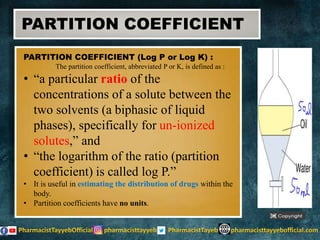
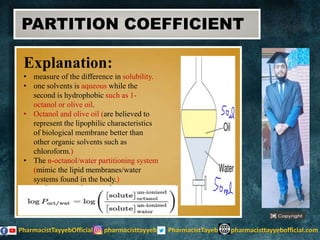
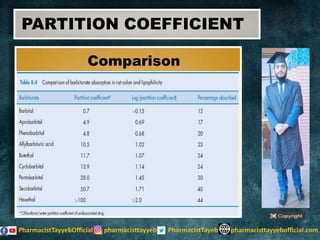
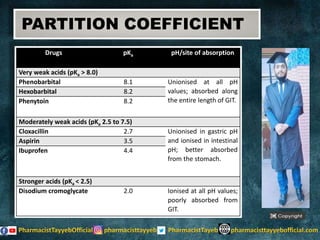
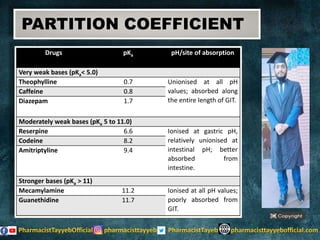
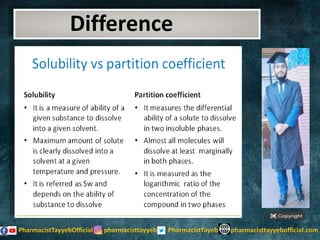
The document discusses the partition coefficient (log P), which measures the solubility of un-ionized solutes between aqueous and hydrophobic solvents, and its relevance in drug distribution within the body. It summarizes methods for measuring the partition coefficient, its limitations, and applications in predicting drug solubility, absorption, and release from pharmaceutical formulations. Additionally, it provides examples of various drugs categorized by their strength as acids or bases related to their absorption characteristics.