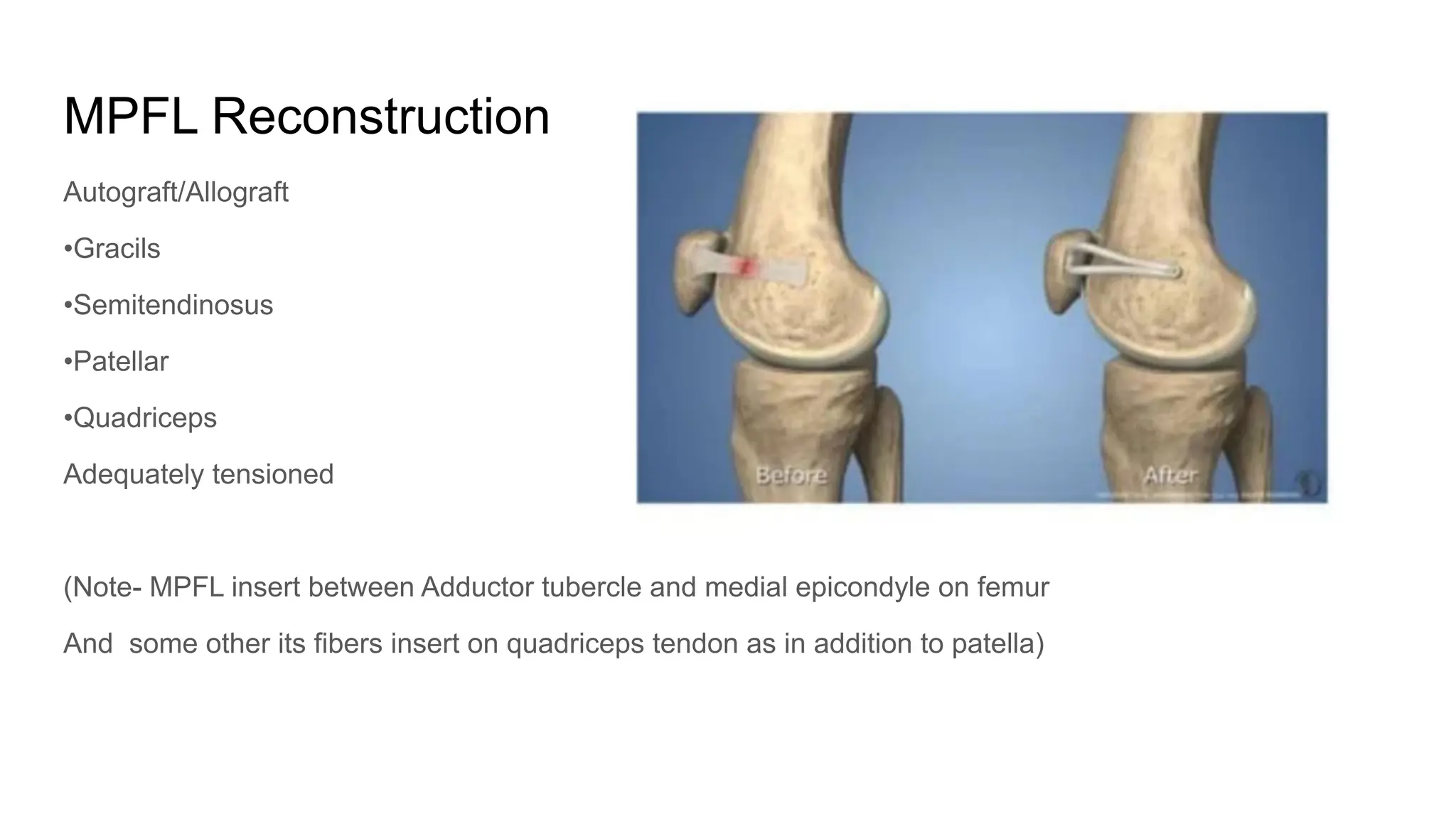
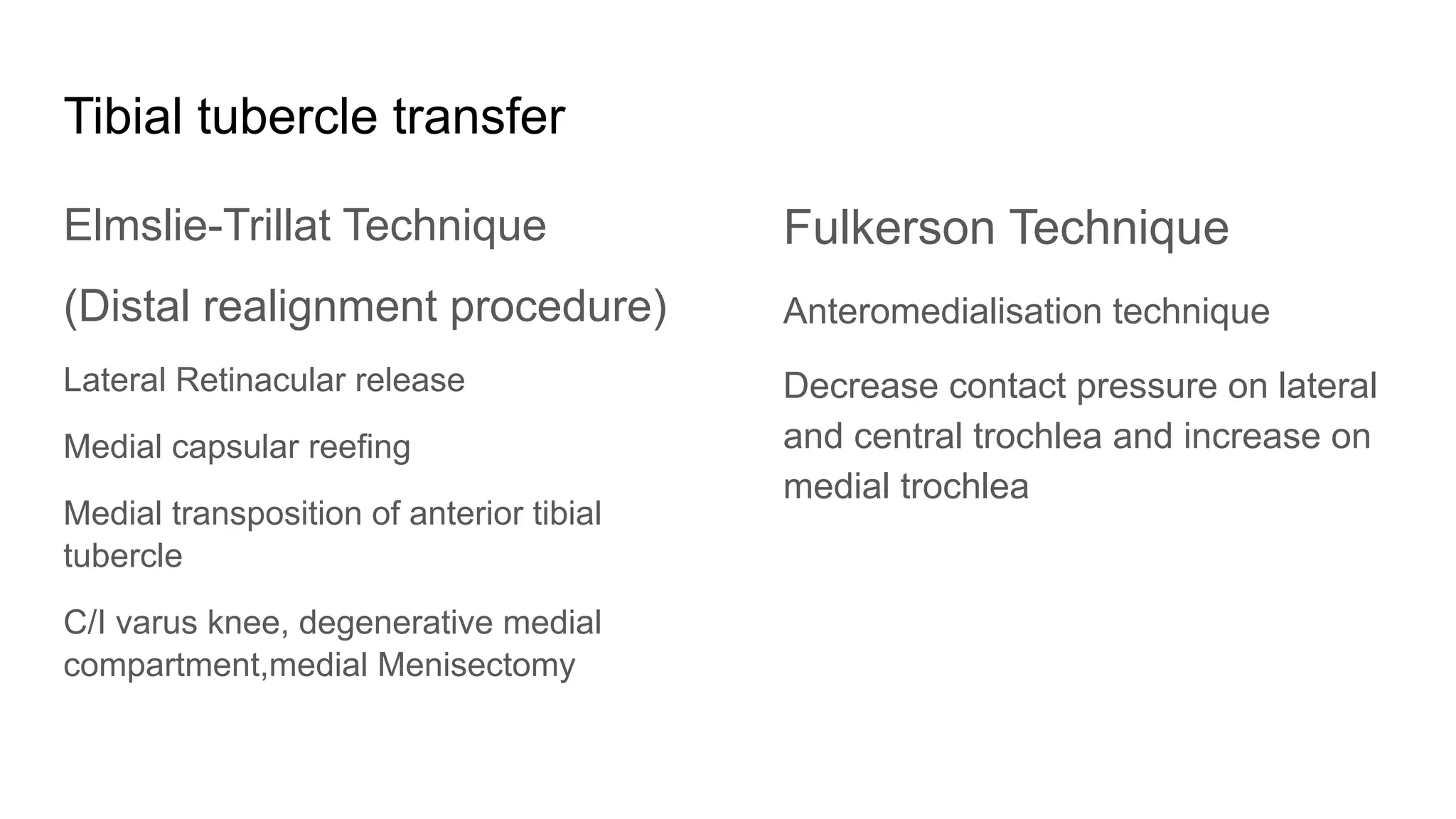
The document discusses patellar instability, including its high recurrence rate and various risk factors such as ligamentous laxity and anatomical abnormalities. It covers classification of instability types, examination techniques, diagnostic imaging, and treatment strategies ranging from conservative management to surgical options like MPFL reconstruction. A systematic review indicates that while surgery can lower the rate of recurrent dislocation, it may not significantly improve functional outcomes.