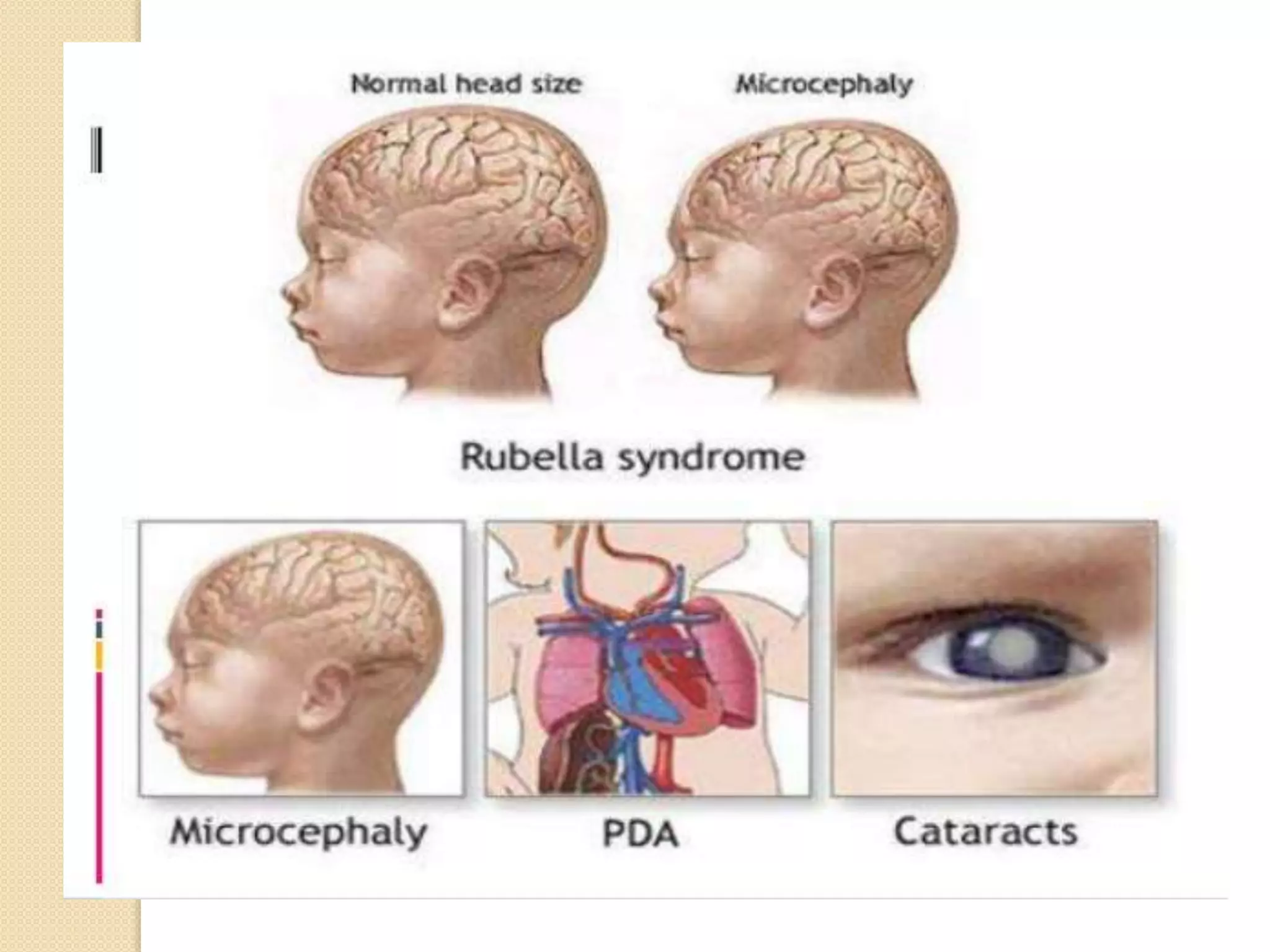
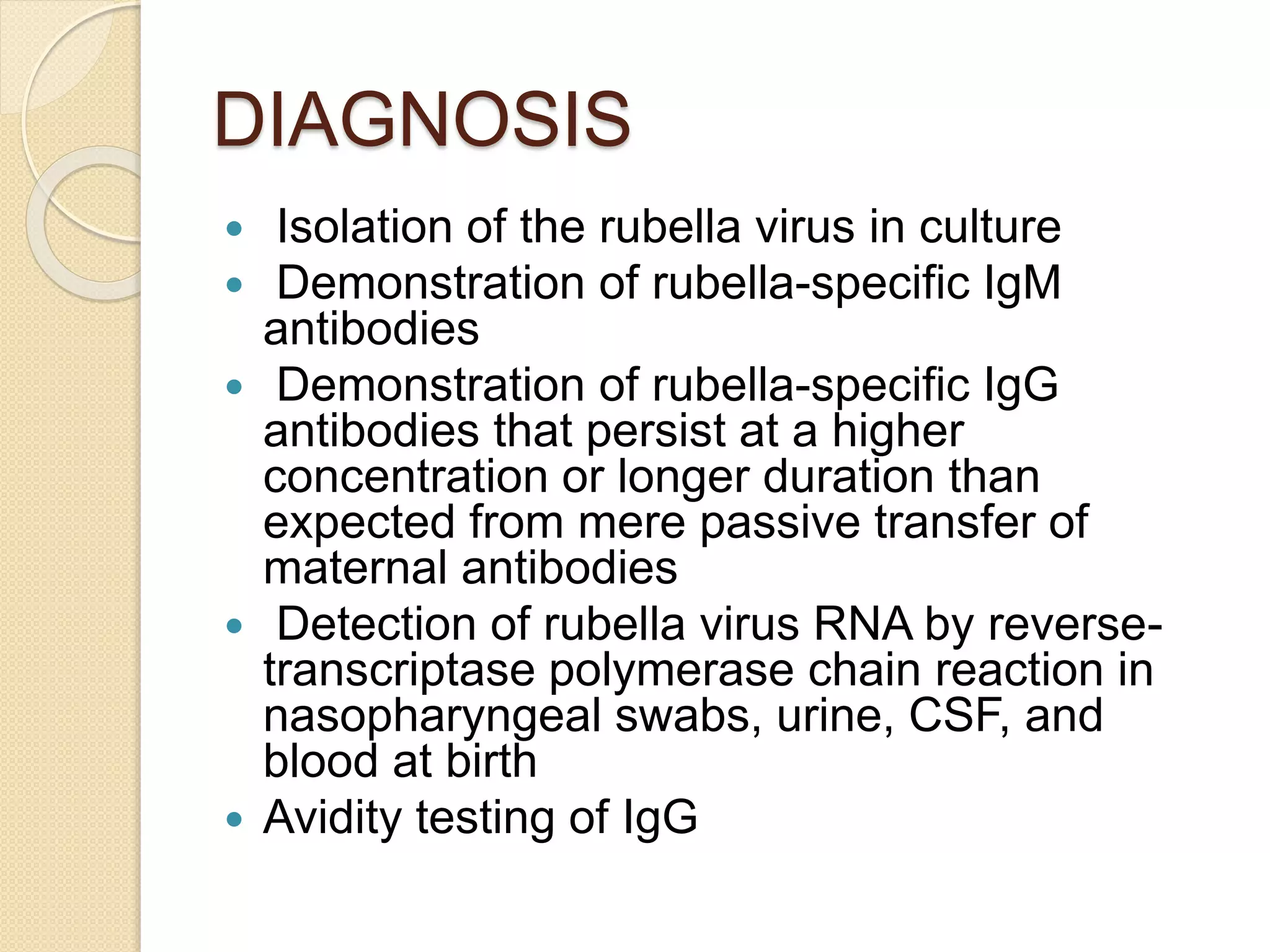
