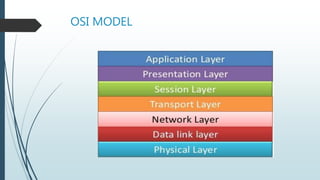
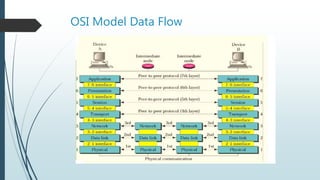
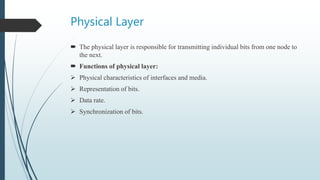
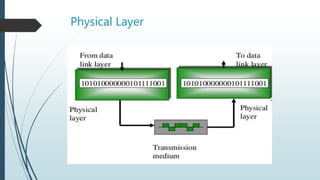
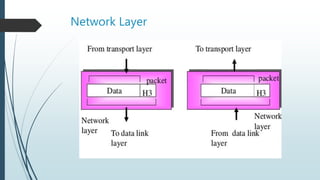
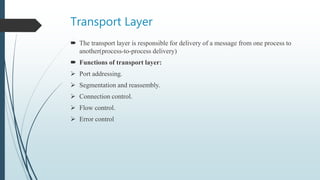
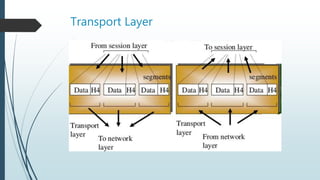
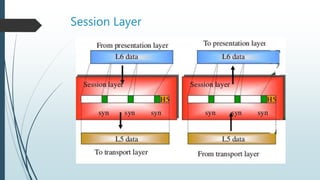
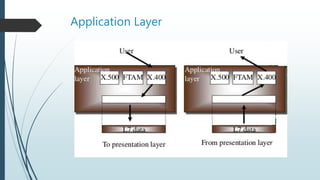
The document presents information on the OSI model, which is a seven-layer model for network communication created by ISO in the late 1970s. It describes each of the seven layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layer - and their basic functions. The OSI model shows how protocols are implemented at each level to allow systems to communicate regardless of their underlying architectures.