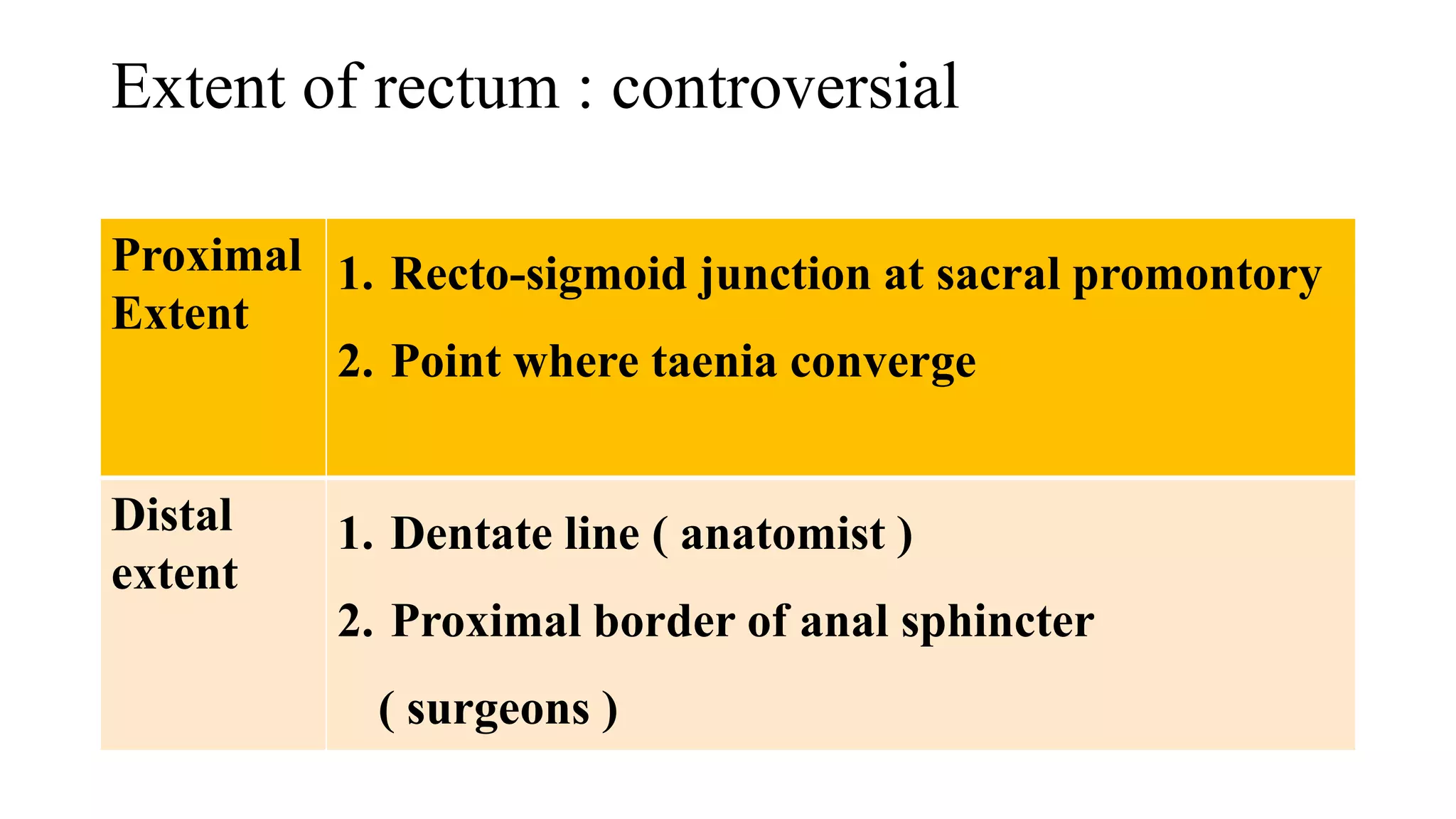
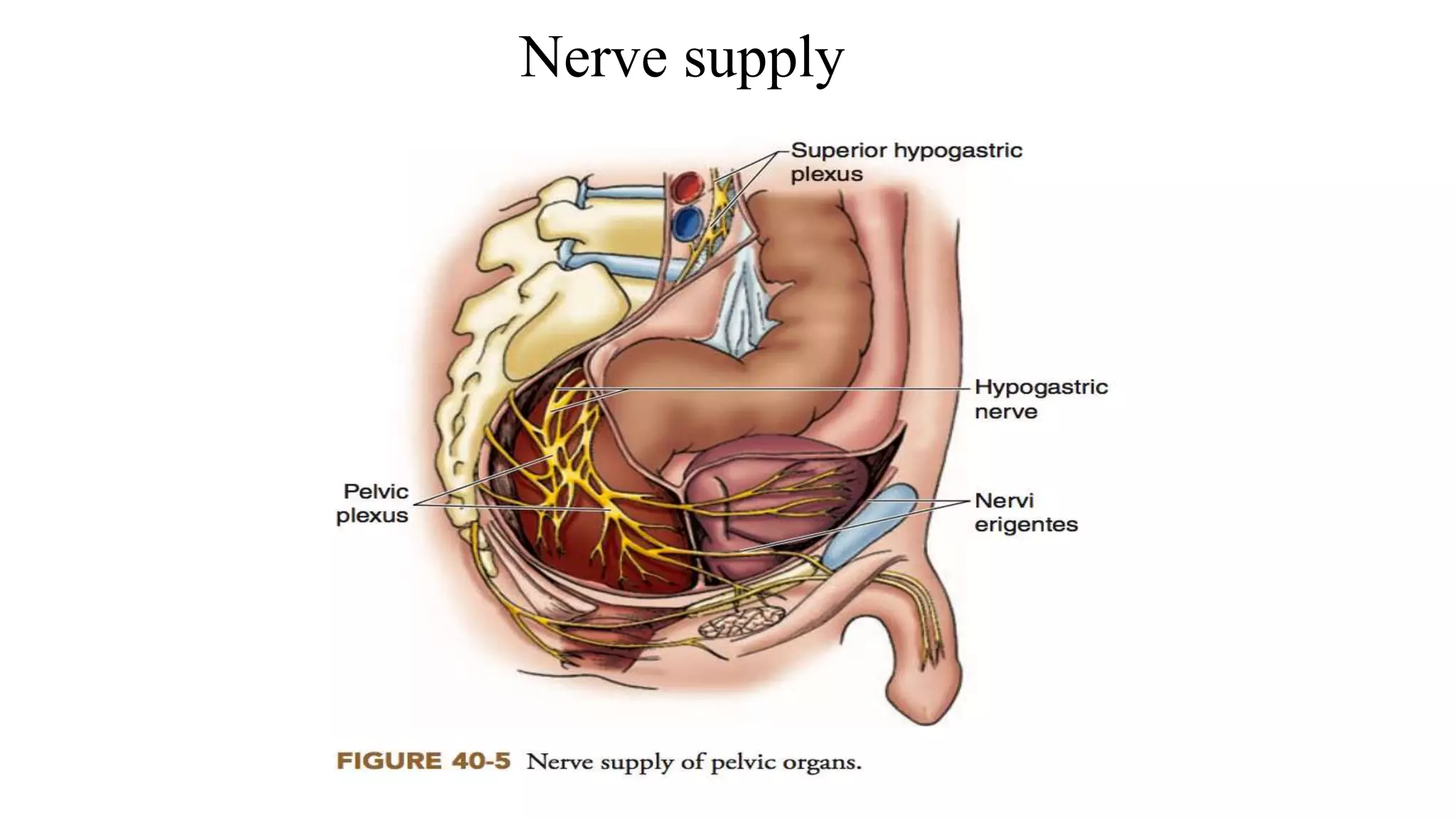
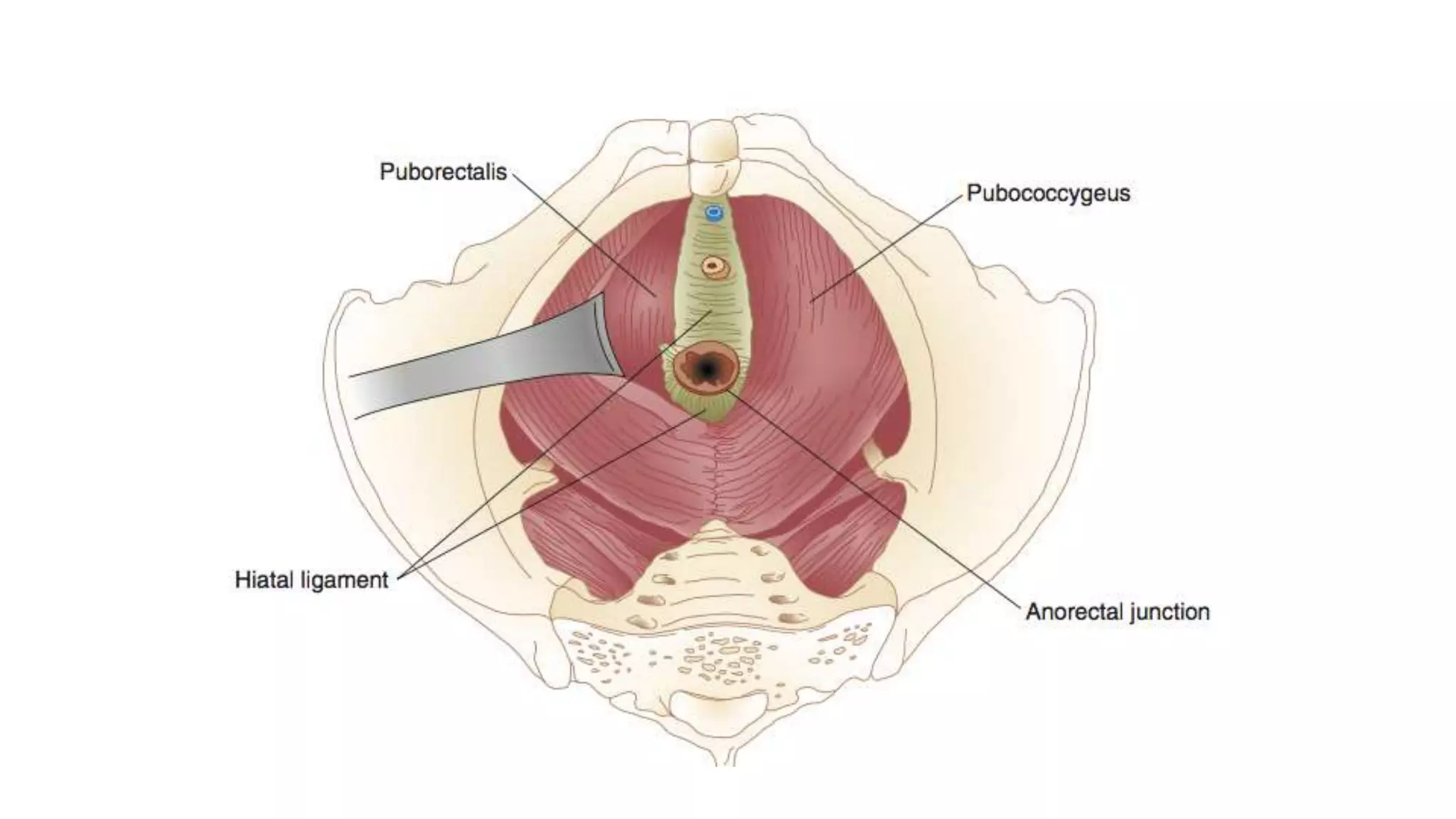
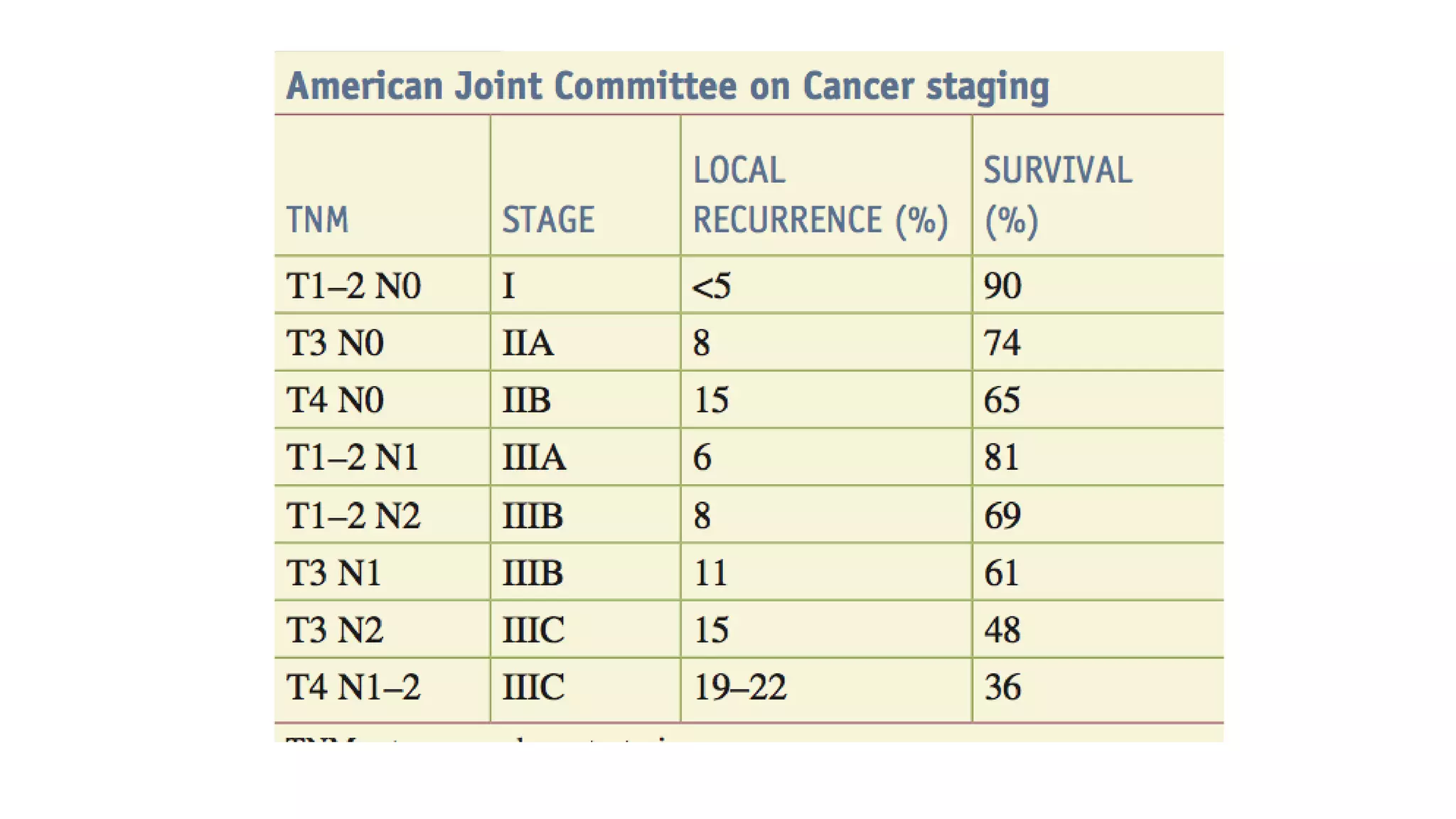
