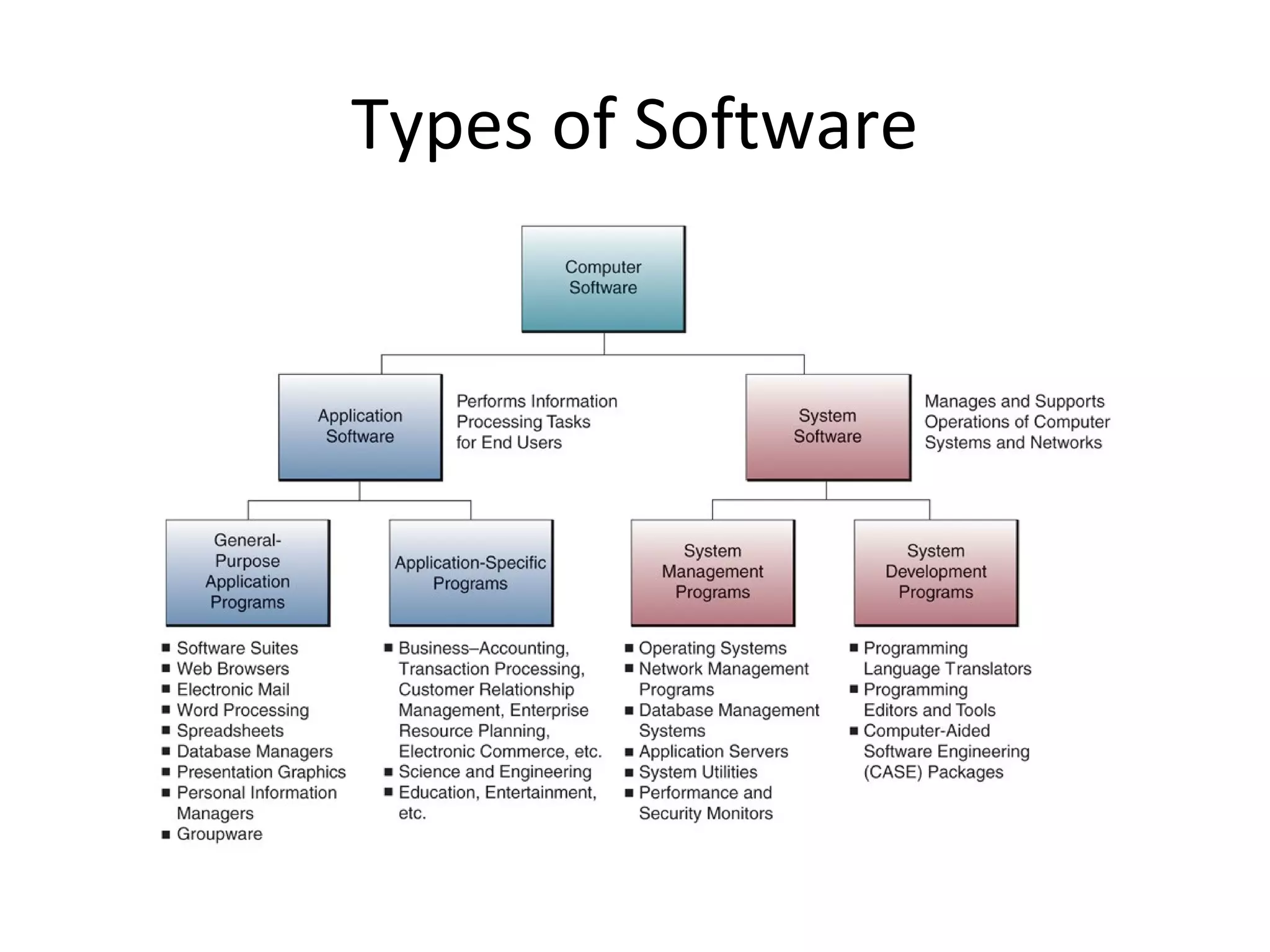
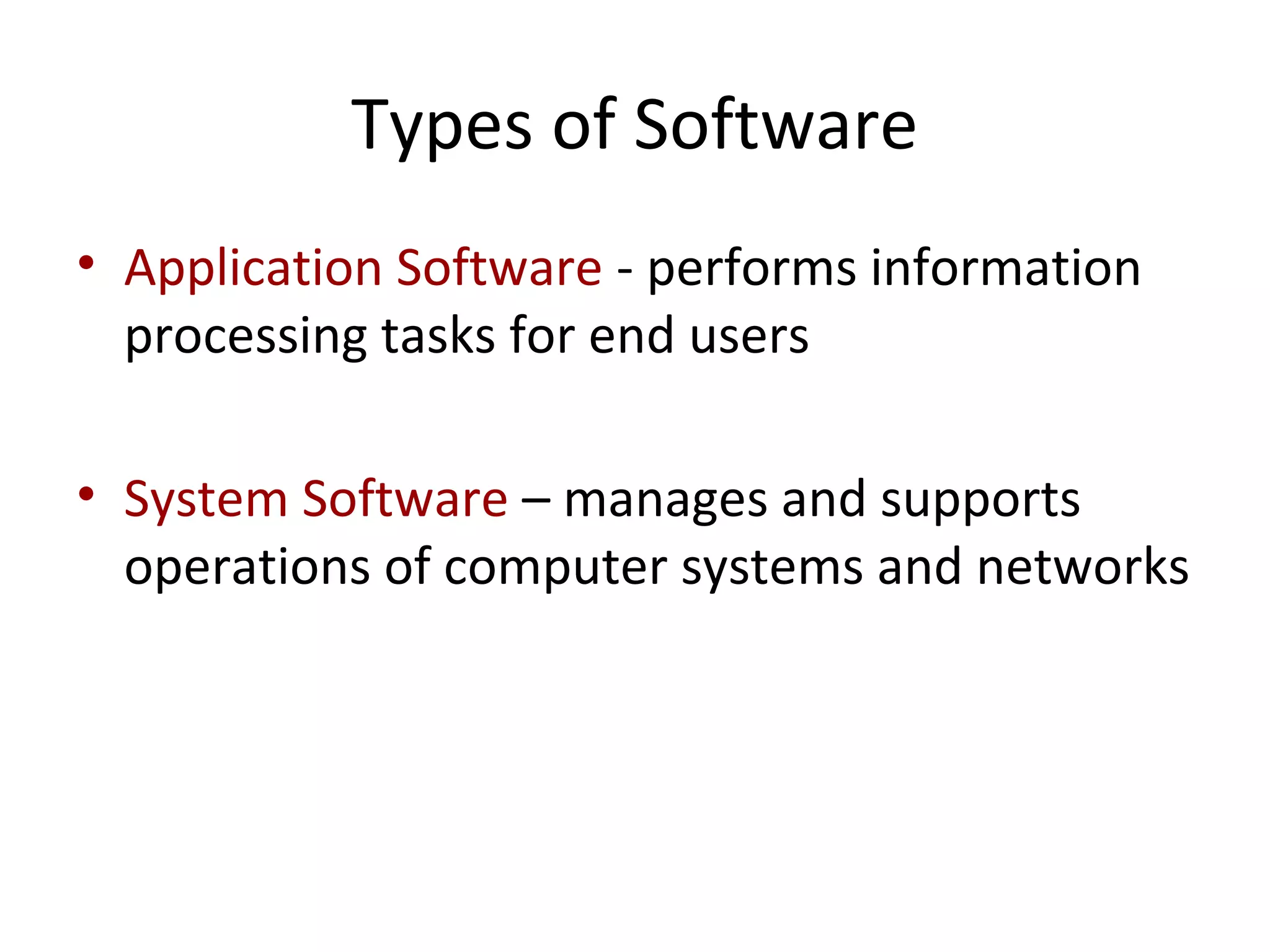
