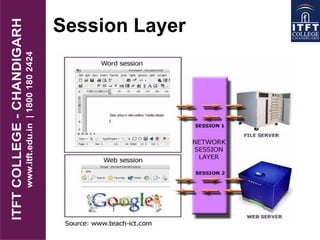
The OSI reference model defines a standard framework for how information is communicated between computers. It consists of 7 layers, with each layer defining a set of rules or protocols for how data is formatted and transmitted between devices. The physical layer deals with physical connections and transmission of raw bits. Higher layers deal with networking, routing, sessions, data translation and presentation for applications. Gateways allow communication between systems that use different protocols by translating between protocol layers. The OSI model provides interoperability standards for network communication.