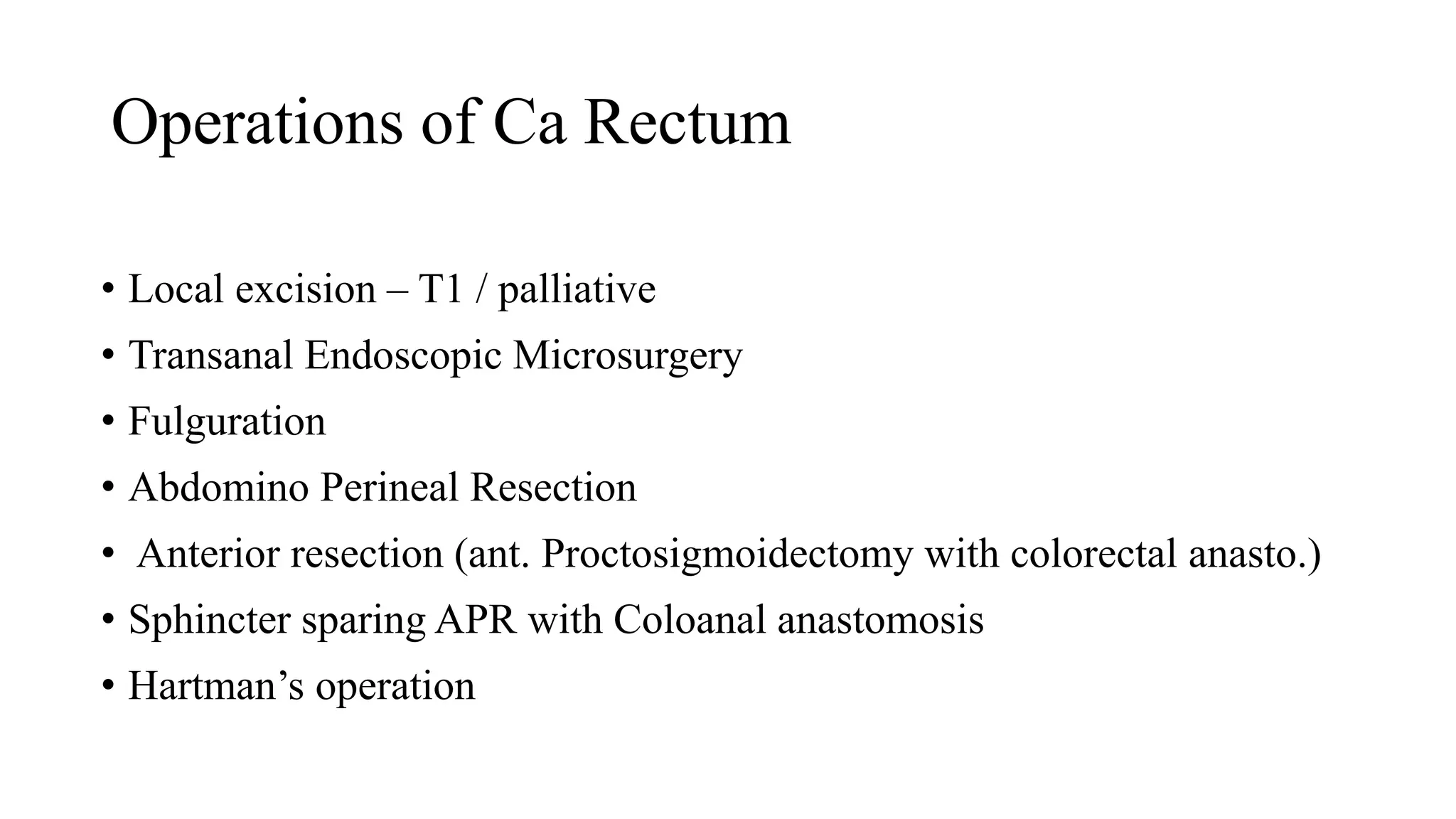
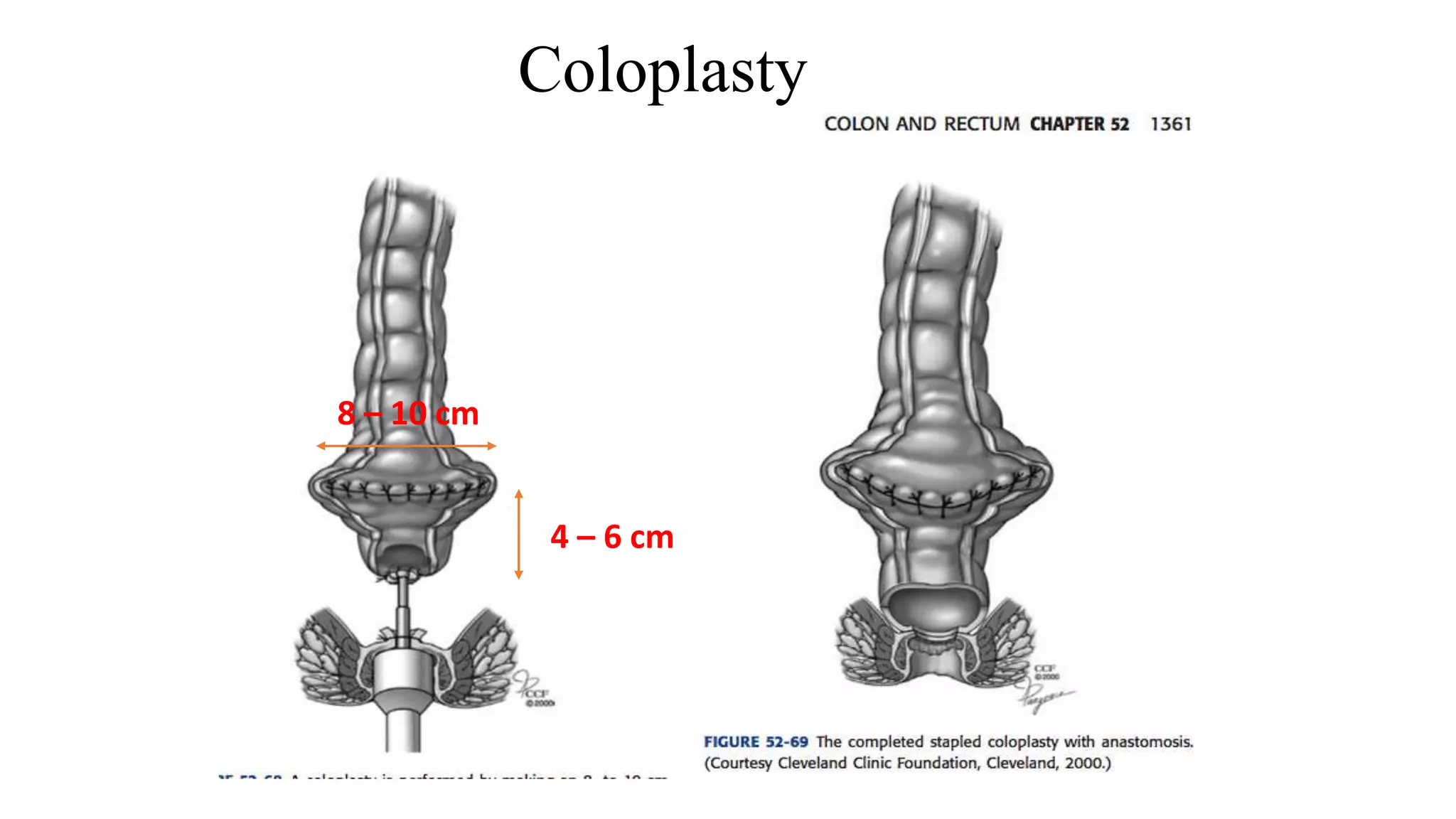
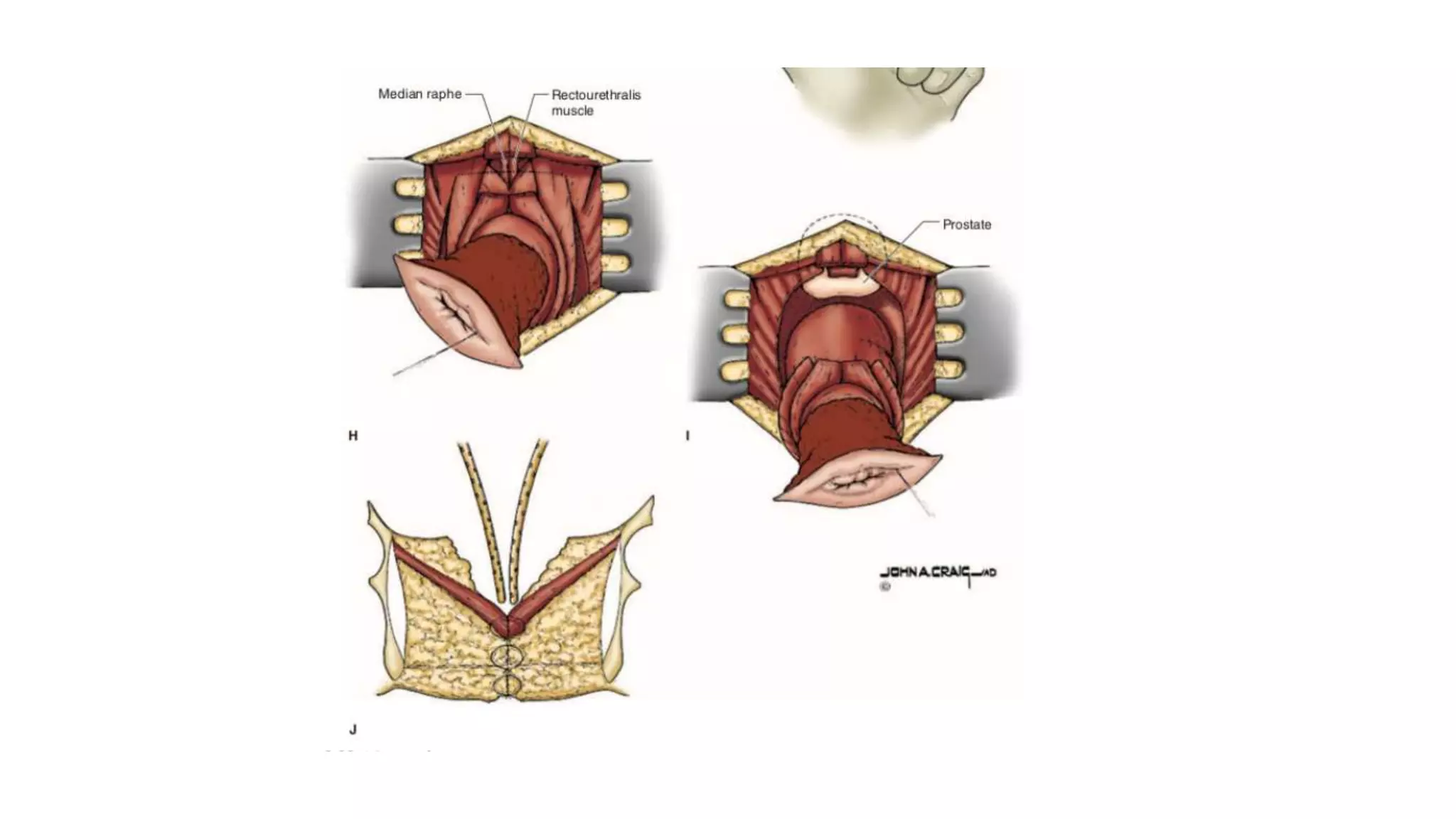
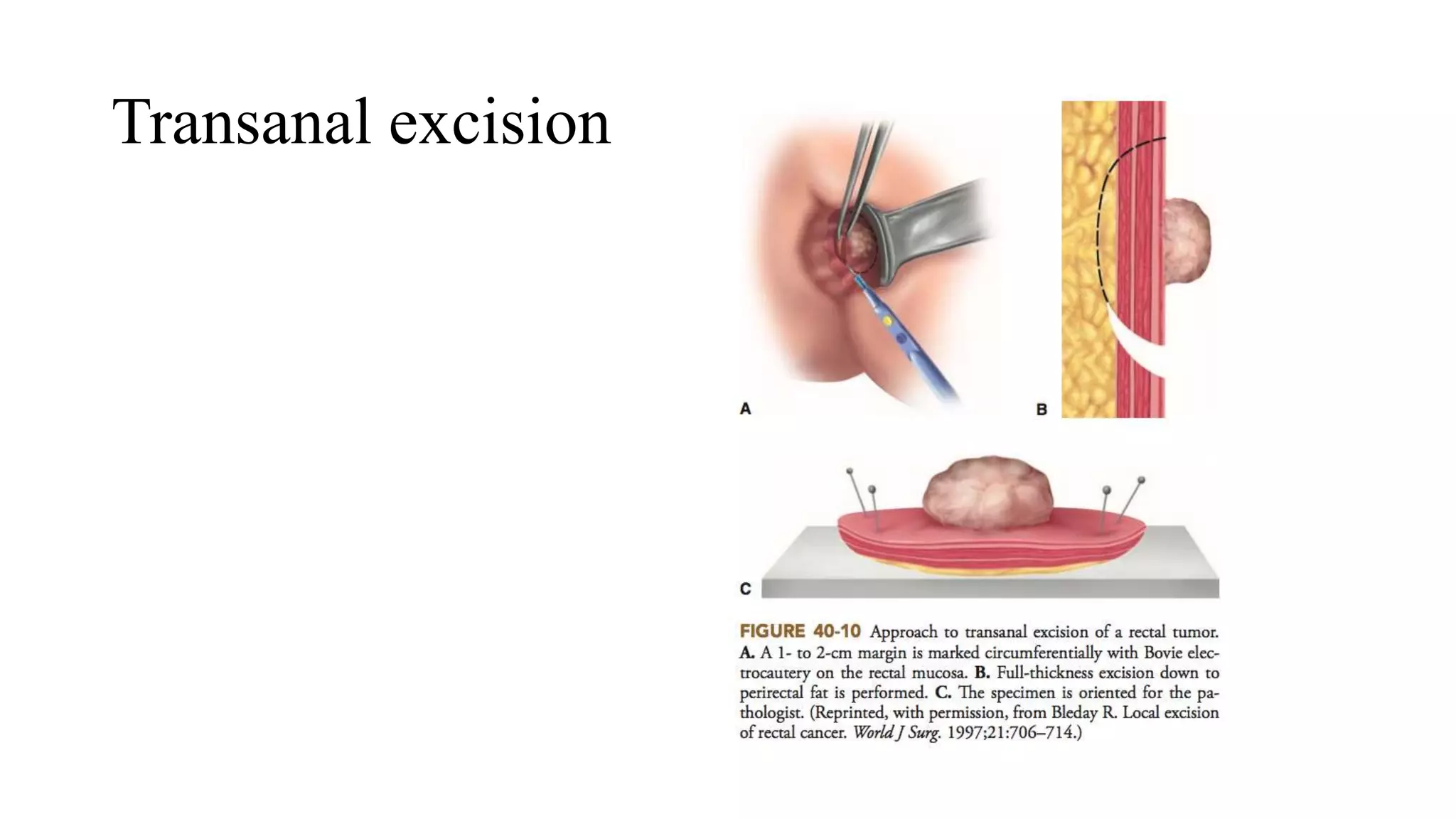
