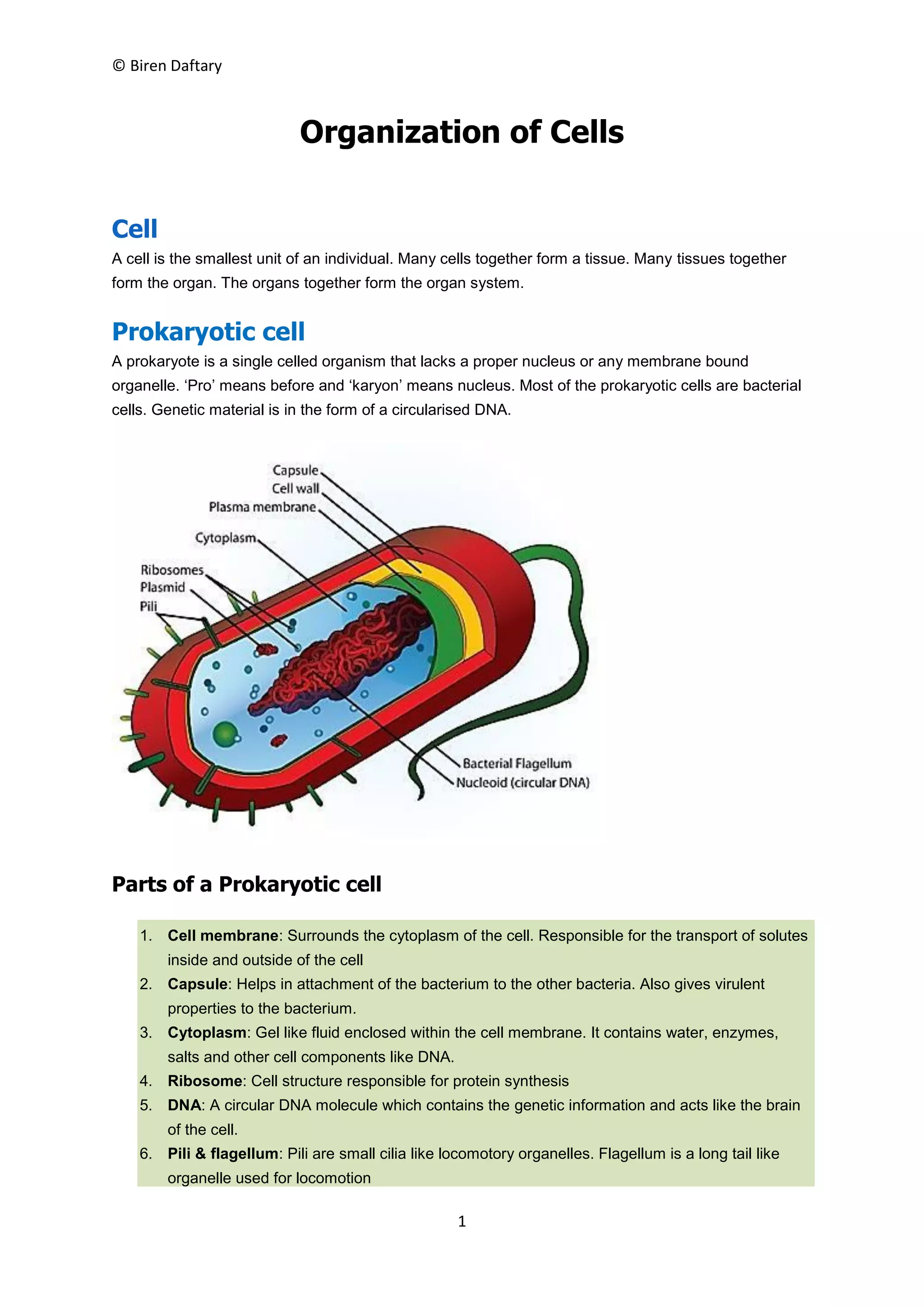
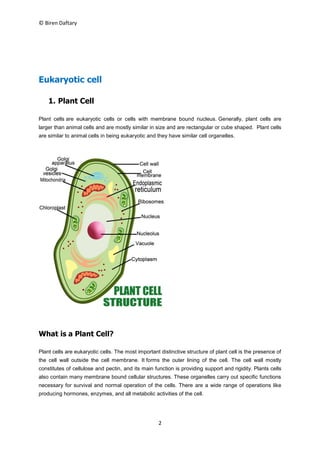
Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells that contain membrane-bound organelles. Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts for photosynthesis, while animal cells lack these features. The key components of plant cells include the cell wall, cell membrane, chloroplasts, vacuoles, nucleus, and mitochondria. Plant cells vary in shape but are generally cube-shaped. Animal cells come in various irregular shapes and sizes, and their organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, and ribosomes. Both plant and animal cells work together through their specialized organelles to carry out functions necessary for survival.