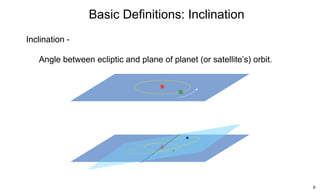
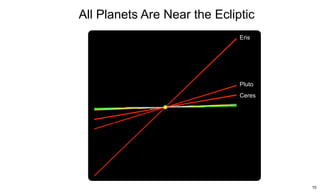
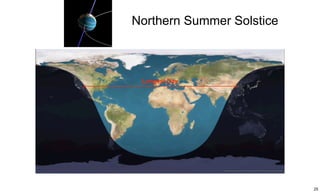
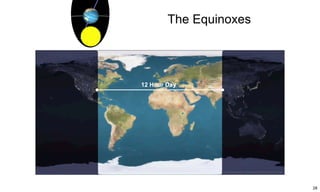
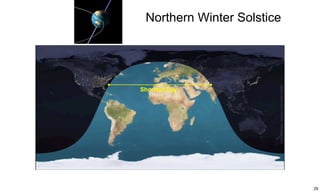
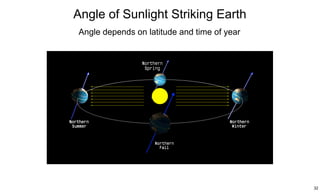
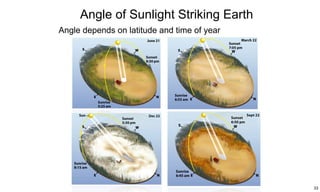
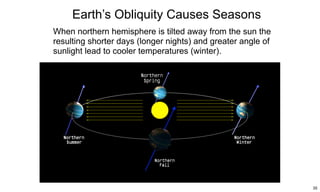
The ecliptic is the plane of Earth's orbit around the sun. The inclination is the angle between the ecliptic and the plane of a planet or satellite's orbit. Earth's seasons are caused by its 23.5 degree axial tilt relative to its orbital plane around the sun (obliquity), not by changes in Earth's distance from the sun. During summer in the northern hemisphere, the north pole leans toward the sun, causing longer days and warmer temperatures, while winter occurs when the north pole leans away from the sun.