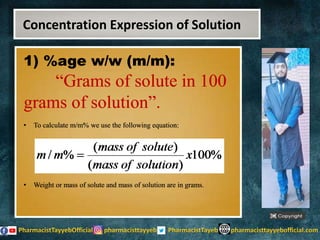
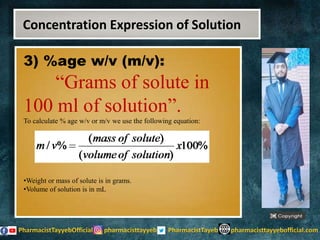
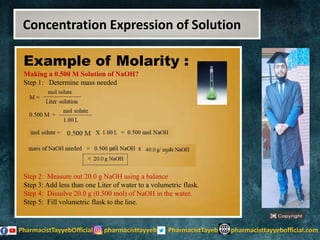
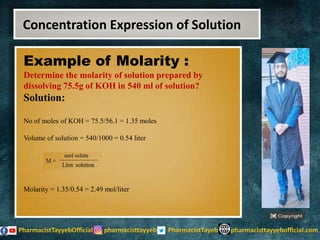
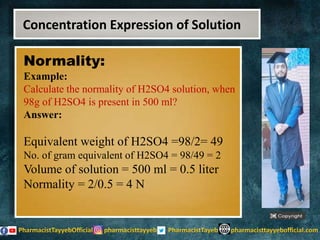
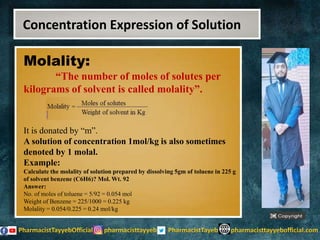
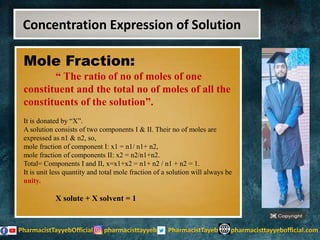
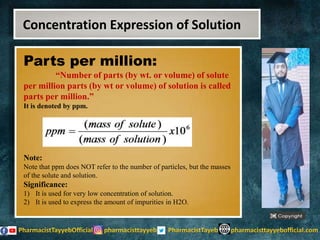
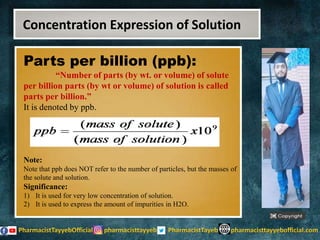
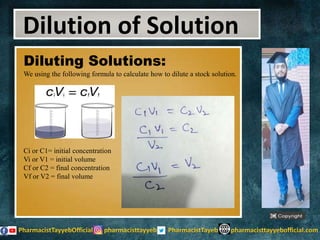
The lecture discusses the principles of solution concentration, defining terms such as dilute and concentrated solutions, and various methods of expressing concentration, including percentage, molarity, normality, and molality. It provides explanations and examples for each concentration expression type along with techniques for diluting solutions. The lecture concludes with a reminder to subscribe for further content and specifies its completion.