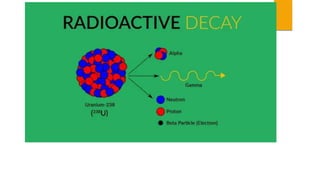
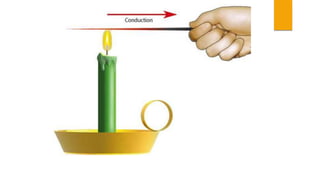
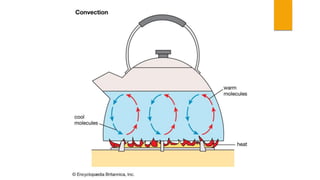
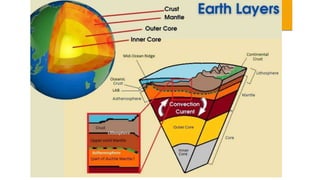
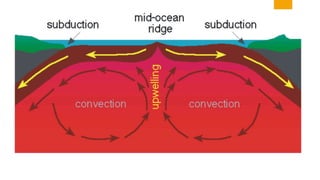
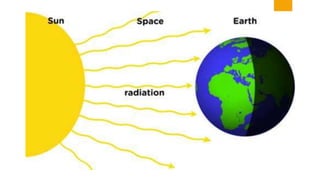
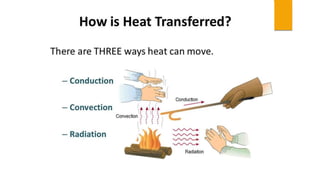
The document discusses the sources and transfer of Earth's internal heat. It identifies two main sources: primordial heat from the planet's formation and radiogenic heat from the radioactive decay of elements in Earth's interior like uranium, thorium, and potassium. It describes three processes for transferring heat within Earth: conduction within solid portions, convection through mass movement in the mantle, and radiation between the Sun and Earth's surface.