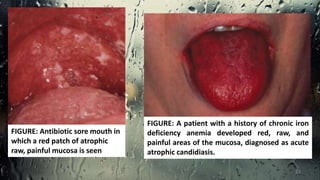
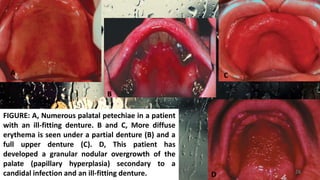
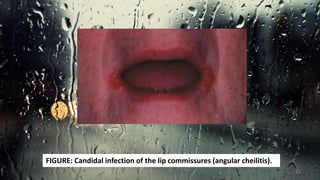
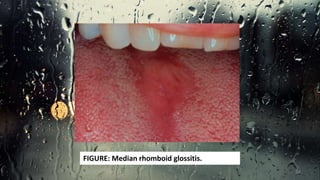
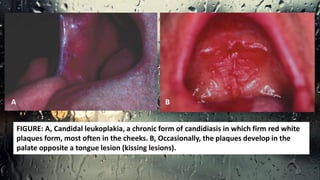
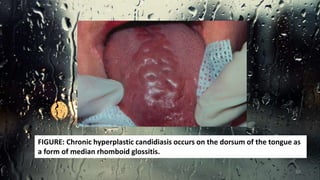
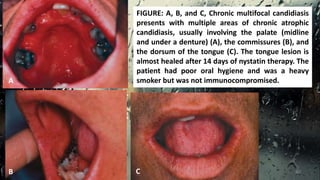
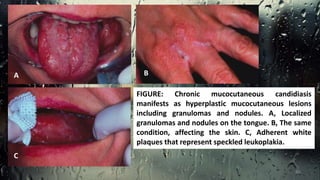
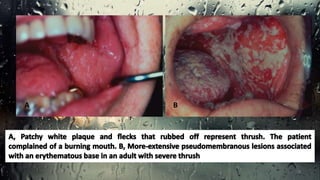
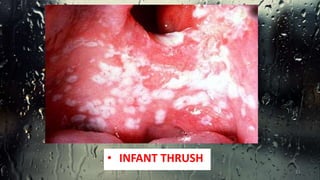
This document discusses various types of oral candidiasis, including acute pseudomembranous (thrush), acute atrophic, chronic atrophic forms such as denture stomatitis and angular cheilitis, and chronic hyperplastic candidiasis. It describes the clinical features, predisposing factors, histological findings, and treatments for each type. Immunocompromised individuals such as those with HIV/AIDS are more susceptible to oral candidiasis. Topical and systemic antifungal medications are used to treat infections, though relapses may occur due to underlying immune deficiencies.












![Predisposing Factors
1. Marked changes in oral microbial flora
1. due to the use of antibiotics [especially broad-spectrum antibiotics],
2. excessive use of antibacterial mouth rinses, or xerostomia
2. Chronic local irritants (dentures and orthodontic appliances)
3. Administration of corticosteroids (aerosolized inhalant and
topical agents are more likely to cause Candidiasis than
systemic administration)
4. Poor oral hygiene
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralcandidiasis-copy-140818091842-phpapp02/85/Oral-candidiasis-15-320.jpg)
![5. Pregnancy
6. Immunologic deficiency
1. congenital or childhood (chronic familial mucocutaneous candidiasis
± endocrine candidiasis syndrome [hypoparathyroidism,
hypoadrenocorticism], and immunologic immaturity of infancy)
2. acquired or adult (diabetes, leukemia, lymphomas, and AIDS)
3. iatrogenic (from cancer chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation,
and head and neck radiation)
7. Mal-absorption and malnutrition
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralcandidiasis-copy-140818091842-phpapp02/85/Oral-candidiasis-16-320.jpg)