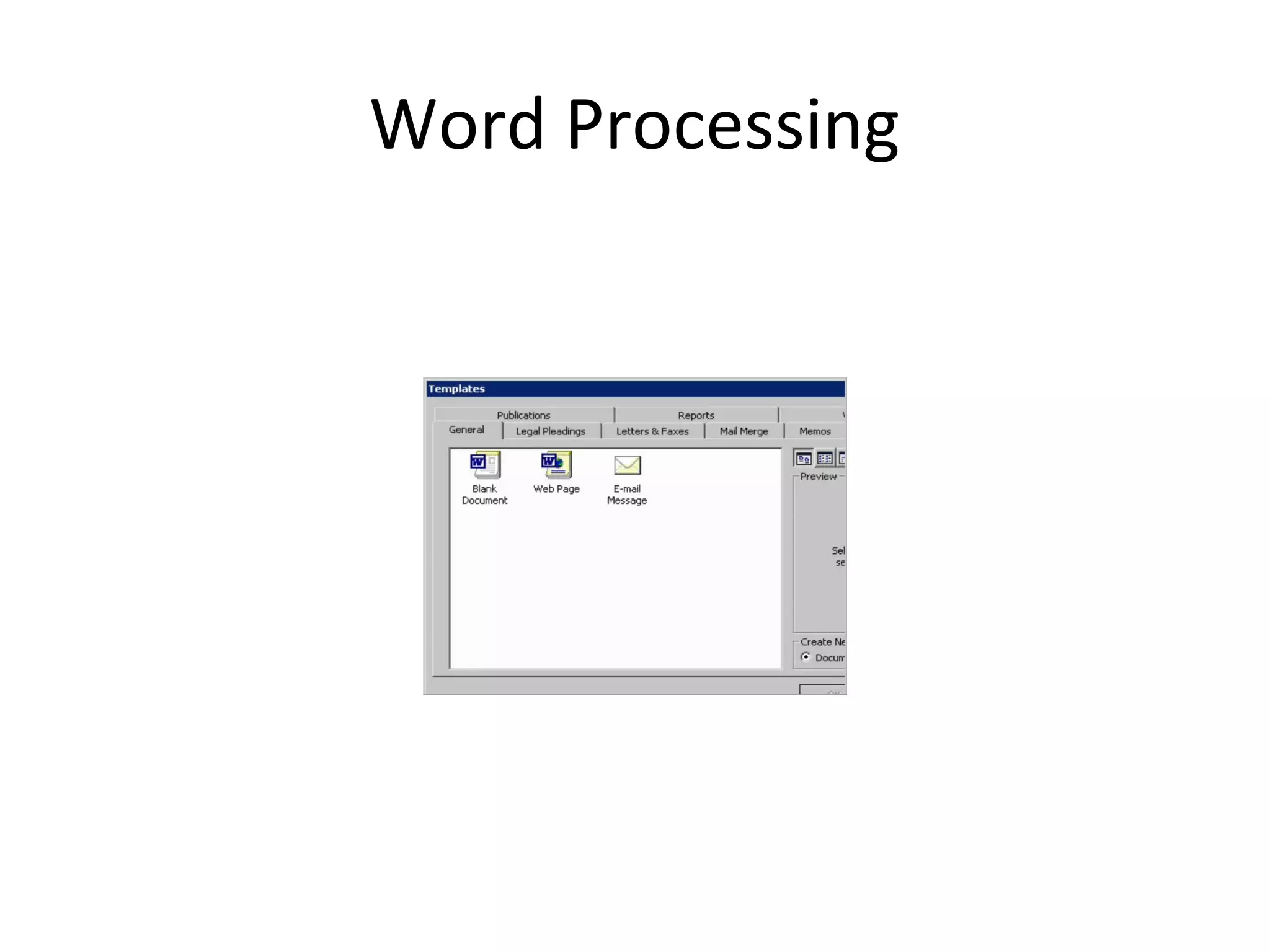
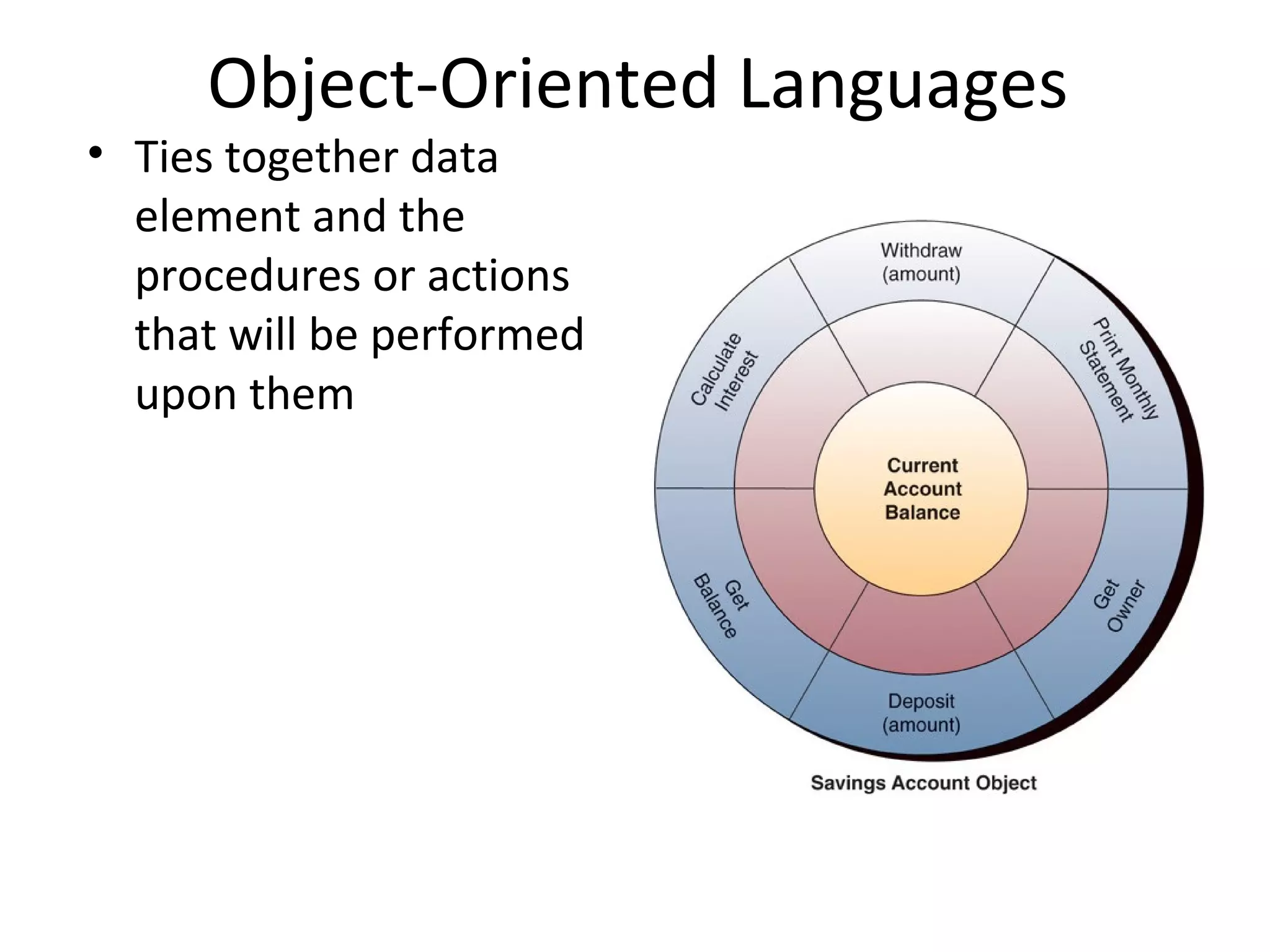
