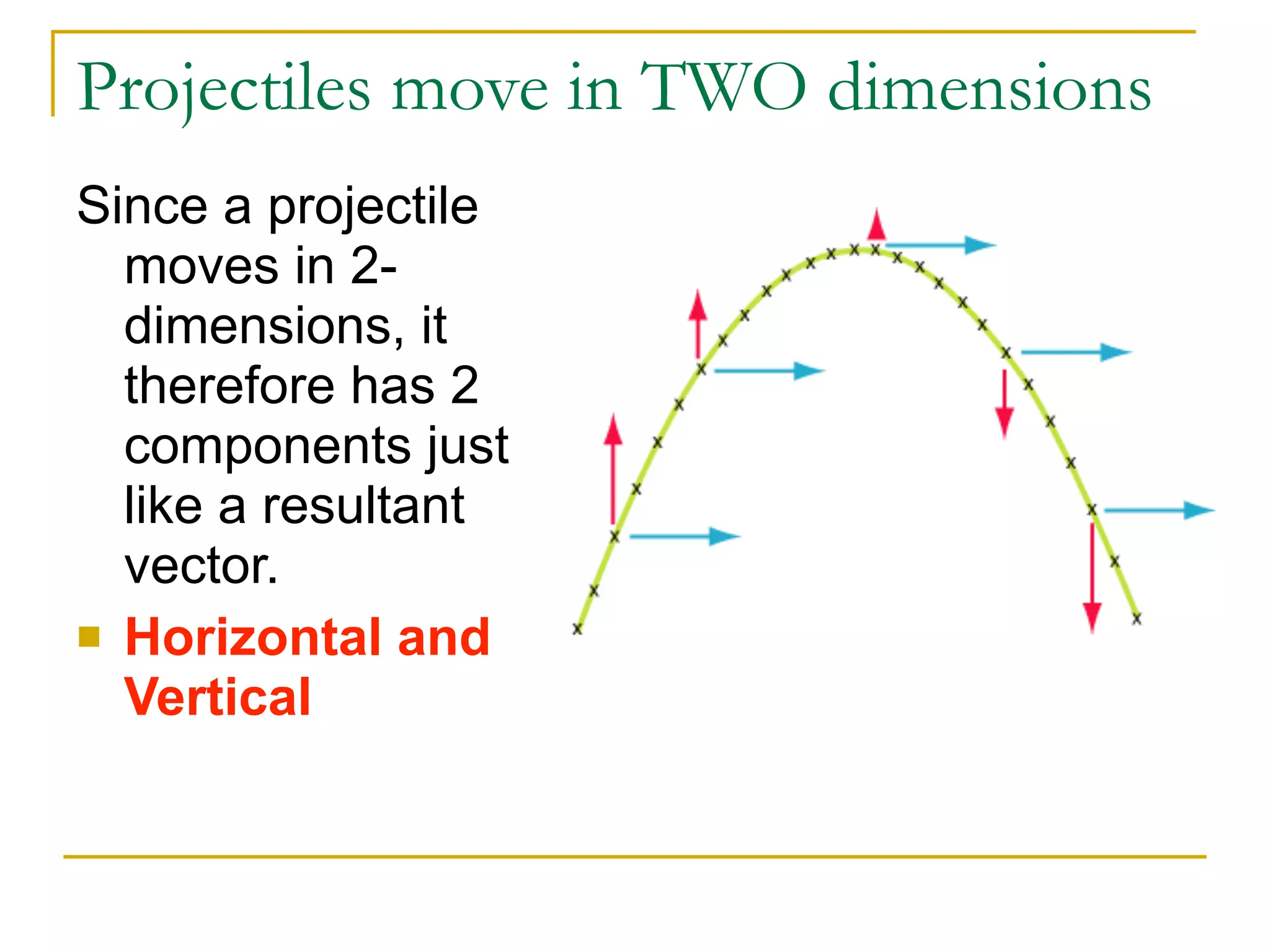
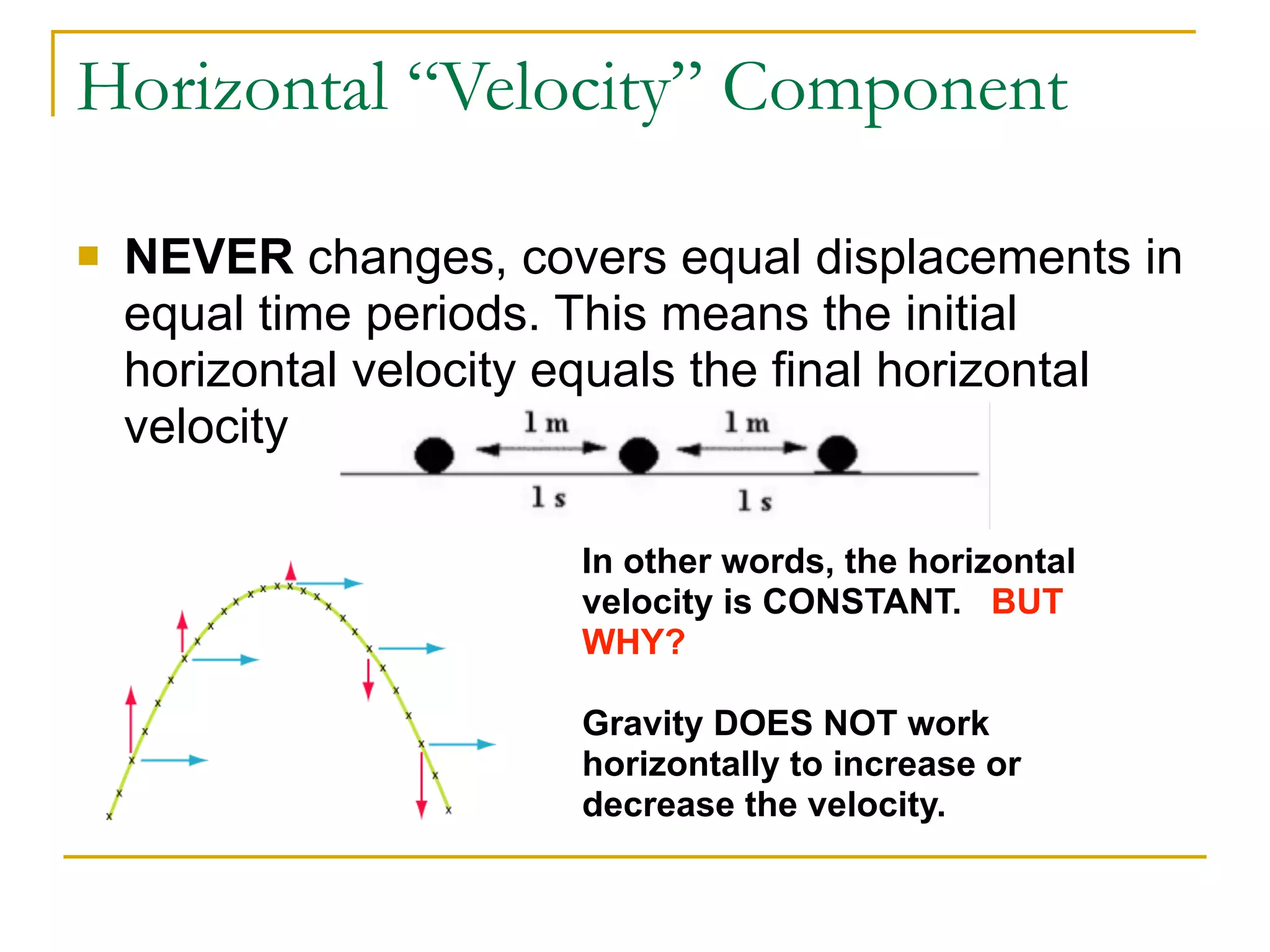
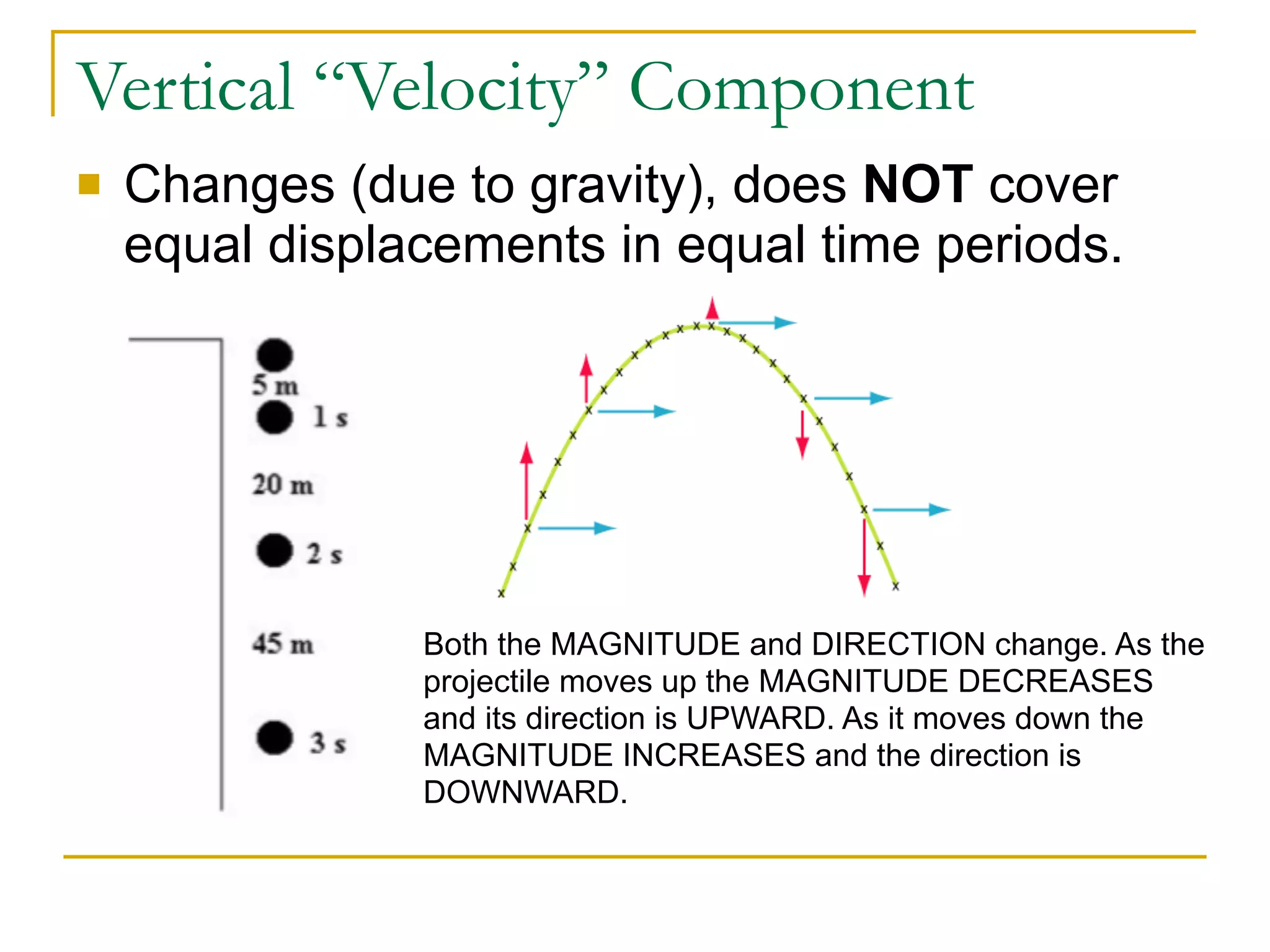