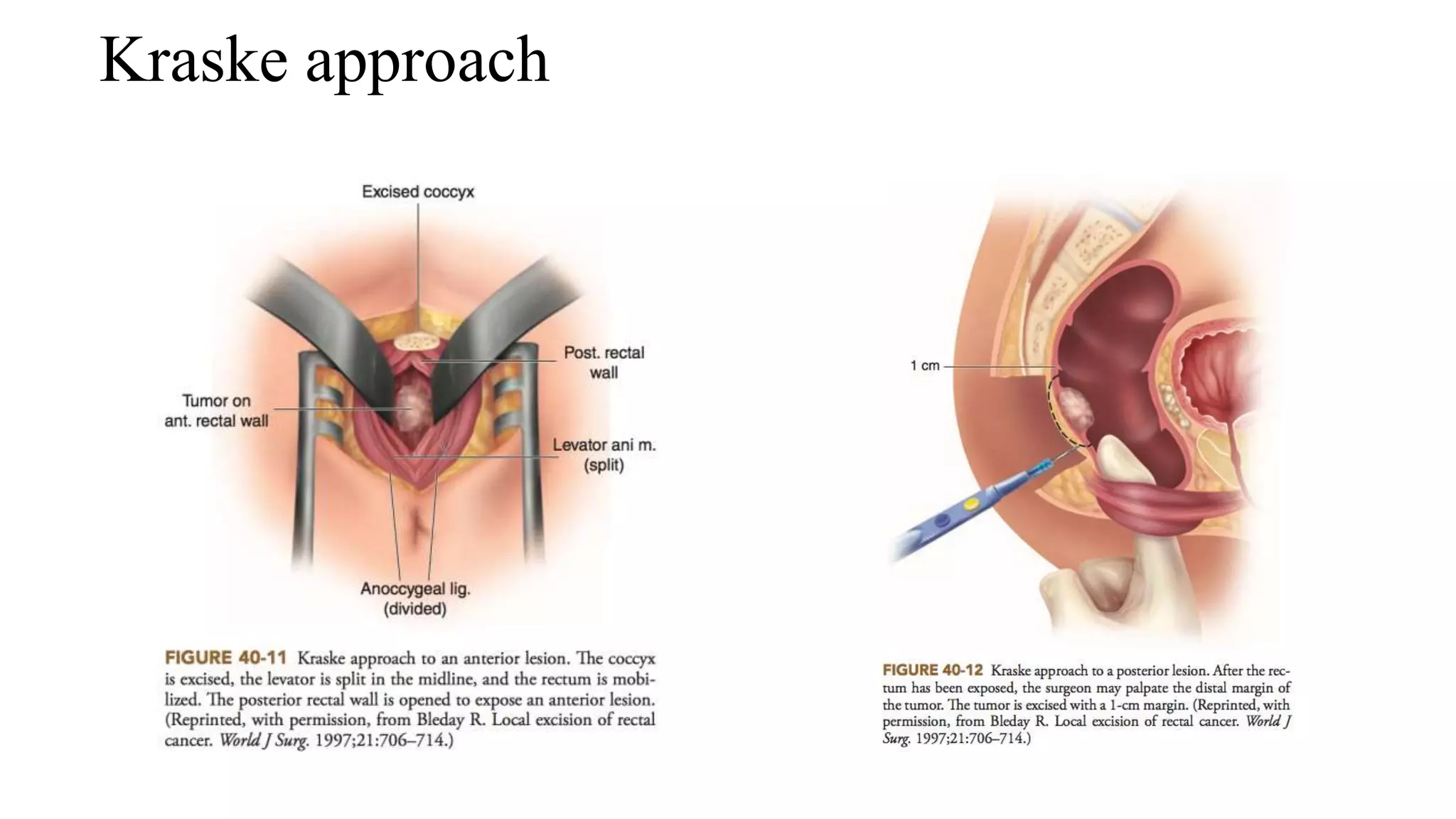
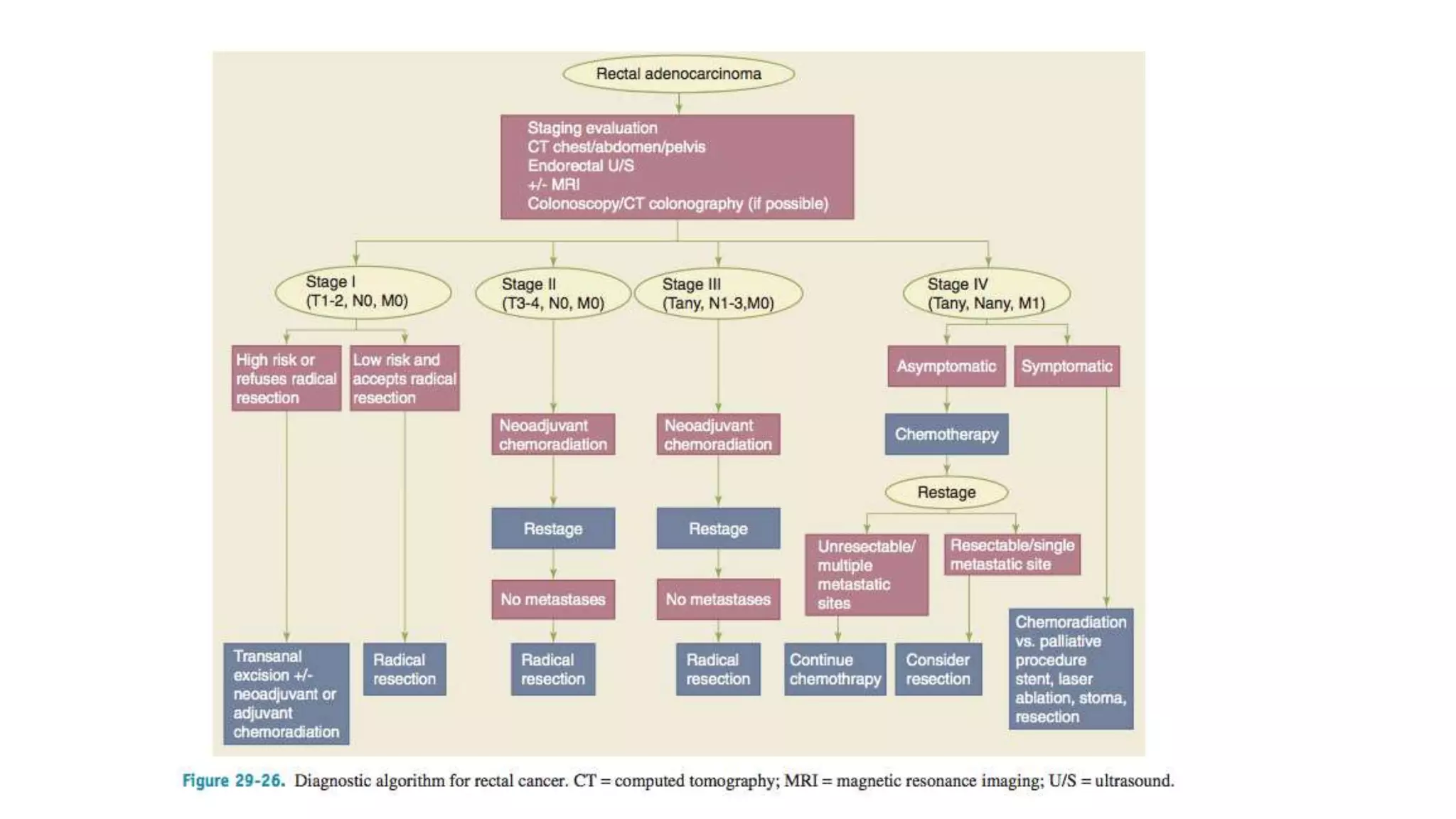
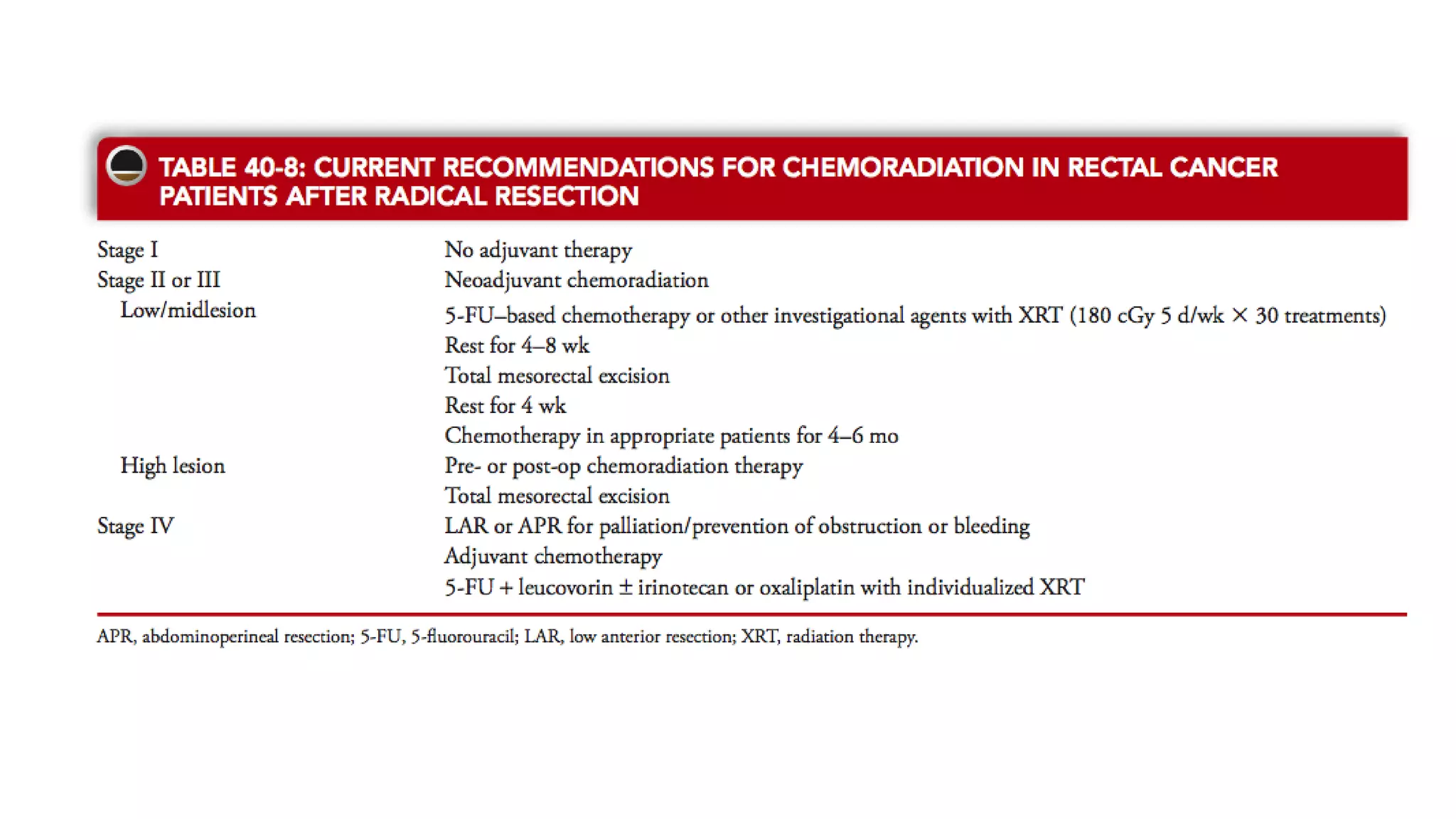
The document discusses