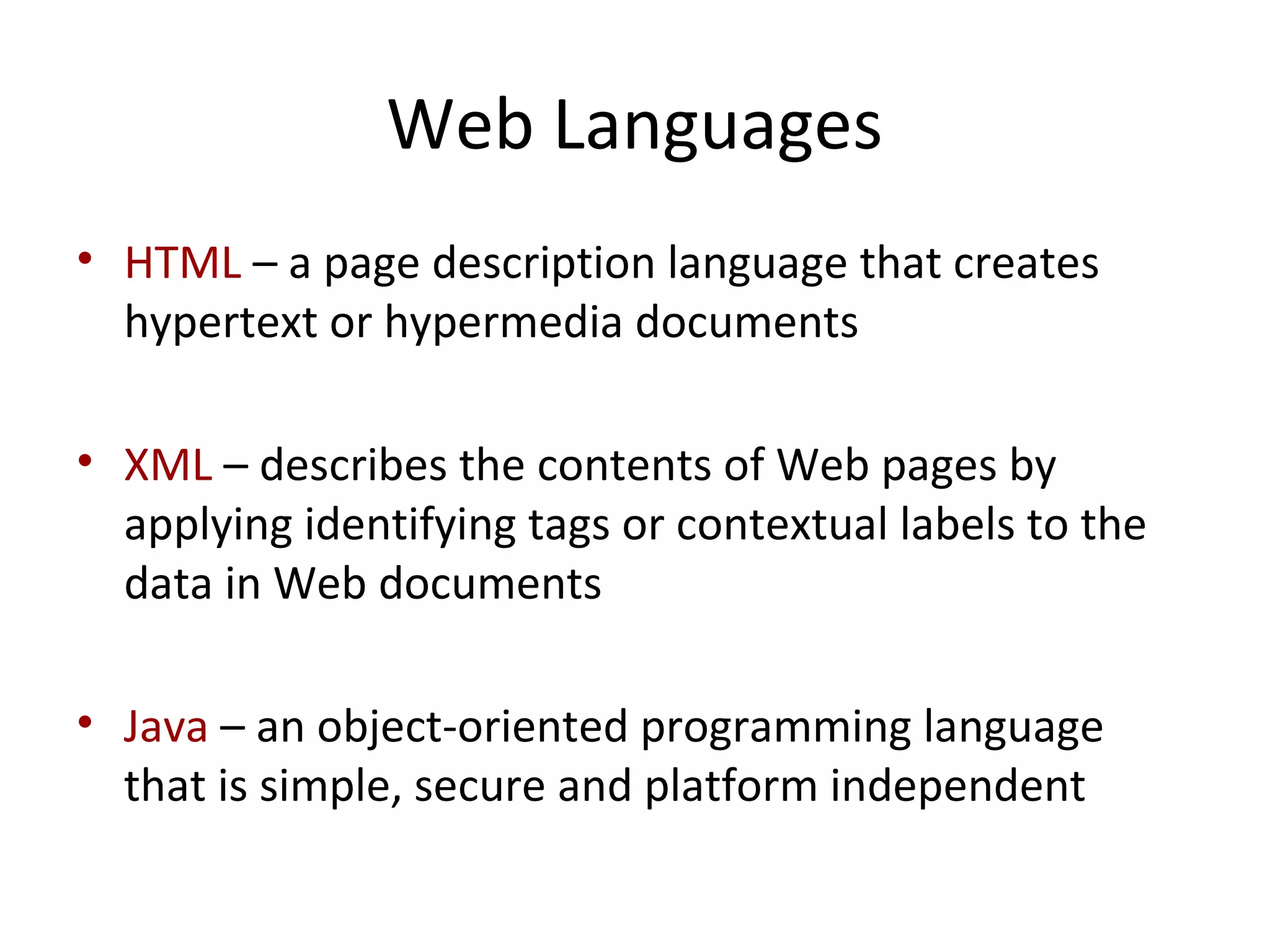
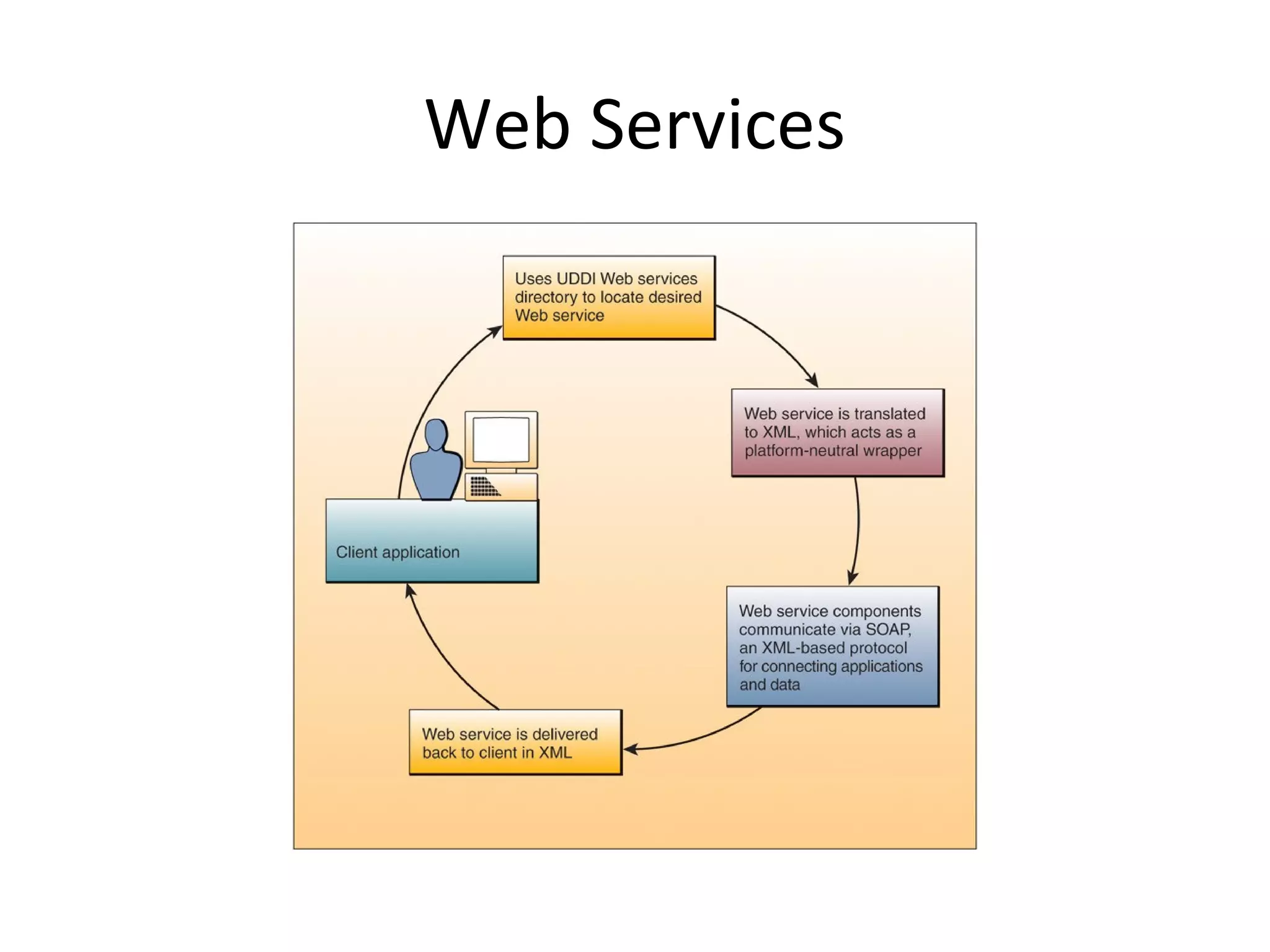
