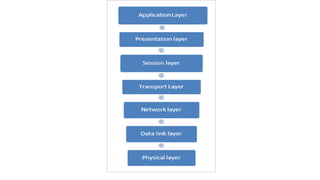
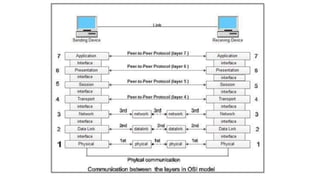
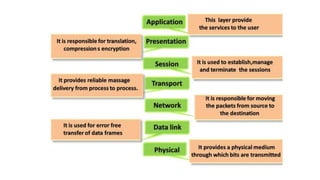
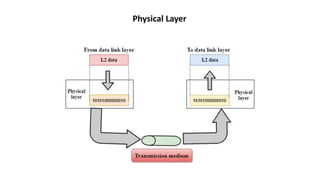
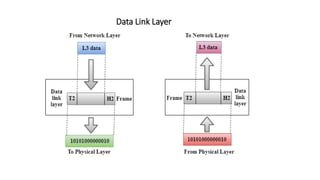
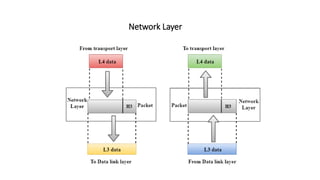
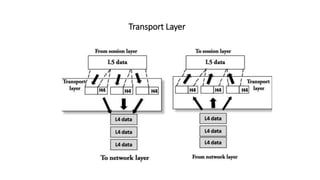
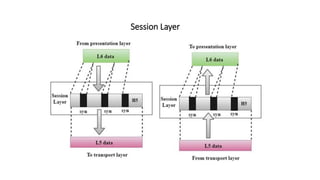
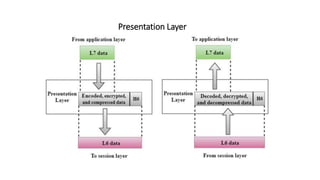
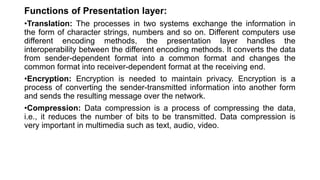
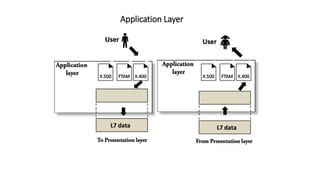
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that characterizes networking functions into 7 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation and application. Each layer has a specific role, with the physical layer defining physical connections and signals and the application layer supporting file transfer, email and directories. Data moves down from the application layer through each layer, with each adding information like headers for routing. This allows interoperability between different network products and software.