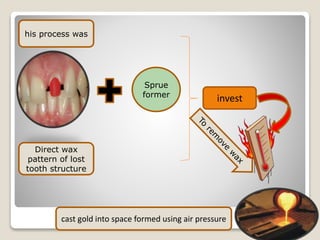
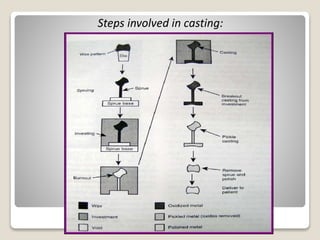
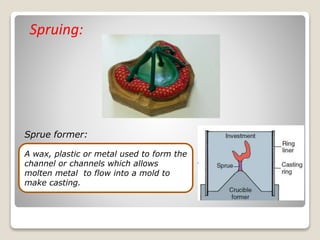
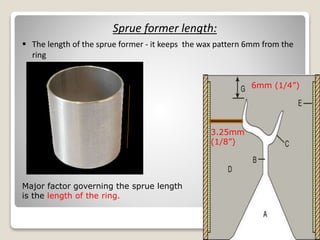
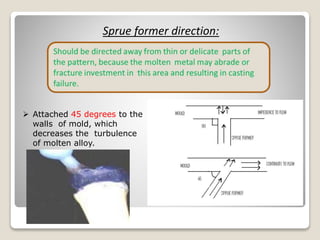
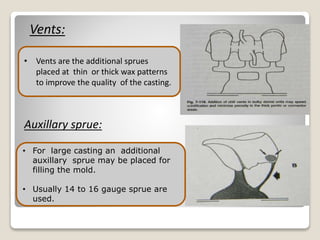
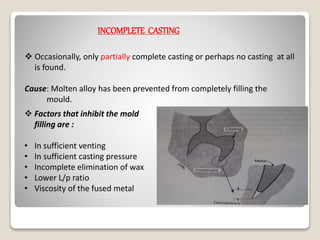
This document discusses casting procedures and defects in dentistry. It begins with definitions of casting and provides a brief history. It then outlines the key steps in the casting process including spruing, investing, burnout, casting machines, and defects. The main steps are spruing the wax pattern, investing it, burning out the wax during heating, and using casting machines to pour molten alloy into the mold. Common defects include distortion, surface roughness, porosity, and incomplete casting details. The document provides causes and prevention of defects.