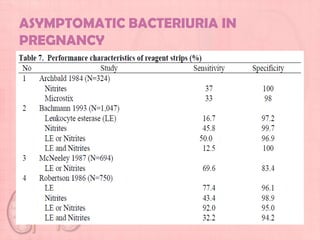
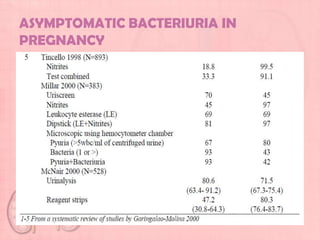
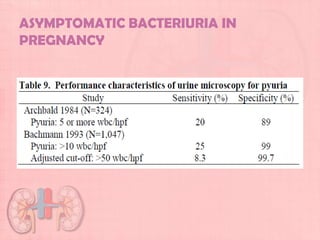
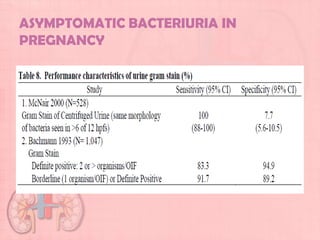
This document provides guidelines for urinary tract infections (UTIs) during pregnancy. It discusses that UTIs are the most common medical complications of pregnancy and are associated with risks like preterm delivery. It outlines recommendations for screening, diagnosing, and treating asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute cystitis, and acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy. Treatment is recommended for asymptomatic bacteriuria to reduce risks, and symptomatic UTIs should be promptly treated with appropriate antibiotics based on culture and sensitivity testing. Post-treatment cultures are advised to confirm resolution of infections.













![ACUTE CYSTITIS IN PREGNANCY
When do you suspect acute cystitis in
pregnancy?
• Acute cystitis is characterized by urinary
frequency, urgency, dysuria and bacteriuria
without fever and costovertebral angle
enderness. Gross hematuria may also be present
[Harris 1984].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utipregnancy-120219111731-phpapp02/85/UTI-in-Pregnancy-19-320.jpg)










![ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS IN PREGNANCY
When is acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy
suspected?
• Urinalysis shows pyuria of > 5 wbc/hpf of
centrifuged urine and bacteriuria of > 10,000 cfu
of a uropathogen/ml of urine [Harris, 1984,
Roberts 1986, Rubin 1992].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utipregnancy-120219111731-phpapp02/85/UTI-in-Pregnancy-30-320.jpg)