various surgical procedures for treating cancer of the rectum, including:
1. Abdomino-Perineal Resection (APR), the classic operation pioneered by Miles, which removes the rectum and anus through an abdominal and perineal approach.
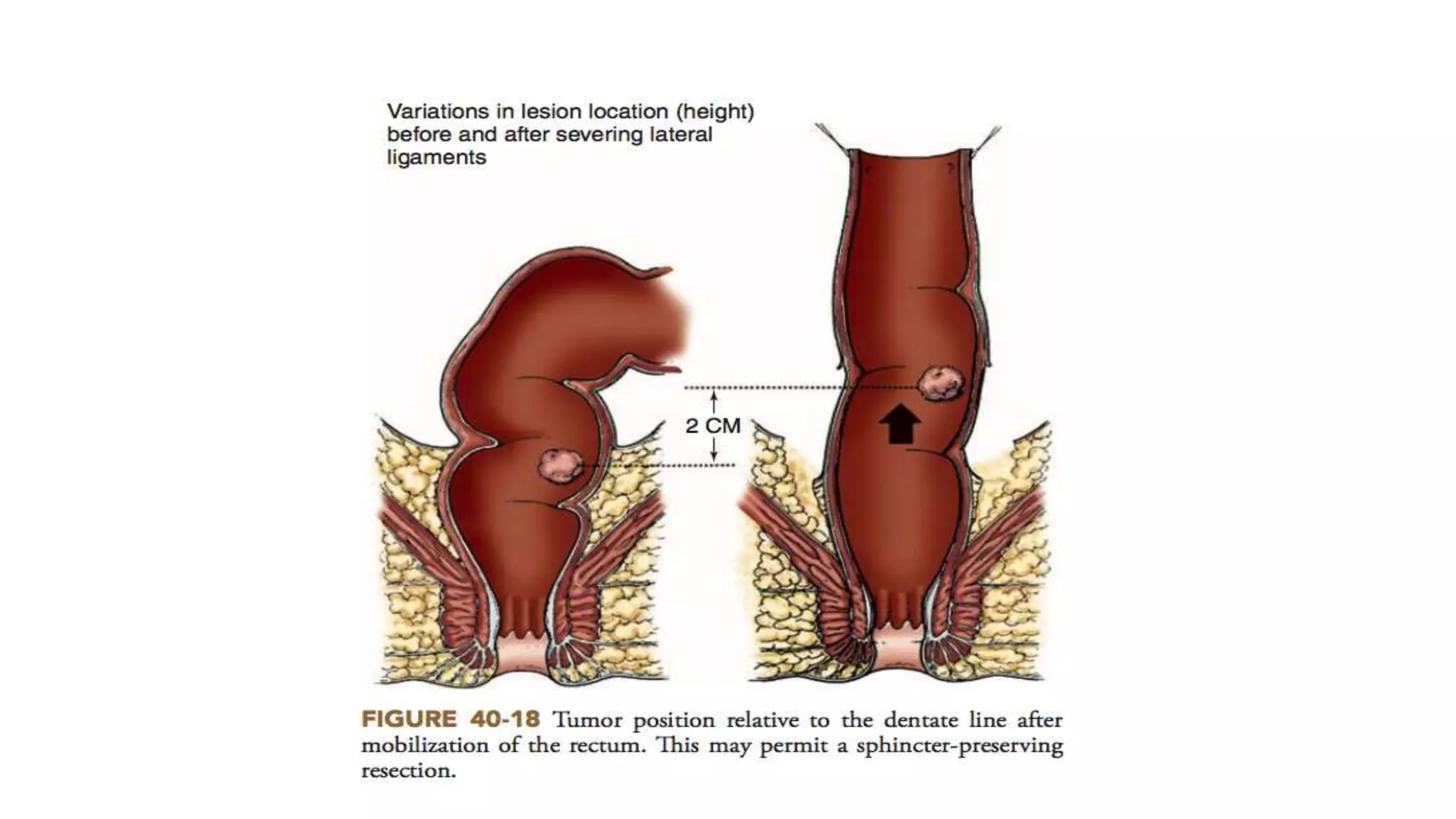
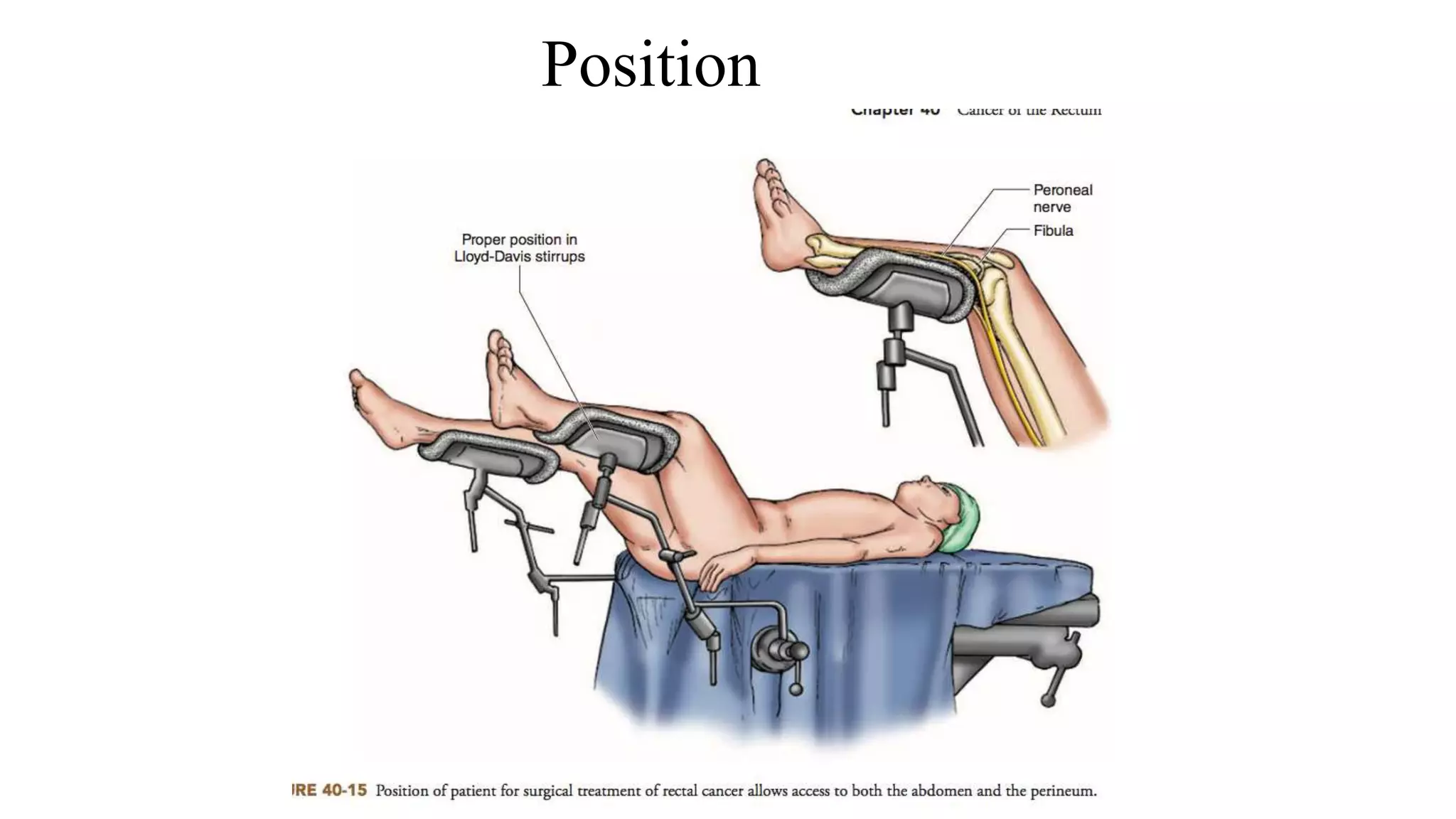