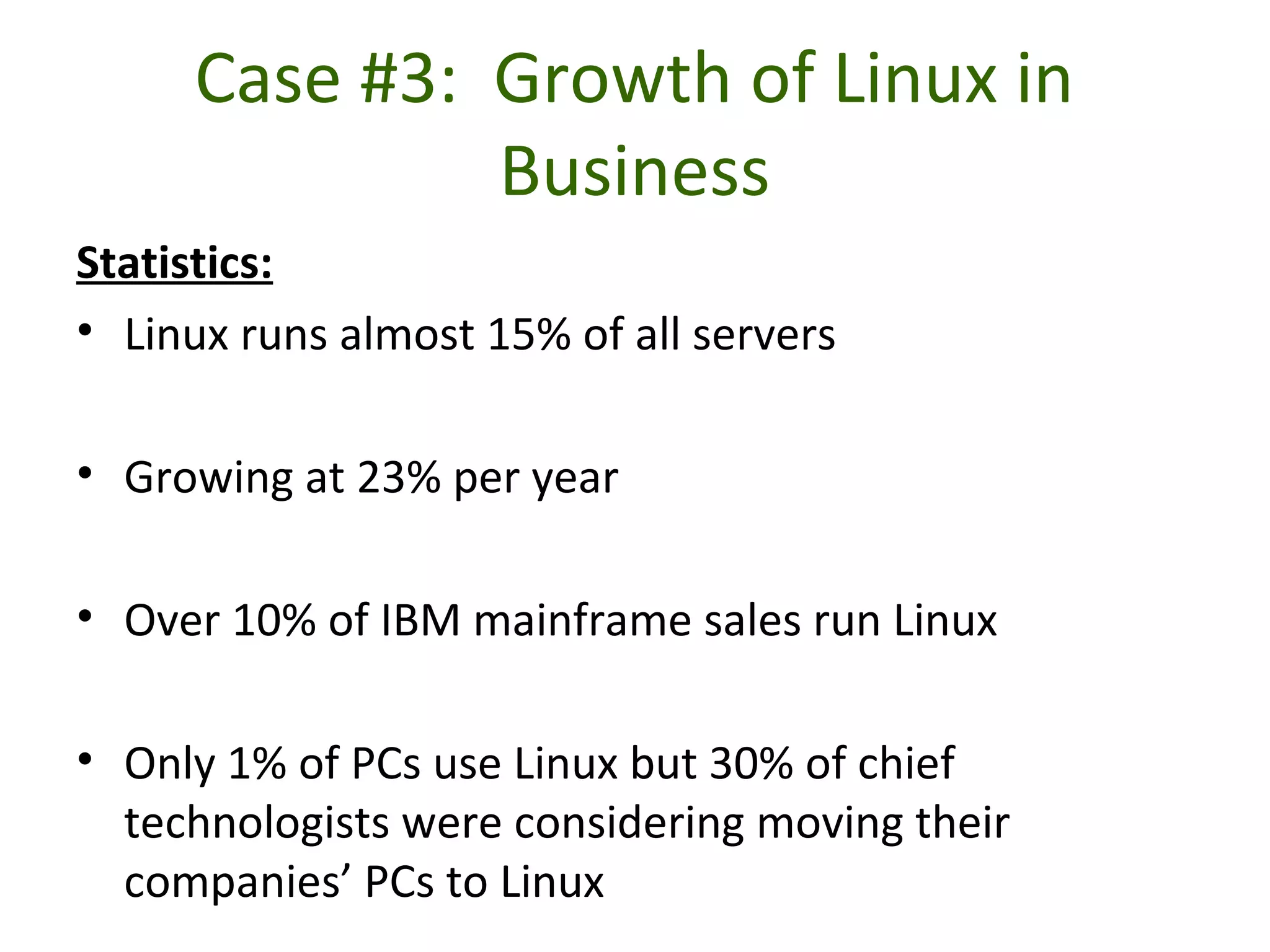
- Software includes application software that directs computer use for specific tasks and system software that controls computer operations.
