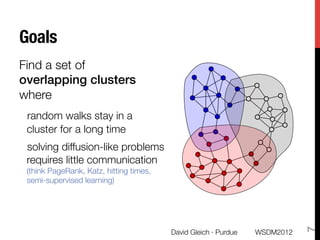
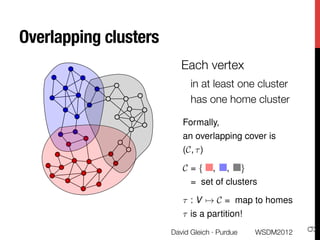
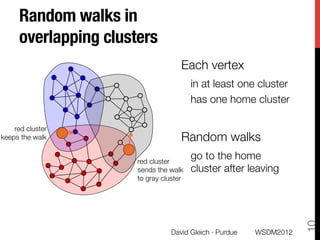
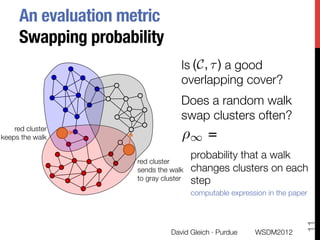
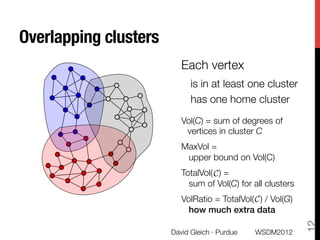
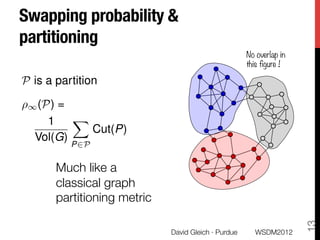
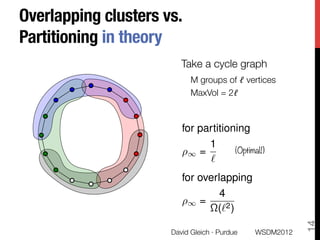
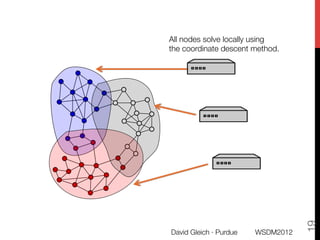
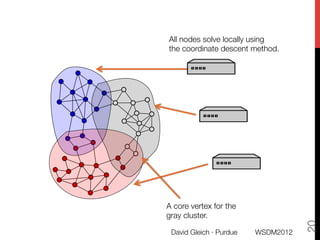
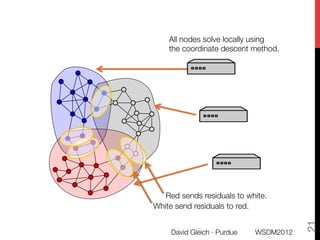
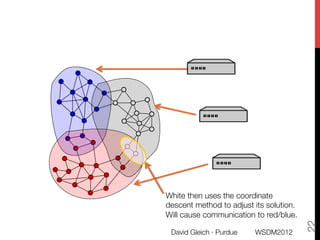
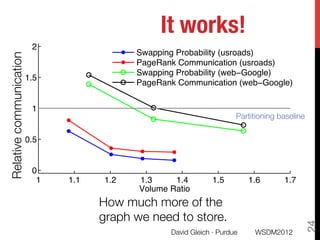
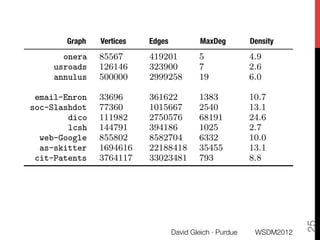
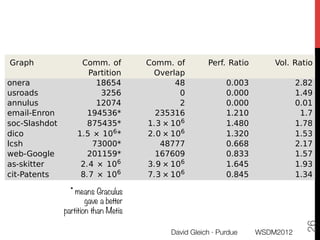
The document discusses the development of overlapping clusters for distributed computation, focusing on optimizing the distribution of large graphs for tasks like linear systems and random walk simulations. It presents theoretical evidence that overlapping clusters can enhance communication efficiency, achieving a reduction of around 20%. The paper outlines a multi-stage heuristic approach to identify effective clusters and emphasizes the practical implications for solving diffusion-like problems in distributed systems.