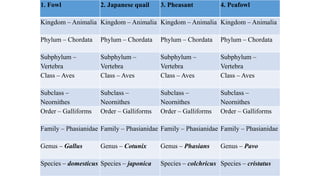
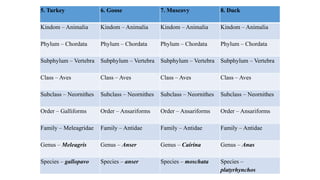
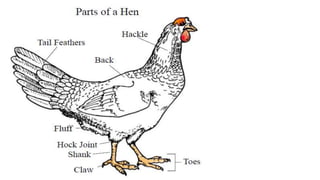
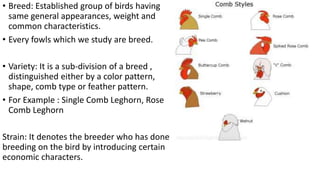
This document discusses the classification and types of poultry. It begins by outlining the zoological classification of poultry from kingdom to species. It then provides examples of common poultry types including their classification and characteristics. Finally, it describes several popular chicken breeds, focusing on their traits, uses, and standard weights.