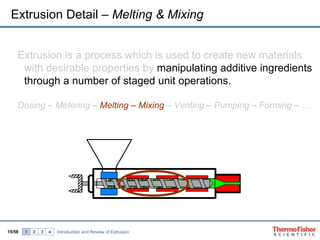
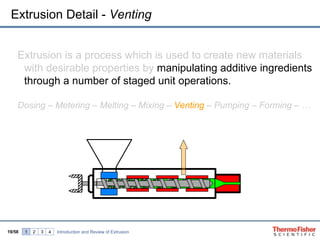
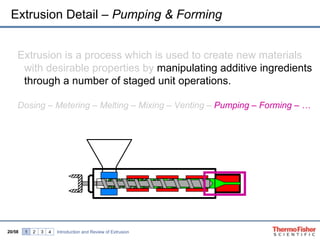
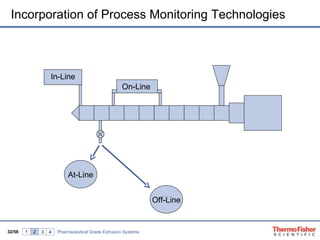
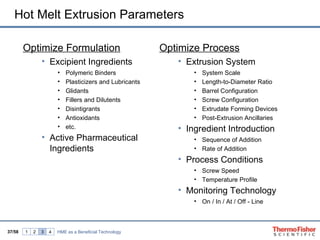
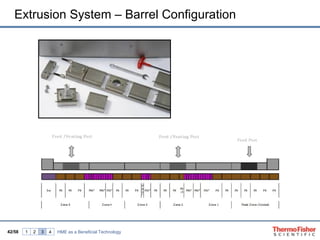
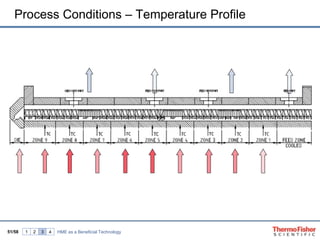
The document discusses hot melt extrusion technology for pharmaceutical applications. It provides an overview of extrusion systems and processes, including different types of extruders and their components. Hot melt extrusion is described as a beneficial processing technology for manipulating ingredients to create materials with unique properties. Key benefits of hot melt extrusion for pharmaceuticals include enhanced solubility, bioavailability and specific drug release characteristics of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Process parameters and considerations for optimizing hot melt extrusion are also reviewed.