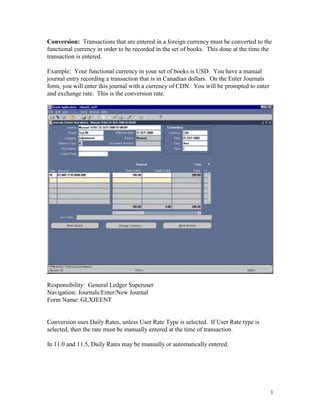
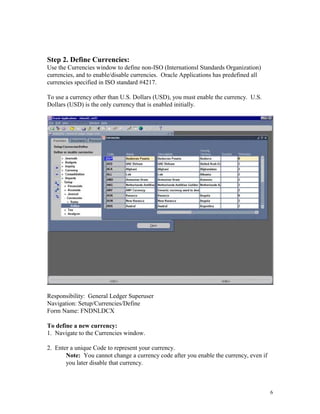
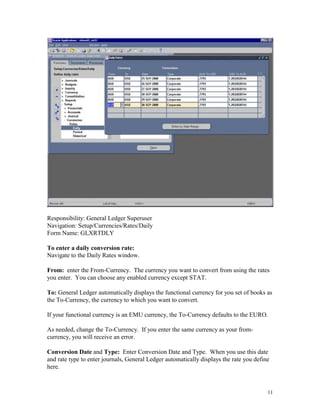
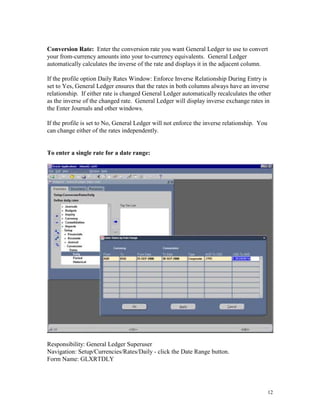
This document provides instructions for currency conversion in Oracle Applications General Ledger. It discusses defining conversion rate types, currencies, and entering daily conversion rates to automatically convert transaction amounts entered in foreign currencies to the functional currency. The document outlines the steps to define currencies, enable currencies for use, and define relationships for European Monetary Union currencies. It also describes using the GL_DAILY_RATES_INTERFACE table to automatically load daily conversion rates into General Ledger to avoid corrupting the data.