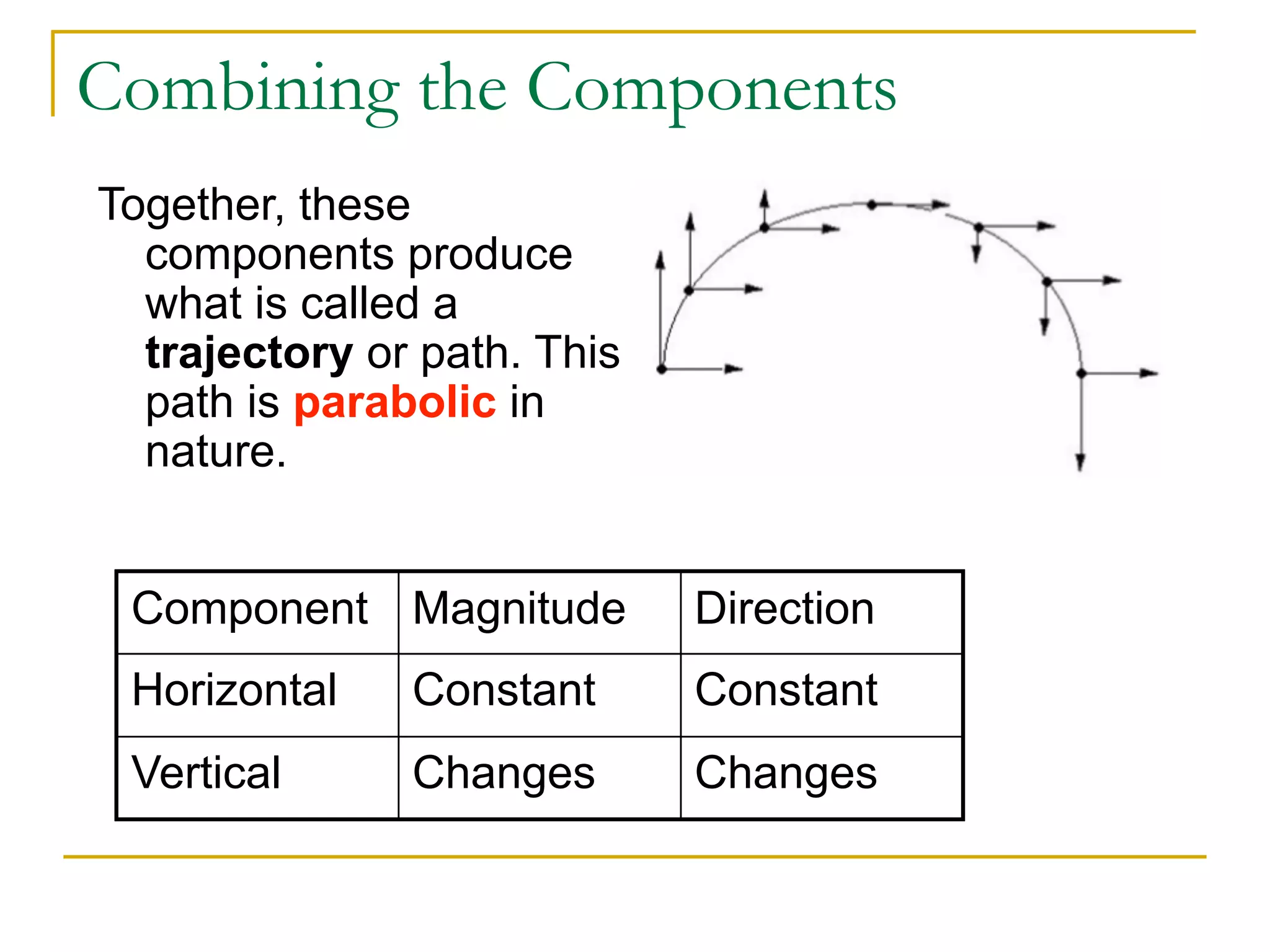
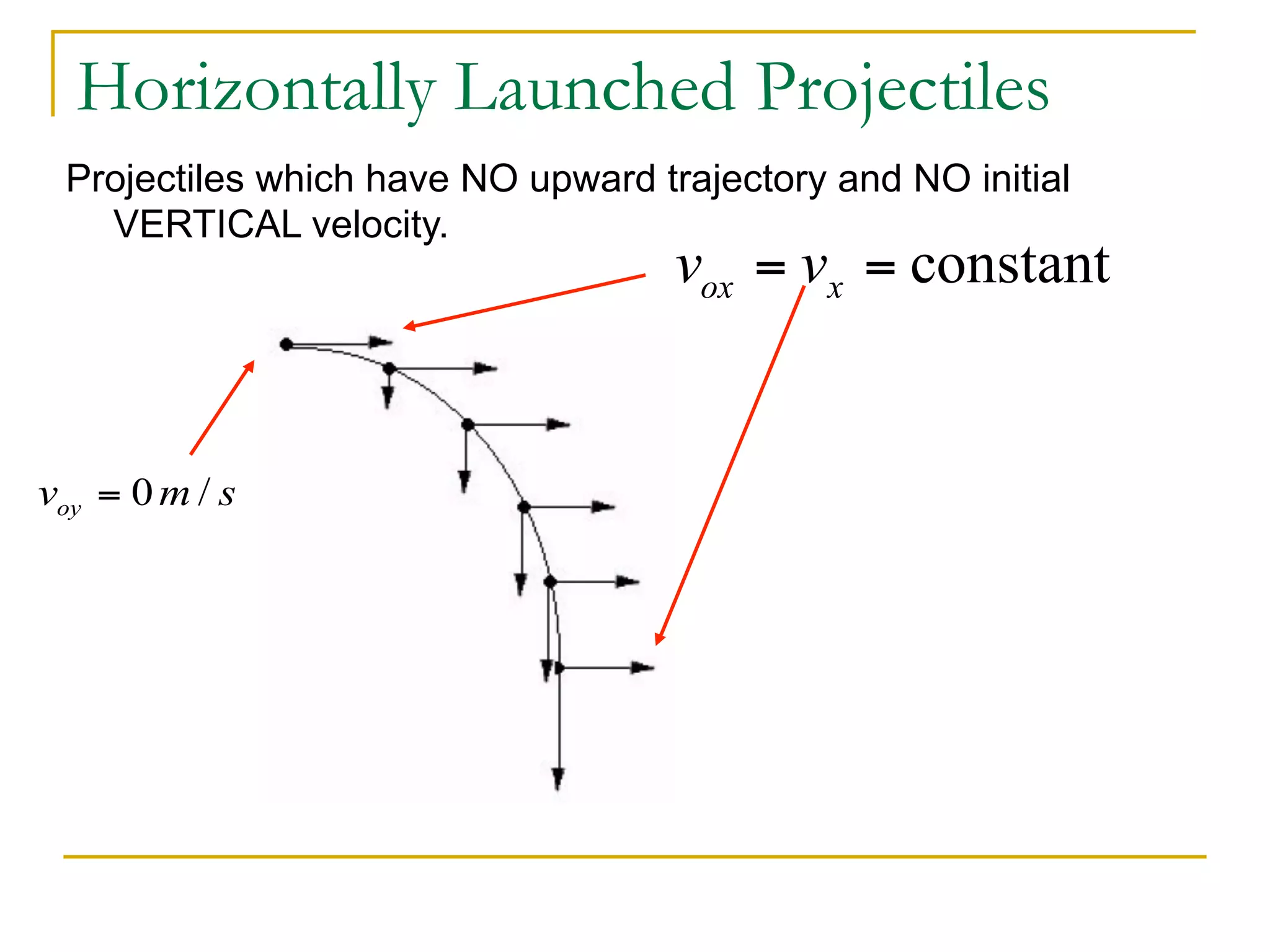
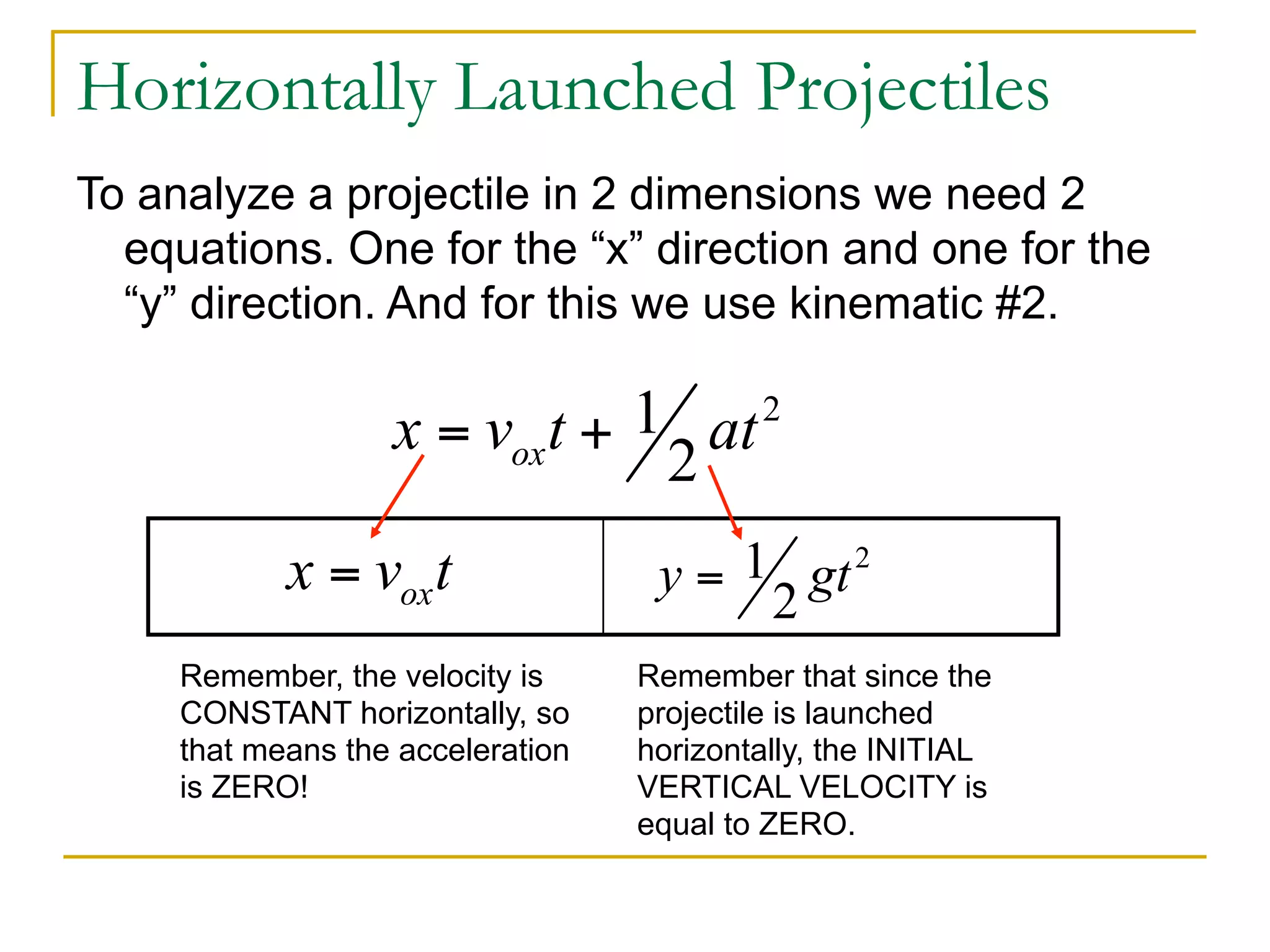
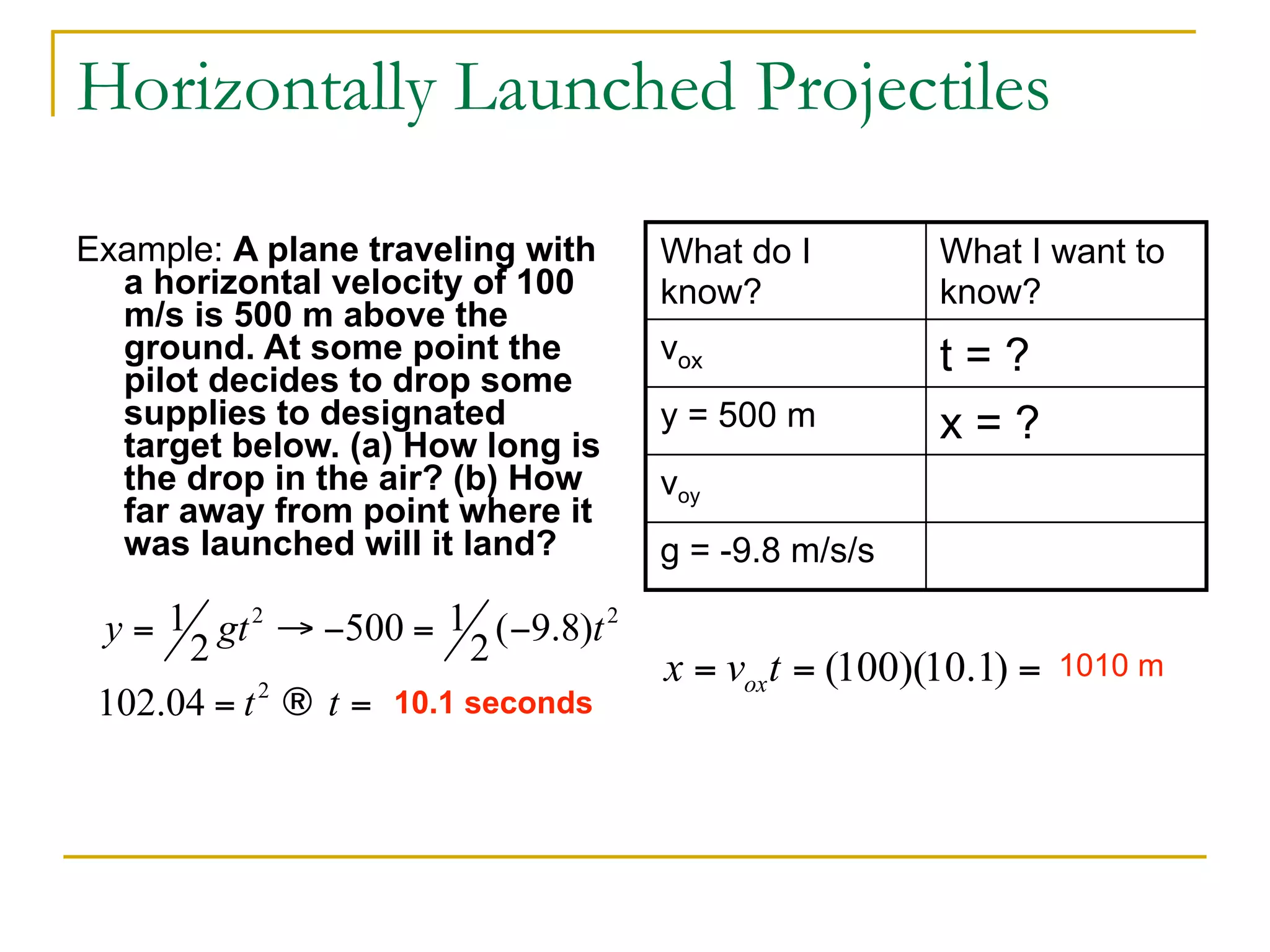
