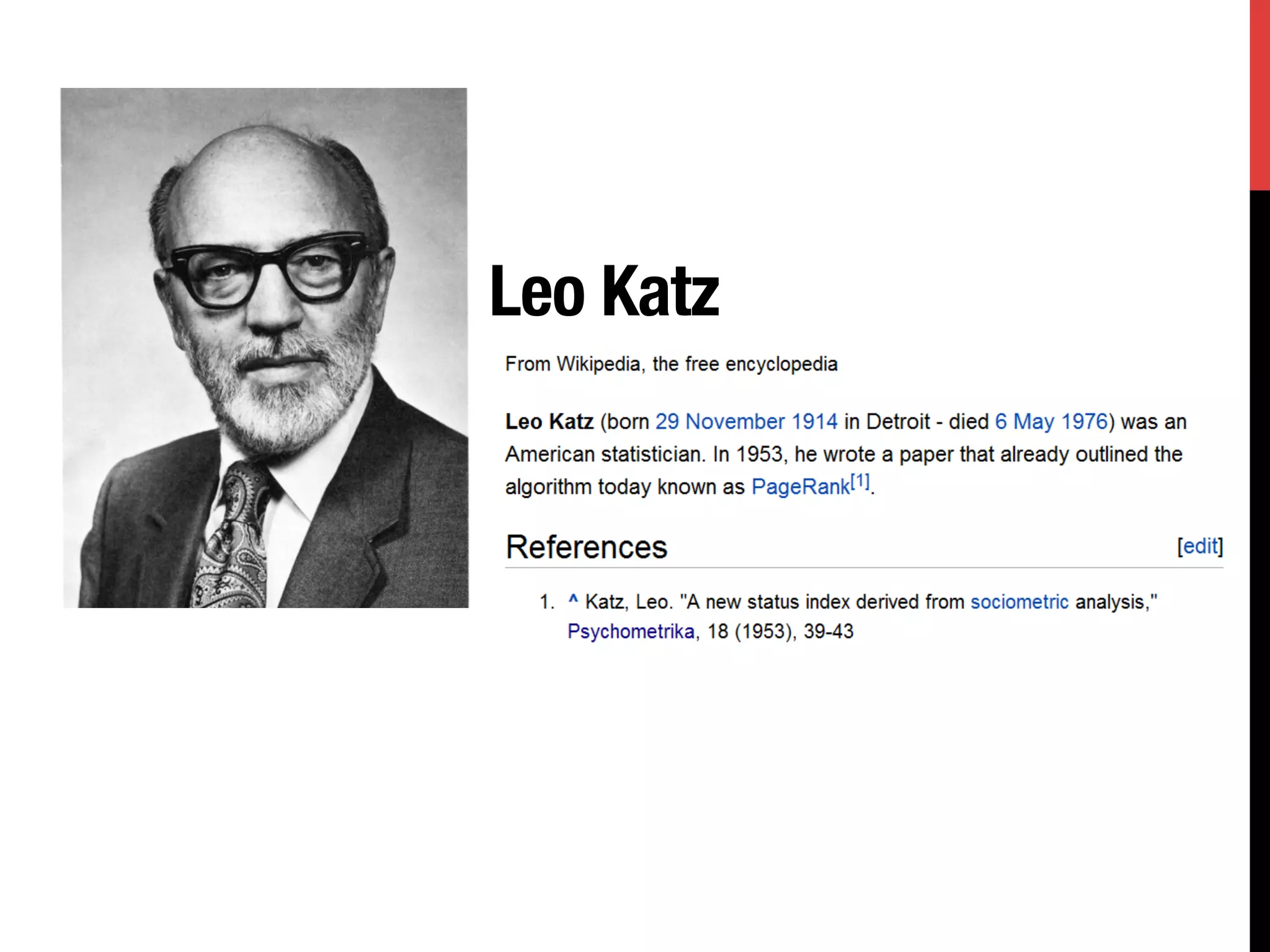
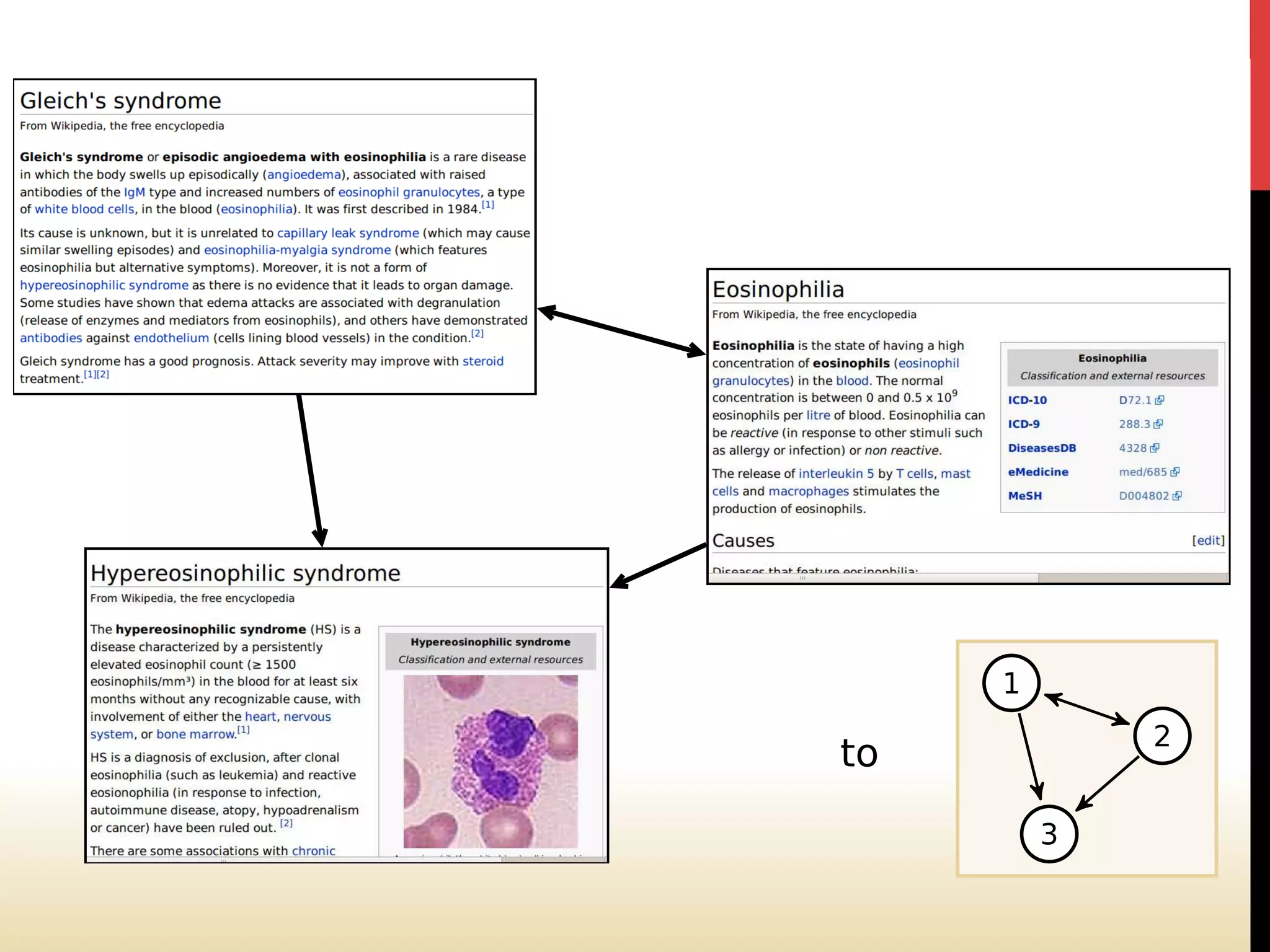
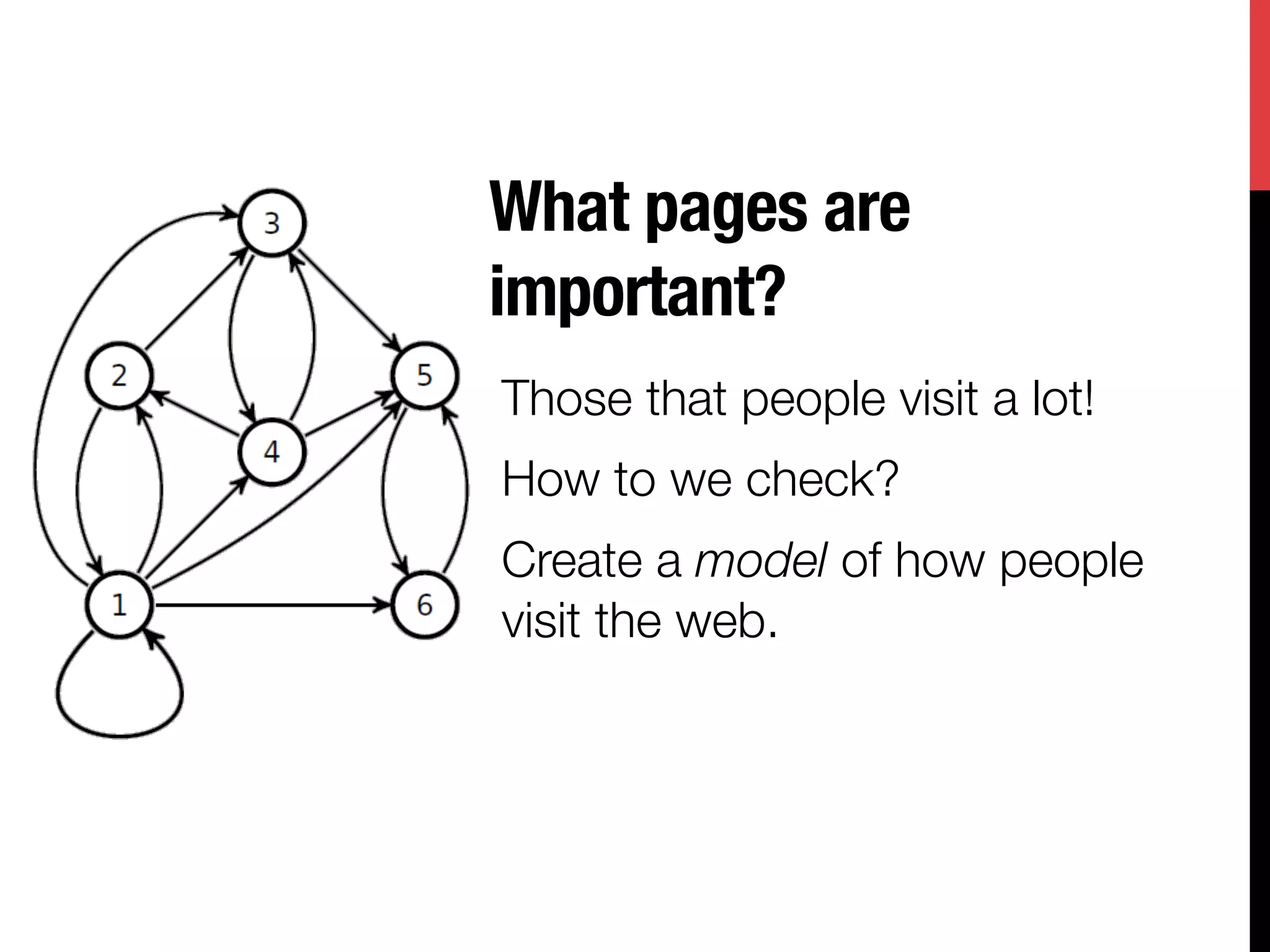
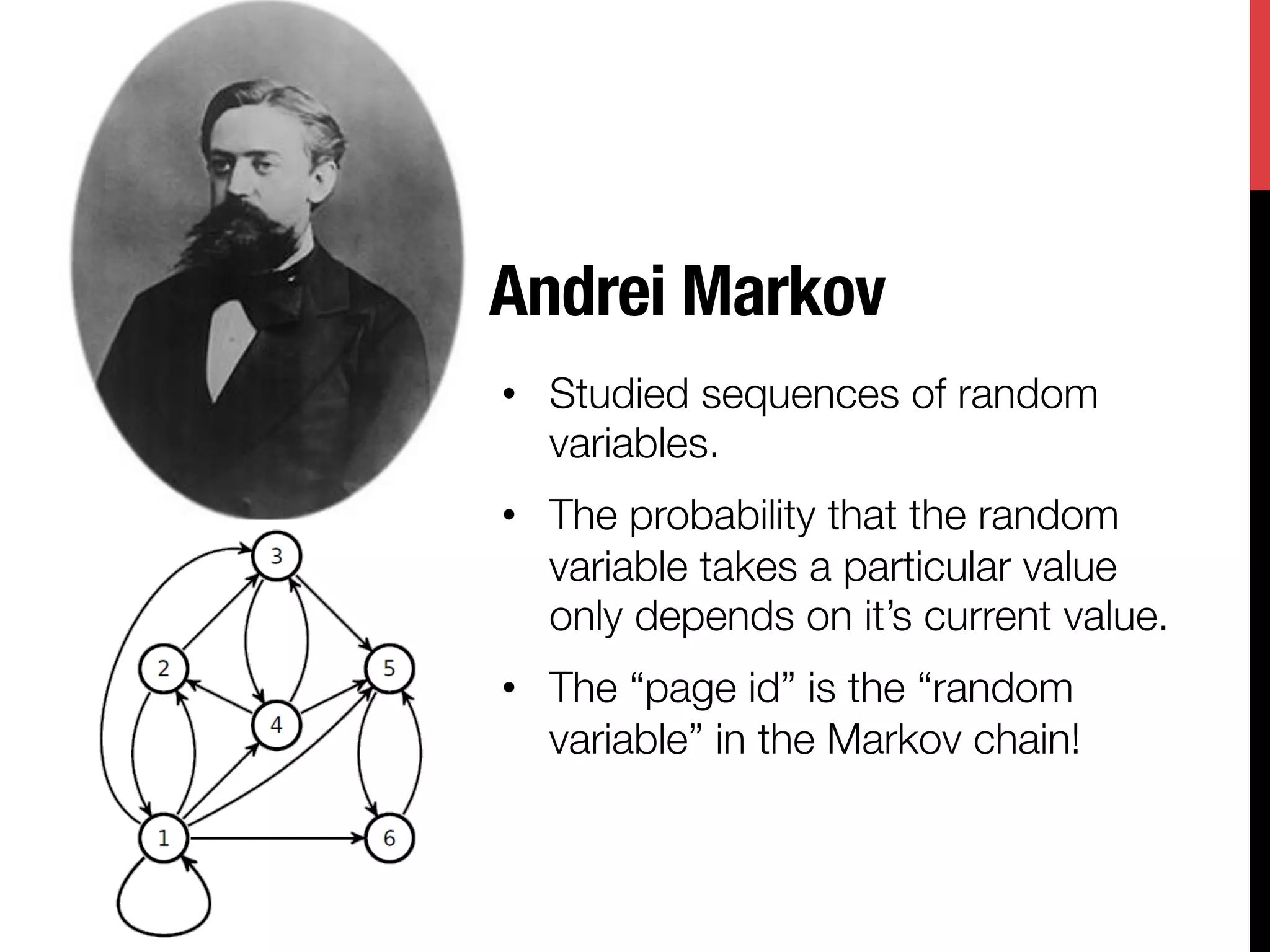
The document discusses the development of Google's PageRank algorithm, tracing its origins to concepts in mathematical theory and artificial intelligence used by its founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin. It highlights the importance of web page ranking, the Markov chain model used to analyze link structure, and historical contributions from figures like Andrei Markov and Richard von Mises. Additionally, it references the impact of other theorists on the information spread and numerical computing landscape.













