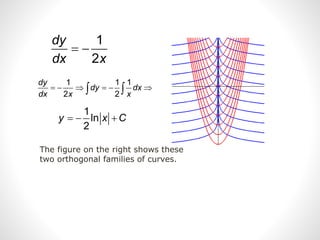
This document discusses orthogonal trajectories and provides examples of finding orthogonal trajectories for different families of curves. It begins by defining orthogonal trajectories as curves that intersect each other at right angles. It then provides a method for finding the differential equation that describes the orthogonal trajectories for a given family of curves. Several examples are worked out, such as finding the orthogonal trajectories of the family of parabolas with equation y = x^2. Applications to equipotential lines and electric fields and electromagnetic waves are also mentioned.