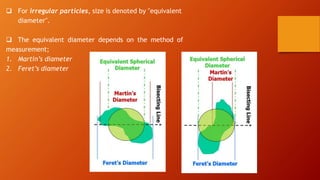
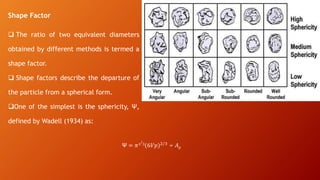
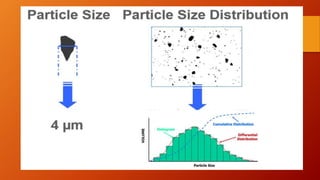
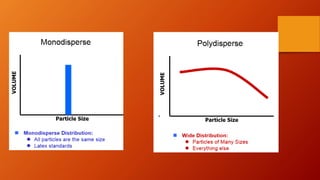
This document discusses particle size distribution (PSD), which is a list or function that defines the relative amounts of particles sorted by size. It explains that PSD is important for industries like pharmaceutical, chemical, ceramics, etc. It describes different size terminology used like micrometers and nanometers. It also discusses different ways to measure particle size based on volume, weight or area. Finally, it provides examples of analytical distribution functions used to model PSD like normal, log-normal and Weibull distributions.