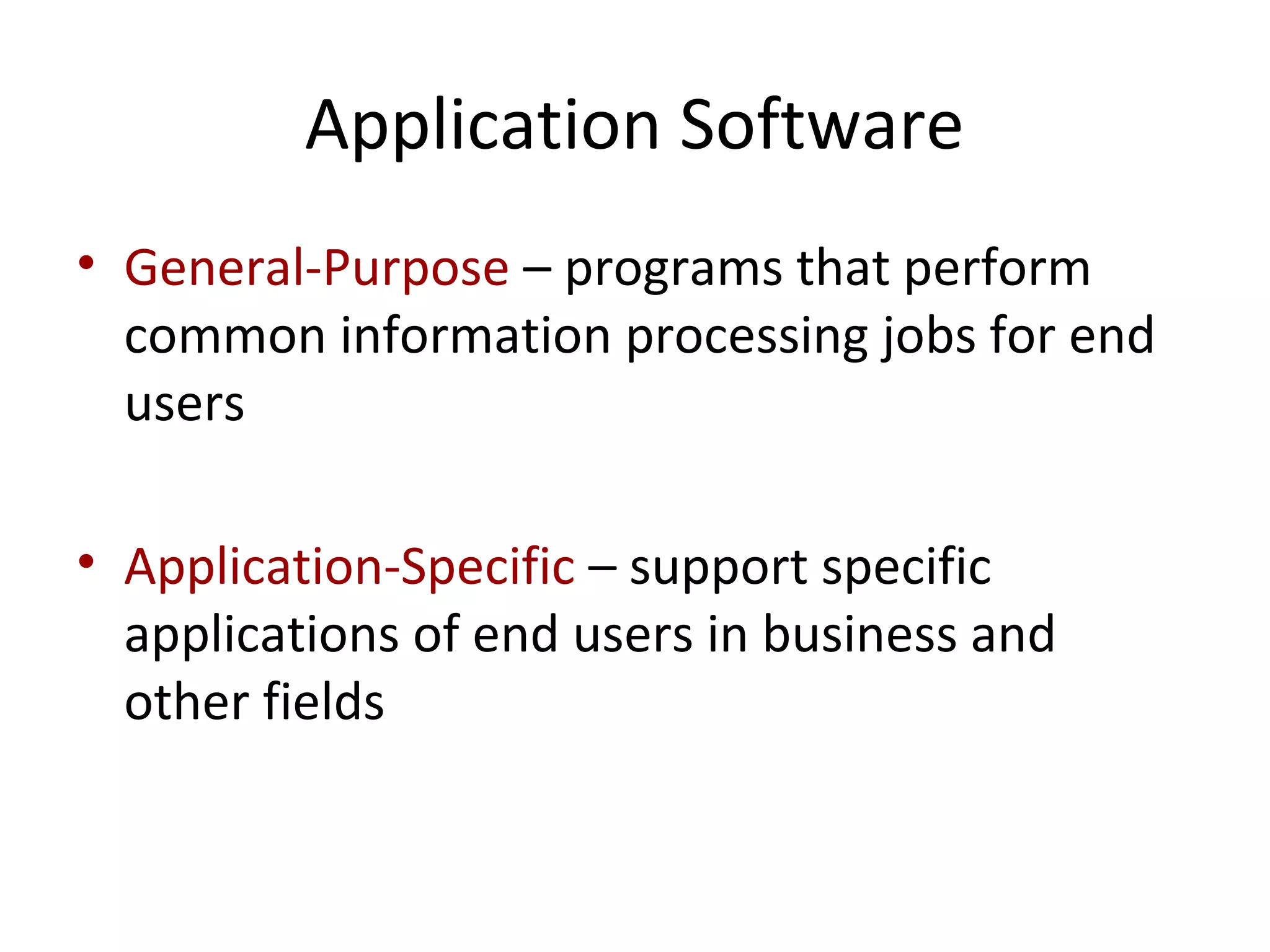
- Application software is divided into general-purpose programs for common tasks and specialized programs for business functions.
