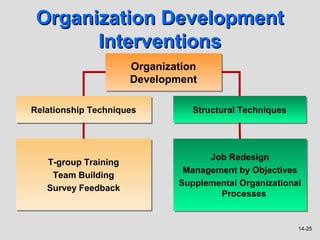
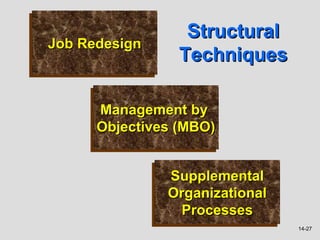
The document discusses organizational change and describes:
1) Organizational change is the process by which organizations move from their present state to a desired future state to increase effectiveness. It occurs in response to internal and external forces.
2) Change can affect people, structure, technology and other elements of an organization. It also impacts the speed and significance of change within an organization.
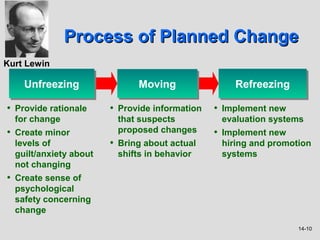
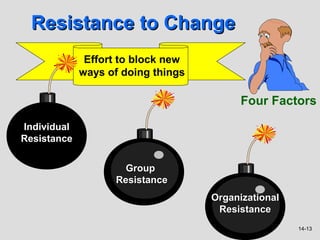
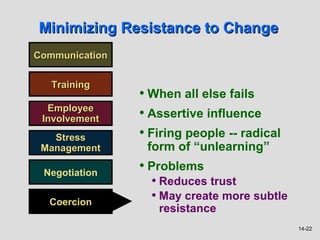
3) Resistance to change stems from individual, group, and organizational factors like threats to power, habits, and economic impacts. Minimizing resistance involves communication, training, employee involvement, and other strategies.