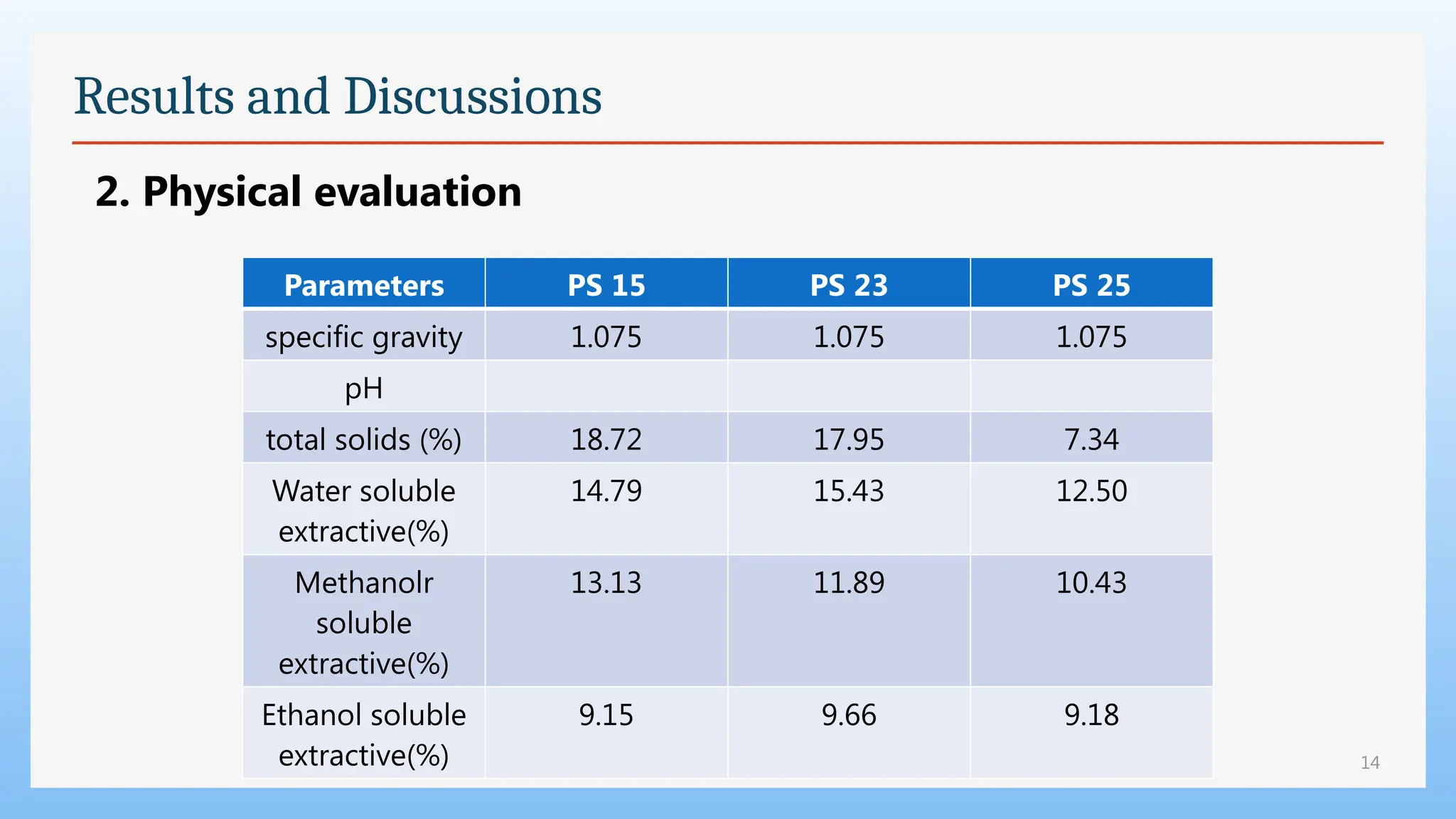
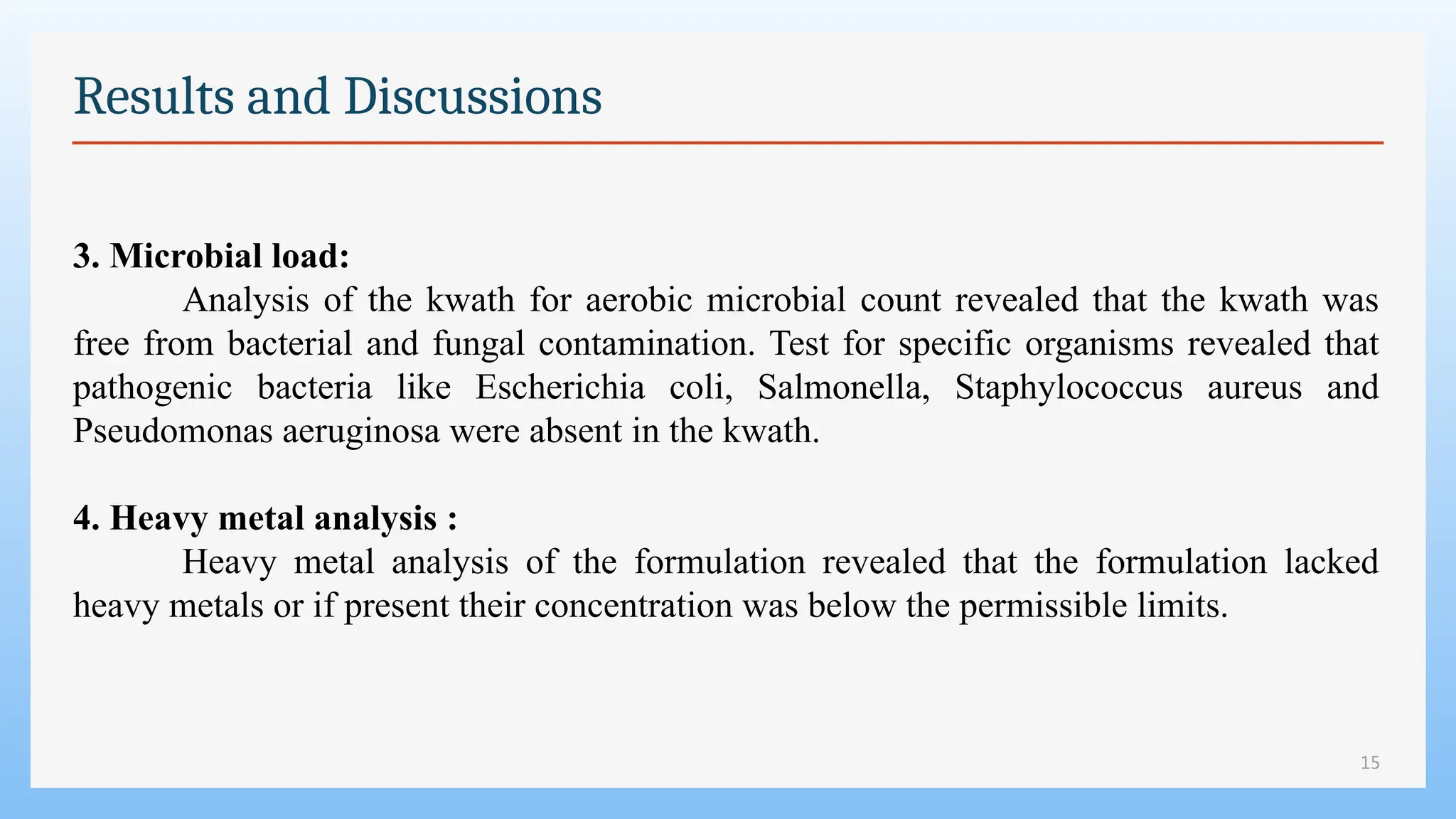
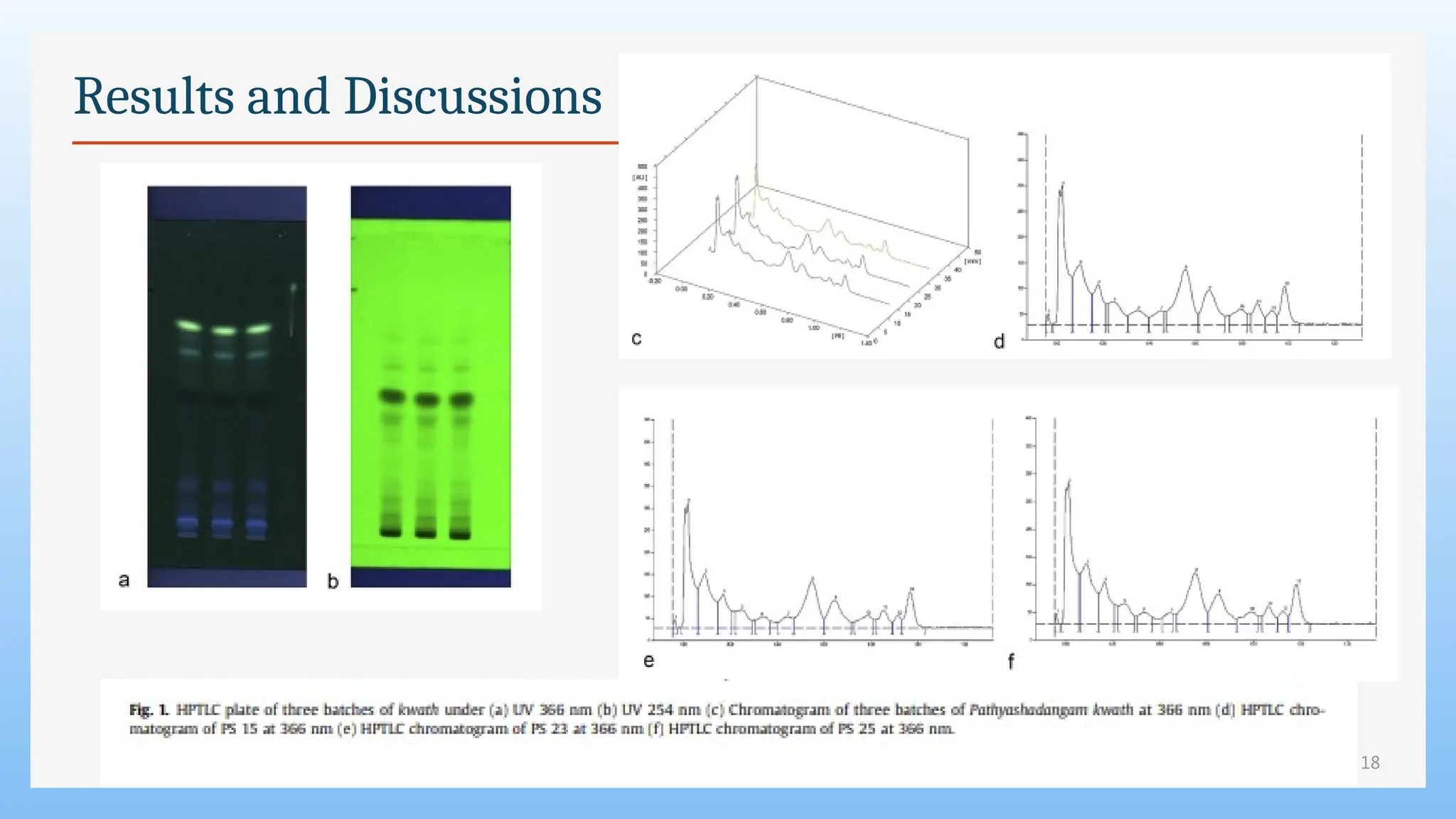