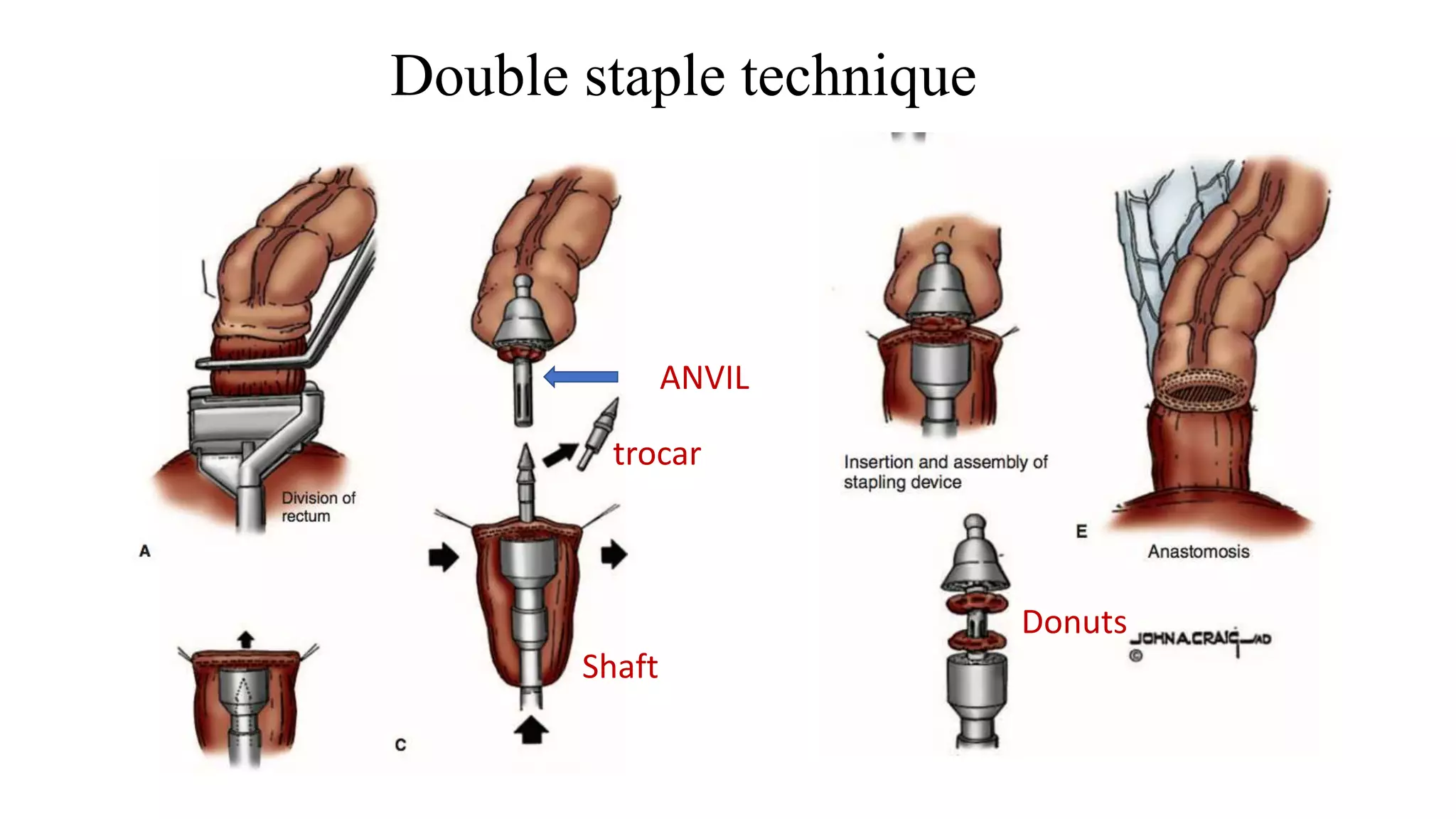
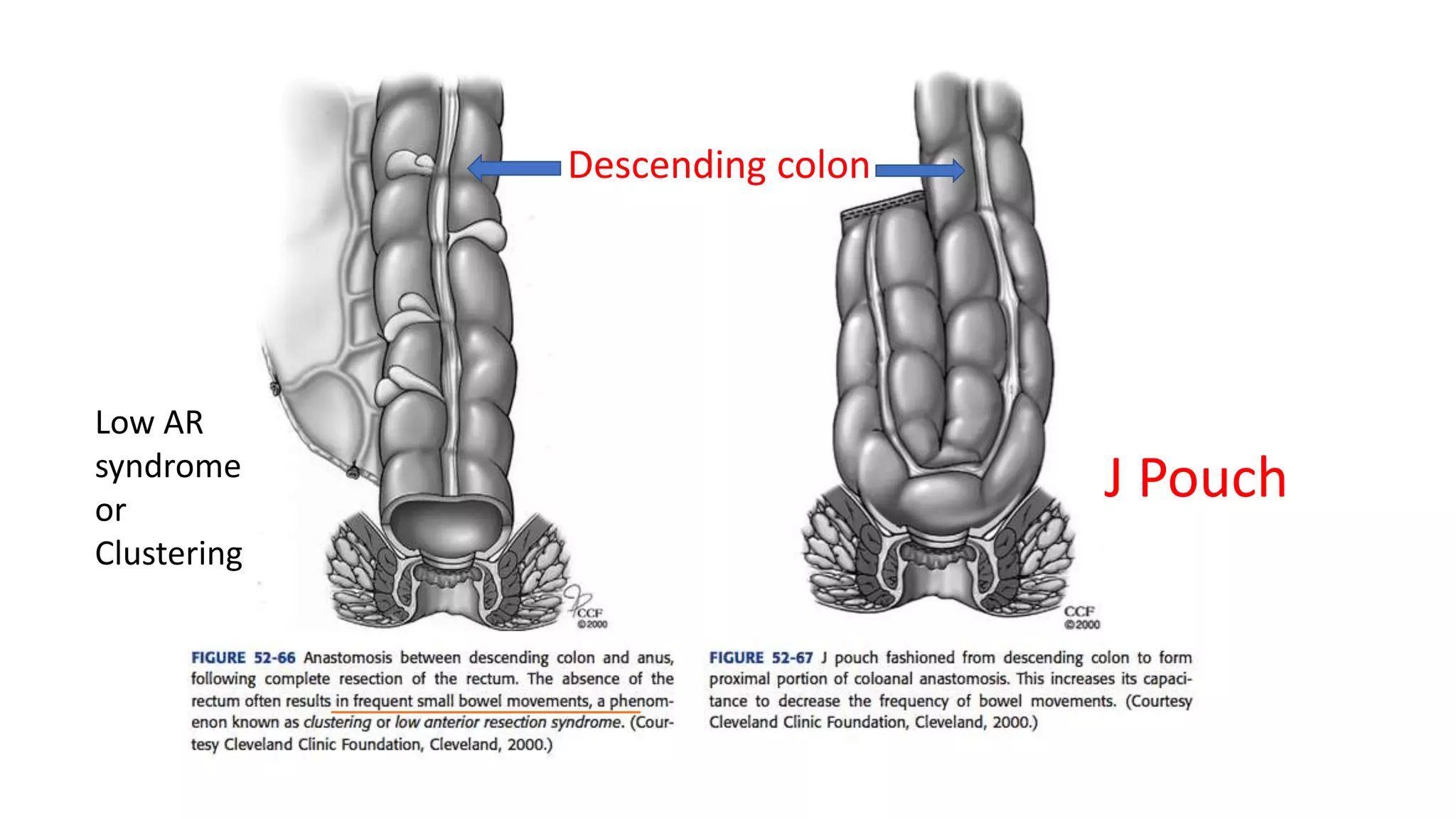
2. Anterior Resection, which removes the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon