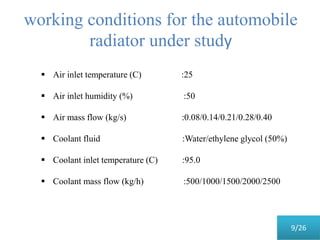
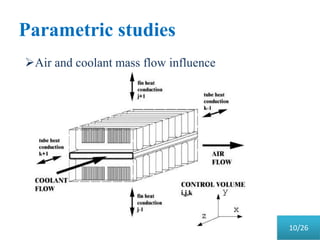
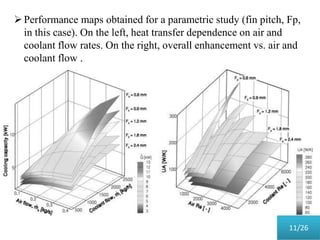
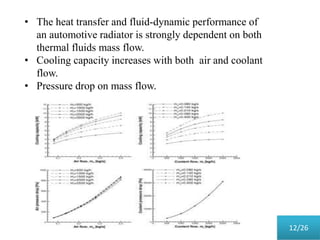
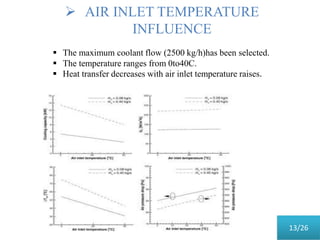
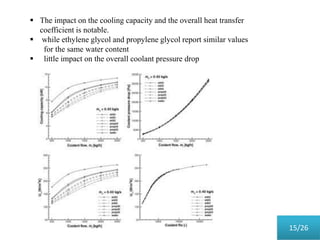
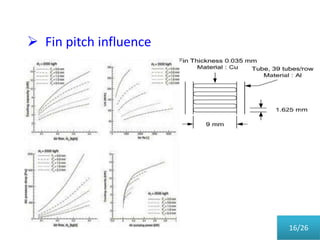
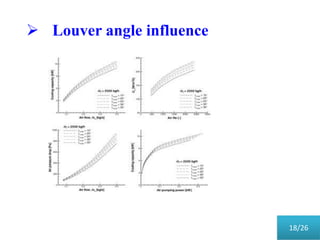
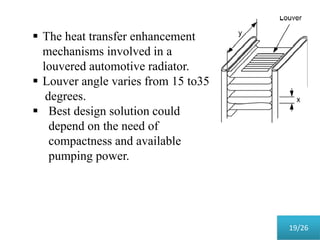
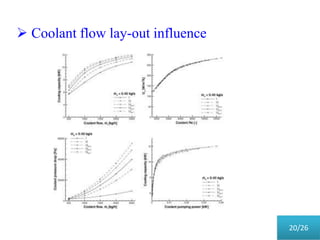
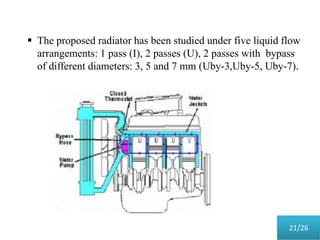
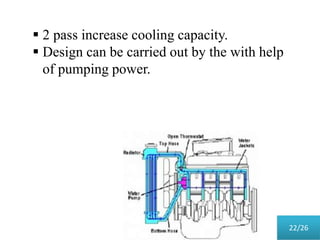
This document presents a parametric study on automotive radiators. It discusses the importance of cooling engines and describes the types and geometry of radiators. It then examines the effects of varying air and coolant mass flow, air inlet temperature, coolant type, fin pitch, louver angle, and coolant flow layout on the radiator's performance. The studies show that heat transfer and cooling capacity increase with higher air and coolant flows. Coolant type, fin pitch, louver angle, and flow layout also impact radiator efficiency. The document concludes that parametric studies help design high performance radiators and that heat exchange depends on temperature gradients between the radiator and inlet air.