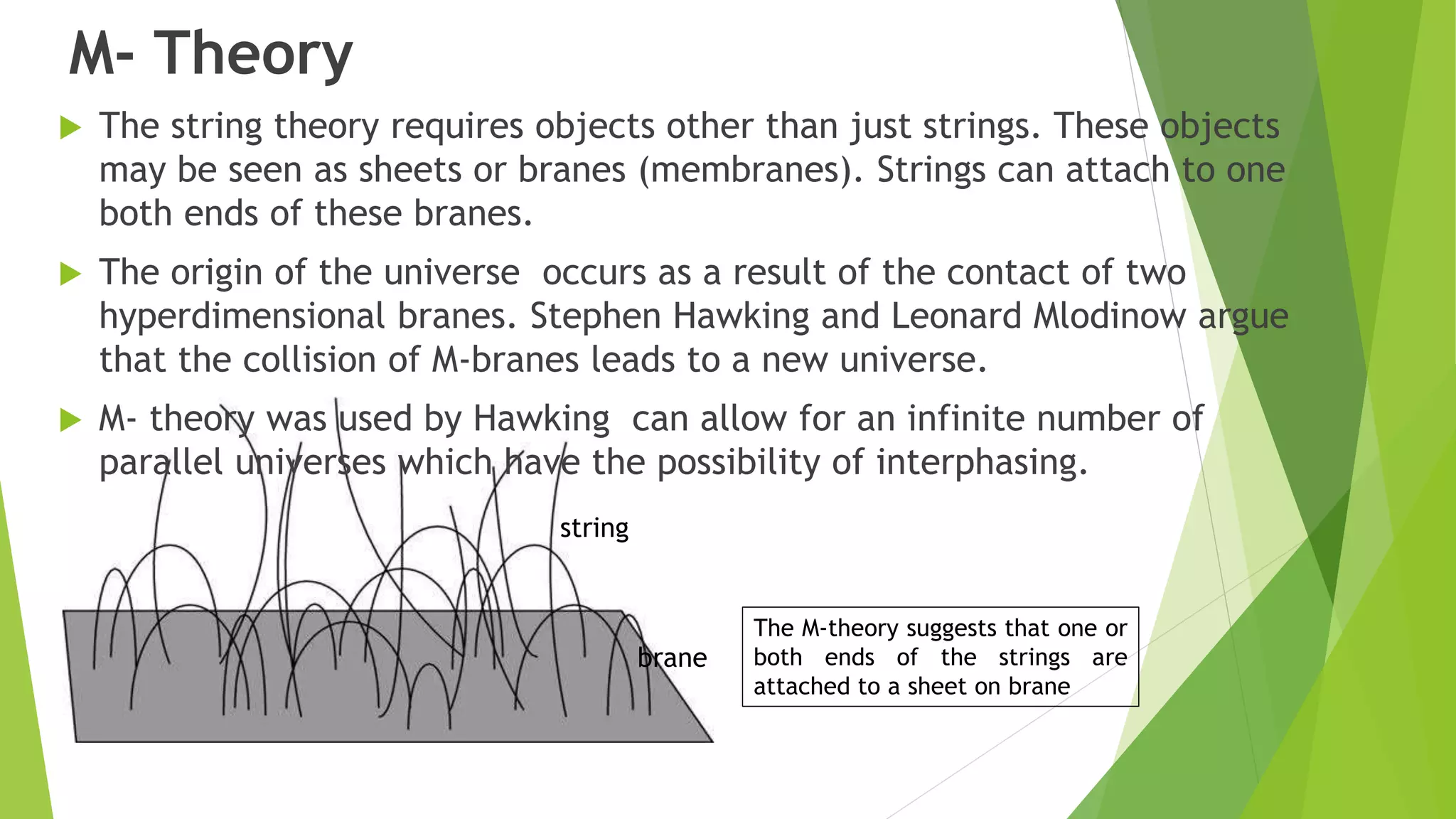
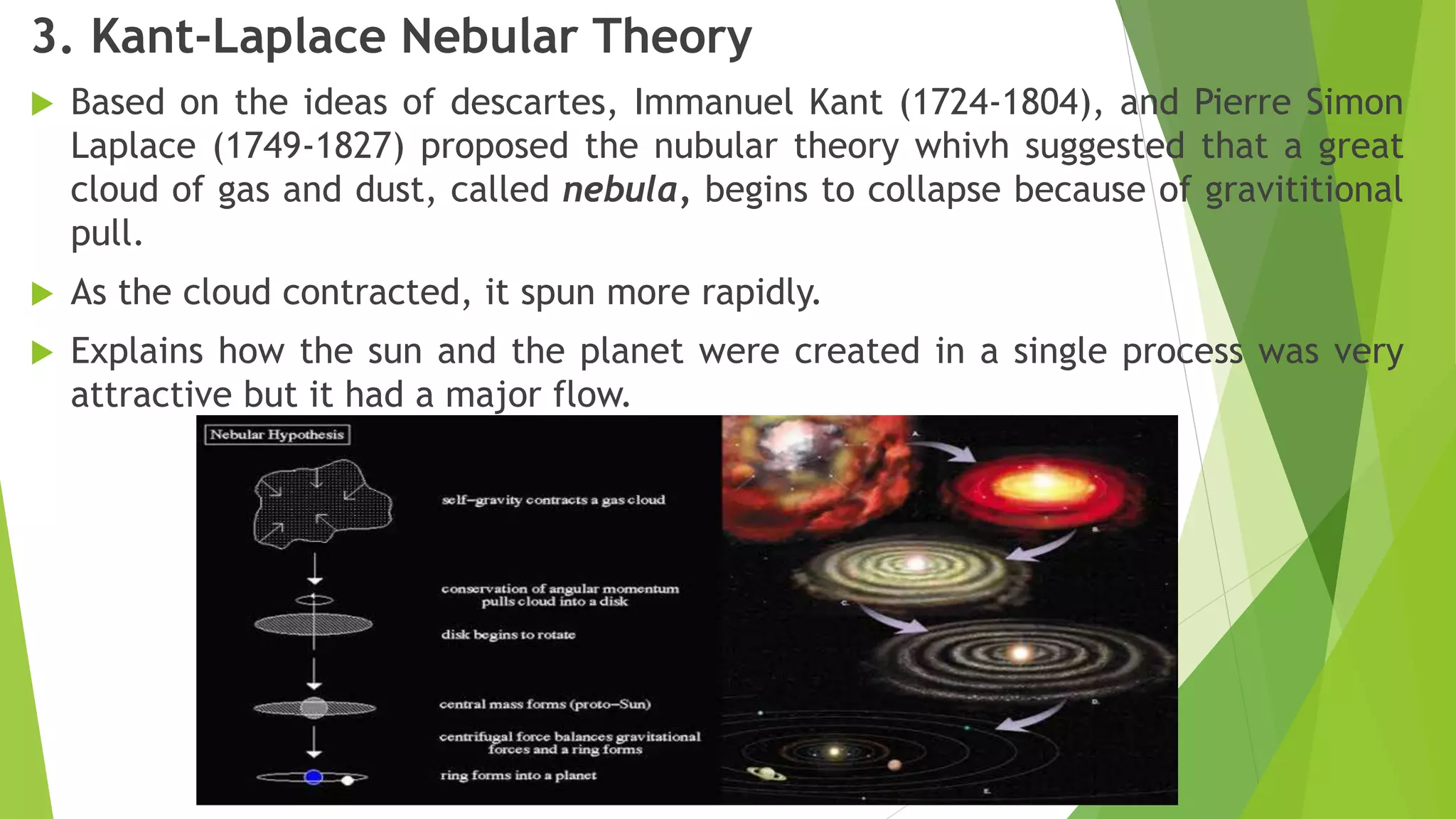
The document summarizes the origin of the universe and the solar system. It discusses the Big Bang theory and other theories such as inflation theory and M-theory. It also discusses early theories on the origin of the solar system such as Descartes' vortex theory and the Kant-Laplace nebular hypothesis. Additionally, it provides details on properties of the current solar system, including classifications of planets and components such as asteroids and comets.