and performs a colorectal or coloanal anastomosis.
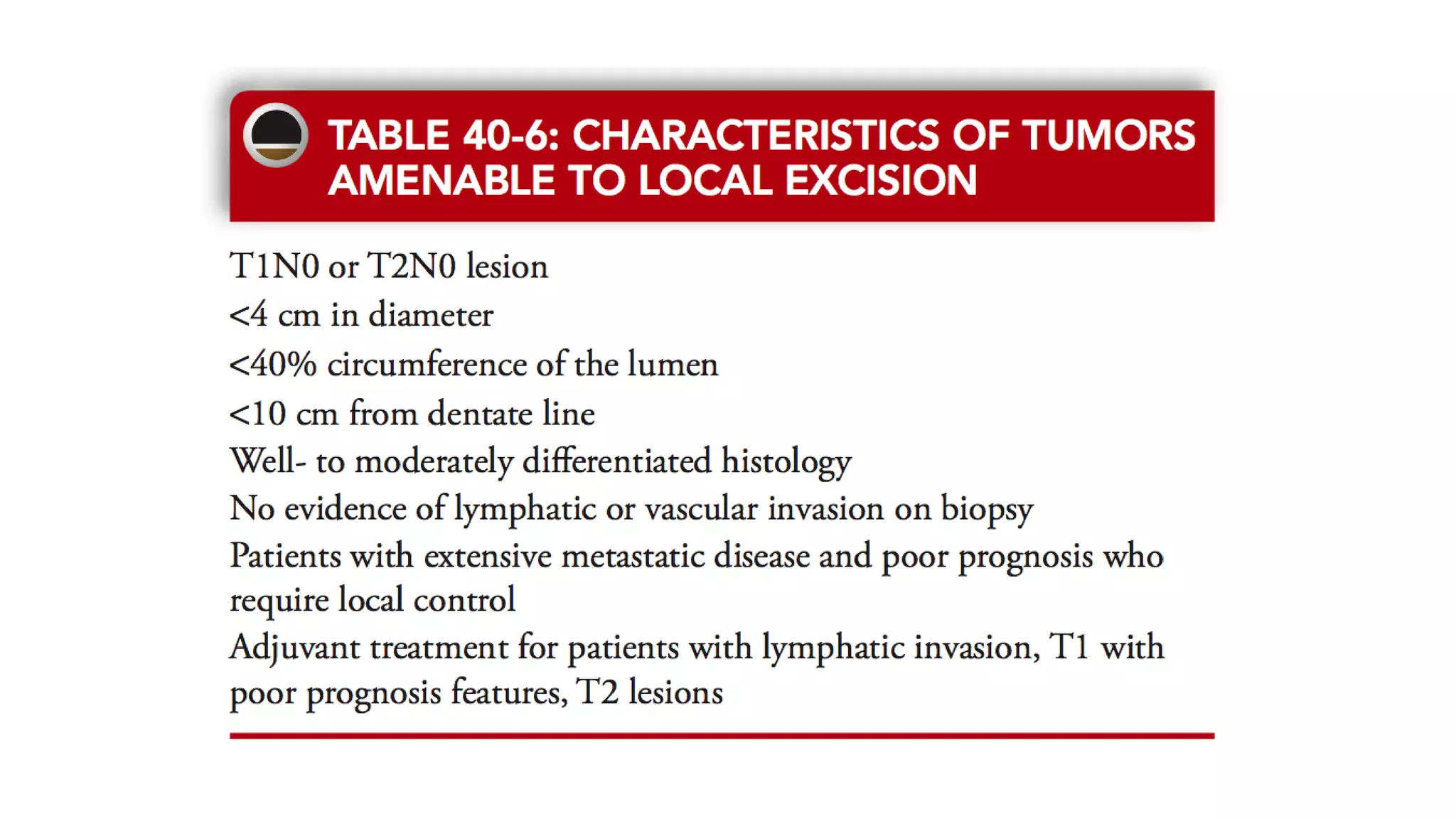
3. Local excision techniques like Transanal Endoscopic Microsurgery (TEM) for early-stage or palliative cases.
4. Other procedures mentioned include Hartman's operation (resection with end colostomy), pelvic exenter