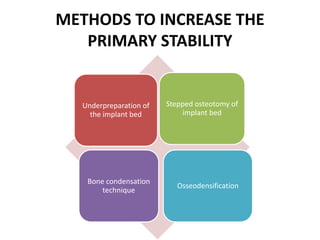
Osseodensification is a novel bone preservation technique that uses specially designed densifying burs to compress and densify bone at the implant site rather than removing it. This increases primary stability and bone density compared to conventional drilling. The densifying burs cut bone in one direction and densify it in the other, creating an autografted layer along the osteotomy walls. Studies have found osseodensification enhances implant stability, reduces treatment time, and facilitates placement in low-density bone or ridge expansion. However, it is an expensive technique that requires specialized burs and training.