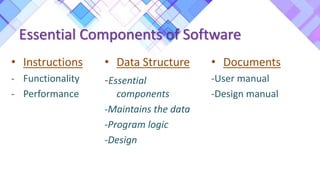
This document discusses software engineering. It begins by defining software as a set of instructions that take inputs and produce outputs as determined by the user. It then discusses the essential components of software including instructions, data structures, and documents.
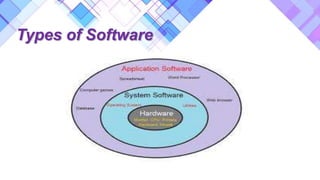
It describes different types of software such as system software, real-time software, business software, scientific software, embedded software, AI software, personal computer software, and internet software. Good software is discussed in terms of attributes like maintainability, correctness, reusability, reliability, portability, and efficiency.
Finally, it defines software engineering as a systematic collection of practices for developing quality software in an efficient and cost-effective manner. The major roles of software engineering are to increase productivity