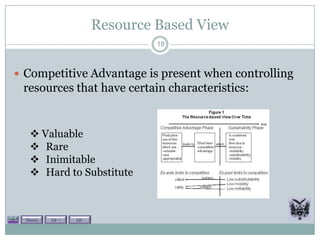
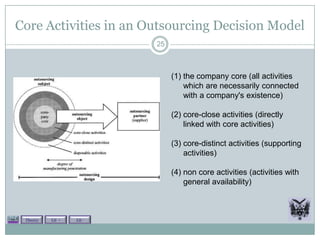
The document discusses several theories related to outsourcing including resource based view, transaction cost economics, total cost of outsourcing, agency theory, and a negative curvilinear model. It also reviews advantages like strategic focus, lower costs, flexibility, and disadvantages like interfaces, hollowing out, and opportunistic behavior. Theories, advantages, and disadvantages are supported with examples and literature. The document provides context for outsourcing decisions and considerations.