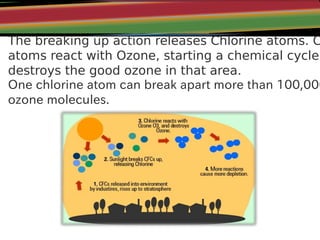
Ozone (O3) is a bluish gas composed of three oxygen atoms that forms a protective layer in the stratosphere. It is produced through chemical reactions involving oxygen and ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Nearly 90% of Earth's ozone is found in the ozone layer between 15-30 km above the surface. The ozone layer protects life on Earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Depletion of the ozone layer is caused primarily by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released into the atmosphere from industry. CFCs rise into the stratosphere where UV light breaks them down, releasing chlorine atoms that catalyze the destruction of ozone molecules. Ozone depletion increases risks