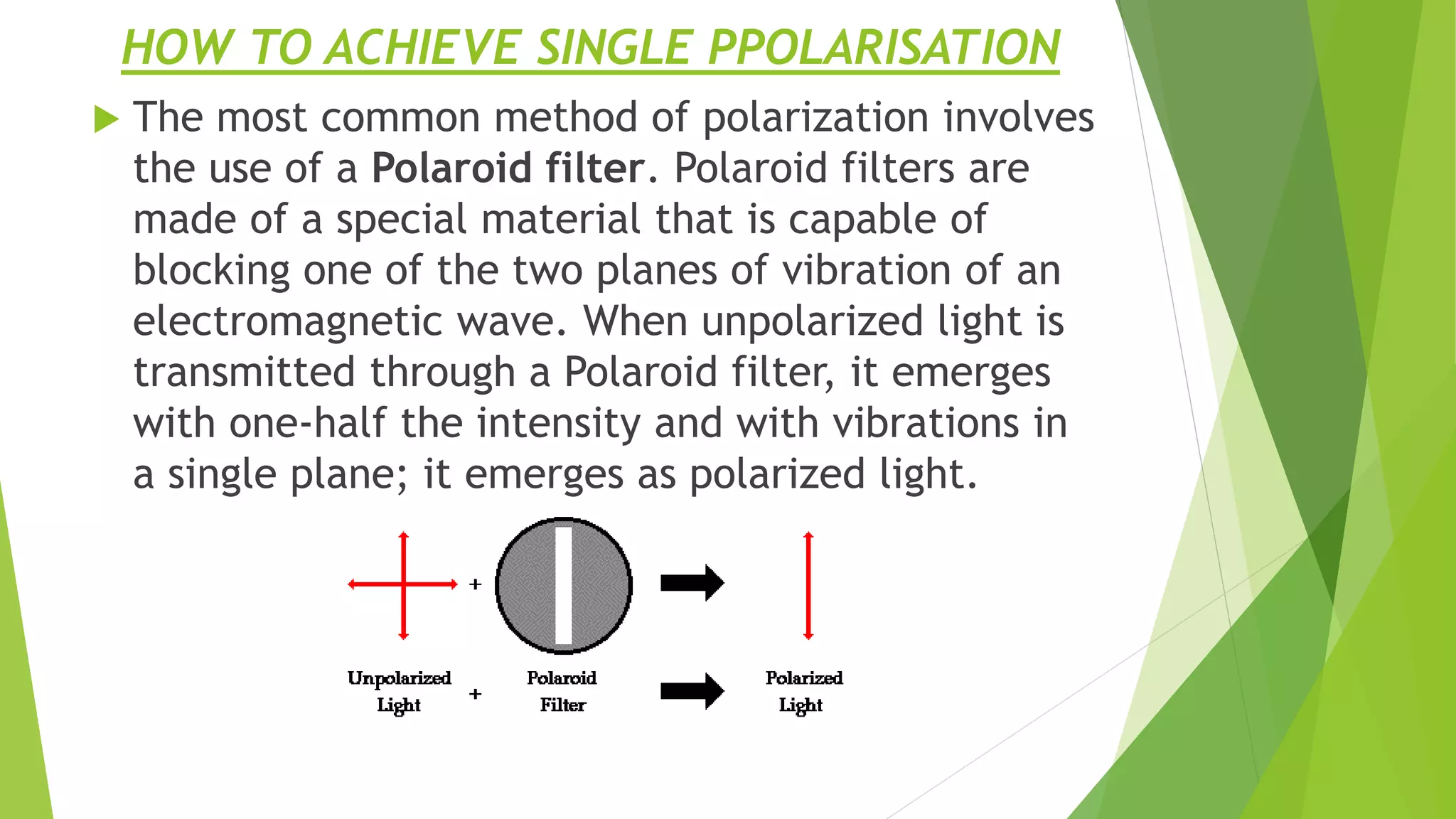
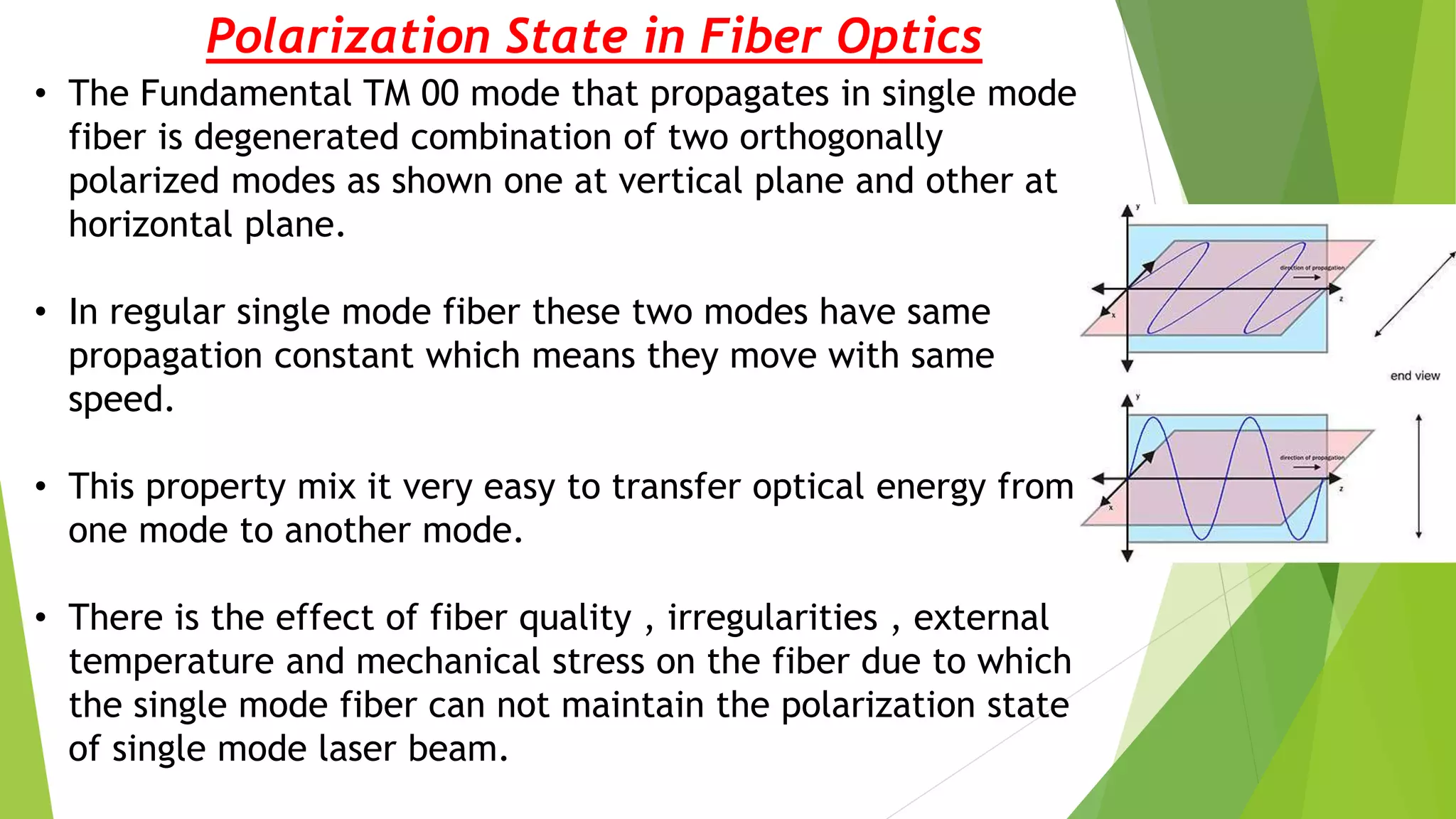
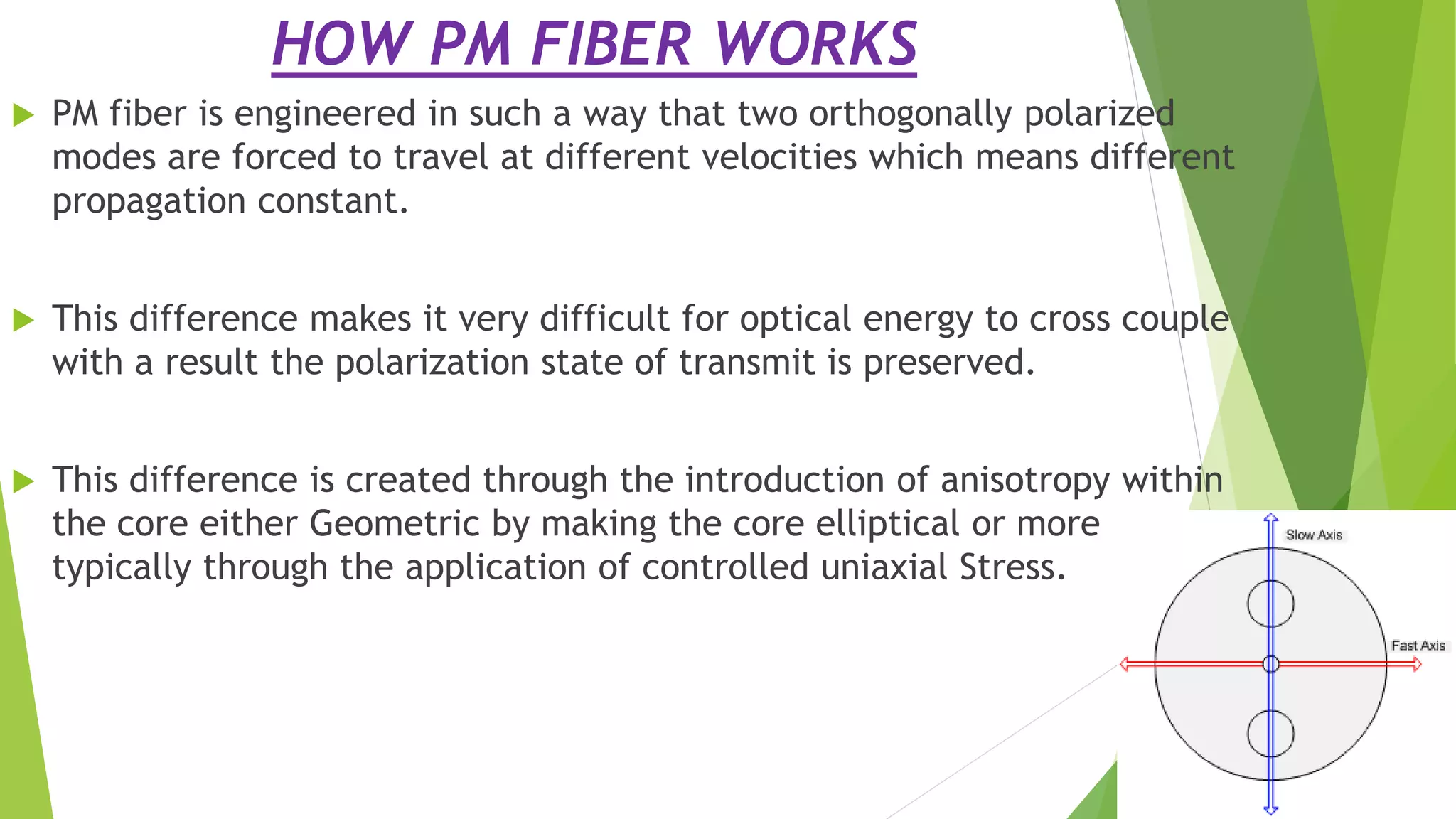
This presentation focuses on polarization maintenance in optical fibers, explaining the concepts of polarized and unpolarized light, as well as birefringence. It discusses the evolution and importance of polarization-maintaining fibers (PM fibers) in coherent optical transmission systems, highlighting their classifications, operational principles, and various applications. PM fibers are crucial for preserving the polarization state in fiber optics, particularly in telecommunications and sensing technologies.