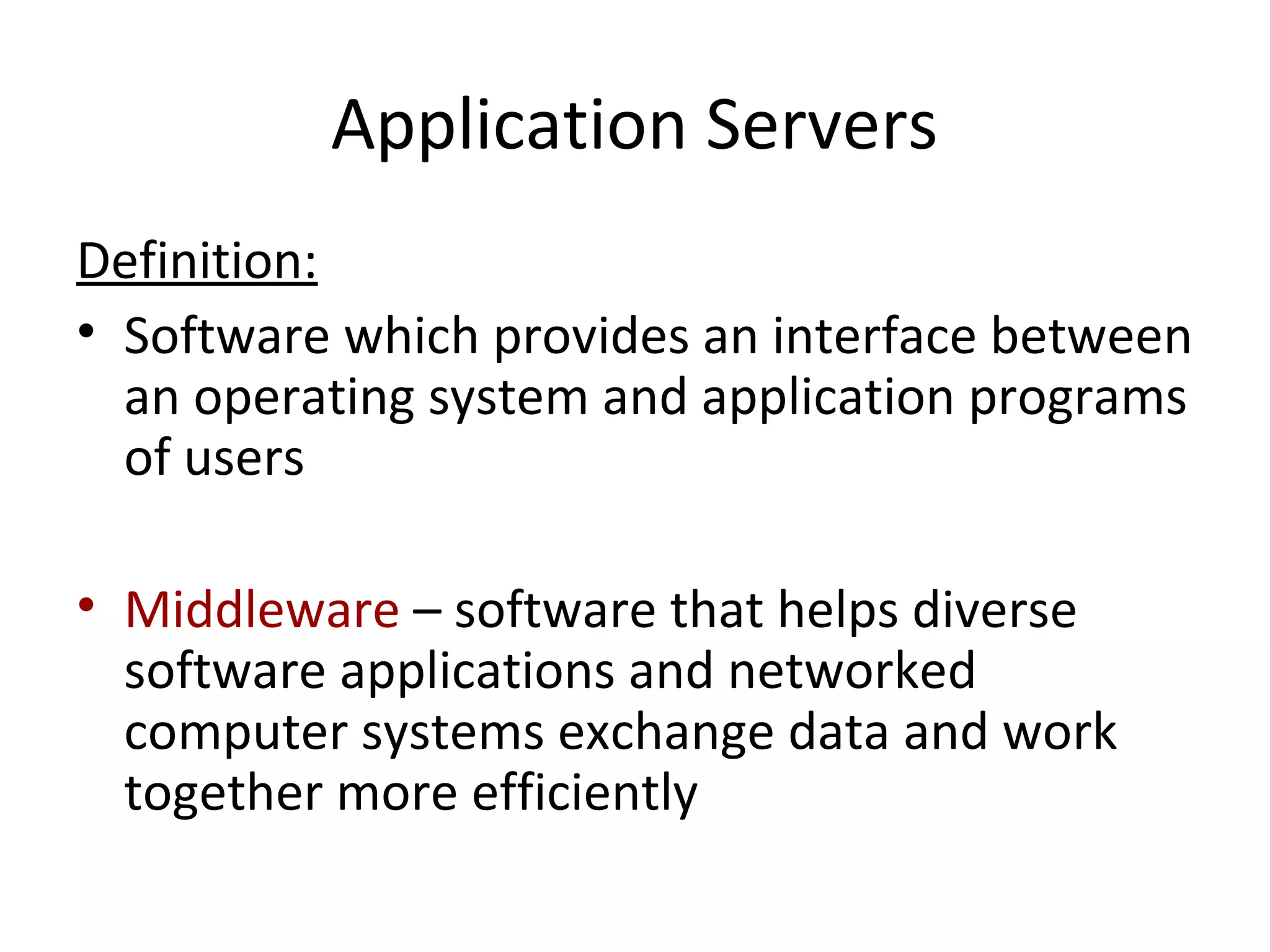
- System software includes programs that manage computer resources and programs that help develop other programs.