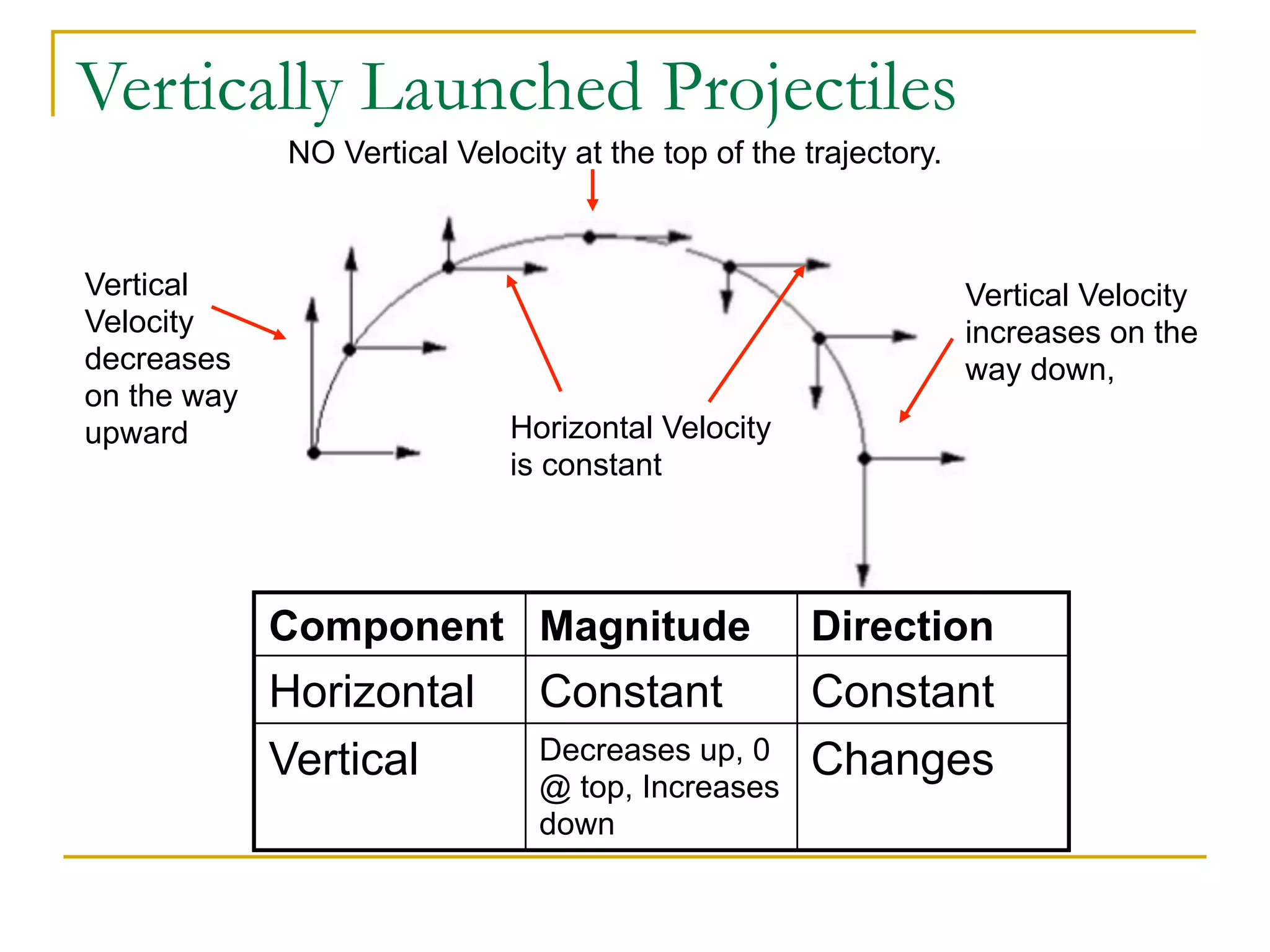
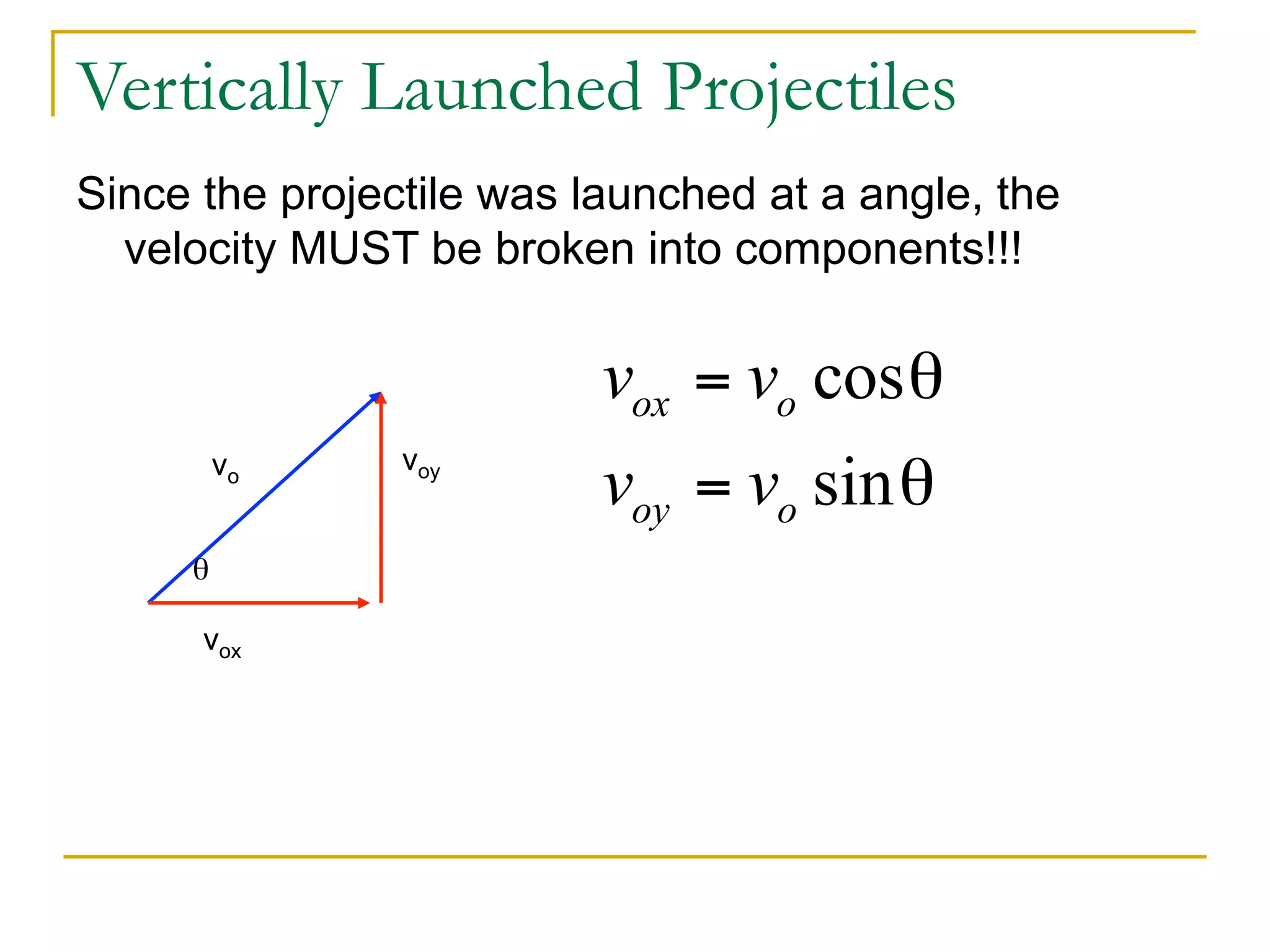
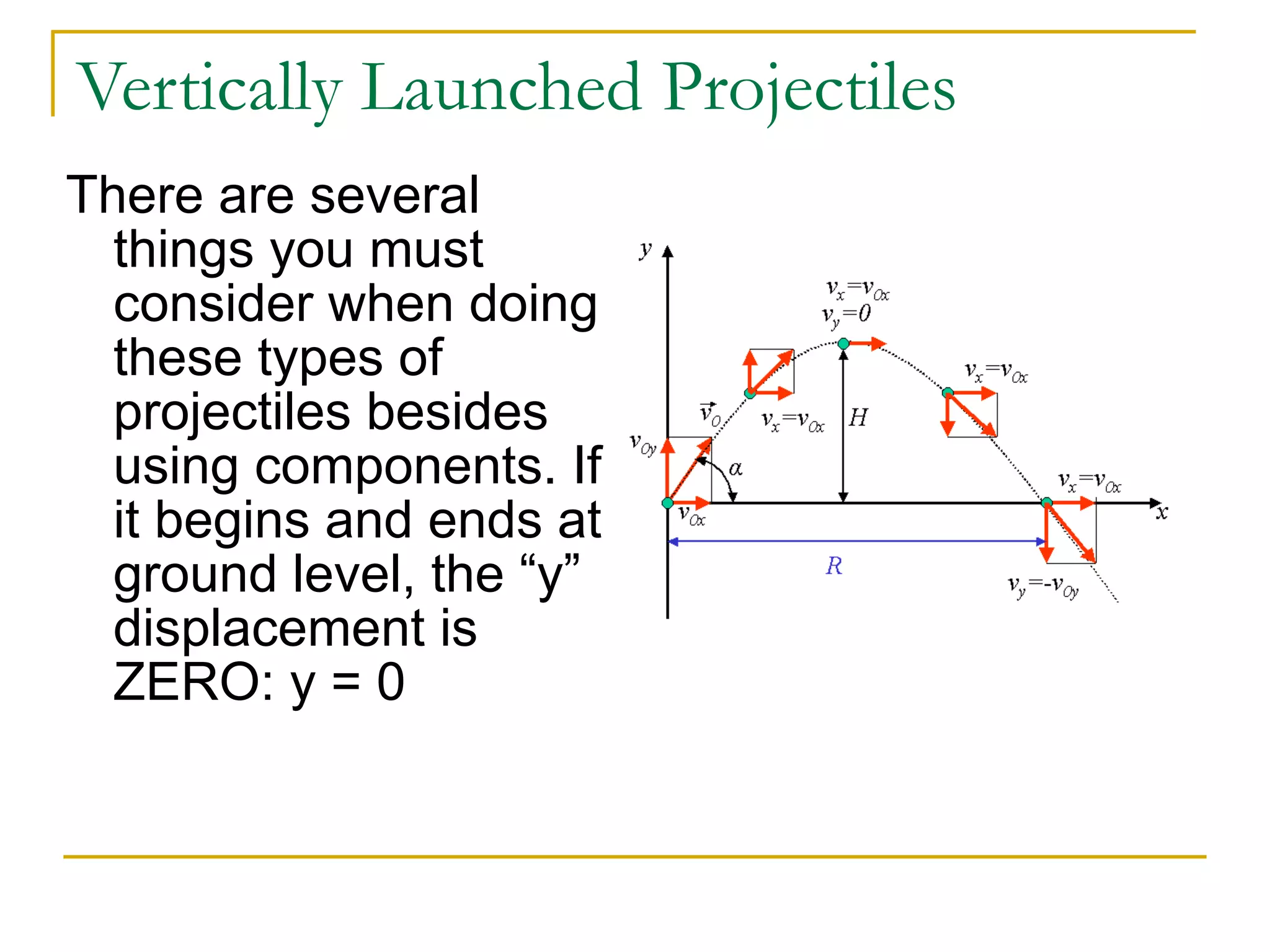
