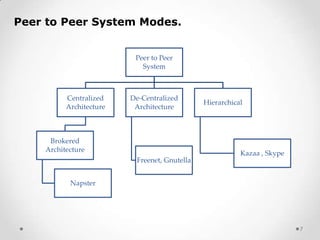
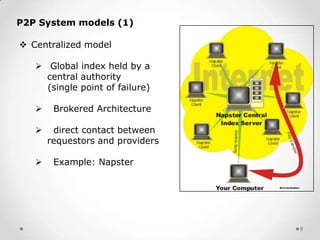
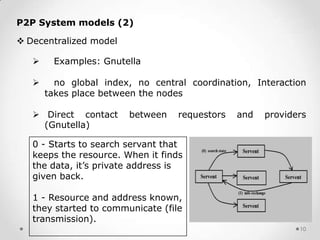
This document provides an overview of peer-to-peer (P2P) communications methods and commonly used P2P programs. It defines P2P as communication between nodes without a dedicated server, where peers can act as both clients and servers. The document describes different P2P network models including centralized, decentralized, and hierarchical, and types of P2P networks for collaborative computing, instant messaging, and file sharing. Examples of commonly used P2P programs discussed in more detail include Skype, which uses both peer-to-peer and client-server components, with audio streams transmitted peer-to-peer and account data stored on central servers.