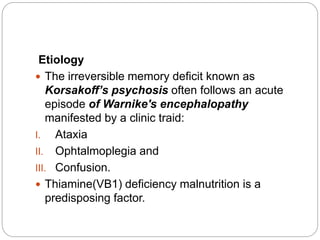
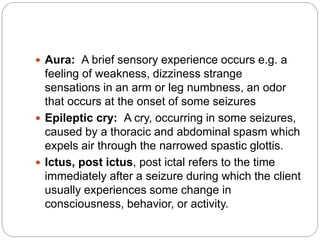
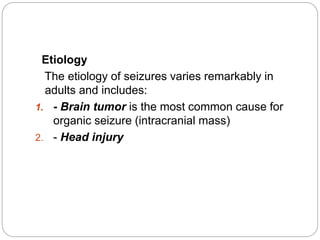
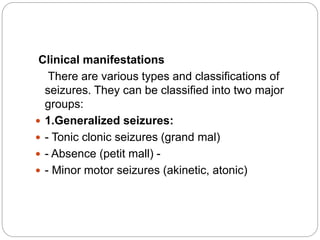
This document defines and describes various terms related to substance abuse, with a focus on alcohol abuse. It defines terms like teetotaler, social drinker, excessive drinker, tolerance, withdrawal, and substance abuse. It then describes the effects of alcohol on the body and central nervous system. It discusses alcoholism, risk factors, medical complications, and treatment approaches for alcohol abuse and withdrawal. It also briefly discusses other substance abuse issues like khat use.