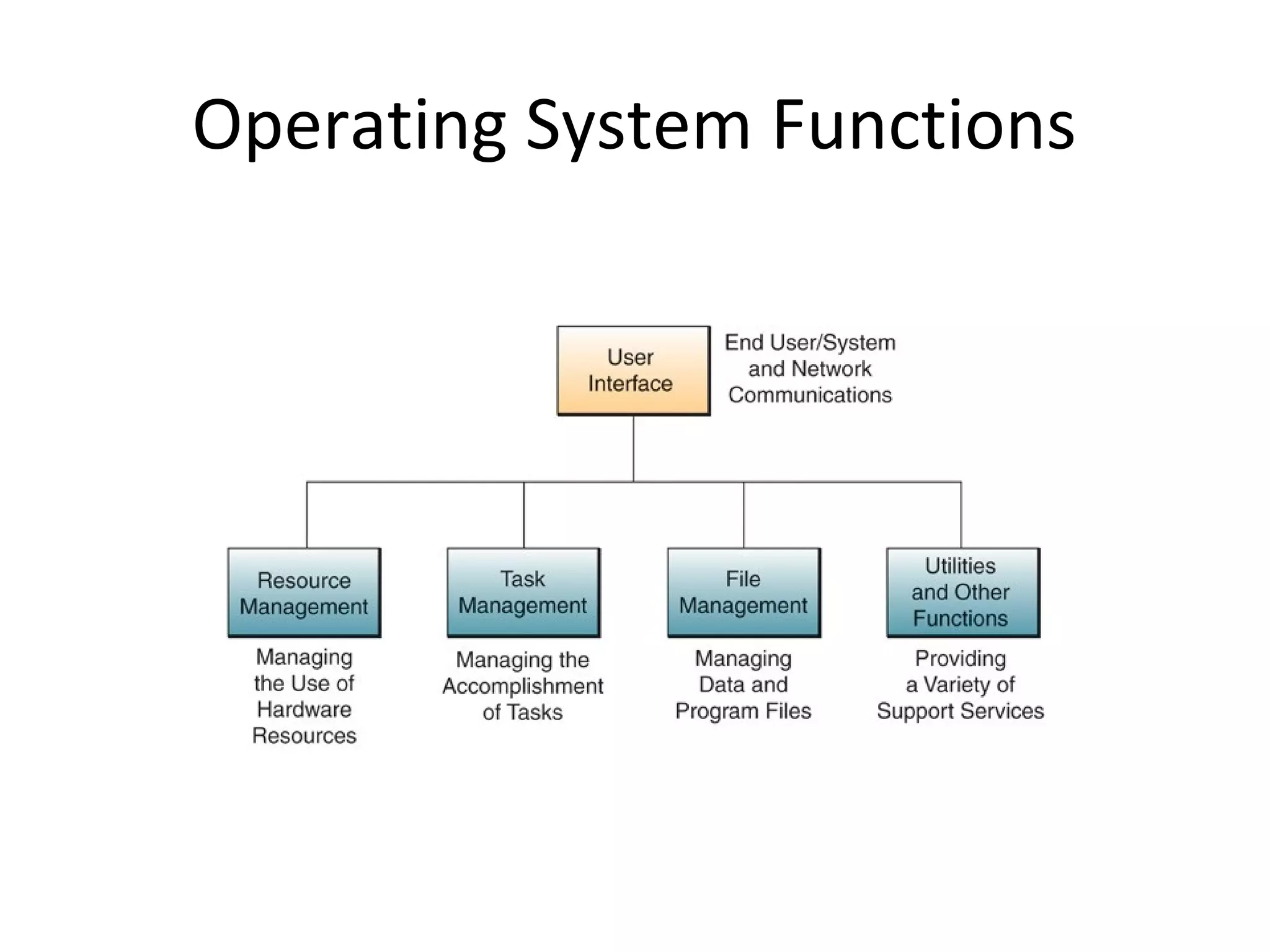
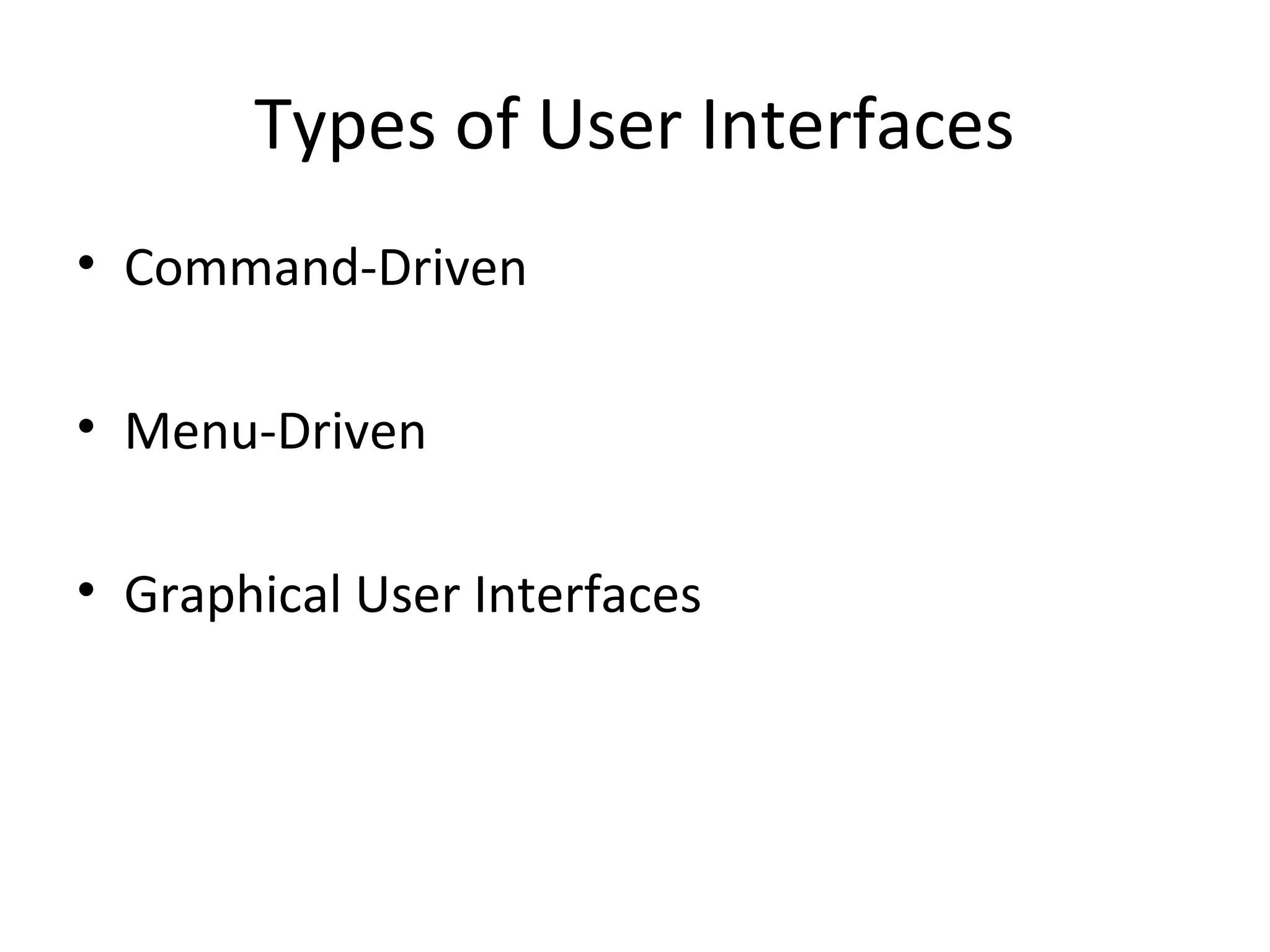
- An operating system integrates programs to manage the CPU, input/output, storage, and provide support services.