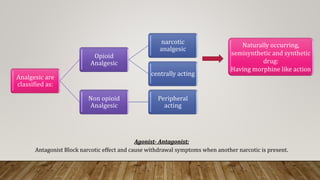
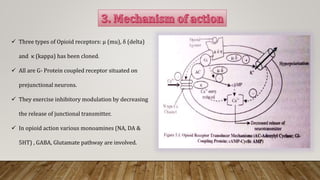
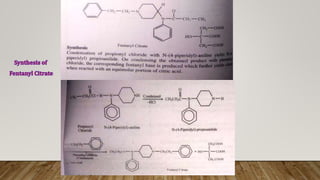
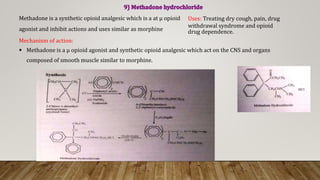
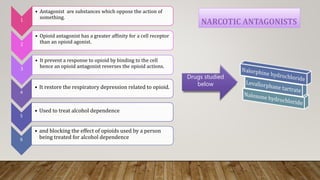
This document provides an overview of non-narcotic analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents. It begins by classifying analgesics as either opioid or non-opioid. It then discusses the mechanisms of action of various opioid analgesics like morphine, codeine, and meperidine. It provides details on their uses, pharmacology, and mechanisms of binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system. The document also covers opioid antagonists like nalorphine and levallorphane that are used to reverse the effects of opioid overdose.