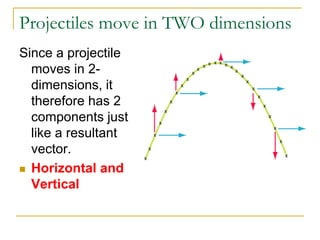
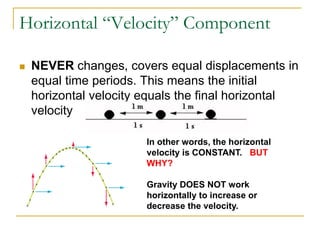
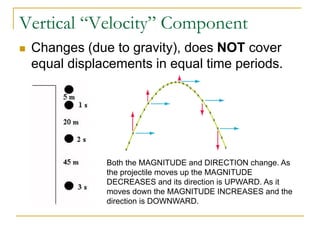
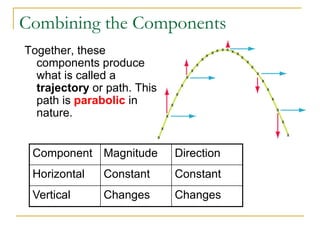
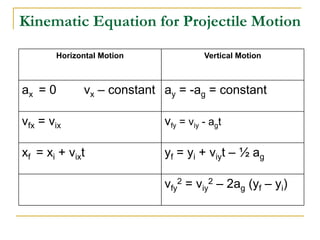
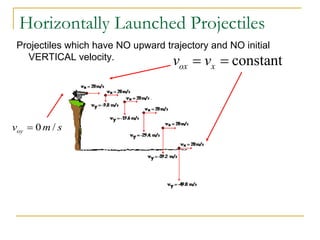
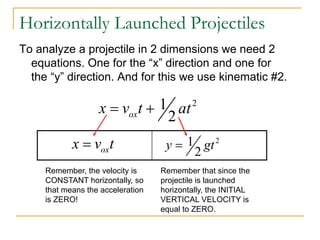
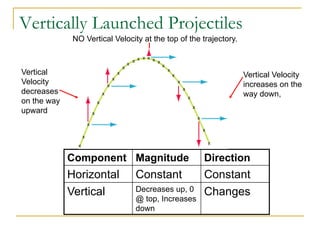
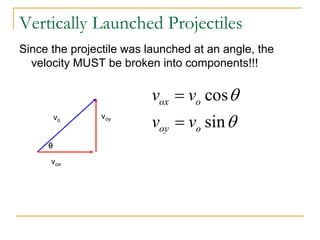
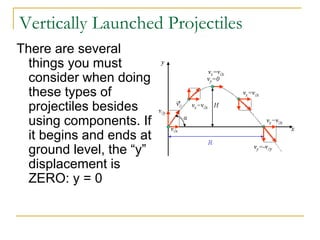
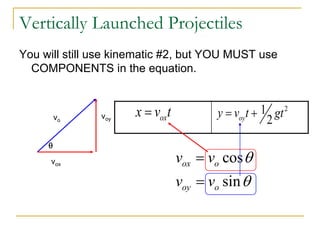
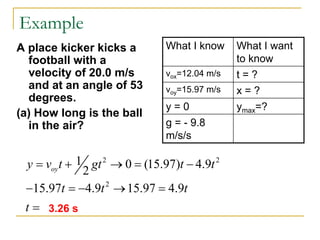
Projectile motion refers to the movement of an object in the x-y plane, influenced primarily by gravity, resulting in a parabolic trajectory. Key components of projectile motion include constant horizontal velocity and changing vertical velocity due to gravitational acceleration. Examples of projectiles include baseballs, bullets, and the space shuttle post-engine cut-off, and calculations are often performed using kinematic equations for both horizontal and vertical motions.