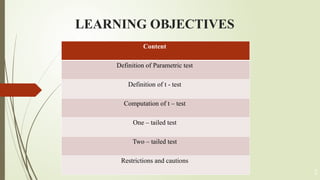
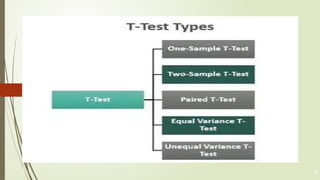
The document discusses the parametric student’s t-test, which is a statistical tool for comparing the means of two groups to determine if they are significantly different. It outlines the definition, types (one-sample, unpaired two-sample, paired t-test), and requirements (normal distribution, interval/ratio data) for conducting the test, as well as the importance of transformation for non-normal data. The content emphasizes the need for correct application and understanding of the test's assumptions for accurate results.