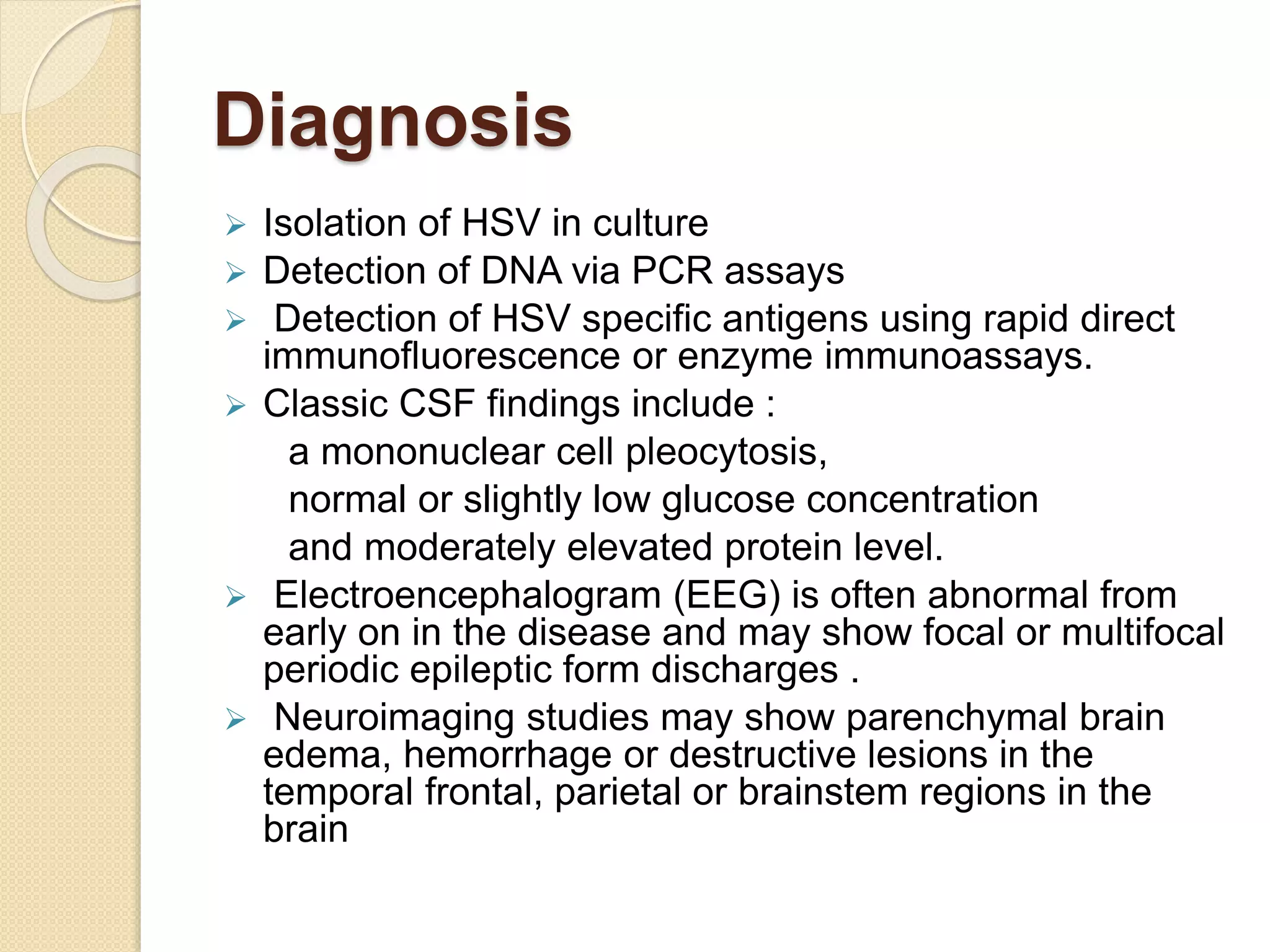
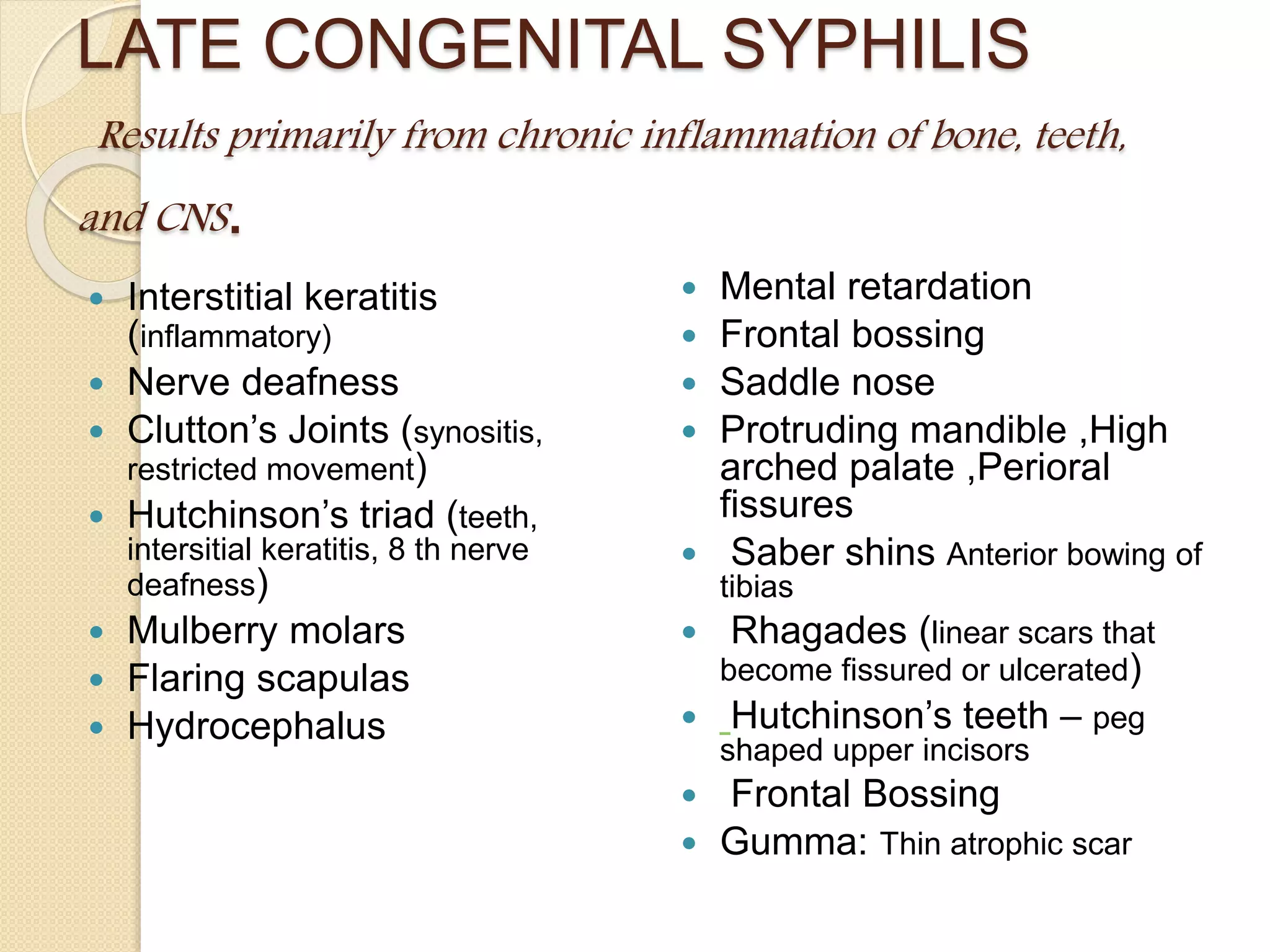
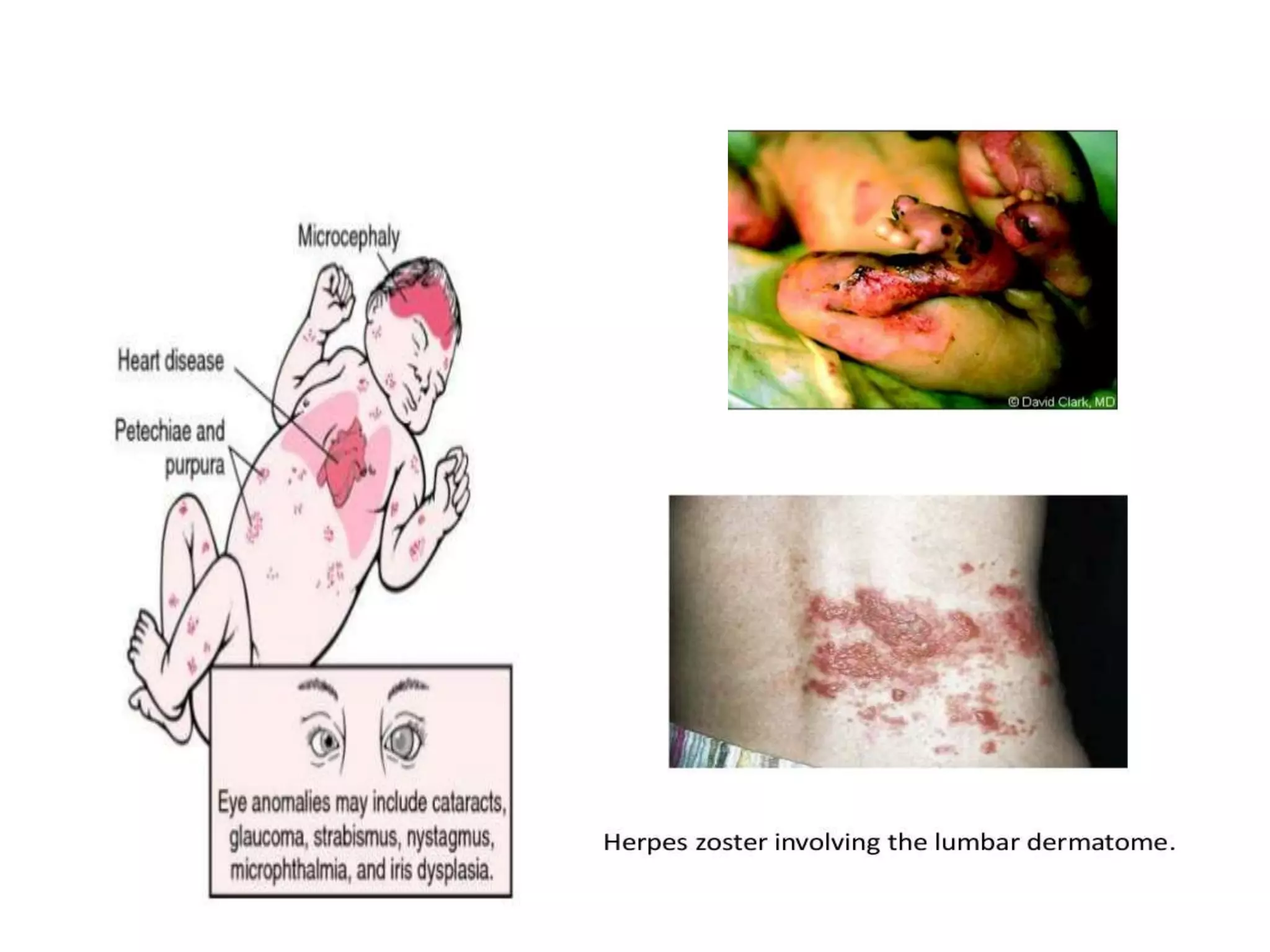