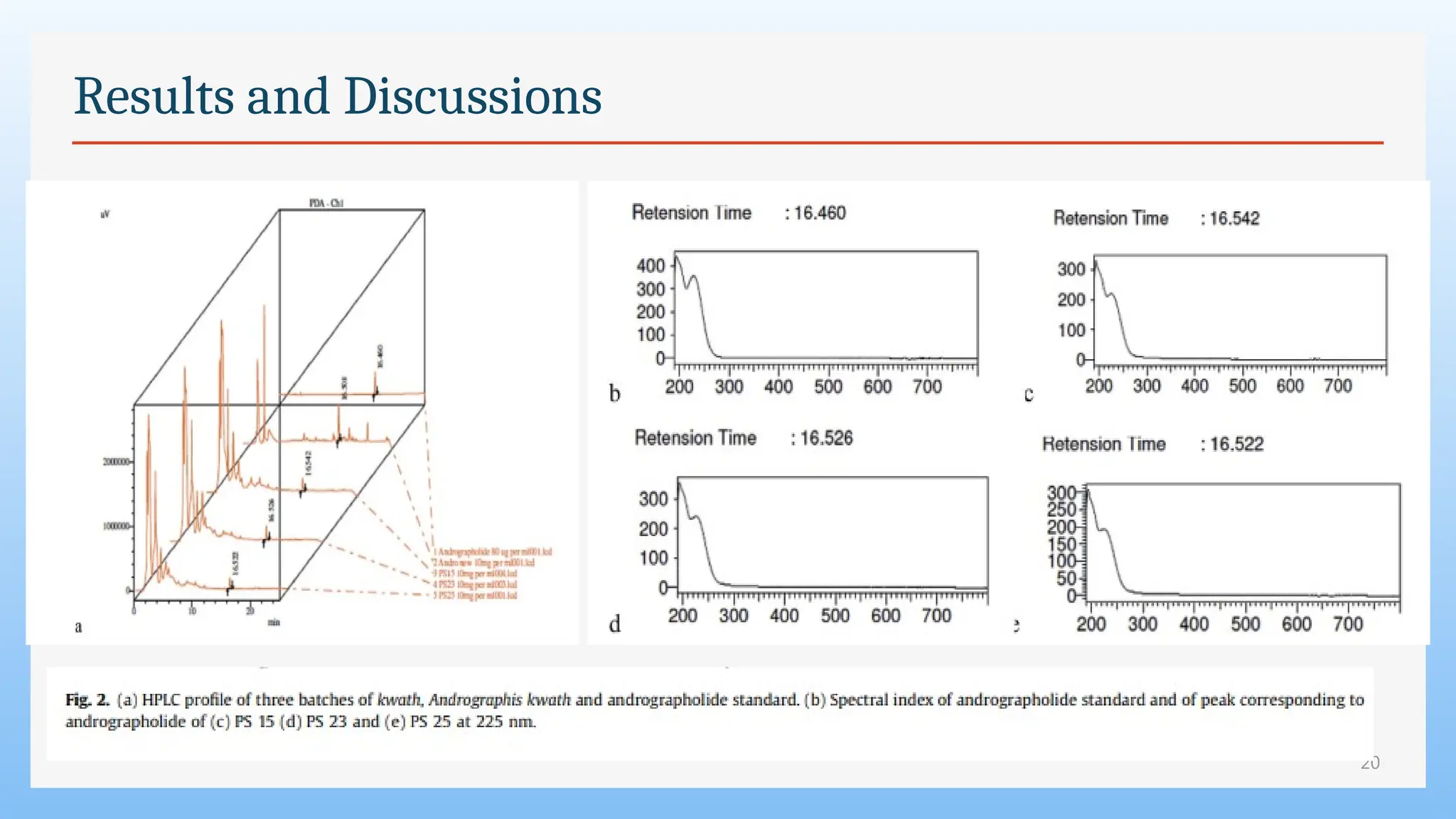
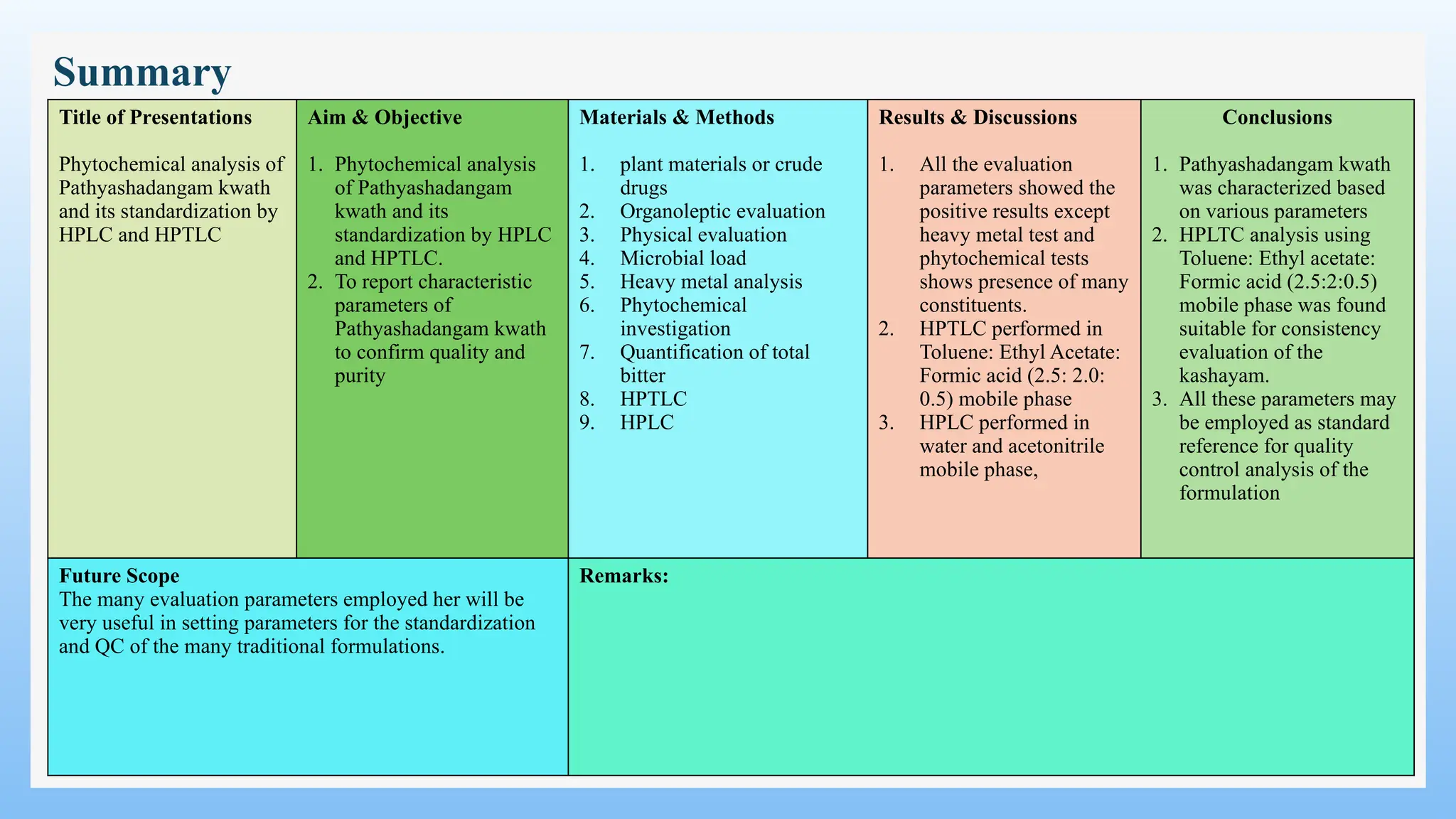
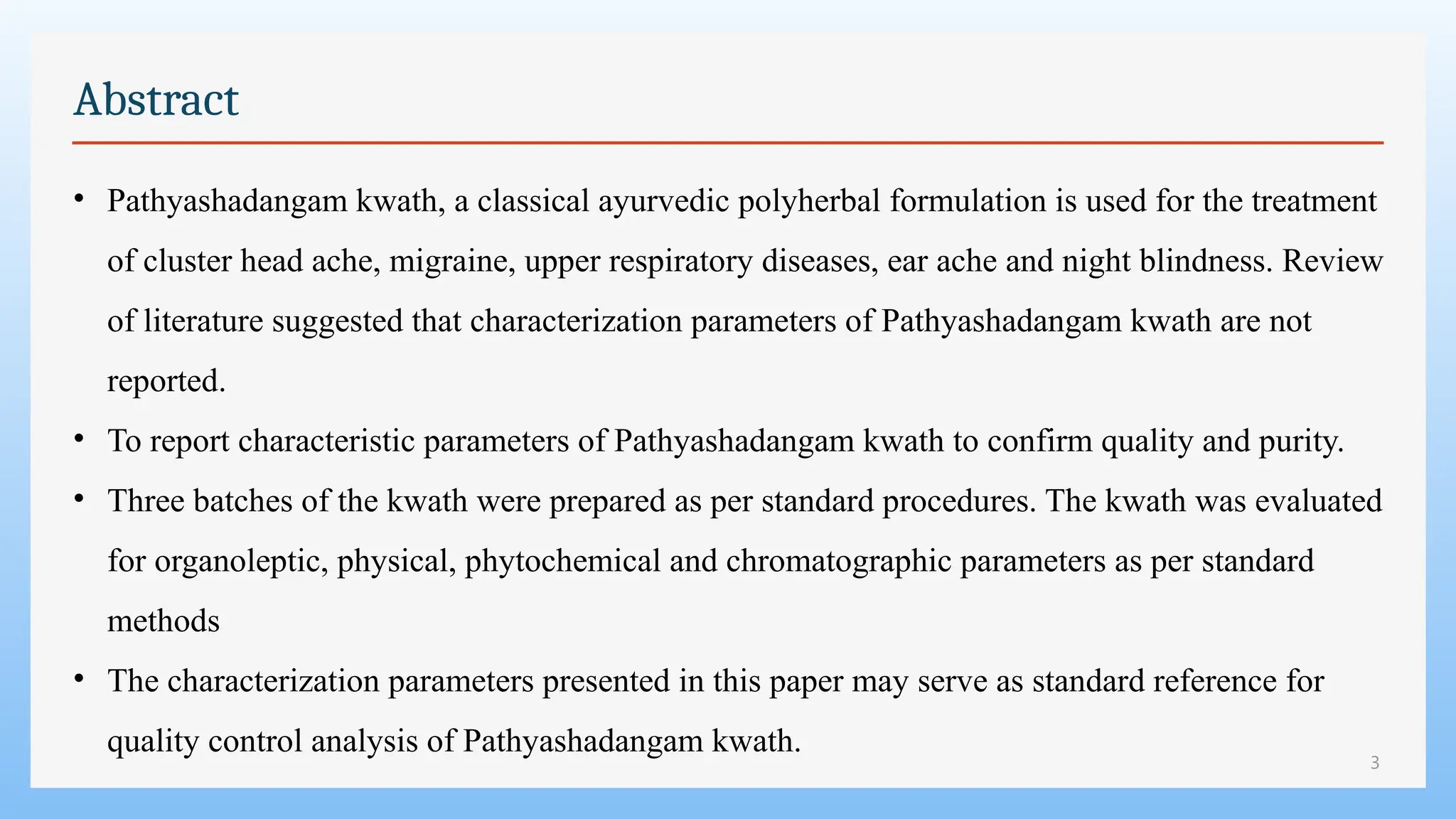
The study focuses on the phytochemical analysis and standardization of Pathyashadangam Kwath, an Ayurvedic polyherbal formulation used to treat various ailments. Characterization parameters, including organoleptic, physical, microbial, heavy metal, and chromatographic analyses were performed to confirm its quality and purity. The results indicated that the formulation is free from microbial contamination and heavy metals, with consistent phytochemical properties, establishing a standard reference for quality control.








