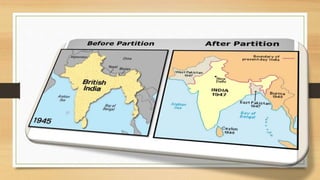
This document summarizes Pak-India relations since their partition in 1947. It outlines key events that have strained their relationship such as the Kashmir dispute, three Indo-Pakistan wars between 1965-1971, the Kargil War in 1999, and recent tensions in 2019. While agreements like the Indus Water Treaty and Simla Agreement have aimed to reduce tensions, disputes over Kashmir and cross-border attacks have typically undermined efforts to build trust and cooperation between the two countries.