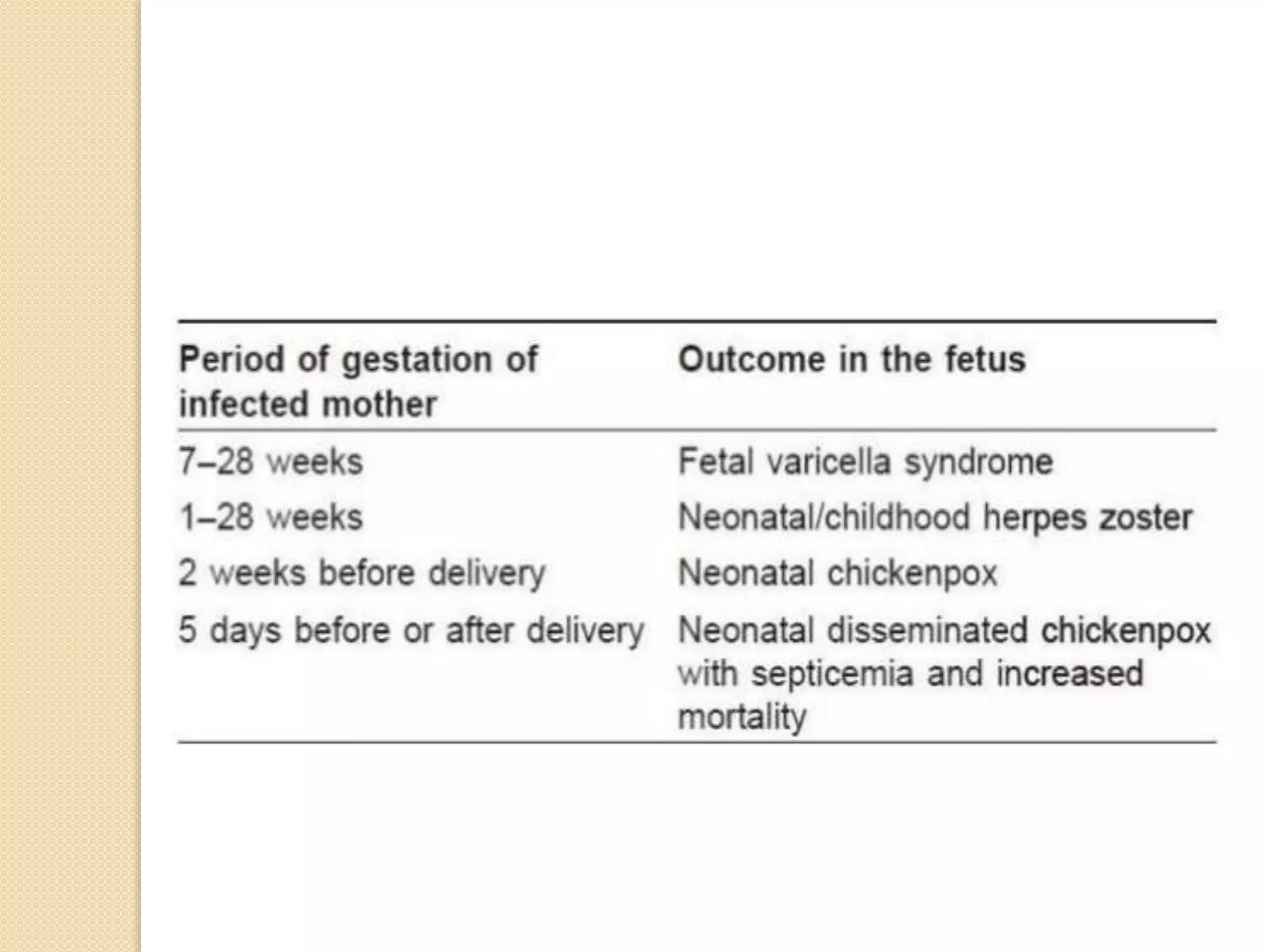
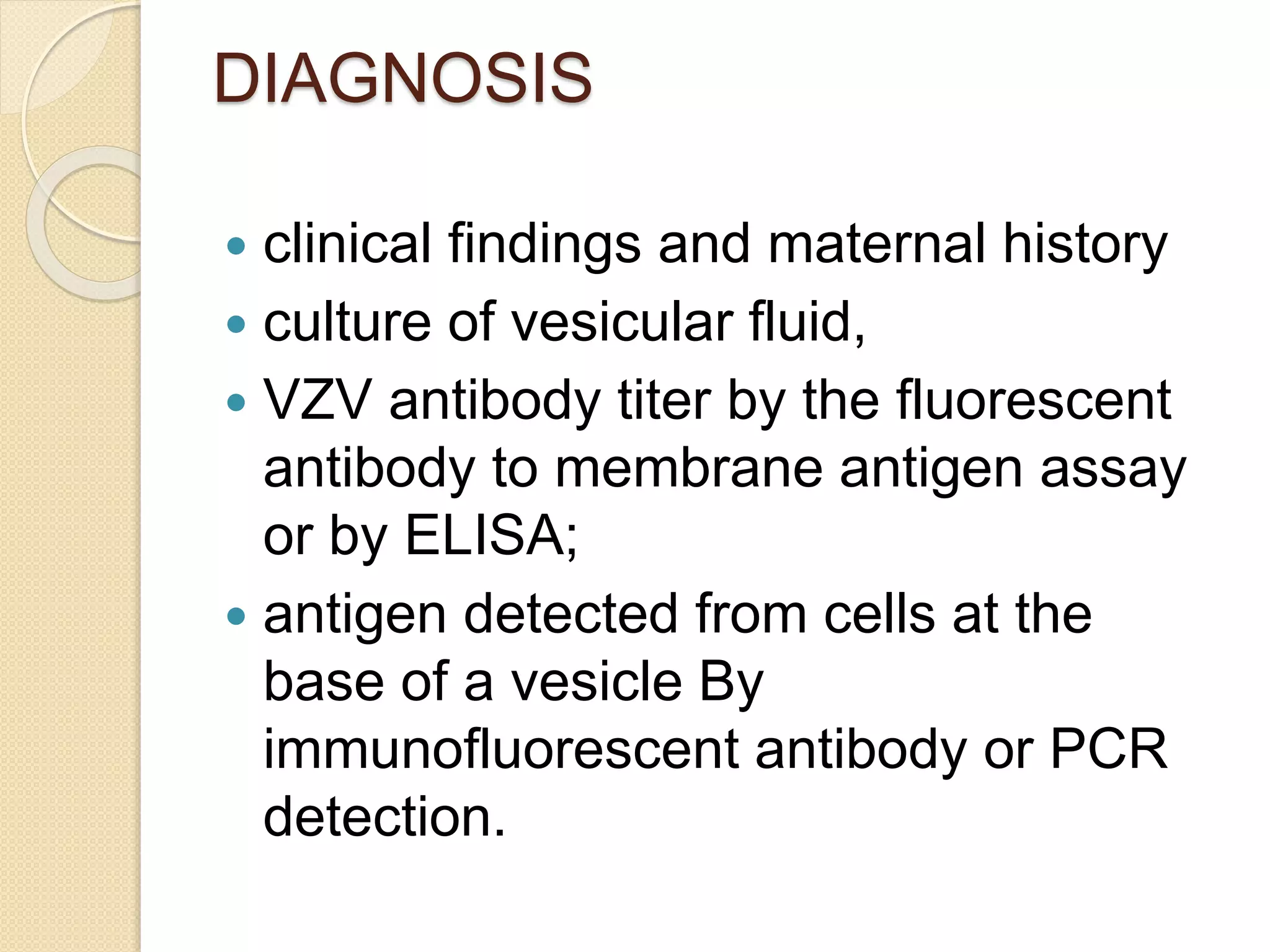
Primary maternal syphilis infection can infect the fetus in utero. Without treatment, fetal infection risks include stillbirth, premature birth, low birthweight, and neonatal death. Fetal infection may also cause deformities of the nose, long bones, and teeth. Diagnosis involves maternal and fetal serology, with treatment of pregnant women and neonates with penicillin to prevent transmission and morbidity.