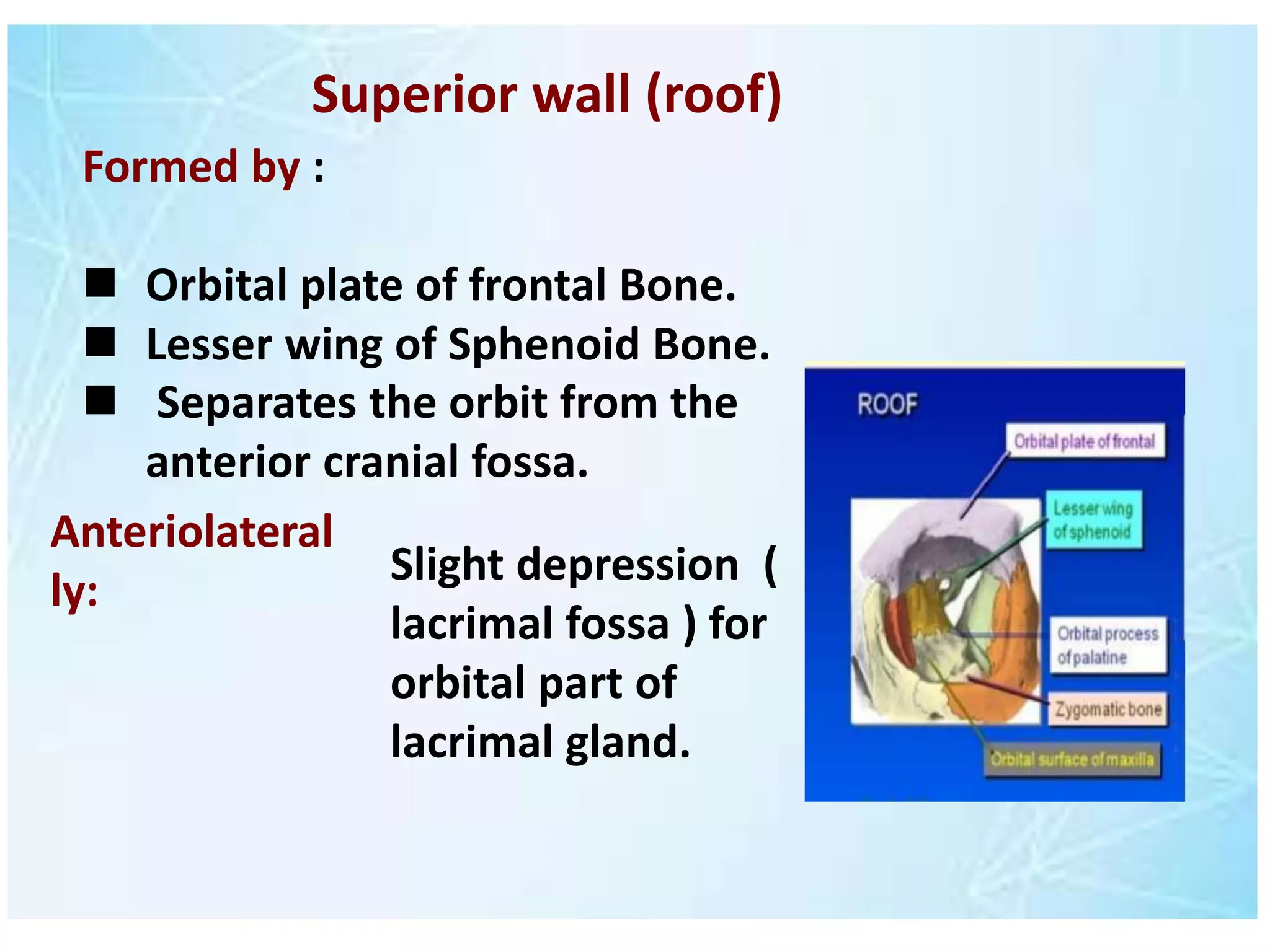
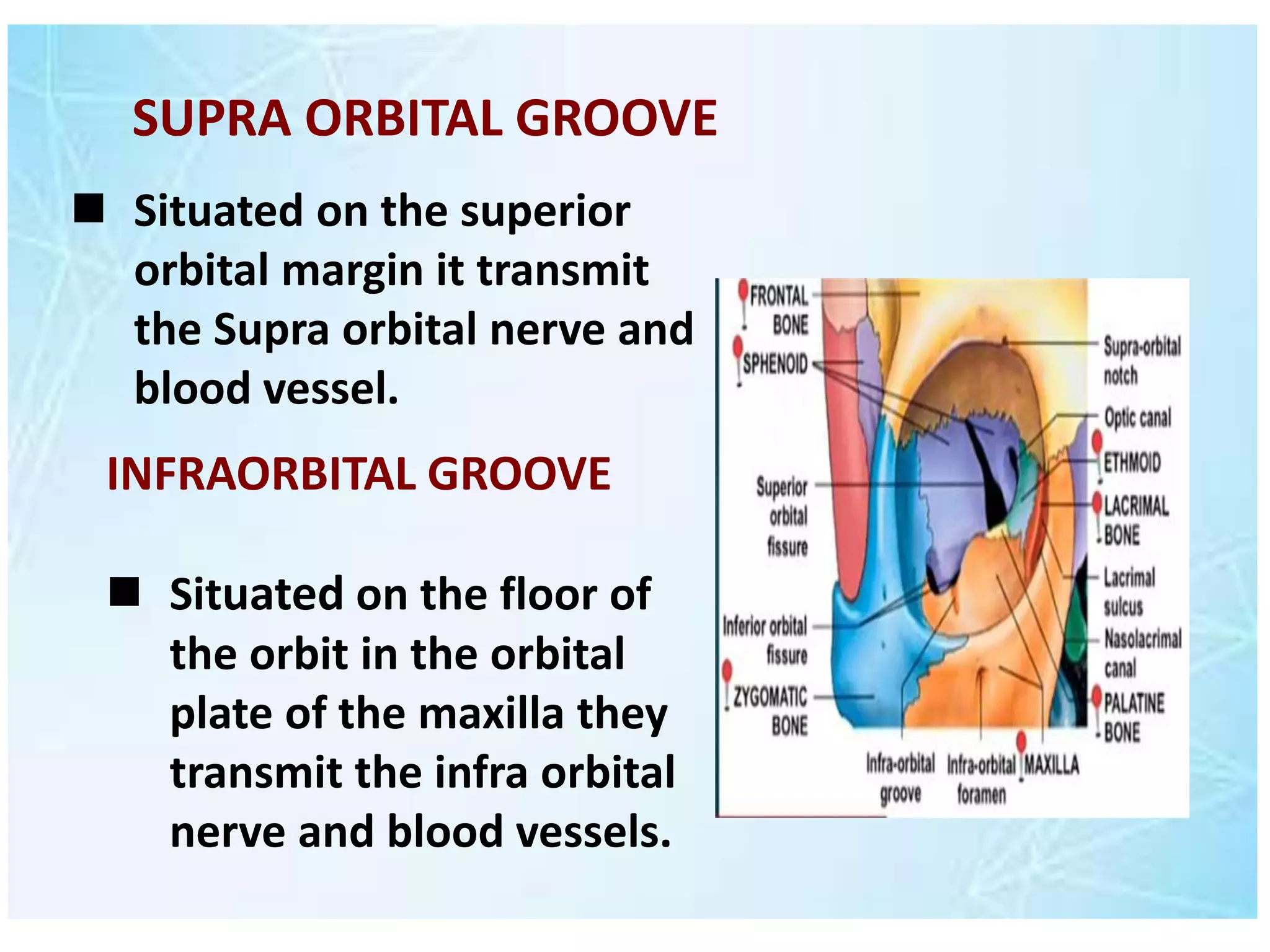
The document outlines the anatomy of the orbit, detailing its structure, dimensions, and components including the optic nerve, ocular muscles, and associated bones. It describes the walls of the orbit, their formation, and fractures that can occur, such as orbital rim and blow-out fractures, emphasizing the locations and implications of these injuries. Additionally, it notes how the shape and size of the orbit changes with age, from fetal stages to adulthood.