![12
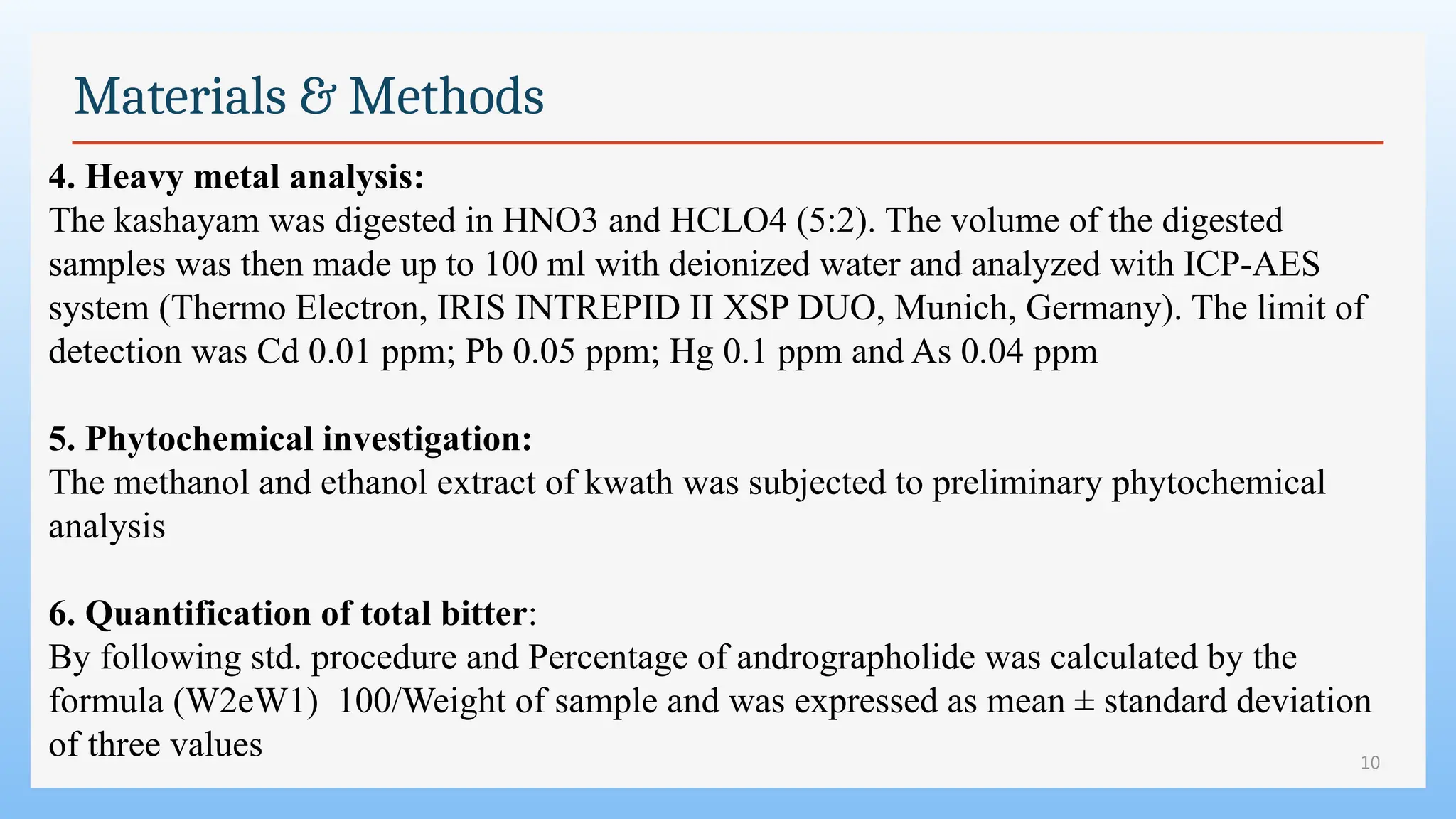
Materials & Methods
7. HPLC:
• The methanol extract of the kashayam was subjected to HPLC using
andrographolide as marker.
• A kashayam was prepared excluding all ingredients of Pathyashadangam kashayam
other than A. paniculata
• The HPLC analysis was carried out using Luna 5u C18 analytical column (250 4.6
mm), Shimadzu LC-10 AT vp binary pump and SPD-M10A vp photo diode array
detector (PDA).
• The mobile phase consisted of water (A) and acetonitrile (B). The elution condition
was 0-25 min, 20%-55% B [14]. The injection volume was 20 ml and flow rate was
1 ml/min. UV spectral range was 190 nm - 400 nm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swapniljournal2-250101082948-930cb4d0/75/Phytochemical-analysis-of-Pathyashadangam-kwath-and-its-standardization-by-HPLC-and-HPTLC-12-2048.jpg)