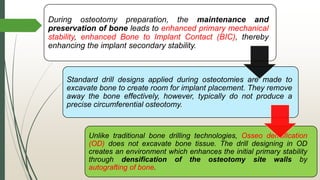
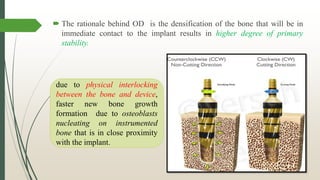
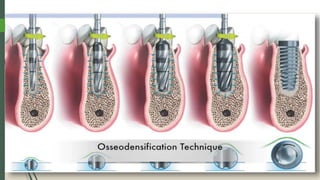
The document discusses osseodensification (OD), a novel technique in implant dentistry aimed at enhancing primary implant stability through bone densification rather than excavation. It highlights the advantages of OD, such as maintaining bone integrity and increasing the bone-to-implant contact, along with the specific design of the densah burs used in the procedure. The conclusion emphasizes OD's potential in providing effective solutions for patients with poor bone quality and reducing treatment time.























![REFERENCES:
Huwais S. Enhancing implant stability with Osseo densification-a case
report with 2-year follow-up. Implant practice. 2015;8(1):28-34.
Huwais S, Meyer EG. Osseo densification: A novel approach in implant
preparation [21] to increase primary stability, bone mineral density and
bone to implant contact. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(1):27-36.
Trisi P, Berardini M, Falco A, Vulpiani MP. New Osseo densification
implant site preparation method to increase bone density in low-density
bone: in vivo evaluation in sheep. Implant Dent. 2016;25(1):24-31.
Gayathri S. “Osseo densification Technique – A Novel Bone Preservation
Method to Enhance Implant Stability”. Acta Scientific Dental Sciences 2.12
(2018): 17-22.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osseodensificationjc-200706083015/85/Osseodensification-29-320.jpg)