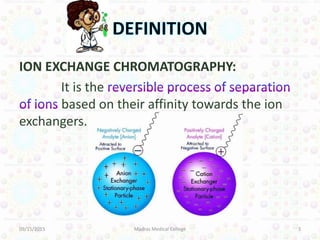
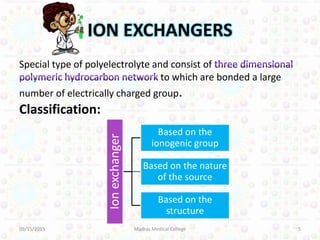
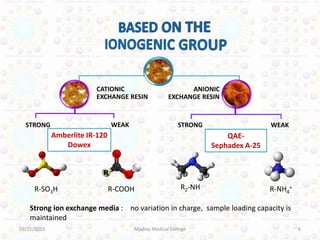
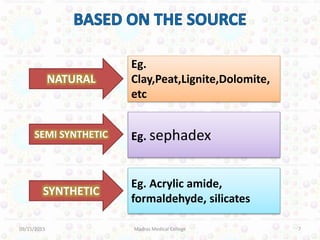
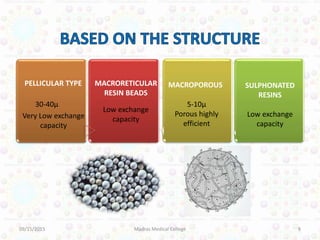
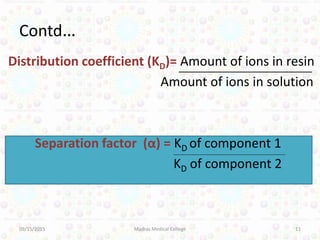
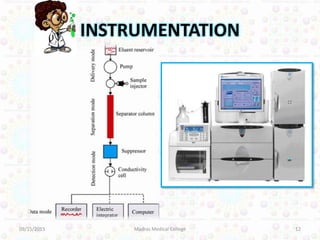
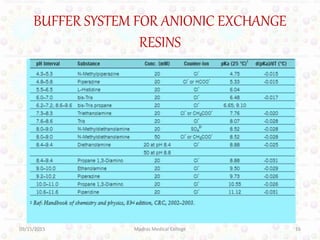
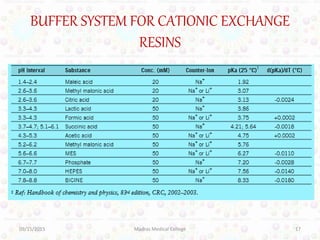
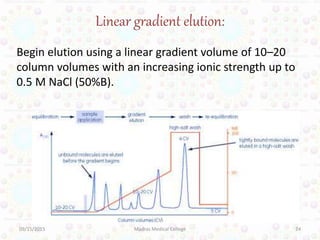
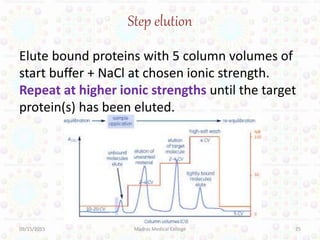
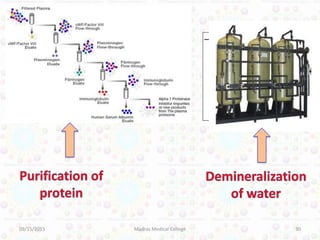
Ion exchange chromatography is a technique for separating ions and molecules based on their affinity for ion exchange resins. These resins consist of an insoluble matrix with ionizable functional groups attached. Separation occurs as molecules exchange ions with the resin based on properties like charge and pH. Ion exchange chromatography has applications in water softening, amino acid separation, and purification of reagents and metals.