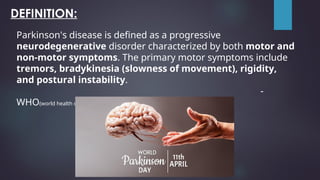
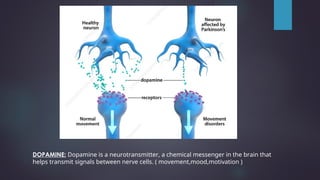
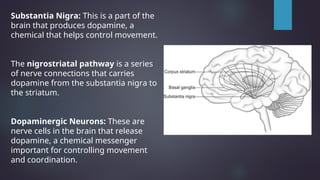
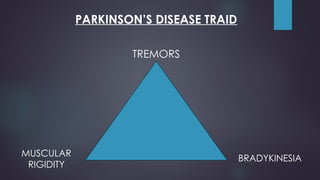
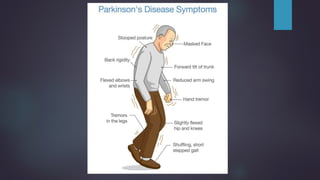
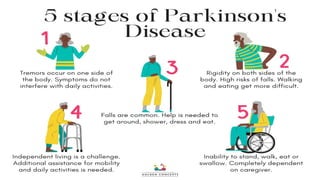
Parkinson's disease, named after Dr. James Parkinson who first described it in 1817, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. It is caused by factors such as loss of dopamine neurons, genetic mutations, and neuroinflammation, affecting approximately 9.3 million people worldwide as of 2023. Management includes pharmacological treatments like levodopa, non-pharmacological therapies like physical therapy, and surgical options such as deep brain stimulation.
![PARKINSON’S
DISEASE
PRESENTED BY :
Ms. Yashaswini Hiremath
2nd
year B.Sc. Nursing
BBC College of Nursing Gangavathi
SUPERVISED BY:
Mr. George.D. Honnalli M.Sc.[N]
HOD, Dept of Medical Surgical Nursing
BBC College of Nursing Gangavathi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/75/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-1-2048.jpg)




![RISK FACTORS:
Age: Over 60 years old
Genetics: Family history
Gender: More common in men
Environmental Factors: Exposure to
toxins[pesticides]
Head Injury: Previous severe head trauma
Other Conditions: Associated conditions like
depression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/85/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-8-320.jpg)


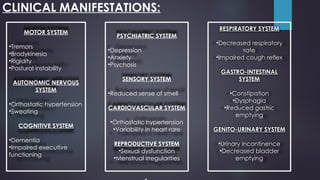
![DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATIONS:
• Medical history
• Physical examination
• Neurological assessment
• Positron Emission Tomography[PET] scan
• Dopamine transporter [DaT] scan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/85/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-16-320.jpg)

![Positron Emission Tomography
NOTE:
DOPA: DOPA in a PET scan it is a
radiotracer, used to visualize
dopamine synthesis and
metabolism in the brain
CFT: CFT [carbomethoxy
fluorophenyl tropane] in PET scans
is a radiotracer that binds to
dopamine transporters to image
and study the dopaminergic
system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/85/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-18-320.jpg)
![DaT scan :
A DaT Scan examines the integrity of the dopamine system by
scanning the brain after injection of a dye
[IODINE-123/I-123LOFLUPANE]
through the vein and watching it bind to the neurons that secrete
dopamine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/85/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-19-320.jpg)
![MANAGEMENT:
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMEMNT
•Anti-parkinsonian medications : Levodopa + carbidopa.
•Dopamine Agonists: Bromocriptine mesylate and Pergolide .
•Monoamine Oxidase B inhibitor: selegiline[Eldepryl] and Rasagiline[Azilect].
•Catechol O-methyltransferase inhibitor: Tolcapone and Entacapone.
•Anti- cholinergics : Benztropine [Cogentin] , Trihexyphenidyl, Cycrimine
Procyclidine.
•Glutamate blocking drugs: Amantadine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonsdisease-240823124930-92e575ae/85/PARKINSON-S-DISEASE-ppt-20-320.jpg)