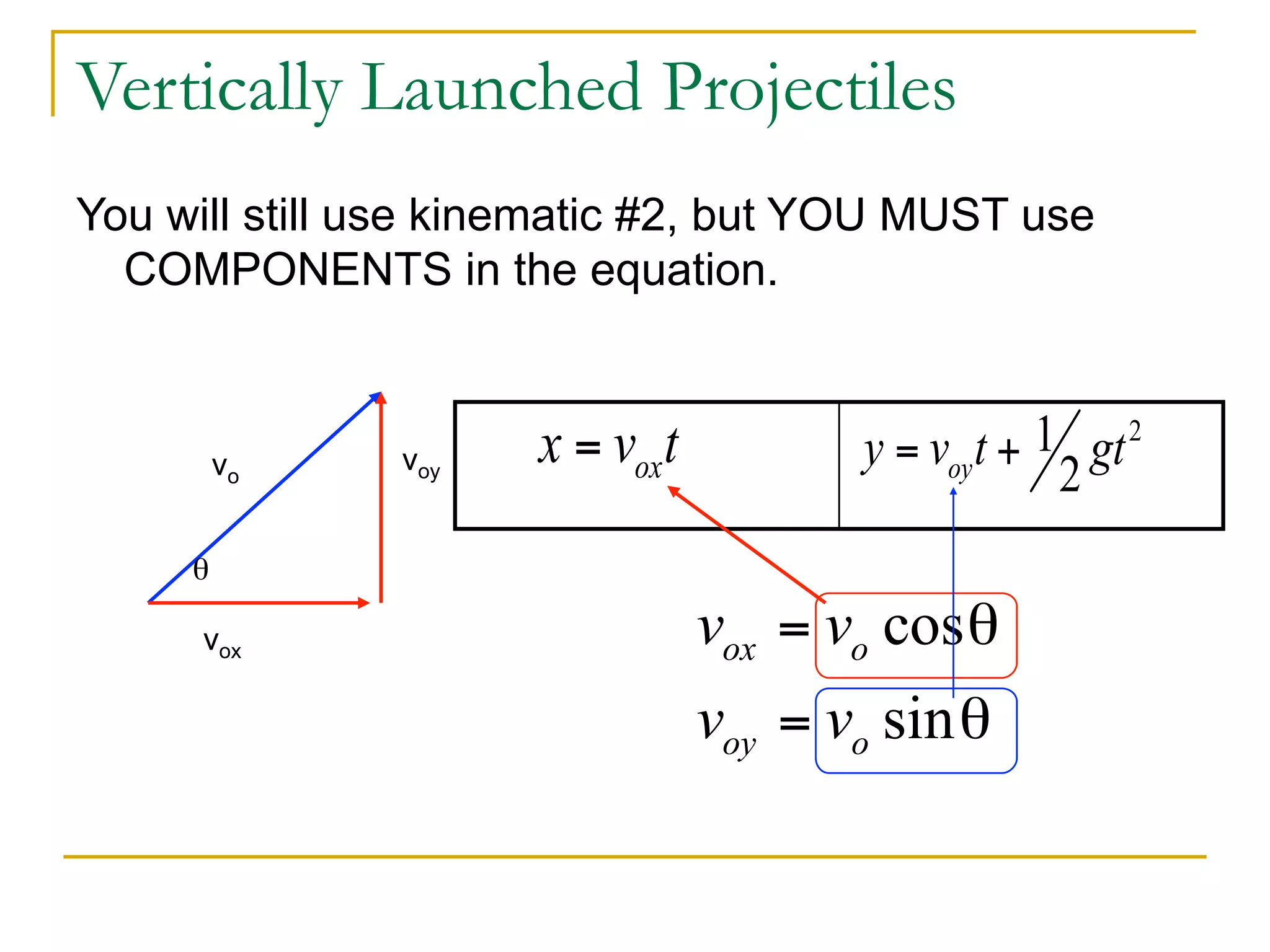
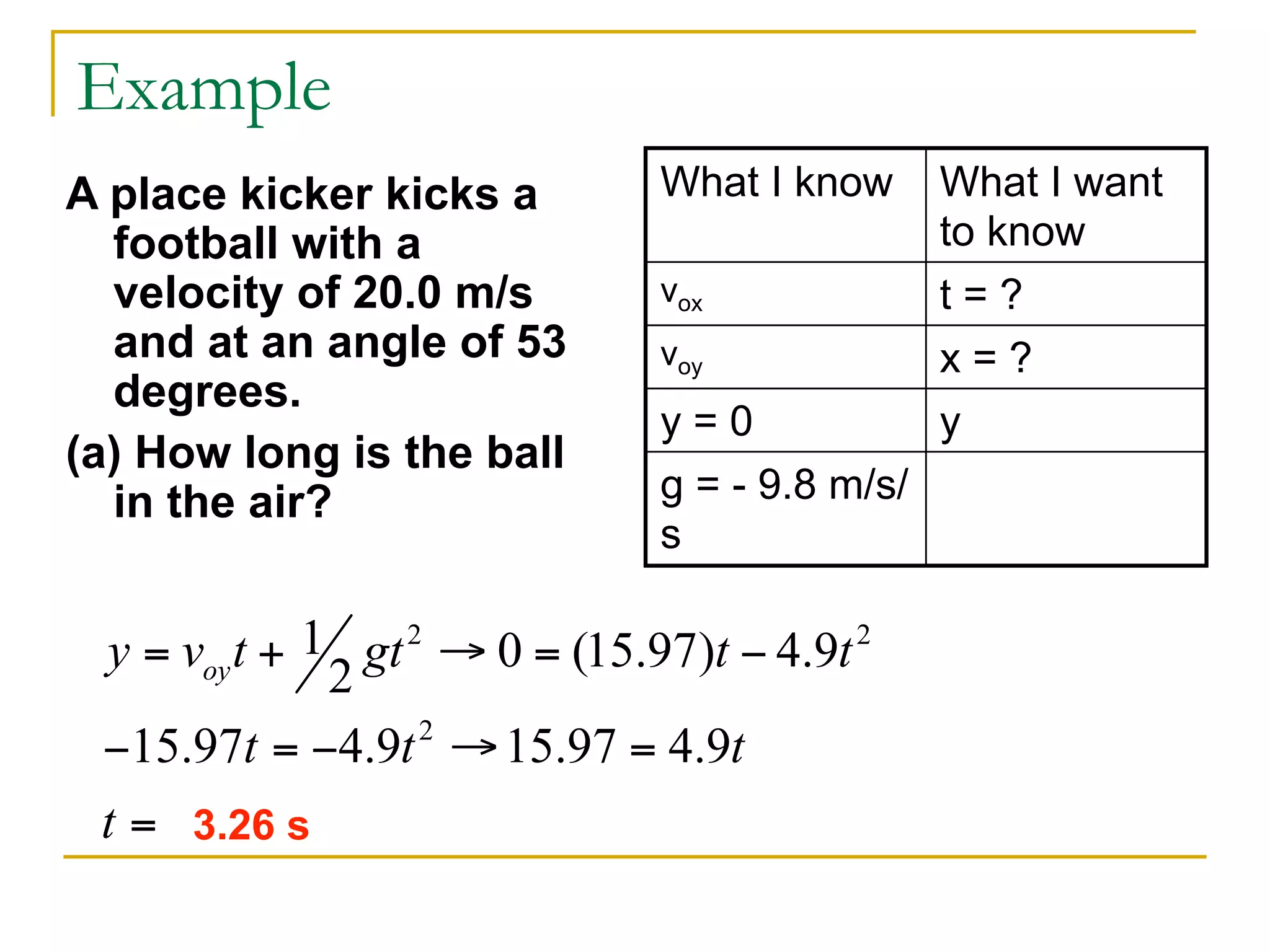
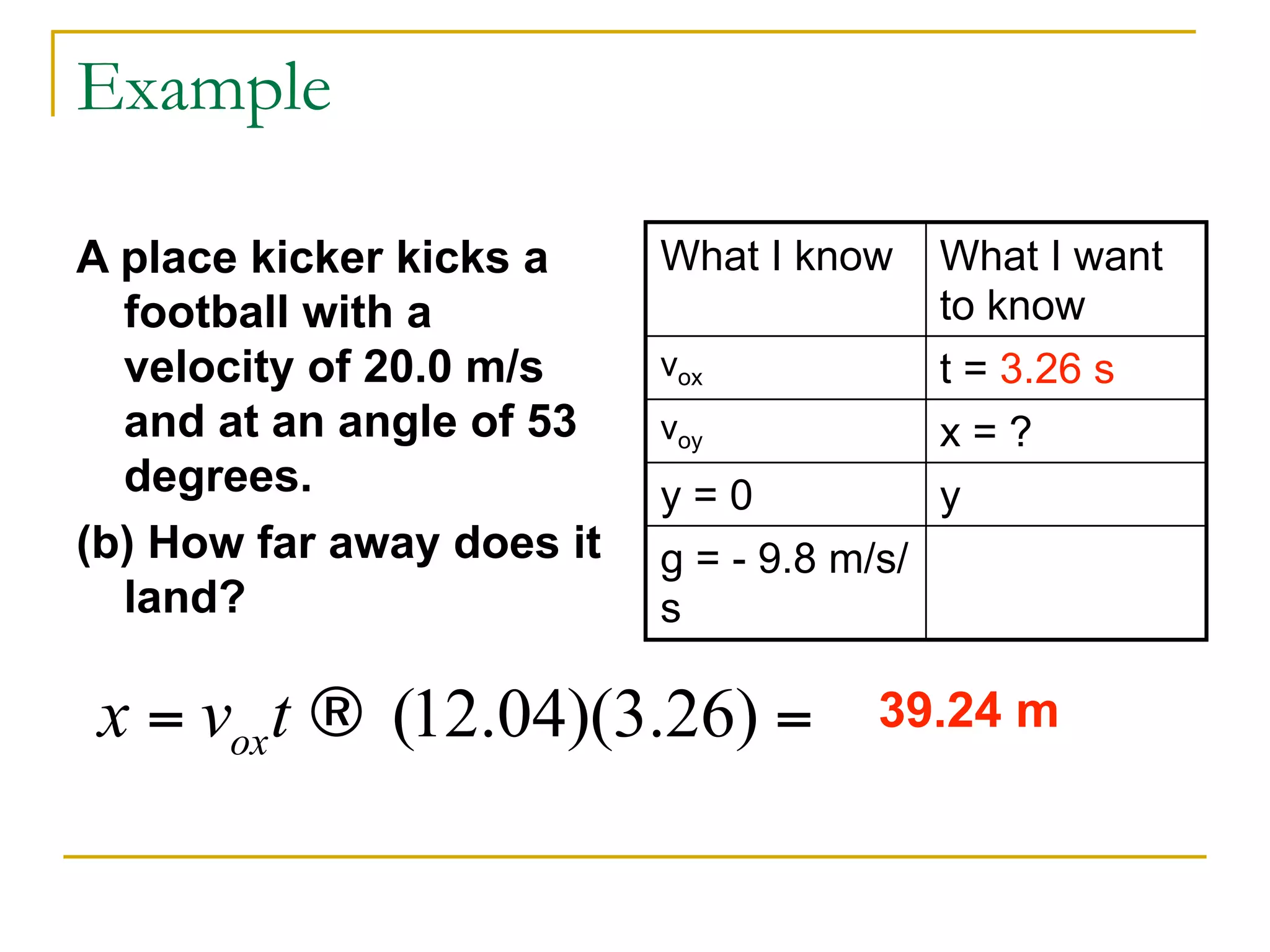
This document discusses projectile motion in physics. It defines a projectile as any object projected by some means that continues to move due to its own inertia. Projectiles move in two dimensions and have both horizontal and vertical velocity components. The horizontal component is constant, while the vertical component changes due to gravity. Together these components produce the parabolic trajectory of a projectile. Examples are provided of analyzing the motion of horizontally and vertically launched projectiles using kinematic equations and taking into account the initial velocity components.