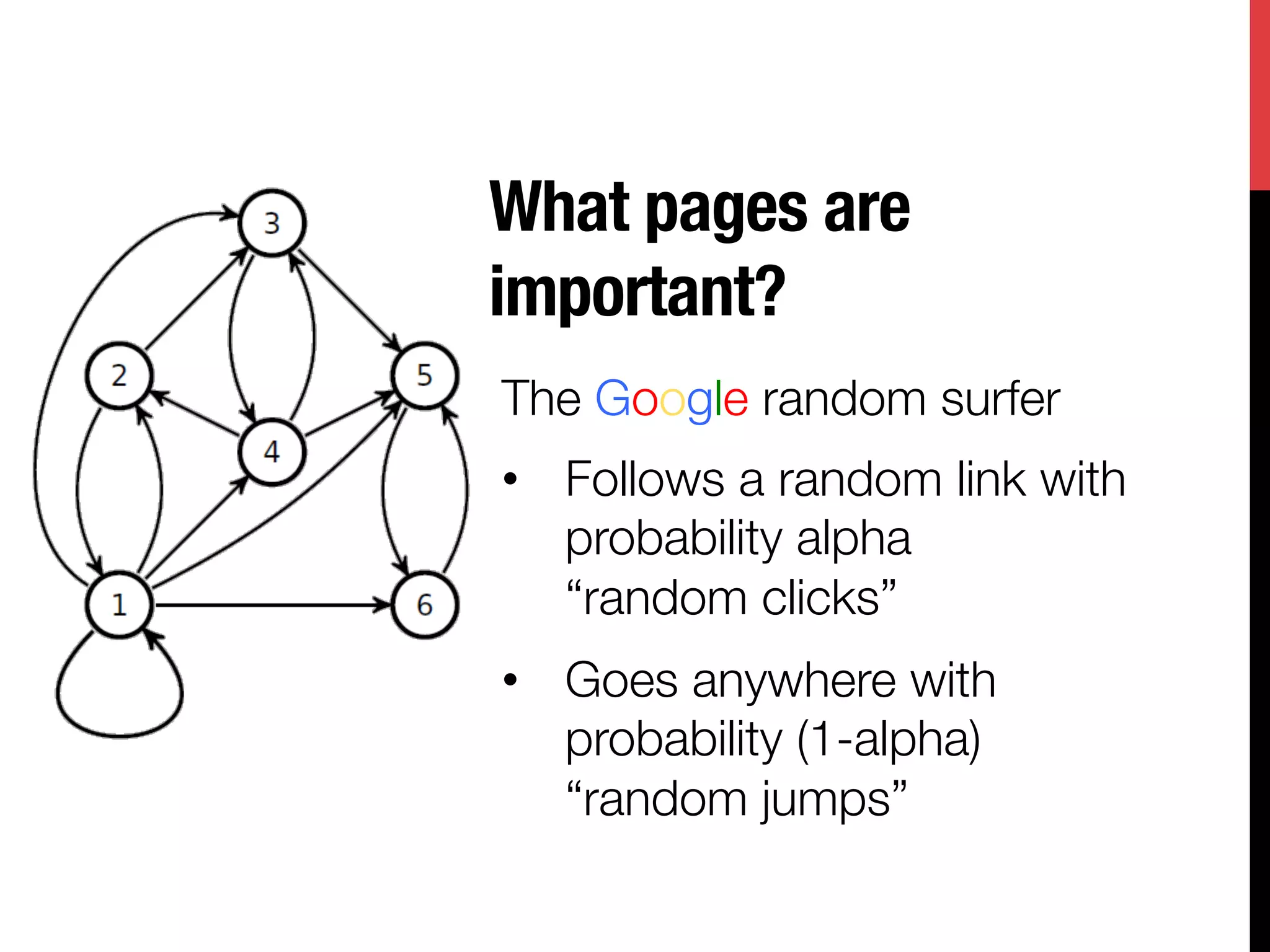


![What pages are
important?
Perron and Frobenius proved the
following algorithm always
converges to a solution…
set prob[i] = 0 for all pages
set p to a random page
for t = 1 to ...
increment prob[p]
if rand() < alpha,
set p to a random neighbor of p
else, set p to a random page](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gleich-pagerankhistory-final-130214122854-phpapp01/75/A-history-of-PageRank-from-the-numerical-computing-perspective-20-2048.jpg)

![What pages are
important?
Using the von Mises method …
set prob[i] = 1/n for all pages
for t = 1 to about 80
set newprob[i] = 0 for all pages
for all links from page i to page j
set newprob[j] += prob[i]/deg[i]
for all pages I
set prob[i] = alpha*newprob[i] +
(1-alpha)/n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gleich-pagerankhistory-final-130214122854-phpapp01/75/A-history-of-PageRank-from-the-numerical-computing-perspective-22-2048.jpg)