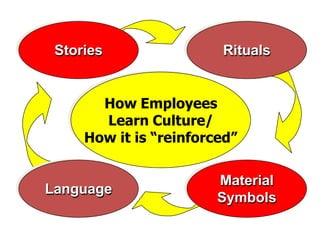
This document discusses organizational culture and climate. It defines organizational culture as a system of shared meanings and defines elements of culture as visible and invisible. Popular companies like Google, Netflix and Zappos are provided as examples of inspiring cultures. Organizational climate is defined as the perceptions of the work environment that influence employee behavior and motivation. The differences between culture and climate are outlined, with culture focusing on long-term values and norms, and climate focusing on short-term attitudes and practices.